IB Biology: Topic 1: Cell Biology
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
The cell theory
- Cells are the smallest most basic unit of life
- All cells are made from pre-existing cells
- Everything is made up of cells
Magnification
magnification = Image/actual
1mm = 1000um
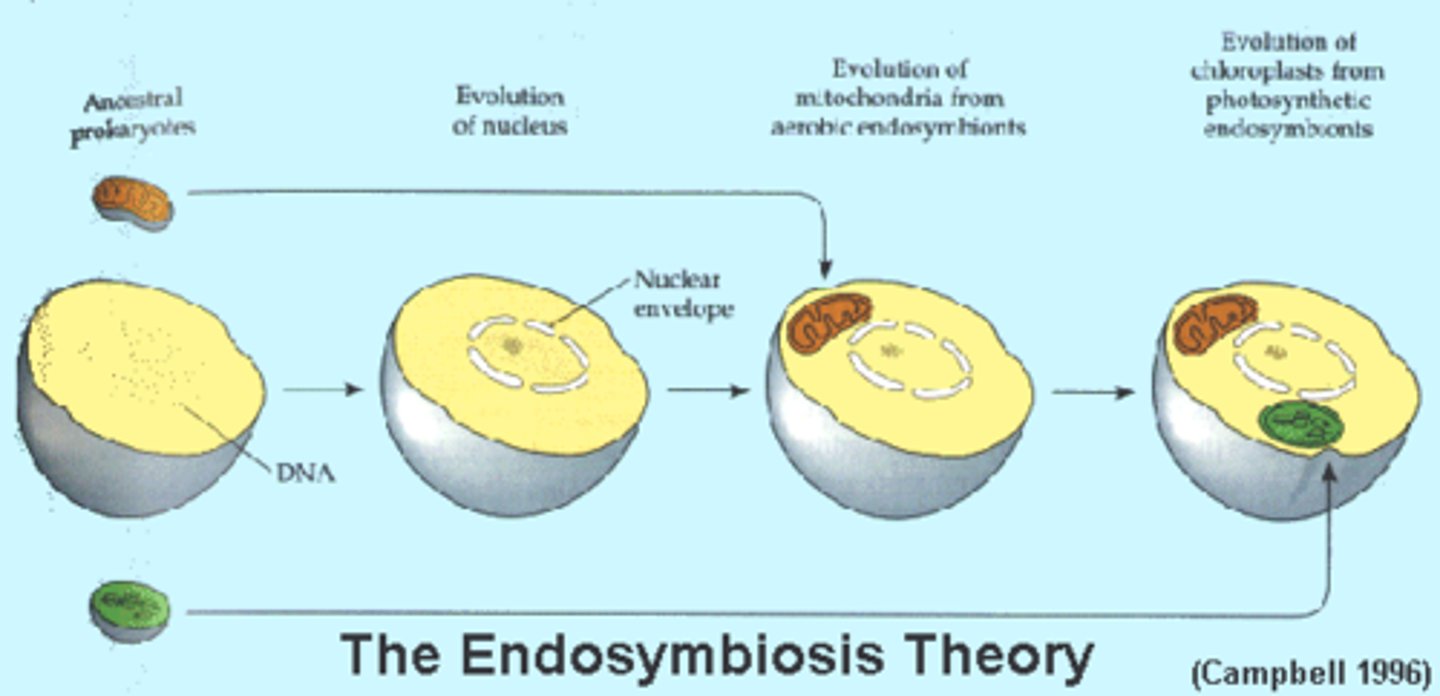
Endosymbiotic Theory
The theory is that a prokaryotic cell that could only respire/photosynthesize was engulfed by another prokaryotic cell and was allowed to survive
resulting in becoming mitochondria or chloroplast
- Prokaryotic engulfs -> mitochondria and chloroplast
- Bacteria 1: used oxygen to produce energy = Mitochondria
