epi final exam
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
diseased, Signs, diagnose, asymtomatic
purpose of screening: identify individuals who exhibit signs of
Being _____ (HIV);
Early ____ of disease (Cancer);
Known risk factors for disease (ie cholesterol, hypertension);
Generally not intended to _____; distinguish btwn those who have the disease/risk factor from those who don’t
usually _______ persons
Early detection: basis for any screening program: in the natural history disease, should be detectable between initiation and clinical symptoms
add examples from homework
observed, inferred, checklist
Associations are _____; causation is _______; evidence must be considered & criteria weighted against each other to infer causal relationship; NOT a ______
history, compare, discomfort
Ideally screening tests
Are acceptable to people;
Is natural ______ of disease understood;
Are the costs acceptable —> Should be inexpensive
Have an acceptable level of ______;
Must have reasonable gold standard with which to ______ (mammography and subsequent tissue biopsy; cardiac stress test and subsequent angiogram)
invasive
mammograms
detection prevents treatment (mastectomy & death from cancer);
Incidence rises w/ age & family history (define target pop)
Sensitivity & specificity; minor discomfort & non _____
blind, burden, listen
Evaluation of screening tests
Independent _____ comparison w/ gold standard;
sample population must include an appropriate spectrum of patients to who are applied in clinical practice; will your patients be better off? Will pop be better off?
What is the _____ of suffering associated w/ the screening protocol? Effectiveness of treatment ?
Labeling effects; psychological effect of test results or diagnoses on patients can help or hurt
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force → When do insurance begin to cover X (they ____ to guidelines)
prioritization
foodborne illness
______: limited resources; high priority are life threatening; high risk; large # ppl, on-going, new cases, political pressure, intentionality;
local PH agency leads outbreaks when exposure and or majority of ill resided within jurisdiction; state PH lead multistate & multi county;
lead, selection, length, slower
screening biases
Prolong life or reducing invasiveness
___ time: perception that the screen-detected case has a longer survival;
______: people who seek screening are different than people who do not;
______ time: proportion of slow growing lesions diagnosed during screening programs is greater than the proportion of those diagnosed during usual medical care;
____-growing tumors makes screening seem to improve survival; usually related to cancer
traceback
______ investigation: how many were sick? Contact info? Specimen? Treatment? Contacted PHD? Local PH gather info & shared w state HD and FDA/USDA; different industries different agencies
control
_____ measures: asap when outbeak; prvenent more disease & protect credibility; do not wait for lab
Education, disinfection, exclusion, avoidance, close, recall
pitfalls
________: “too long ago”, incomplete questionnaires, no casedefinition, not interviewing well ppl, no specimen, communication
consistency, strength
relative risk of breast cancer for alcohol drinkers as compared to persons who did notdrink alcohol were 2.5, 3.4, 5.2, 2.6, 4.2, and 3.2 in the six cohort studies. __________ & _________
consistency
review of literature identified 6 cohort studies that had investigated the associationbetween alcohol use and breast cancer. All found a positive association between alcohol consumption and increased risk of breast cancer.
______
done response
in the study by Smith-Warner, 1998, the findings indicated that as alcohol consumption increased, the relative risk of having breast cancer also increased. ______ ________
plausibility, coherence
Alcohol may increase the risk of breast cancer by its effect on estrogen levels. Simplyput, it is known that estrogen is a cancer promoting hormone in high levels; and alcohol tends to increase the availability of estrogen in the body.
