lecture 6 blood spatter analysis
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
crime scene reconstruction
the reconstruction of events that occured before, during, and after the commision of the crime. Based on physical evidence and statements. made by individuals involved with the incident, require team effort
reconstruction is based on
physical evidence
forensic lab results
investigators common sense and experience
witnesses statements
statistical analyses
Crime scene reconstruction consists of
wound patterns
gunshot residue patterns
glass fracture patterns
fire burn patterns
blood spatter patterns
Blood stain patterns can reveal
direction of origin of bloodstain
angle of impact of bloodstain
speed of bloodstain from its origin
location and position of victim/suspect
movement of victim/suspect from the crime scene
minimum number of blows/shots
Direction of origin of bloodstain
the tail tells the tale, narrow end of blood drop points in the direction of blood.
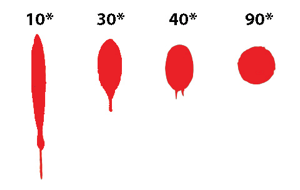
90 degree fall bloodstain
when a blood droplet strikes a surface from 90 degrees it creates a circular stain, there will be no long or short exes and spines, scallops, and satellites will occur moderately. very little difference will be discernable between drops that impact anywhere between 90 and 75 degress.
Harder nonporous surface: 90 degree fall
glass or smooth tiles, causes less spatter around the stain
rough surface: 90 degree fall
wood/cloths causes ireegularly shaped stain with serrated edges sometimes satellite spatter .
90 degree fall effect of height
dimater of the bloodstain increases with height but no changes in diameter after 7 feet.
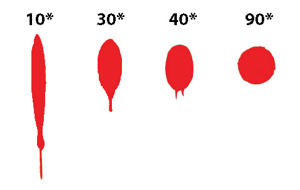
45 degree fall
as the angle of impact gets lower and lower, generally between 75 and 40, the elongation of the spatter stain becomes more and ore apparent, and the spines, scallops, and satellites are more focused and more to the side opposite the angle of impact.
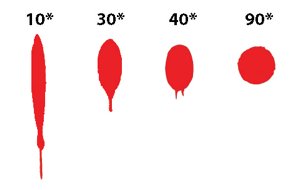
25 degree fall
at highly acute angles, generally below 40 degrees, the nature of the outflow changes. A single satellite tends to form, acting essentially like a second spatter emenating from the first one, causing a distinctive exclamation point.
area of convergence
think of the dexter red strings, the area on a 2D plane, from which bloodstain pattern originated.
area of origin: string method
place pole at an area of convergence
attach one end of string next to each droplets
using protractor, align string in line with angle of impact
attach other end of string to the pole
area of origin is an area where all strings appears to meet.
impact bloodstain patterns; low velocity spatter
applied force of <5 ft/sec
bloodstain diameter > 3mm
normally, produced by gravity alone, object dropping into a blood pool
impact bloodstain patterns; medium velocity
