Physics OCR A-level: Gravitational fields
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Gravitational field
A field created around any object with mass, extending all the way to infinity, but diminishing as the distance form the centre of mass of the object increases
Gravitational field strength, g
The gravitational force exerted per unit mass at a point within a gravitational field. (units NKg-1 or ms-2)
Gravitational field lines
lines of force used to map the gravitational field pattern around an object having mass
Radial field
A symmetrical field than diminishes with distance2 from its centre, such as the gravitational field around a spherical mass or the electrical field around a spherical charged object
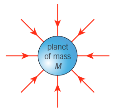
Point mass
A mass with negligible volume
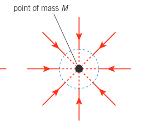
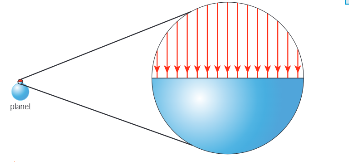
Uniform gravitational field
A gravitational field in which the field lines are parallel and the value for g remains constant
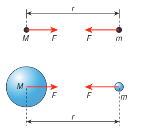
Newton’s law of gravitation
The force between two point masses is directly proportional to the product of the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the separation between the centres
F=\frac{-GMm}{r^2}
Gravitational constant, G
The constant in Newton’s law of gravitation With value: 6.67×10-11NKg-2m2
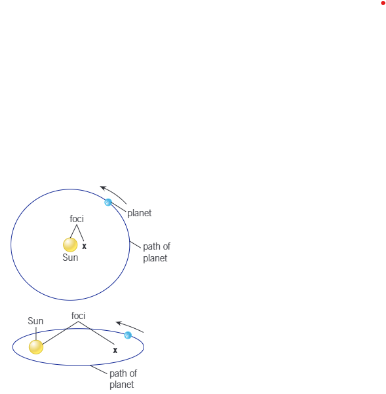
Kepler’s first law of planetary motion
The orbit of a planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one of the two foci
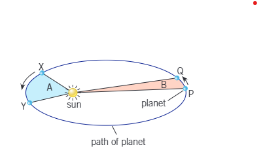
Kepler’s second laws of planetary motion
A line segment connecting a planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas during equal time intervals.
Kepler’s third laws of planetary motion
The square of the orbital period T of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of its average distance r from the sun
\frac{T^2}{r^3}=k or T^2=\left(\frac{4\pi^2}{GM}\right)r^3
Kepler’s third law derived
centripetal force on planet = Gravitational force on planet\frac{mv^2}{r}=\frac{GMm}{r^2} or v^2=\frac{GM}{r}
since moving in circular motion speed can be determined using v=\frac{2\pi r}{T}
substitute this in to give \frac{4\pi^2r^2}{T^2}=\frac{GM}{r}
rearrange to give T^2=\left(\frac{4\pi^2}{GM}\right)r^3