- Bacteria 2: used sunlight energy to produce food = Chloroplast
- Mitochondria developed before chloroplast
- Similar DNA to prokaryotic DNA
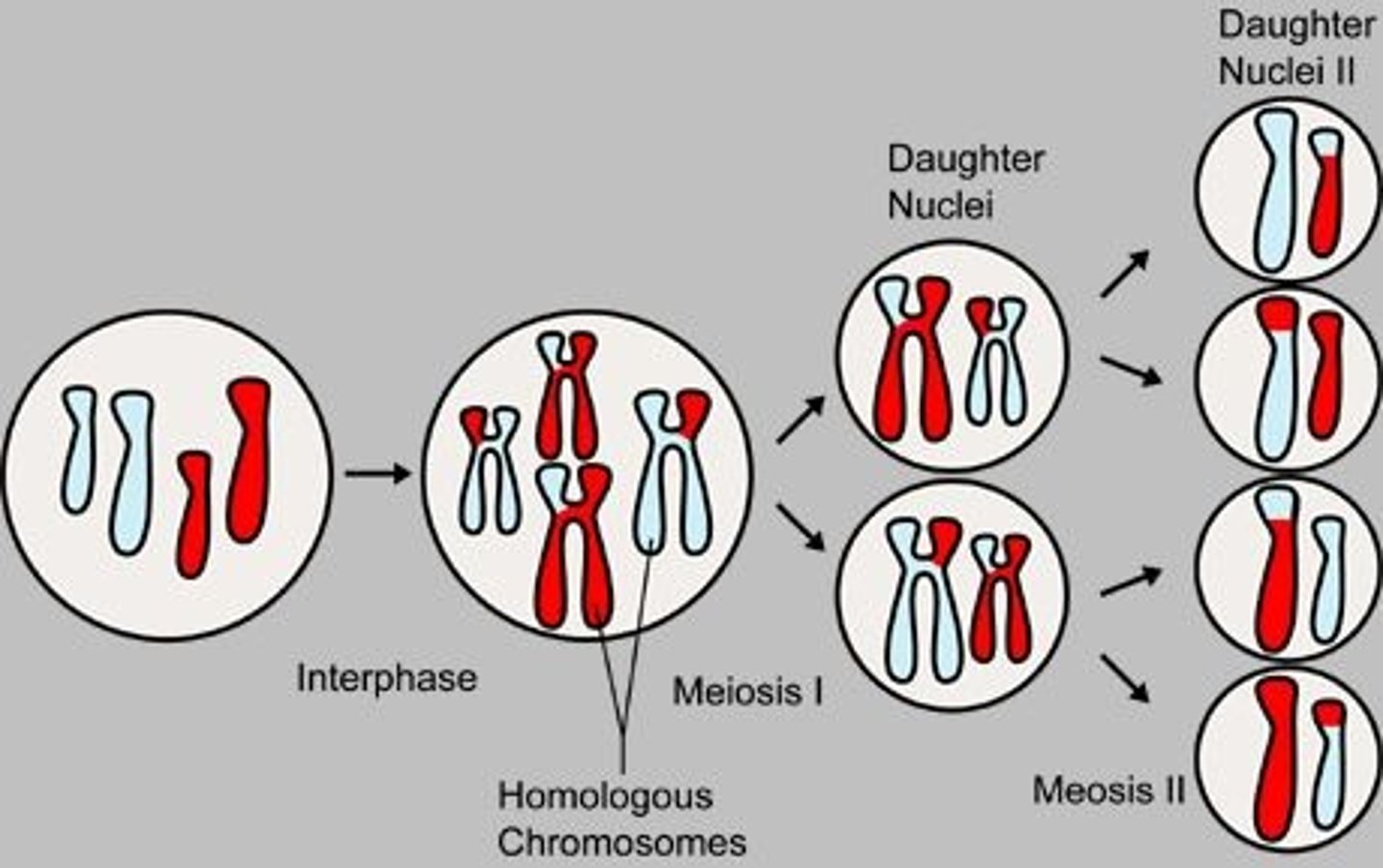
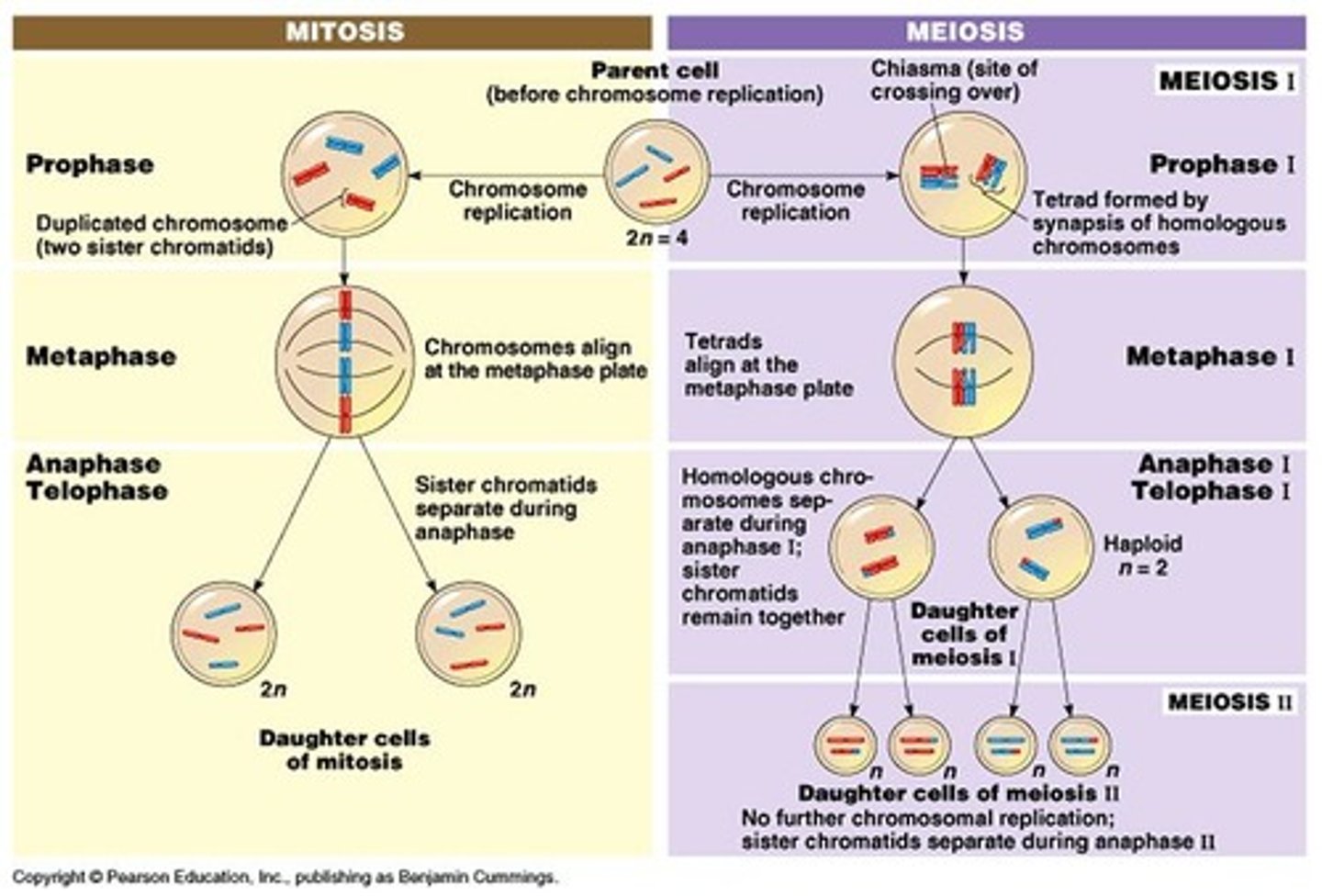
Meiosis 1
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms
- Makes sex reproduction cells = Gametes
- Humans have 46 Chromosomes
- Sperm = 23 chromosomes
- Eggs = 23 chromosomes
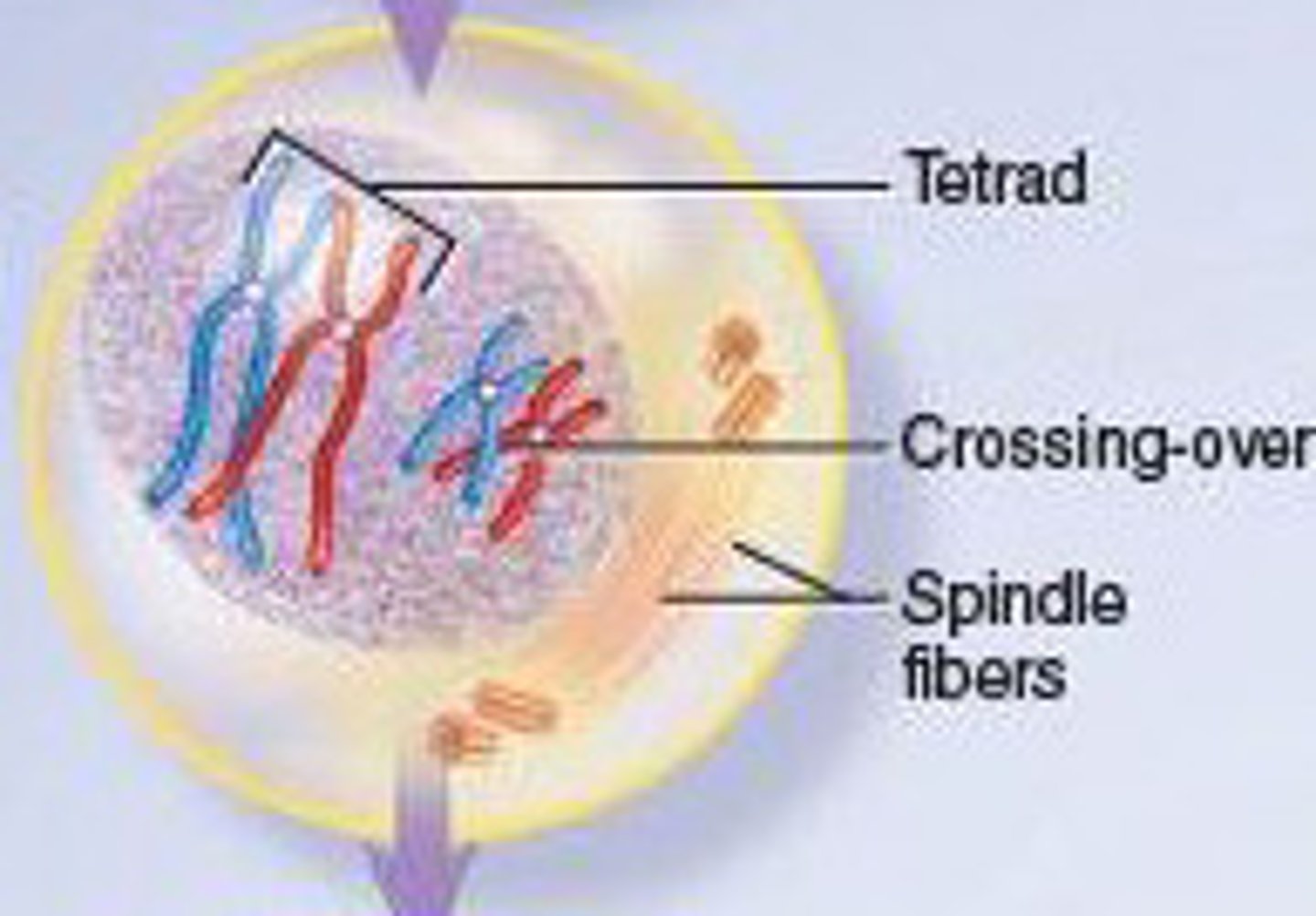
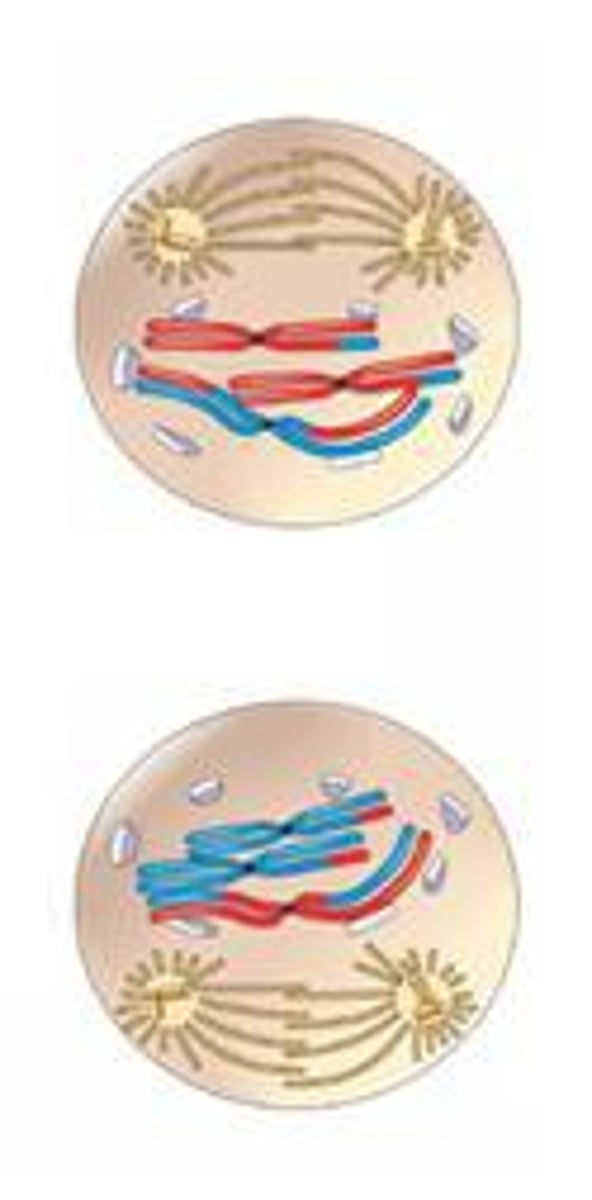
Meiosis 1: Prophase 1
- Homologous chromosomes condense, pair up, and swap segments (Crossing over)
- Spindle microtubules attach to chromosomes as the nuclear envelope breaks up