applied force of 5-25 ft/sec
bloodstain diamete of 1-3 mm'
blunt force trauma
impact blood stain patterns;high velocity
applied force of >100 ft/sec
blood stain diameter <1mm
gunshot exit bloodstain pattern, bloodstain patterns by explosion
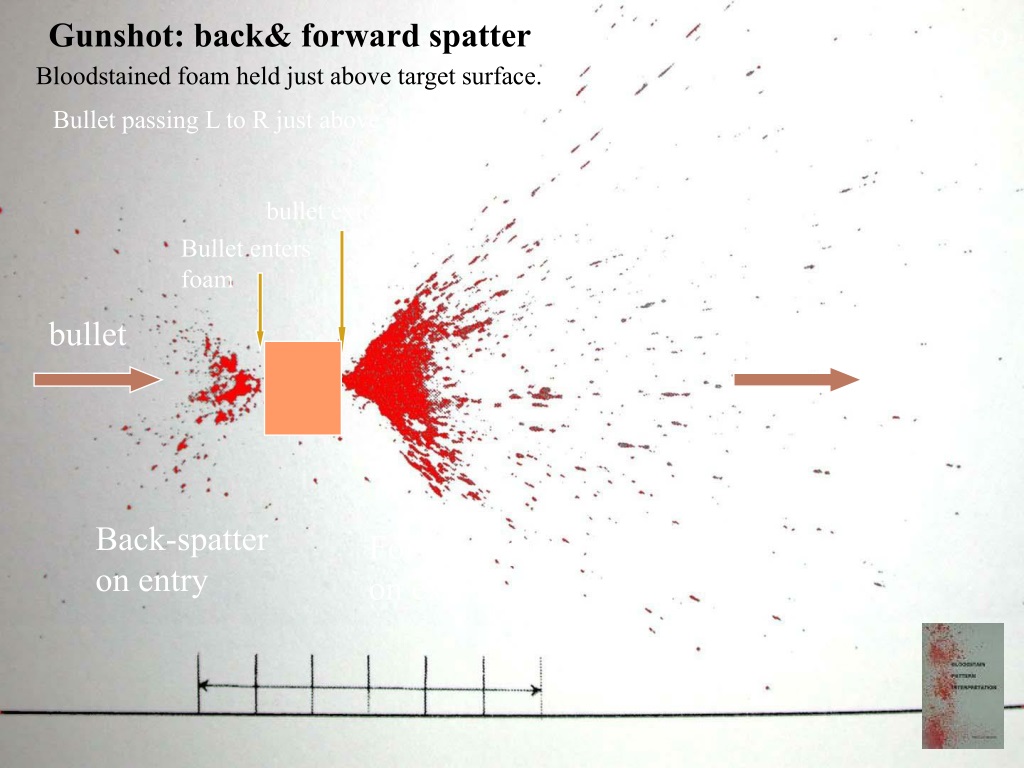
gunshot spatter
back spatter is created where the bullet enters, and forward spatter is created where the bullet exits.
backspatter are generally fewer and smaller than forward spatter
drawback effect
when backspatter strikes gun man and enters the gun muzzle.
cast off spatter
created when blood-covered object flings blood in an arc onto a nearby surface.
bloodstain arc pattern
helps in determination of direction in which impact object was moving
number of arcs
can help in determination of minimum number of blows delivered
size of the droplets for cast-off spatter
helps in determination of object used for creation of patterns
smaller drops from small pointed objects
larger drops from large blunt objects

arterial spray spatter
A blood spatter pattern resulting from a bleeding artery, typically characterized by a misty or fine spray, often seen in cases of severe trauma.
expirated blood patterns
blood from mouth, nose, and lungs under high pressure.
void patterns
created when an object blocks the deposition of blood spatter onto a target surface.
contact/transfer patterns
when an object with blood on it touches one that does not have blood on it.
simple transfer patterns
no movement of the object
swipe patterns
results from the transfer of blood from a blood-bearing surface onto another surface
wipe patterns
results from an object moving thorugh a pre-existing bloodstain
flows patterns
movement of small or large amount of blood because of gravity. clotting time outside the body ranges from 3-15 minutes, the flow direction may show movements of objects or bodies while the flow was still in progress or after the blood dried.
blood pools
a pool of blood occurs when blood collects in a level (not sloped) and undisturbed place
skeletoniztion occurs when the edged of a stain dry
usually within 50 seconds of deposition but may take longer time for larger volumes of blood
drip trail patterns
series of drops that are separate from other patterns, formed by blood dripping off an object or injury, the stains form a kind of line or path usually made by the suspect after injuring or killing the victim. or injuring themselves, show direction and speed of movement.
Documenting bloodstains: grid method
a grid of squares of know dimensions are set up over the entire patter using string and stakes. Overall, medium range, and close up photographs taken with and without the grid.
Documenting bloodstains: perimeter ruler method
a rectangular border of rulers is set up around each pattern. Large ruler show scale in overall and medium range and a smaller ruler show scale in close-up photograph.