kin 232 quiz 2
1/218
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
219 Terms
role of water in body
-maintain homeostasis (pH, temp, etc)
-facilitate enzymatic reactions for energy production
-helps maintain blood volume (supports CV fin, nutrient transport, and o2 delivery)
-transports nutrients and removes waste
-sweat cools body
-protects joints, lubricates movement, and hydrates cells
-water helps food breakdown and absorption
-electrolyte balance for muscle contractions and nerve function for nerve signalling
most of water comes out as
urine
factors that affect the individual need for fluid
body size and comp
physical activity
environmental factors (heat/altitude)
health status
medications
some herbal supplements
recommended amount of fluids
2.7 for women
3.7 for men
How caffeine works
crosses the blood brain barrier
blocks adenosine receptors
increases neural activity
how caffeine crosses blood-brain barrier
it is fat-soluble so can quickly reach brain and affect CNS
caffeine as an Adenosine Receptor Antagonist
blocks adenosine receptors, therefore keeping you alert and energized
what does adenosine do for the body
promotes sleepiness and relaxation
caffeines increase in neural activity
stimulates the release of dopamine and norepinephrine, increasing focus, concentration, and wakefulness
also impacts serotonin
caffeine stimulates the release of
dopamine and norepinephrine
peak levels of caffeine
45min after consumption
how long does caffeine last
about 5 hours
maximum amount of caffeine according to health Canada
no more than 400mg/day on a regular basis
energy drinks are marketed to
enhance mental and physical performance
common ingredients in energy drinks
caffeine, ginseng, taurine, herbal extracts
main use of hydration during exercise
thermoregulation
muscle contractions during exercise result in ____.
most is transferred to ___.
metabolic heat production
most is transferred to the core
what detects the rise in body temp
thermoreceptors in brain and skin
what happens when thermoreceptors detect increasing heat
hypothalamus responds by increasing blood flow to the skin, initiating sweating
how sweating works
vasodilation increases blood flow to skin, helping transfer heat from core to skin by evaporation
what detects hypo hydration?
mostly the brain and kidneys
when do we start to see increases in plasma osmolality
around 2% dehydration
osmoreceptors
detect changes in osmolality
in kidney
how kidneys react to dehydration
release renin to vasoconstriction blood vessels to conserve sodium and water
baroreceptors
in brain
detect changes in pressure due to dehydration
how brain reacts to dehydration
after baroreceptors detect dehydration, brain releases ADH which causes the feeling of thirst.
thirst sends signal to kidneys to release renin
role of renin in dehydration
vasoconstricts blood vessels to conserve sodium and water
effect of vasoconstriction conserving sodium and water on urine
decreased urine output due to increased water reabsorption = concentrated urine
dehydration range for exercising
want to be around 2 or 3%
effects of mild dehydration (2%) on exercise performance
high fatigue and RPE
impaired attention and psychomotor skills
impair immediate memory skills
impair neuromuscular control
decrease accuracy, power and strength
decrease muscular endurance
decrease motivaation
decrease sprint performance
effects of more severe dehydration (3-4%) on exercise performance
decreased swear rate and evaporative heat loss
increased body temp
decreased blood volume
decreased blood pressure
cardiovascular strain
altered metabolic and CNS functioning
gold standard of assessing hydration status
plasma osmolality
measures concentration of solutes in plasma
commonly used tools for hydration status assessment
urine osmolality
urine specific gravity
changes in body weight
urine colour chart
urine osmolality uses what device
osmometer
cons to urine specific gravity for hydration status assessment
prone to human error
on an osmometer, a high number signifies
high dehydration %age
how to calculate dehydration percentage
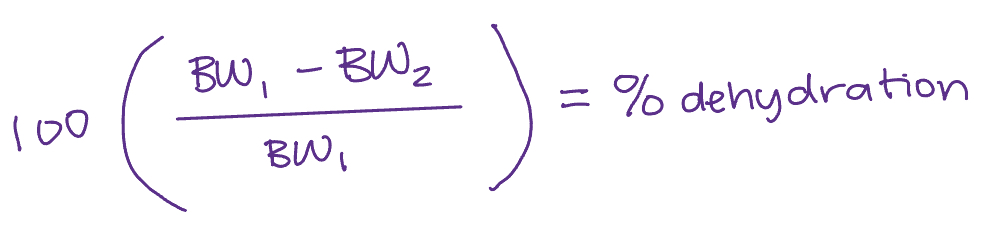
best fluid for short exercise (<45min)
water
nutrition and hydration for longer duration, steady state, high intensity exercise (45-75min)
maybe small amounts of CHOs, drink water
nutrition and hydration during start and stop sports (1-2.5hrs)
30-60g/h of carbs, an isotonic drink
nutrition and hydration during ultra endurance exercise (>2.5hrs)
up ti 90g/h of mixed carbs, and an isotonic drink
tonicity
amount of CHO in a fluid
hypotonic fluids
lower osmolality than blood
<6% CHOs
hydration is the goal, not calories
isotonic fluids
similar osmolality to human blood
6-8% carbs
used for most sporting situations
hypertonic fluids
higher osmolality than human blood
>8%carbs
high caloric intake is the goal, dehydration is not a concern (drag racing cars)
tonicity calculation
CHO (g) / volume
how to calculate sweat rate during exercise
[(pre exercise weight - post exercise weight) + fluid intake]/duration in hours
how much fluid to replace post exercise
150% of fluid deficit (1.5L for every 1kg body weight lost acutely)