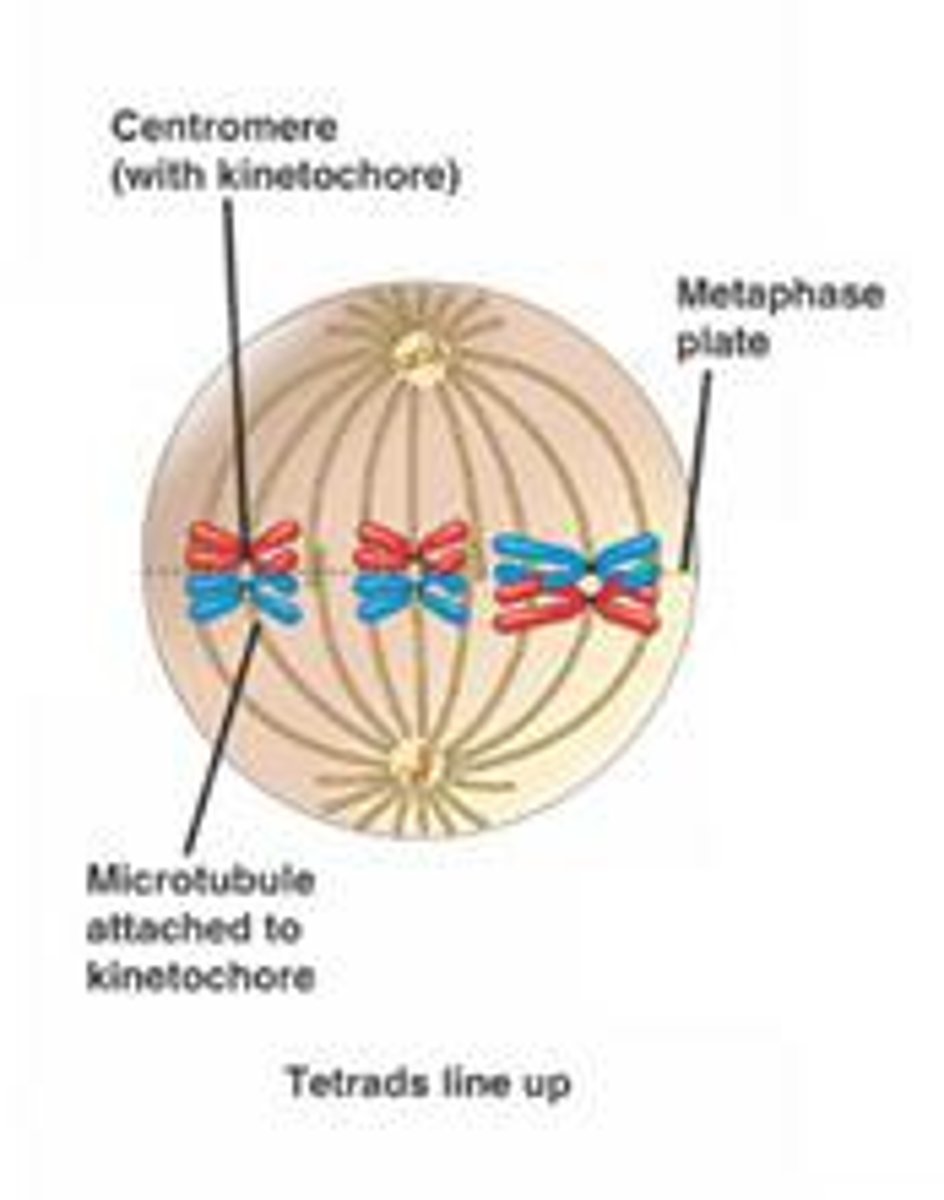
Meiosis 1: Metaphase 1
The homologous chromosome pairs are aligned midway between spindle poles
Meiosis 1: Anaphase 1
The homologous chromosomes separate and begin heading toward the spindle poles (opposite sides of the cell)
- Reduces the number of chromosomes
- Chiasmata move to the end of the chromosome
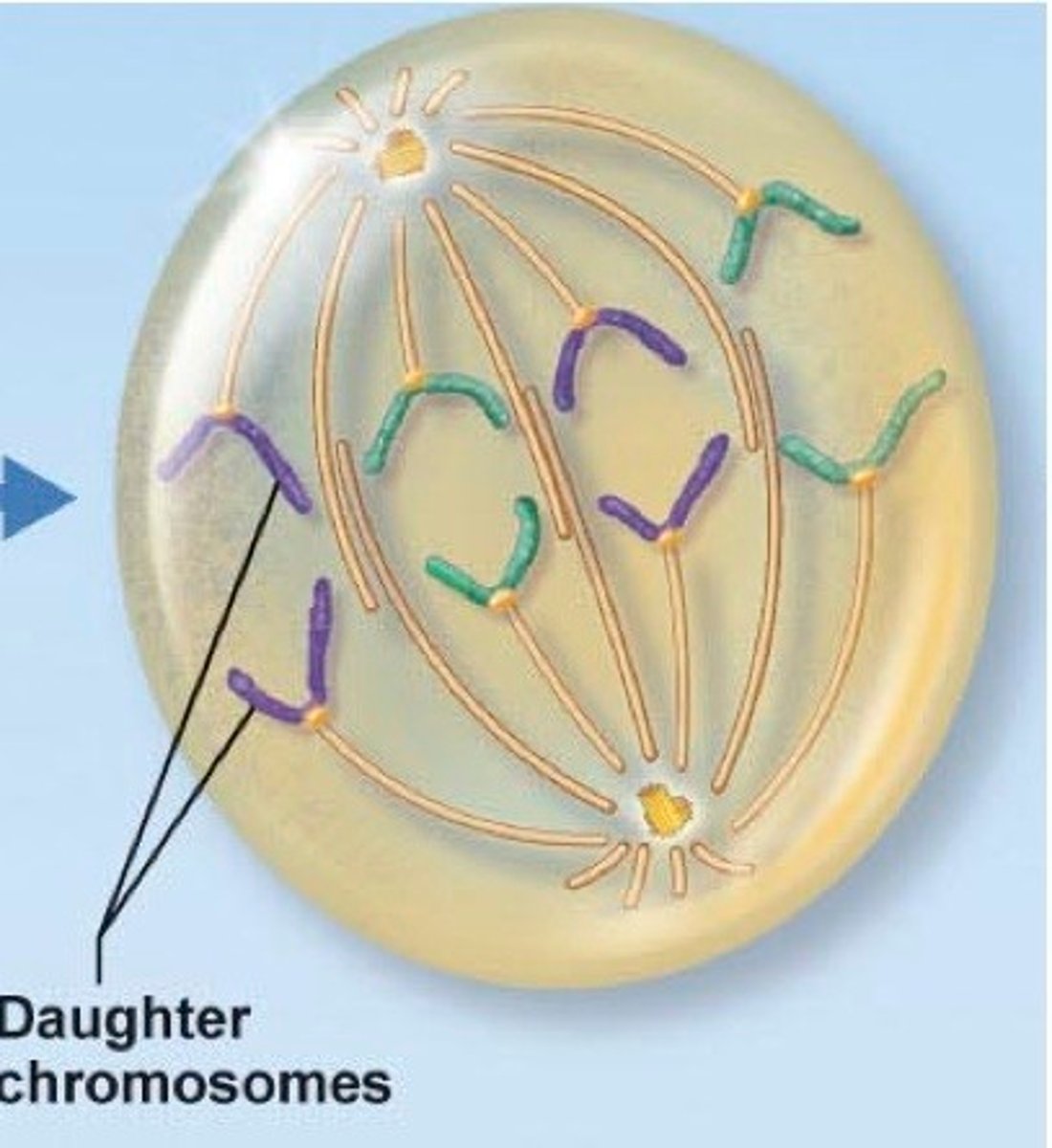
Meiosis 1: Telophase 1
- Duplicated chromosomes have reached the poles.
- Chromosomes arrive at the spindle pole and the cytoplasm divides
- A nuclear envelope re-forms around chromosomes in some species.
- Each nucleus has a haploid number of chromosomes.
