Clinical Bacteriology II final review
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
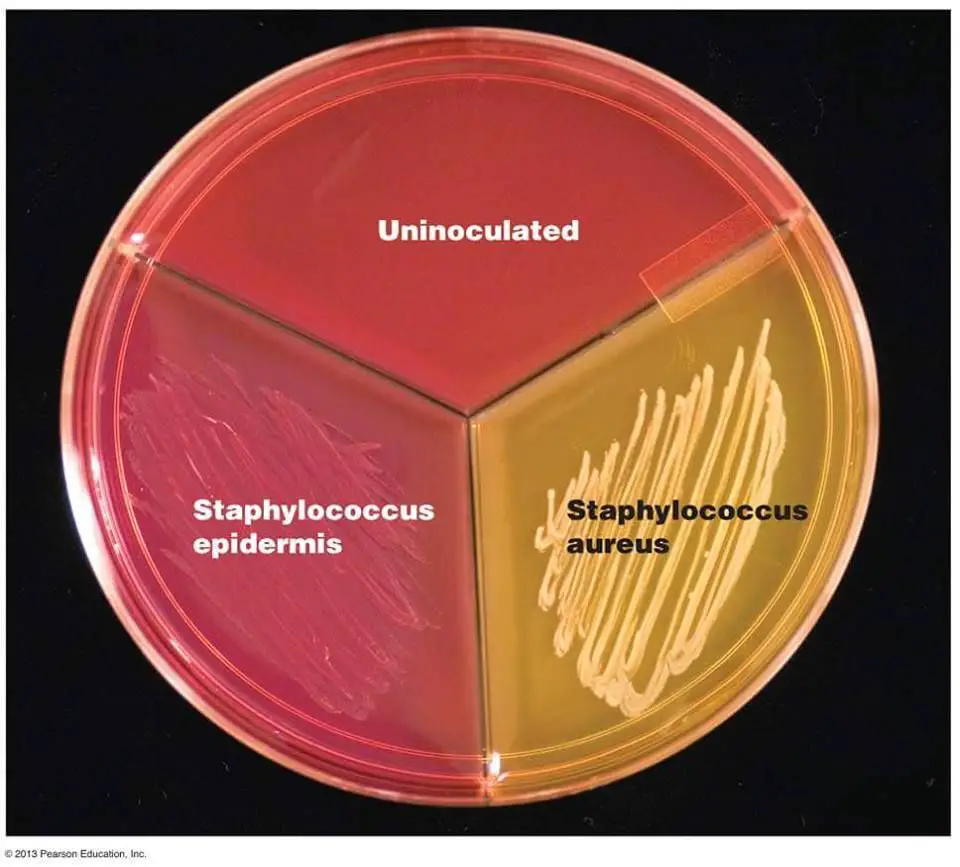
Staphylococcus aureus general features
gram positive cocci in clusters
facultative anaerobe
beta hemolytic
non motile and non spore forming
Staphylococcus aureus infections
skin infections: furuncles, carbuncles, impetigo, Hair Follicle Infections, cellulitis, Necrotizing fasciitis
pneumonia in children
endocarditis
enterocolitis
scaled skin syndrome
food poisoning
toxic shock syndrome
chronic lower respiratory infections in cystic fibrosis patients
Human bite infections
conjunctivitis, keratitis, endophthalmitis
IV catheter associated bacteremia
staphylococcus aureus identification
grows on BAP and is beta hemolytic, mannitol salt agar, PEA
coagulase positive
catalase positive
novobiocin susceptible
can oxidize and ferment
staphylococcus aureus virulence factors
teichoic acid for adherence
enterotoxin
toxic shock syndrome toxin
hyaluronidase for spreading factor
penicillinase
MRSA is a concern
staphylococcus epidermidis general features
gram positive cocci in clusters
facultative anaerobe
non hemolytic
non motile and non spore forming
staphylococcus epidermidis infections
nosocomial infection from implantation of prosthetic devices and immunocompromised
bacteremia (is a common contaminant)
endocarditis
Burn Infections
endophthalmitis
staphylococcus epidermidis identification
grows on BAP and PEA
catalase positive
coagulase negative
can oxidize and ferment
novobiocin susceptible
staphylococcus saprophyticus general features
gram positive cocci in clusters
facultative anaerobe
non hemolytic
non motile and non spore forming
staphylococcus saprophyticus infections
UTIs (if found in high numbers may mean contamination)
staphylococcus saprophyticus identification
grows on BAP and PEA
catalase positive
coagulase negative
novobiocin resistant
streptococcus pyogenes general features
gram positive cocci in chains
aerotolerant
beta hemolytic
non motile and non spore forming
streptococcus pyogenes (group A) infections
skin: impetigo, erysipelas, necrotizing fasciitis, cellulitis
pharyngitis frequent in children between 5-15
toxin shock like syndrome
acute rheumatic fever
acute glomerulonephritis
conjunctivitis
streptococcus pyogenes identification
grows on BAP
catalase negative
bacitracin susceptible
PYR positive
streptococcus pyogenes virulence factors
M protein
hyaluronic acid capsule
streptolysin O
streptolysin S
erythrogenic toxin
DNase
Hyaluonidase
streptococcus agalactiae (group B) general features
gram positive cocci
facultative anaerobe
beta hemolytic
non motile and non spore forming
lim broth
streptococcus agalactiae (group B) infections
leading cause of pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis during first 2 months of life
endocarditis
upper respiratory tract infections
acute meningitis in infants
bacteremia
streptococcus agalactiae (group B) identification
grow on BAP
catalase negative
hippurate hydrolysis and camp positive
polysaccharaide capsule
streptococcus pneumoniae identification
gram positive cocci in pairs
aerotolerant anaerobe
alhpa hemolytic
non motile and non spore forming