_______, ________
dose response
The rate of second heart attacks (MI) decreases progressively with higher dosage formulations _______ ________
plausibility
Studies have shown that lipitor decreases the formation of blood clots, which precede MI’s
____________
strength
In the 1990’s, it was established that lipitor reduced the risk of 2nd MI by 5-7 times _______
consistency
Nearly all studies show a positive association between lipitor use and reduced rate of recurrent MI. _______
temporality
The risk of MI decreases soon after lipitor use has begun
false +, specificity
If the diagnostic (confirmatory) test is expensive orinvasive, or anxiety provoking Minimize _____ ______ & use _______ cutpoint
length time bias
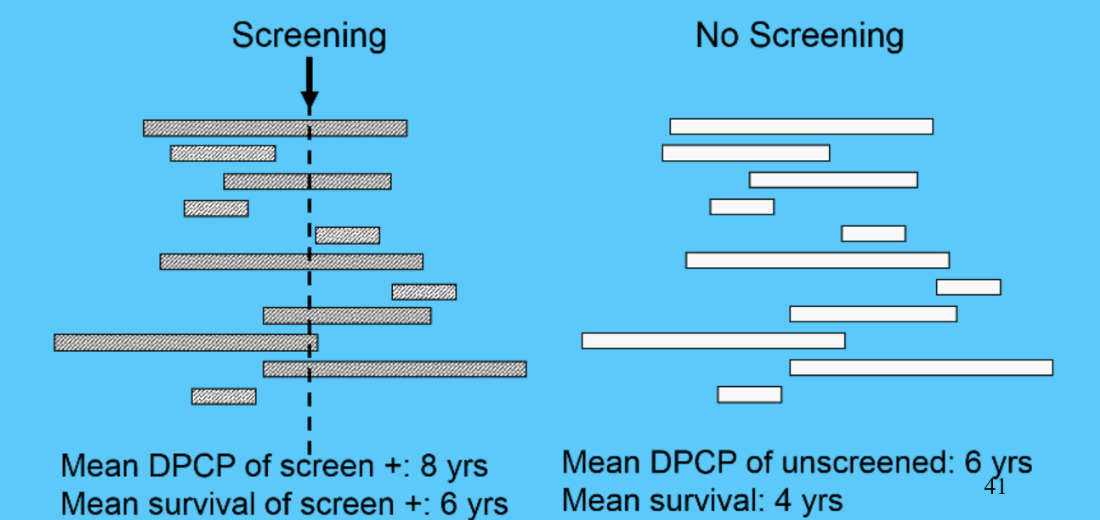
lead time bias
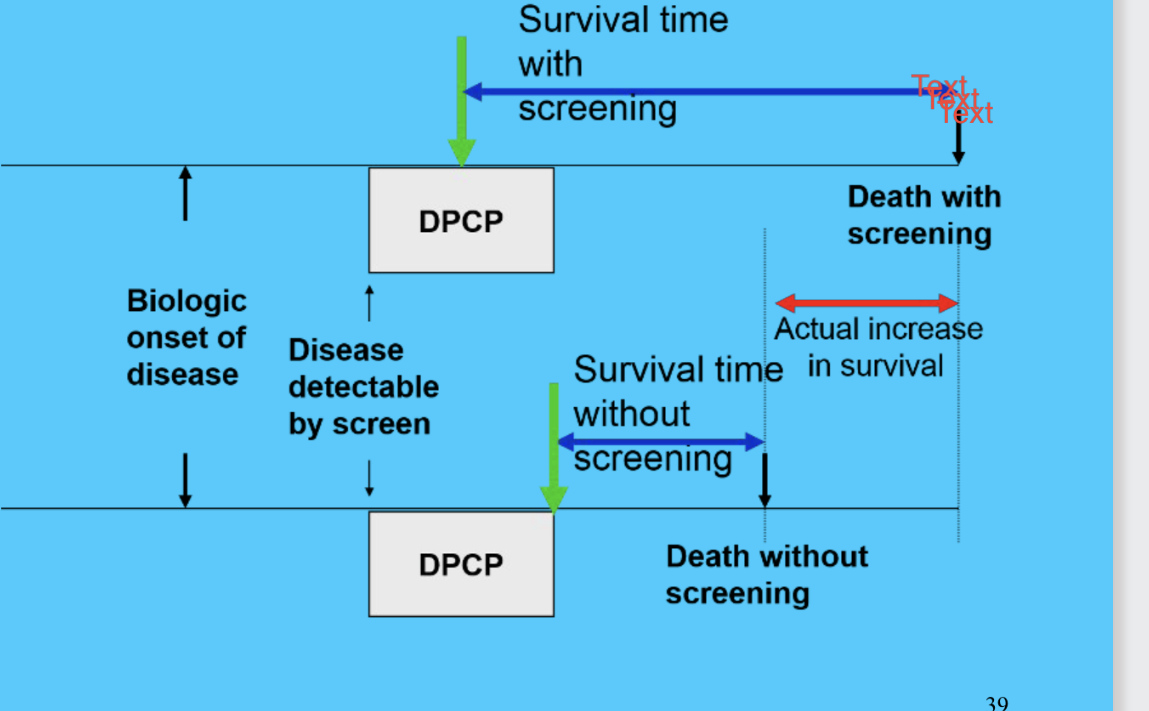
lead time bias
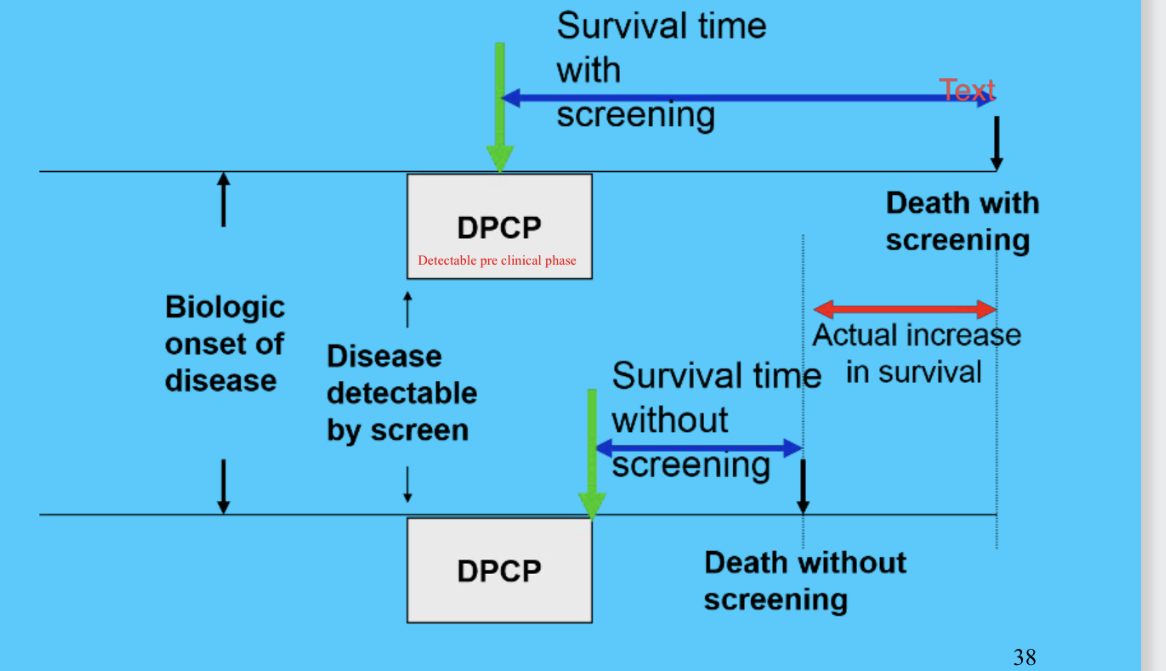
opposite
screening measured in 2 ways
true + / total positives or _____
necessary
types of cause: Causal pies
________ cause ≡ found in all cases
contributing
_______ cause≡ needed in some cases
sufficient