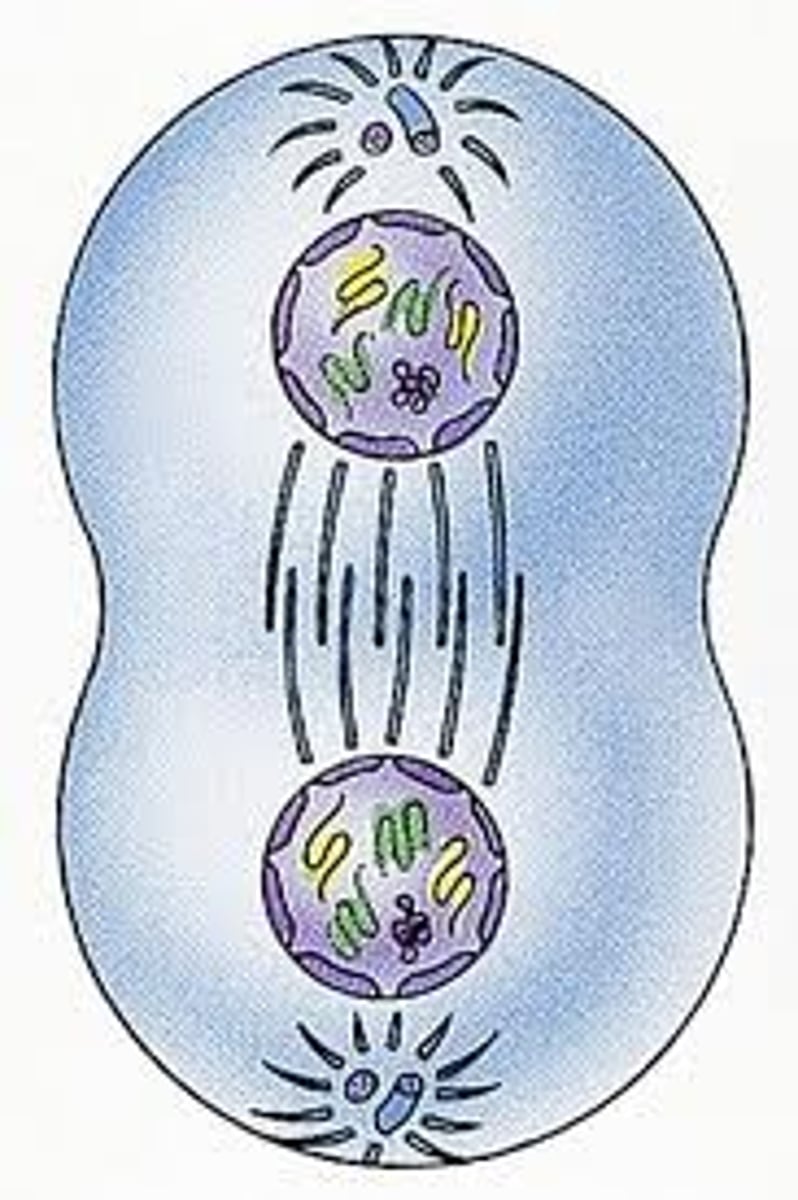
Meiosis 2
- Reproduction process that splits the sister chromatids and results in haploid cells
- Occurs with 23 chromosomes
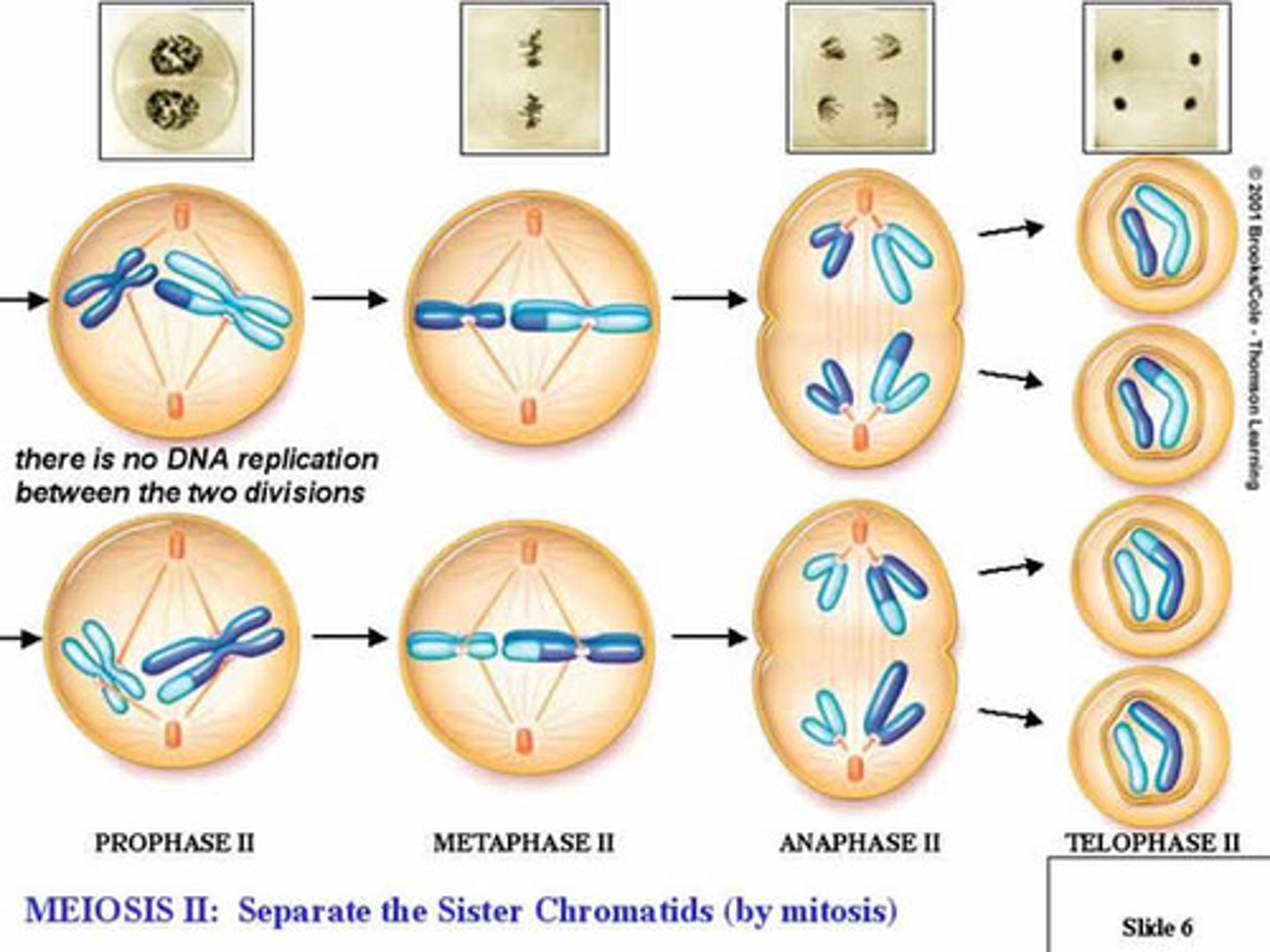
Meiosis 2: Prophase 2
- A spindle forms and moves chromosomes toward the middle of the cell.
- Chromosomes recondense
- Spindle apparatus forms
- No crossing over
Meiosis 2: Metaphase 2
Duplicated chromosomes align at the cell equator (centre of cell)
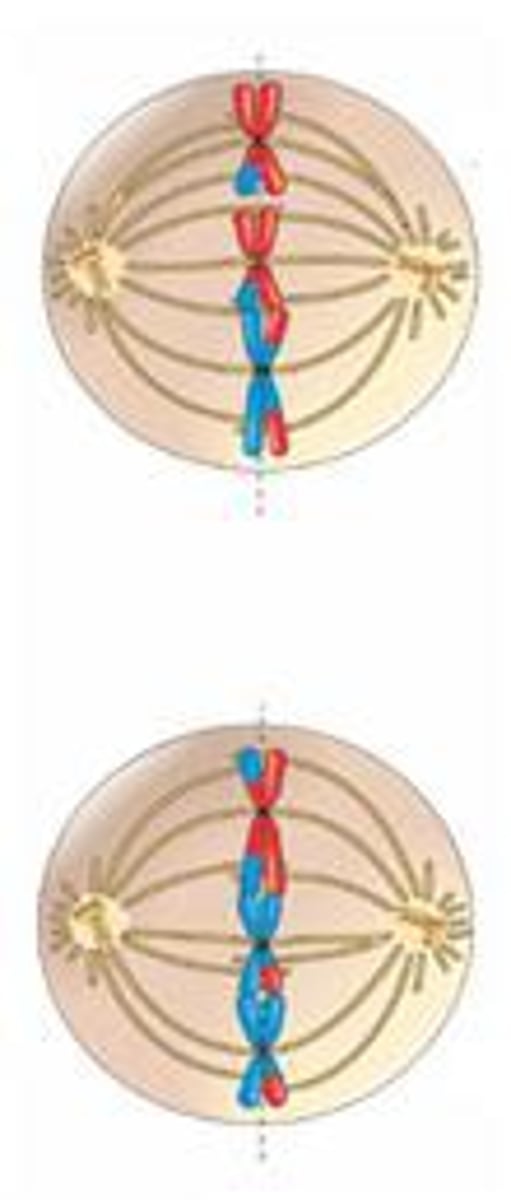
Meiosis 2: Anaphase 2
- Sister chromatids separate and chromosomes move toward opposite poles
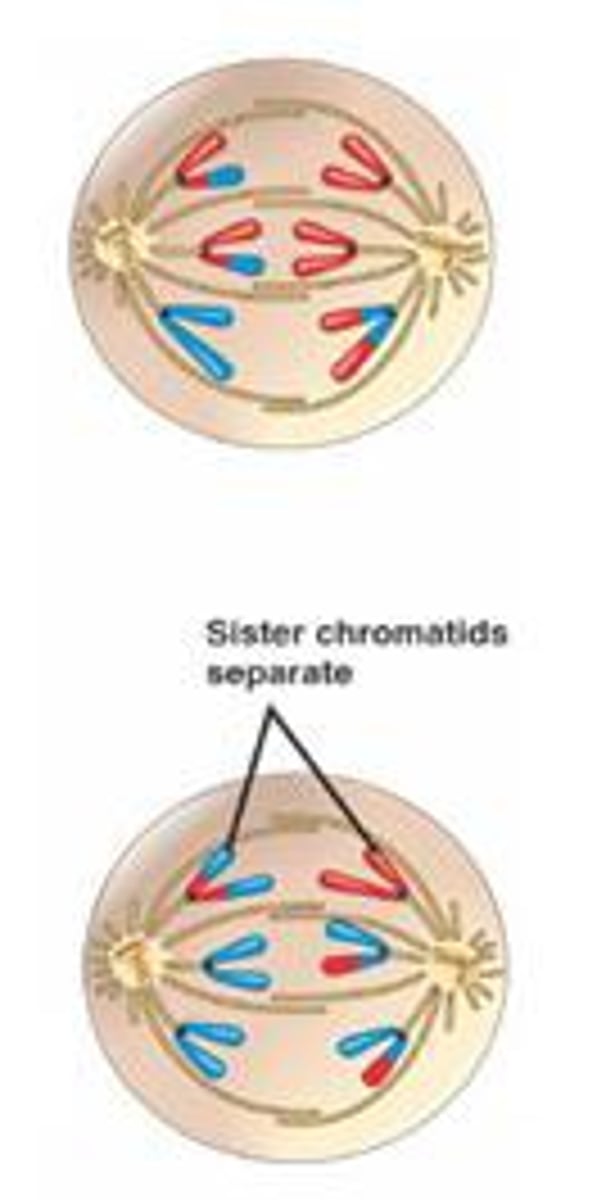
Meiosis 2: Telophase 2
- Chromosomes have reached the poles of the cell
- A nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes
- With cytokinesis, four haploid cells are produced.