side effects of overhydration
confusion, blurred vision, poor coordination, rapid breathing, vomiting
over hydration can result in
cellular edema and hyponatremia → dangerously low blood plasma levels
dangerously low plasma sodium levels
<135mmol/L
how do proteins differ from CHO and fats
they contain nitrogen
how do amino acids differ from each other
their R side chain determines AA size, shape, composition, electrical charge, and pH
how many essential amino acids
9
without enough essential amino acids the body could…
enter a diseased state
BCAAs
Branched-Chain Amino Acids
what are BCAAs (Branched-Chain Amino Acids)
subset of essential amino acids that are necessary for muscle health and metabolism
key BCAAs
leucine, isoleucine, and valine
leucine
a BCAA, key for protein synthesis and muscle recovery
essentially the master switch for creating or healing proteins or muscles
isoleucine
supports energy regulation and immune function → not as important in protein synthesis
valine
important for muscle metabolism and tissue repair → not as important in protein synthesis
most important BCAA in protein synthesis
leucine
primary protein structure
sequence of AAs that forms at least one polypeptide chain
secondary protein structure
coiling or folding of polypeptide chains
result of hydrogen bonding between amino acid chains
tertiary protein structure
three dimensional shape caused by weak interactions between side groups
quaternary protein structure
final 3D structure formed by all the polypeptide chains that form the protein
has a chaotic shape → important for making the protein do its role
denaturing of proteins
shape comes apart, can’t function properly
things that can denature protein
pH
stress
disease
temperature
mechanical digestion of proteins in the mouth
chewing
chemical digestion of protein in the mouth
nonexistent
digestion of protein in the stomach
first, hydrochloric acid denatures proteins into long polypeptide chains
then pepsin breaks these proteins into smaller polypeptides
role of hydrochloric acid in protein digestion
denatures proteins into their long polypeptide chains
role of pepsin in protein digestion
begins breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides
digestion of protein in small intestine
enzymes from pancreas and from the brush border of the small intestine break polypeptides down even more than the stomach did, turning them into free amino acids and smaller peptides
enzymes from pancreas that help protein digestion
trypsin and chymotrypsin
absorption of proteins
amino acids and small peptides are absorbed by enterocytes that line the small intestine
transport of proteins
once absorbed, amino acids enter bloodstream and are transported to the liver and other tissues for use in protein synthesis and other metabolic processes
storage of protein
not really a thing. excess gets excreted
4 things that can happen to amino acids
undergo deamination
have their carbon skeletons enter the Krebs cycle
be incorporated into body proteins or used to synthesize other nitrogen-containing compounds (nonessential AAs)
rare but sometimes oxidized for energy
functions of protein
structure and motion
transportation
chemical messaging
catalysis
immune function
proteins used for structure and motion
collagen, keratin, contractile fibres of muscle
protein used for transport
hemoglobin
role of nucleus in protein synthesis
DNA contains info needed to make protein
steps in protein synthesis
recognition of need
transcription
translation
transcription
DNA is unwound and transcribed to produce mRNA which carries the recipe for a protein
role of mRNA in protein synthesis
carries the recipe for a protein
translation
the mRNA instructions are read by ribosomes to assemble amino acids into a polypeptide chain, which ultimately forms a protein
role of ribosomes in protein synthesis
they read the mRNA instructions to assemble amino acids into a polypeptide chain, ultimately forming a protein
impact of insufficient amounts of an AA on protein synthesis
will stop or slow the formation of the protein
what happens when body is missing a nonessential AA needed for protein synthesis
body will either make it or will take it from the amino acid pool in the liver (will travel through the bloodstream)
what happens when body is missing an essential AA needed for protein synthesis
synthesis will stop, the incomplete protein will be broken down / degraded. AAs will be sent to the amino acid pool to be used elsewhere
protein intake guidelines
RDA = 0.8g/kg
10-35% of energy intake
protein intake recommendation for athletes
1.6g/kg
criteria to determine quality of protein
bioavailability - how much of the protein that we consume is absorbed and used by the body
amino acid profile - the essential and nonessential AAs that it contains
bioavailability of protein
how much of the protein that we consume will be absorbed and used by the body
complete protein source
contains all 9 essential AAs
complete protein source examples
meat, fish, eggs, dairy, quinoa, soy
reference food for DIAAS content of food
whey isolate = 100%
DIAAS score grades
100%+ excellent
75-99% good
less than 75% no claim