streptococcus pneumoniae infections
pneumonia in children and adults
acute meningitis in infants, children, and adults
upper respiratory infections (not pharyngitis or tonsillitis)
conjunctivits
keratitis
endophthalmitis
extravascular blood infection
streptococcus pneumoniae identification
grows on BAP
catalase negative
insulin fermentation
optochin susceptible
bile soluble
capsule
enterococcus and group D strep general features
gram positive cocci
facultative anaerobe
non motile and non spore forming
viridans strep general
gram positive cocci
facultative anaerobe
non motile and non spore forming
lack lancefield antigen
viridans strep infections
most common cause of endocarditis (dental procedures)
viridans strep identification
grows on BAP
catalase negative
optochin resistant
cannot hydrolyze BE
Corynebacterium diphtheriae general features
gram positive rods
facultative anaerobe
non motile and non spore forming
beta hemolytic
pleomorphic (Chinese letters)
uneven staining
humans are the only reservoir
Corynebacterium diphtheriae infections
respiratory: nasopharyngeal and throat, bull neck
skin lesions
laryngitis
Corynebacterium diphtheriae identification
Loeffler’s, cysteine-tellurite blood, Tinsdale, and blood agar
toxin detection
catalase positive
corynebacterium ulcerans
Animal pathogen: human contact with animals
Milder
Lower levels of toxin
corynebacterium jiekeium
Strict aerobe
Bacteremia with prosthetic devices, immunocompromised
highly resistant to antibiotics expect vancomycin
Corynebacterium urealyticum
Urine pathogen
Slow growing
Strict aerobe
catalase positive
urease positive
does not ferment glucose
Corynebacterium xerosis
Grows on SBA: dry, tan
Prosthetic valve endocarditis
Disease in immunocompromised
Corynebacterium pseudodiphthericum
Nasopharynx
Endocarditis
Infection in immunocompromised: respiratory, UTI, wound
No Chinese lettering, stains evenly and cells in parallel rows (palisades)
Corynebacterium striatum
Nasopharynx
Nosocomial infections
Arcanobacterium general features
Gram positive rods
Non-spore forming
Catalase negative
Beta hemolytic (narrow zone)
Aerobic
•and lecithinase positive
Resistant to penicillin
A. haemolyticum , A. pyogenes, A. bernardiae
Arcanobacterium haemolyticum infections
10-20 year old patients with pharyngitis
Desquamation of skins from hands and feet
Rothia
Gram positive rods, branching filaments, In broth, appear as cocci
Nitrite positive
non-motile
Urease negative
Most are catalase positive
endocarditis
Rhodococcus equi
Found in soil, causes respiratory infections in animals
Disease in immunocompromised
May demonstrate branching filaments
Partially acid fast
Salmon-pink pigment if left to incubate
Does not ferment carbohydrates
listeria monocytogenes general features
Gram positive coccobacilli
Facultative anaerobe
Pleomorphic
Non-spore forming
Beta-hemolysis
Listeria monocytogenes infections
acute meningitis in infants
extravascular blood infections
listeria monocytogenes identification
tumbling motility
Catalase positive
hippurate positive
bile esculin positive
Positive CAMP (block appearance)
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae general features
Gram positive , slender, filamentous bacilli