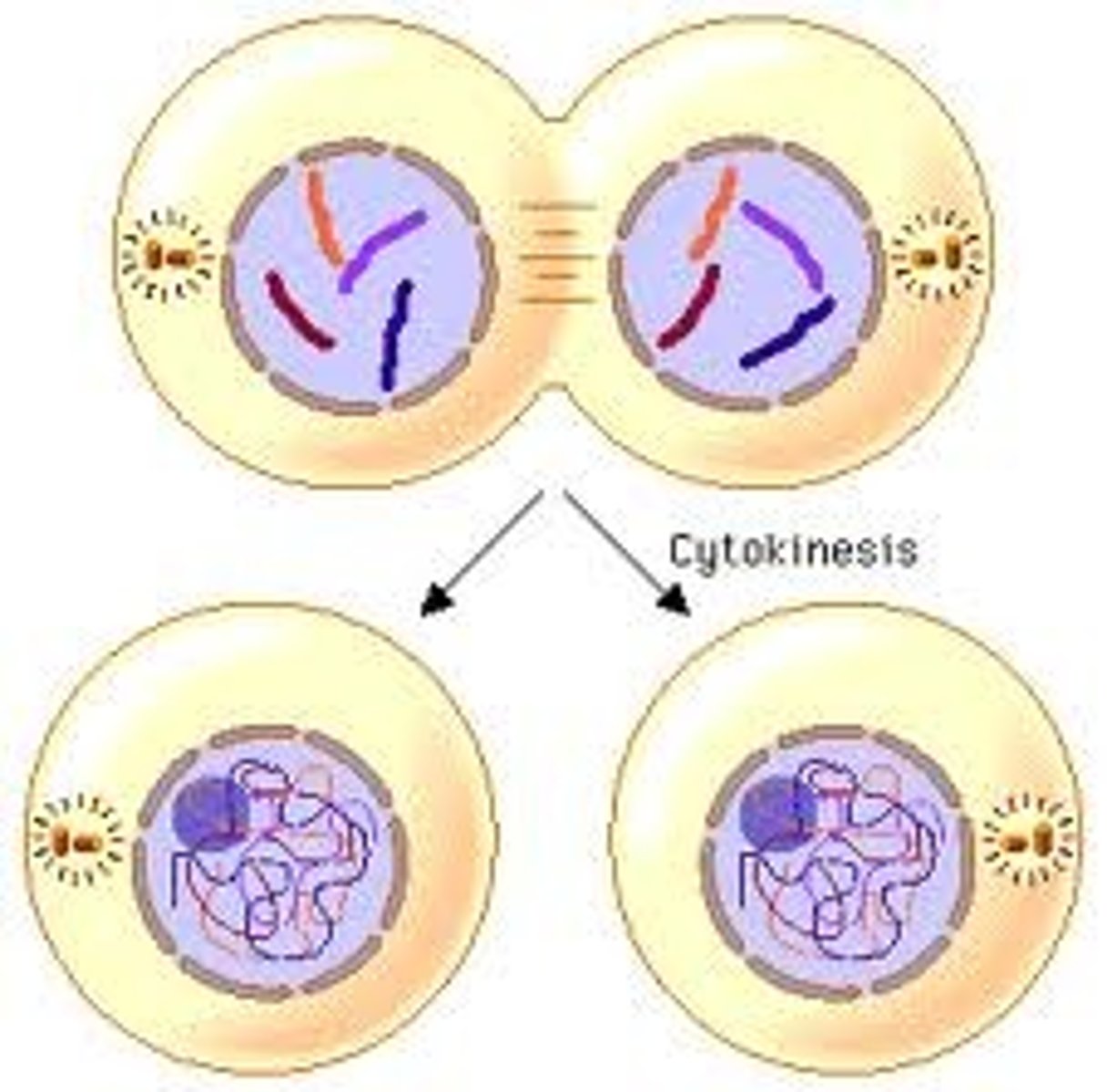
Meiosis: Non-Disjunction
- Chromosomes font separate properly
- Cell receives too many or not enough chromosomes during separation
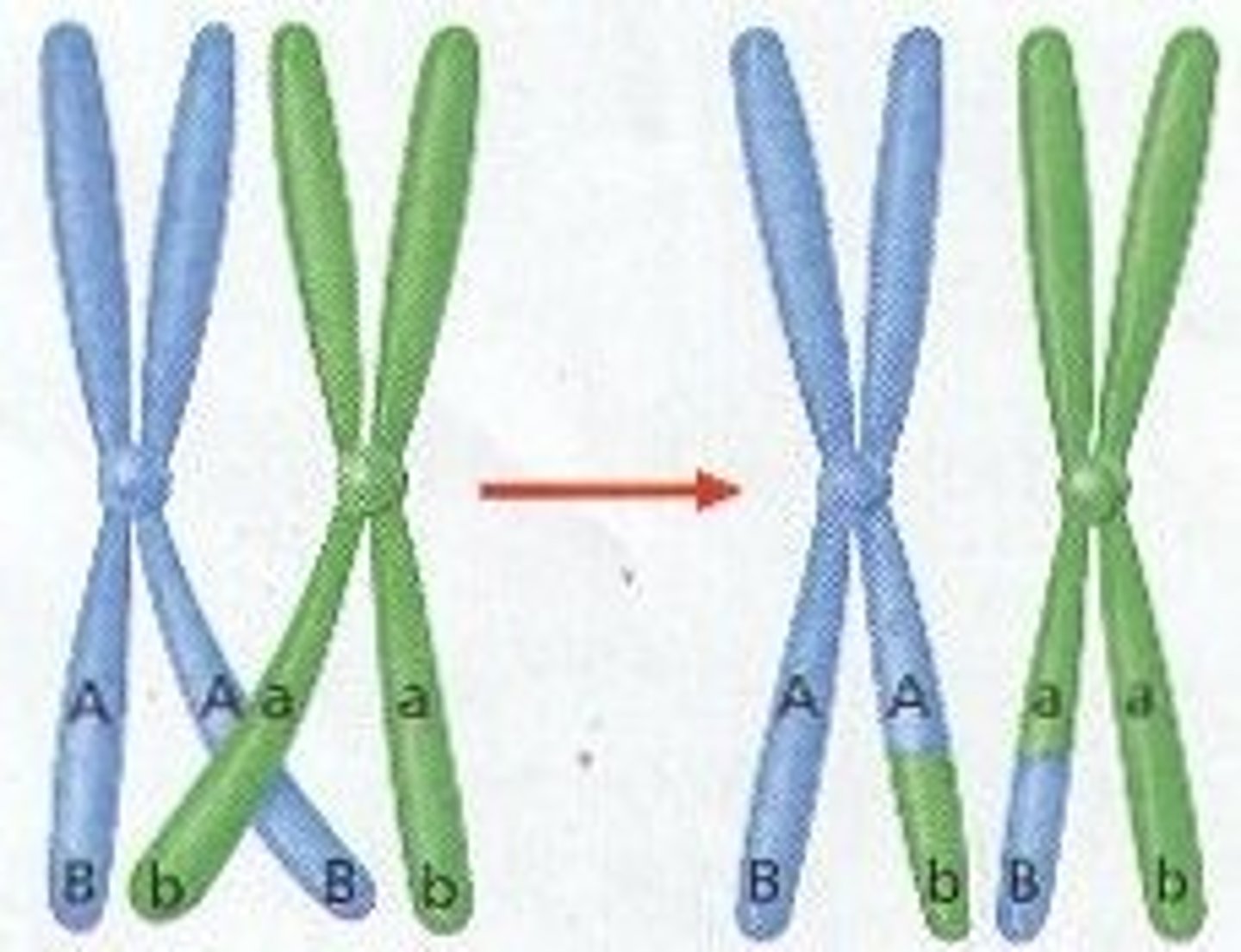
Meiosis: Crossing over
The exchange of alleles between homologous chromosomes, resulting in a mixture of parental characteristics in offspring. Occurs in prophase I.