_______ cause ≡the constellation of necessary &contributing causes that make disease inevitable in an individual
susceptibility
Causal complement = the set of factors that completes a sufficient causal mechanism
ex. in tb the bacteria is the necessary agent but the causal component is
proof
causal webs (hierarchy)
____ is impossible but causal statements can be made strong
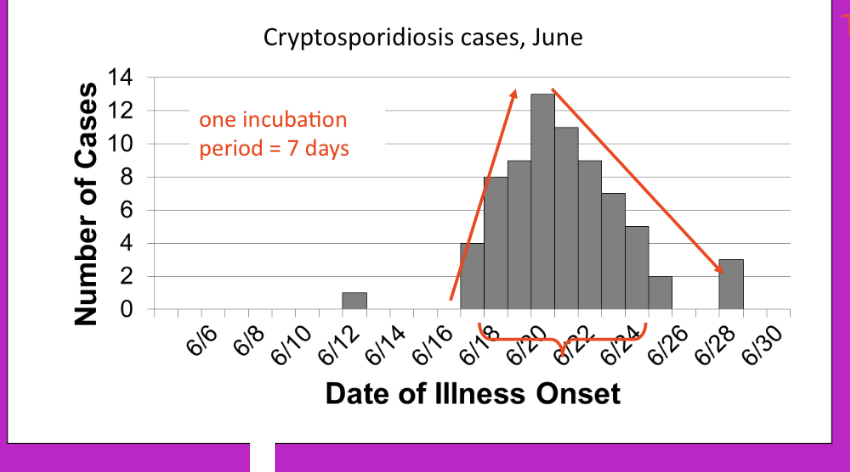
point source outbreak
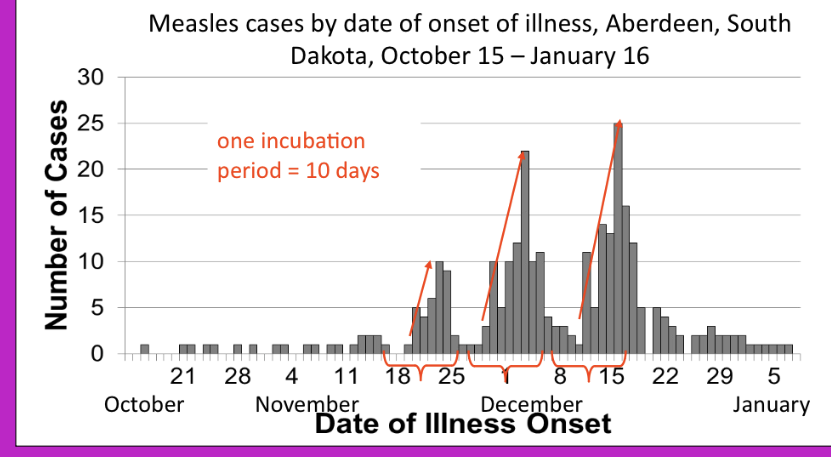
propagated outbreak
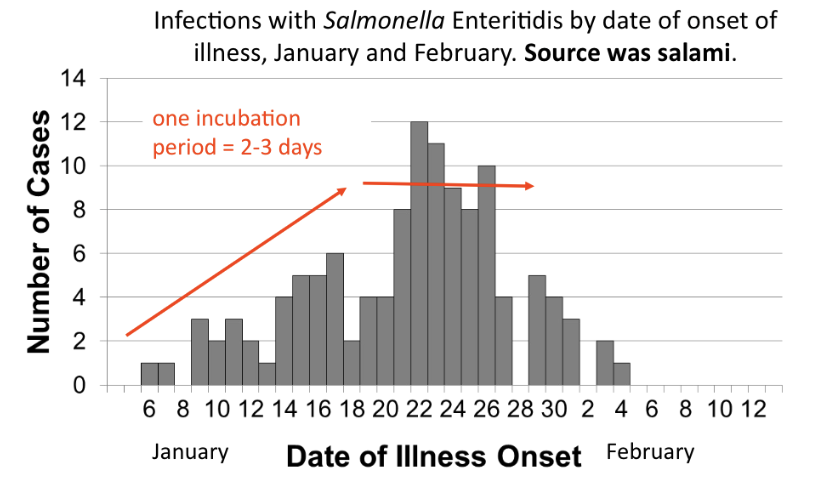
continuous common source