Facultative anaerobe to microaerophilic
Pleomorphic
Non-spore forming
Alpha-hemolytic
Pigs are the main reservoir
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae infections
Endocarditis
skin: Eysipeloid
septicemia
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae identification
Brush pattern at 22oC in gelatin-stab cultures
Catalase negative
hydrogen sulfide production
VP negative
Lactobacillus acidophilus general features
Gram positive
Facultative anaerobe
Highly pleomorphic, spaghetti
Non-spore forming and Non-motile
Alpha-hemolytic
Natural flora of female urogenital tract also found in mouth and GI tract
Bacillus anthracis general features
Gram positive bacillus
Aerobic
Spore-forming
non-motile
Non-hemolytic
Bacillus anthracis infections
Skin: Black scar (eschar), erythematous ring
Pulmonary: Woolsorters disease
Gastrointestinal
Bacillus anthracis identification
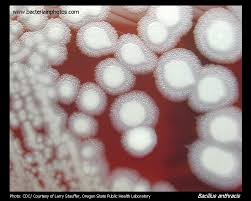
Swirling projections (Medusa head)
Catalase positive
produces lecithinase
Glutamic acid capsule
Susceptible to penicillin
Bacillus cereus general feautres
Gram positive bacillus
Aerobic
Spore-forming
motile
Beta-hemolytic
Bacillus cereus infections
Food poisoning from enterotxin, fried rice
Opportunistic infections: post-op eye infection, endocarditis, and bacteremia (IV drug users or immunocompromised)
Bacillus cereus identification
Catalase positive
produces lecithinase
grows on Egg yolk agar ( creates a zone of opacity)
Penicillin susceptibility
Bacillus subtilis
Gram positive bacillus
Aerobic
Spore-forming
Not part of normal flora
Rarely causes human disease
May be pigmented
Aerobic Actinomycetes
Branching filamentous hyphae
Non-spore forming
Not commonly seen in US, but can cause significant human disease
Nocardia general features
Gram stain is weak, beaded appearance
Aerobic
Branching, filamentous
weakly acid fast
Nocardia infections
Pulmonary
cutaneous: pus may contain sulfur granules
Neisseria gonorrhoeae general features
Gram negative diplococci
Aerobic
Non-spore forming and non-motile
Glucose fermenter
Not normal human flora (always pathogenic)
Usually intracellular
Neisseria gonorrhoeae infections
genital
rectal
pharyngeal
conjunctivitis
epididymitis
Neisseria gonorrhoeae identification
grows on Choc, Modified Thayer-Martin, Martin-Lewis, New York City
capsule
beta-lactamase
kidney bean shaped
catalase positive
oxidase positive
Intracellular diplococci is evidence of gonococcal infection in male urethral specimens (not female samples)
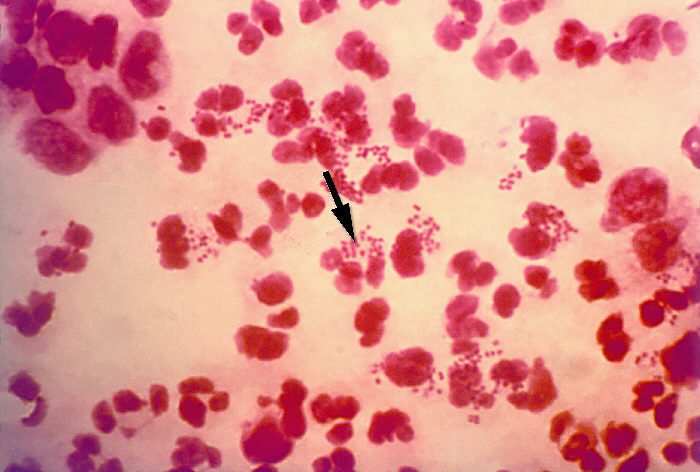
Neisseria meningitidis general features
Gram negative diplococci
Aerobic
Non-spore-forming and non-motile
Ferment glucose and maltose
Usually intracellular
Neisseria meningitidis infections
naopharyngeal
Acute meningitis in children and adolescents
extravascular blood infections
Moraxella catarrhalis geneal features
Gram negative coccobacilli or diplococci
Non-fermentative (asaccharolytic)
hockey puck appearance
Moraxella catarrhalis infections
Upper respiratory tract: children and elderly
Lower respiratory tract: adults with preexisting conditions
3rd most common cause of otitis media and sinusitis in children
Moraxella catarrhalis identification