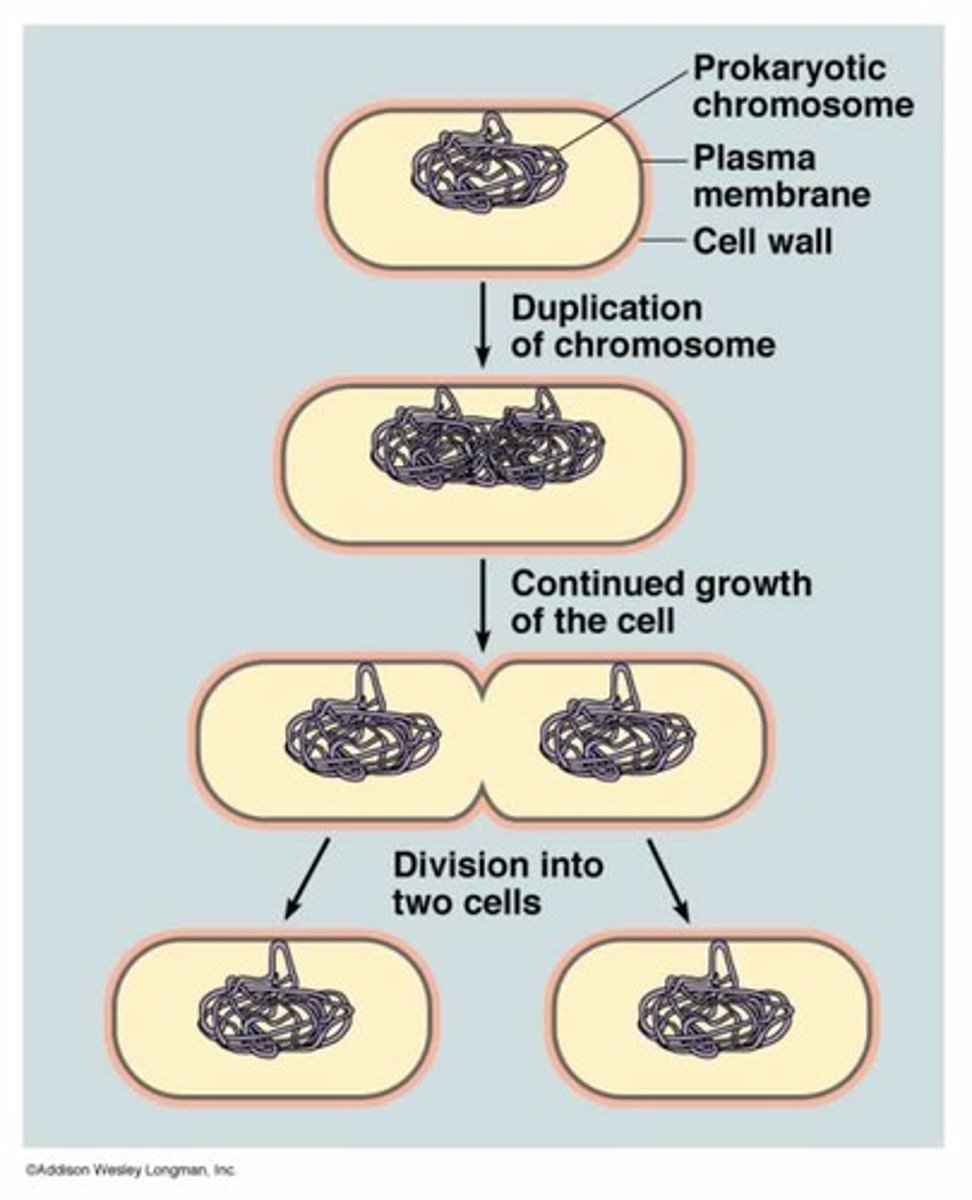
Binary Fission
- Prokaryotic organisms divide and reproduce
- Divide rapidly
- Single-celled eukaryotes
Process
- Prokaryotic cell
- DNA replication
- Call growth
- Pinching of Membrane
- Division of cell wall
- Creates two daughter cells
Difference between mitosis and meiosis
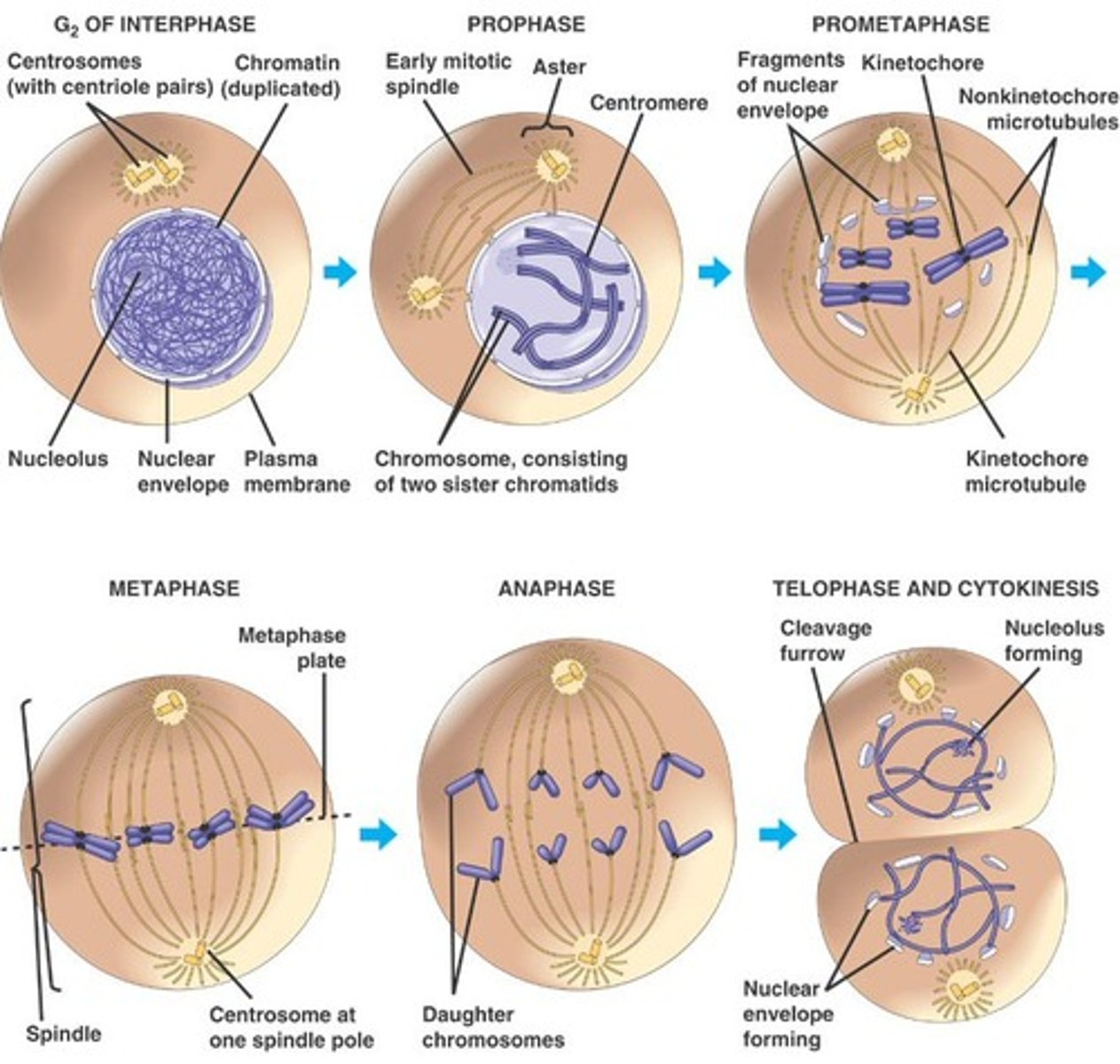
Mitosis
part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides
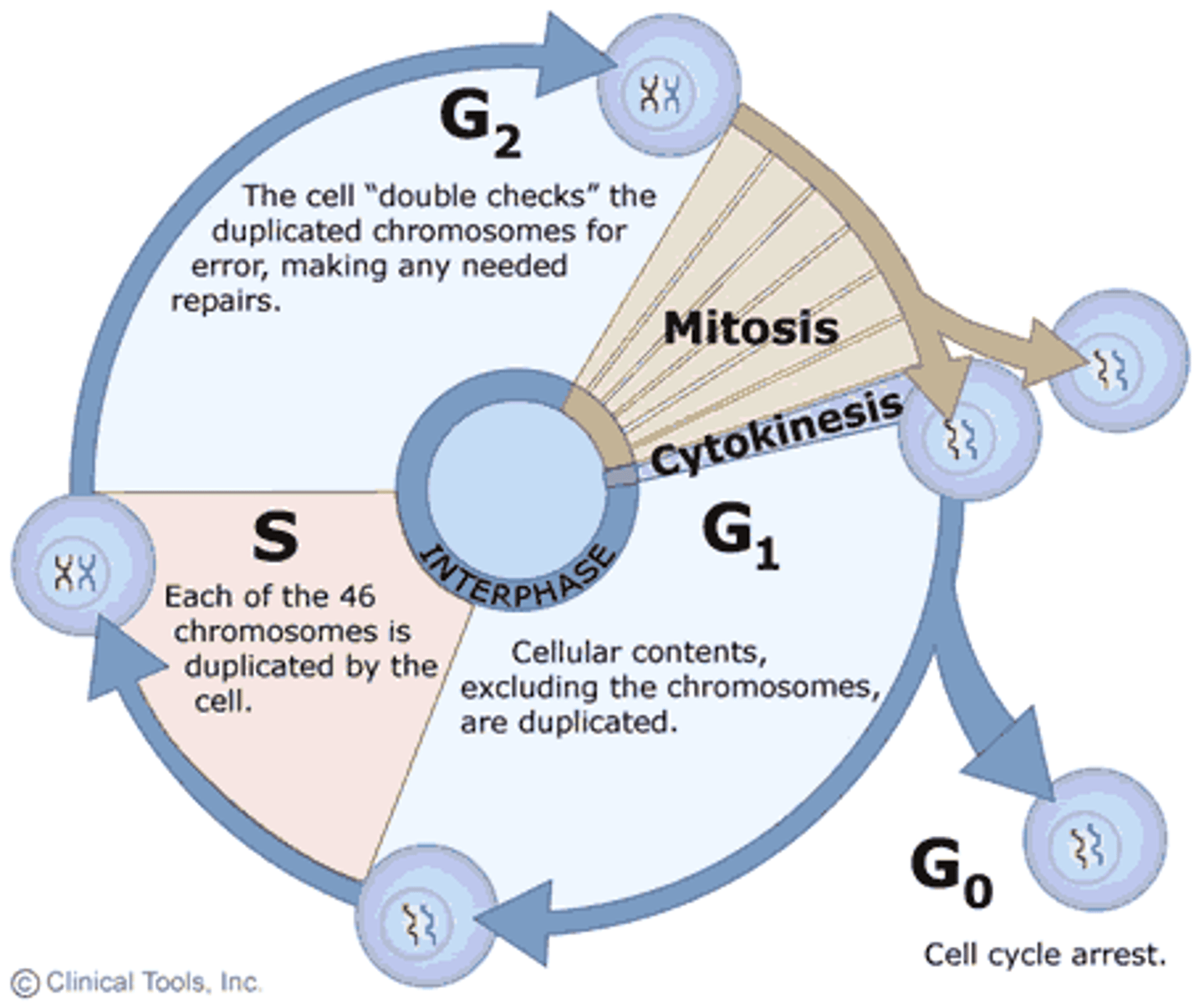
Mitosis: Interphase
- Before mitosis
- Resting phase
- DNA reproduction
- Getting ready for mitosis
- Gap 1: Cell grows
- Synthesis: Cell replicates DNA held by the cohesion loop
- Gap 2: Cell grows more as prep for mitosis
- Cell goes through checkpoints
- If the cell doesn't pass the checkpoints in interphase (G1, S, G2) apoptosis occurs
- Apoptosis: Gap 0; cell self-destructs = forever resting place= death
Mitosis: Prophase
- Chromatins in the nucleus condenses to form chromosomes. - Nucleus membrane begins dissolving
- Centrioles separate and move to opposite poles of the cell
- Spindle fibers attach to the centromeres

Mitosis: Metaphase