grows on SBA and CHOC
Inhibited by colistin
Catalase positive
oxidase positive
Susceptible to: Erythromycin, tetracycline, Trimethoprim-sulfa, Ampicillin with beta-lactamase inhibitor
Neisseria cinerea
Dnase negative
Misidentified as gonococcus but is susceptible to colistin
Asaccharolytic
Neisseria flavescens
Yellow-pigment
Asaccharolytic
SBA and CHOC at RT
Neisseria lactamica
Ferment maltose, lactose, glucose
Nasopharyngeal commensal in children, peaks at 2 but declines
Positive ONPG
Morphology similar to meningococcus
Neisseria mucosa
Reduce nitrate and nitrite
Mucoid
Lacks pigments
Neisseria sicca
Dry, wrinkled breadcrumb
Commensal respiratory in adults
Neisseria subflava
Less yellow
SBA and CHOC at RT
Kingella denitrificans
Reduce nitrate
Normal flora of URT
Catalase negative
oxidase positive
infective endocarditis
Haemophilus influenzae general features
Gram negative coccobacilli
Facultative anaerobe
non-motile
ferment carbohydrates
Haemophilus influenzae infections
septicemia
cellulitis
epiglottis
pneumonia in children
acute meningitis in infants, and children
bronchitis
conjunctivitis
Chronic Lower Resp infections in Cystic fibrosis patients
extravascular blood infections
Haemophilus influenzae identification
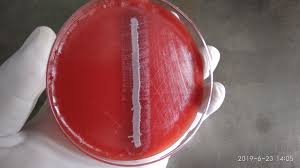
Requires Chocolate agar: Require X (hemin) and V (NAD) factor
satellitism
capsule
catalse positive
reduce nitrates
Haemophilus aegyptius
difficult to differentiate from H. influenzae
Acute conjunctivitis
Haemophilus influenzae biogroup aegyptius
Conjunctivitis in pediatric patients
Can cause systemic disease, Brazilian purpuric fever
Haemophilus ducreyi
Not normal part of human flora
Causative agent of chancroid
grows best in 33oC, and requires special media such as GC that contains vancomycin to reduce growth of normal flora
Haemophilus parainfluenzae and Aggregatibacter aphrophilus
Endocarditis one month after dental procedures
Haemophilus aphrophilus
Gram negative pleomorphic
Ferment carbohydrates: sucrose, glucose, maltose, lactose
Catalase negative
Reduce nitrates to nitrites
Do not grow on Mac
infective endocarditis
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
Gram negative rods
tar formation in center of colony
fermenter with addition of serum to media
Catalase positive
Oxidase variable
Negative for urease, indole, esculin, citrate
Do not grow on Mac
infective endocarditis
Cardiobacterium hominis
Gram negative pleomorphic rod
Nonmotile
Form rosettes or swellings
Ferment but needs serum to enhance reaction
Catalase negative
Oxidase positive
Indole positive
Grow on blood and CHOC agar
infective endocarditis
Eikenella corrodens
Gram negative
Nonmotile
Odor of bleach
Common cause of infection after trauma: Clench fist wounds, Dental manipulation, surgery
Catalase negative
Oxidase positive
Asaccharolytic
Human bite infections
infective endocarditis
Kingella spp
Gram negative coccobacilli or rods
Nonmotile, but may be twitching
Ferment glucose
Catalase negative
Oxidase positive
Do not grow on Mac
Capnocytophaga spp
Gram negative rods (mucoid)
Long thin tapered rods
Common cause of septicemia in granulocytopenic patients
Fermenter with addition of serum to media
Catalase negative
Oxidase negative
Do not grow on Mac
Dog/cat bites
Pasteurella multocida
Gram negative coccobacilli, filamentous, or rods
Nonhemolytic
Bipolar staining: safety pin appearance
Localized cellulitis and lymphadenitis from animal scratch or bite
Acid butt TSIA
Does not grow on OF media
Oxidase, catalase, Indole and ONPG positive
Urease negative
Dog/cat bites
Brucella
Gram negative coccobacillary
Non-spore forming, non-motile
Infection of sheep, cows, pigs, and other animals
Enriched media BAP Require thiamine, niacin, biotin
capsule
extravascular blood infections
Francisella tularensis
Gram negative coccobacilli
Facultative anaerobe
Category A select biological agent
Intracellular within macrophages
Bipolar staining
Glandular Fever, Tularemia, Rabbit Fever, Tick Fever, Deerfly Fever
Glucose-cysteine agar, CHOC with cysteine
Bordetella pertussis general features
Gram negative coccobacilli
Strict aerobe
nonmotile
appear to be pearls or drops of mercury
Humans are the only reservoir
Bordetella pertussis infections
Whooping cough
Complications: pneumonia
bronchitis
Bordetella pertussis identification
Reagan-Lowe transport medium
Direct plate coughing (best)
Bordet-Gengou
Legionella pneumophila general features
Gram negative coccobacilli
Motile
Aerobic
Facultative intracellular bacteria
lakes, rivers, hot springs, mud
Growth on BYCE agar
Legionella pneumophila infections
Legionnaire’s Disease
cutaneous abscesses
wound infections
pericarditis
myocarditis
bacteremia
community acquired pneumonia in hospitalized individuals
Uropathogenic E. coli
Most common cause of UTI
Originate in intestinal flora
Produce pili
recurrent complicated UTIs
Enterotoxigenic E. coli
Exotoxins
heat labile and heat stable
Traveler’s Diarrhea
A high infective dose
Enteropathogenic E. coli
Plasmid-borne adhesion factor (EAF) enabling adherence to mucosal cells
Outbreaks in hospital nurseries and daycares
Diarrhea; vomiting; nausea; low-grade fever; malaise; stool with mucous
Enteroinvasive E. coli
Dysentery-like illness
Direct penetration, invasion, and destruction of intestinal mucosa
do not ferment lactose
Enterohemorragic E. coli
Best known strain O157:H7
Associated with hemorrhagic colitis and HUS
Verotoxins I and II: verotoxin I
Fimbriae
MAC with sorbitol: O157:H7 does not ferment sorbitol
Salmonella identification
Non-lactose fermenters
H2S production
most are lysine decarboxylase+
Indole, VP, PAD, urease negative
Salmonella infections
Gastroenteritis
Enteric fever, Organism multiples in skin (rose spots)
extravascular Bacteremia
Asymptomatic carriage: Individuals who recover from infection may harbor organisms in gallbladder, antimicrobial therapy may be necessary or gallbladder removal
undercooked chicken, eggs, unpasteurized milk, beef gravy
Shigella general features
Not part of normal flora
Non-motile
Low infective dose
S. dysenteriae (Group A ), S. flexneri (Group B), S. boydii (Group C),S. soneii (Group D)
Shigella infections
Causes bacillary dysentery
Caused by penetration of intestinal epithelial cells following attachment to the mucosa
Shigella identification
Except for S. flexneri, they do not produce gas from glucose
Urease, H2S, decarboxylate lysine negative