- Chromosomes meet in the middle of the cell
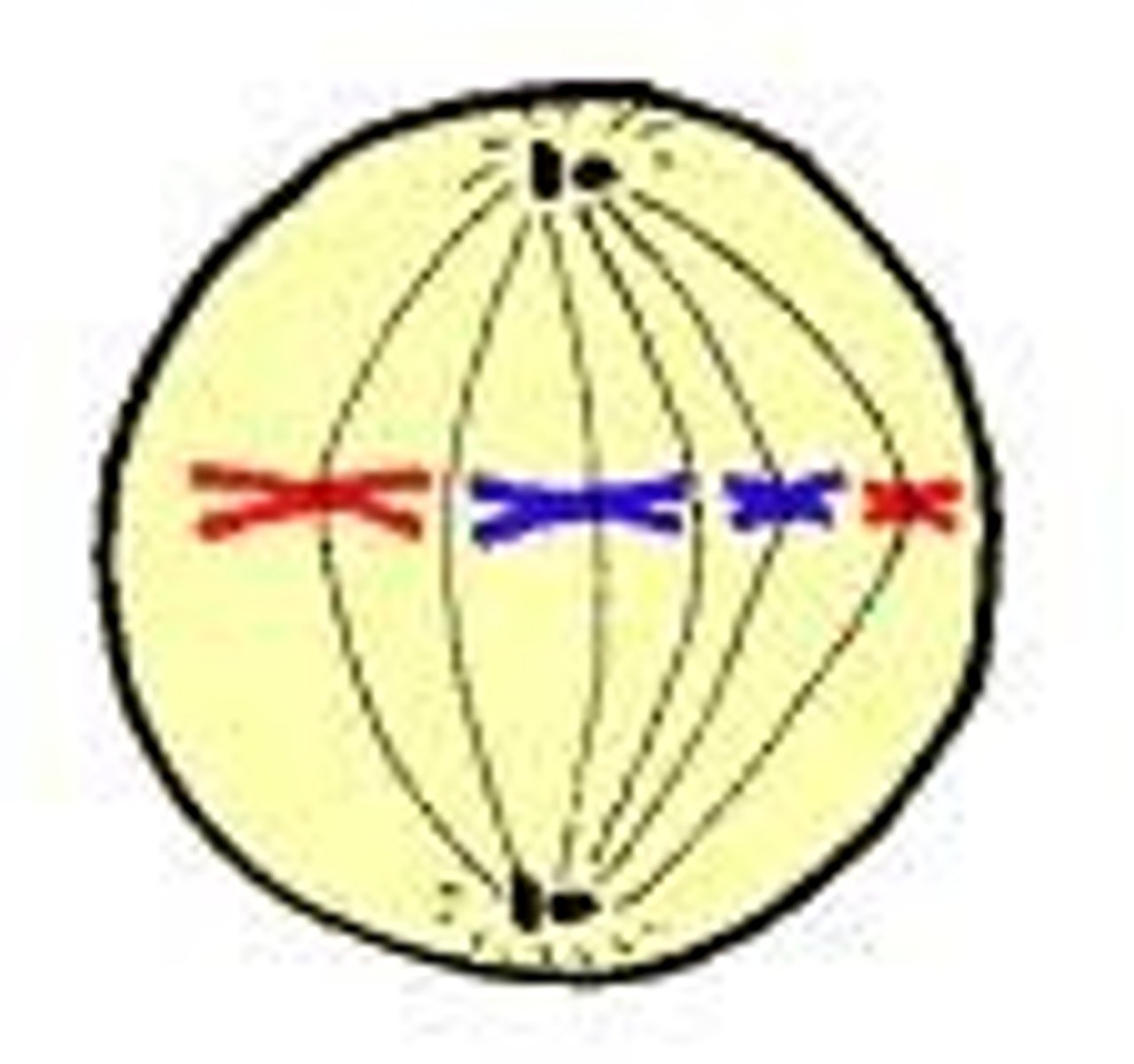
Mitosis: Anaphase
- Sister chromatids separate
- Them move to opposite poles of the cell
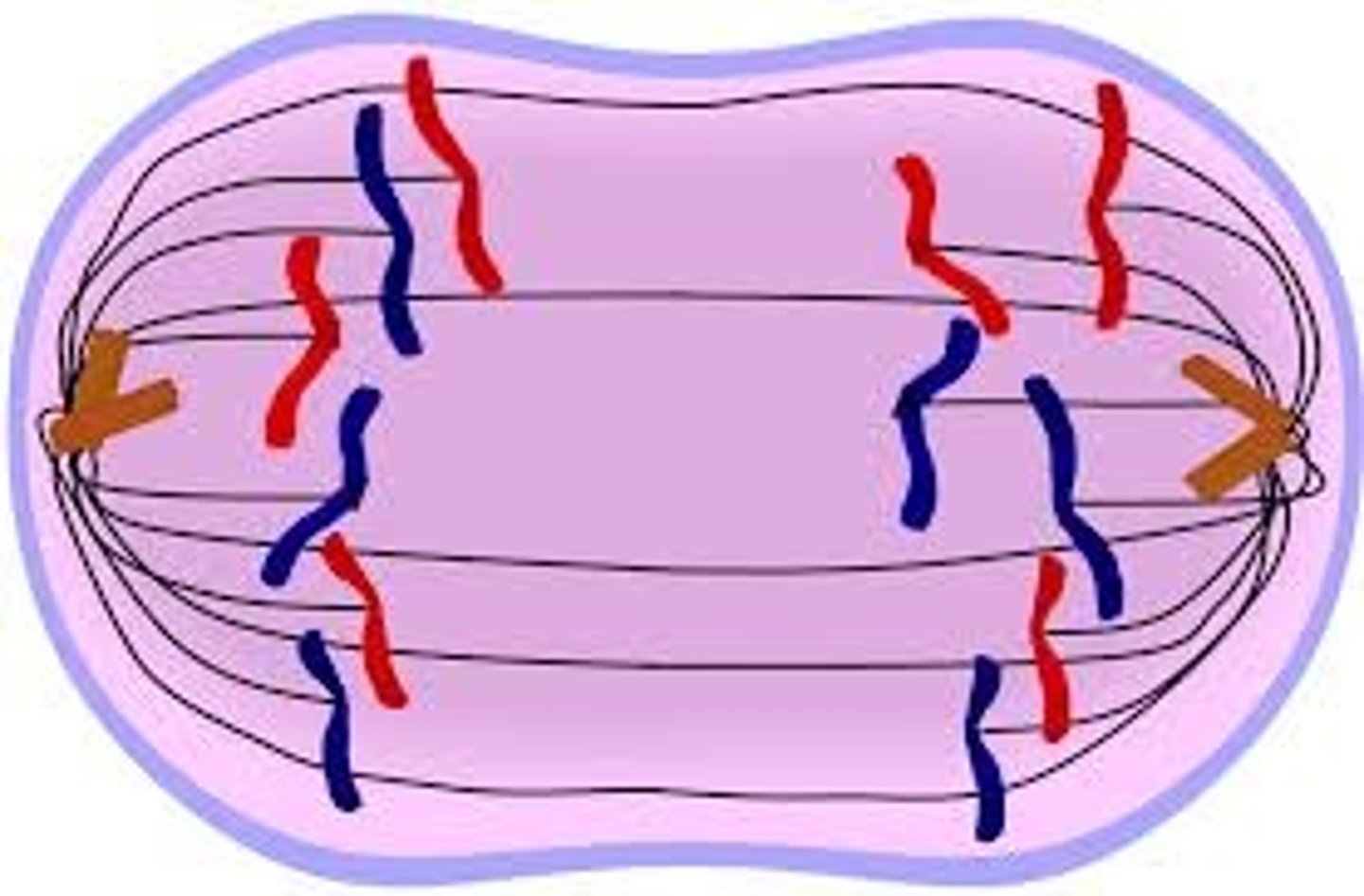
Mitosis: Telophase
- Nuclear membrane forms around the separated chromosomes
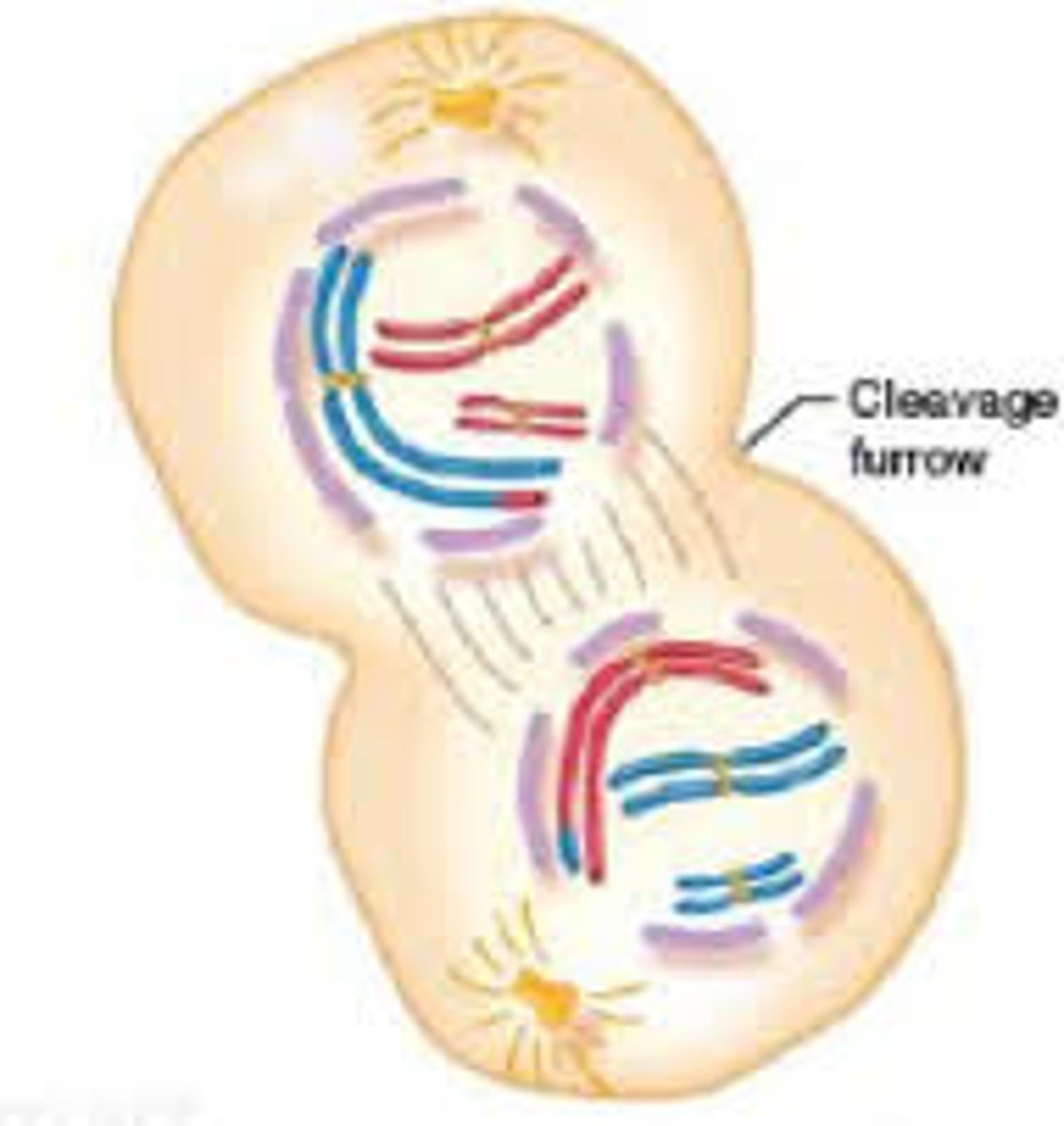
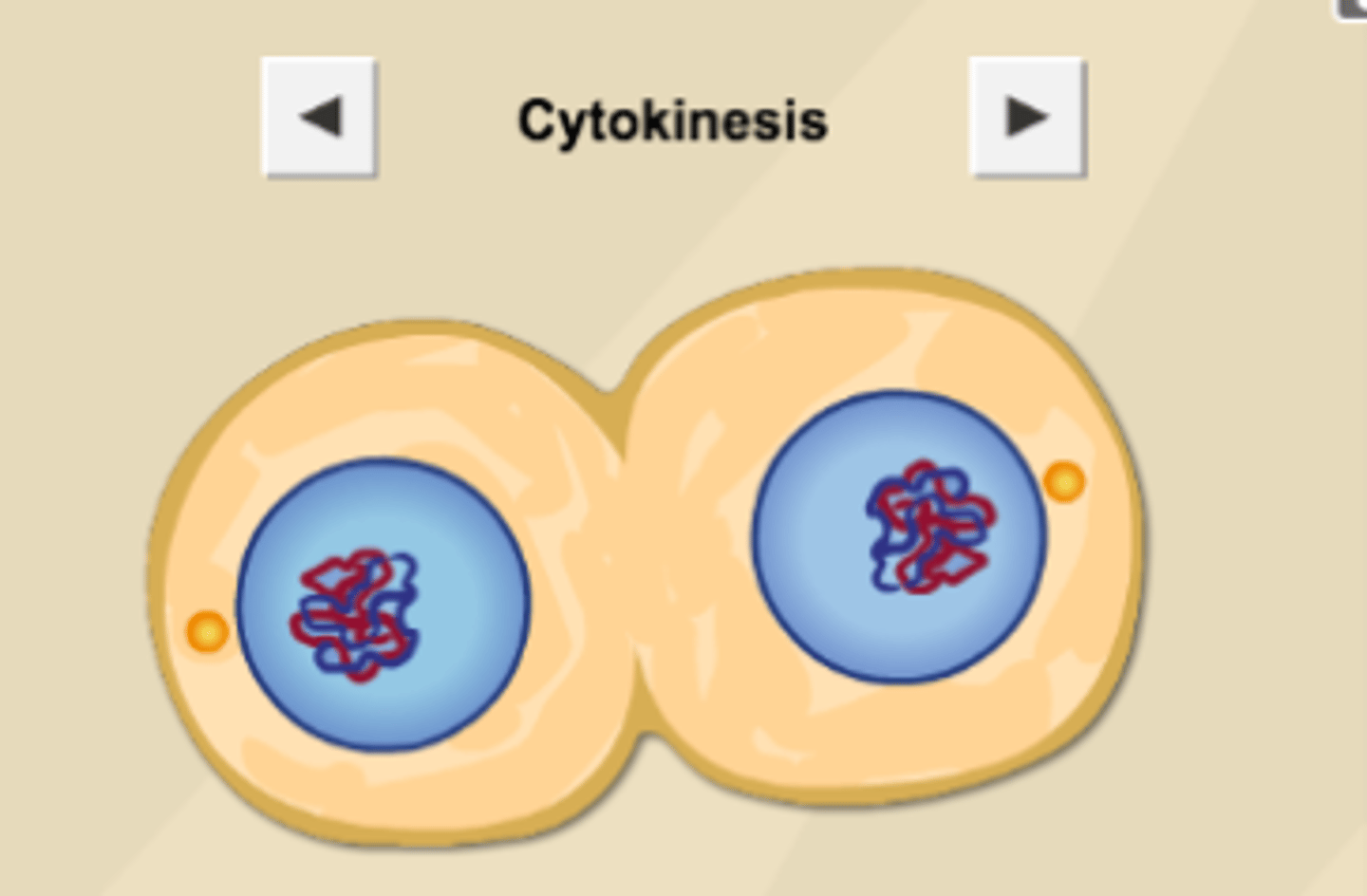
Mitosis: Cytokenesis
- Two daughter nuclei form
- Same structure and chromosomes as the parent cell
Homologous Chromosomes
- Same size
- Same type of DNA in the same locations
- Crossing over
- Line up in homologous pairs
- Transfer
-Recombinant chromosomes
- Bivalent = Homologous pairs in Meiosis metaphase 1
- Chromosomes = chromatin = DNA + Protein
- DNA wound around proteins = histones = nucleosomes (beads on a string)
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Similarities
- DNA
- Organelle: Ribosomes
- Makes proteins
- Cytoplasm
-Jelly-like fluid
- Plasma/Cell membrane
Prokaryotic Structures
- No nucleus
- Free-floating DNA
- No membrane-bound organelles
Eukaryotic Structures
- Large
- Complex
- DNA in nucleus
- Has membrane organelles
- Nucleus
- Mitochondria
- Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Golgi Apparatus
Mitochondria
- Generates ATP = energy
- Cellular respiration makes ATP
- Found in animal cells
- Found in every plant
- Utilizes oxygen to breakdown carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to reduce CO2 , H2O, and ATP
Chloroplast
- Sunlight energy = glucose (sugar)
- Photosynthesis
- CO2 + H2O = Oxygen + Carbohydrates(sugar)
- Found in only plants and algae
- Stores energy in organic material
Unicellular Organisms
- Single-celled
- Metabolism: Makes chemicals needed to sustain life from organic materials
- Growth
- Response: Detects changes and reacts to favorable or unfavorable conditions
- Homeostasis: Controls its internal environment
- Example: The kidney does it all
- Nutrition: Obtain food
- Reproduction: Sexual or Asexual
- Excretion: Removal of wastes produces during metabolism
- Movement: Need a method of movement
-Cilia and Flagella
sickle cell anemia
a genetic disorder that causes abnormal hemoglobin, resulting in some red blood cells assuming an abnormal sickle shape