Anatomy and Speech Science - Respiratory Exam
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
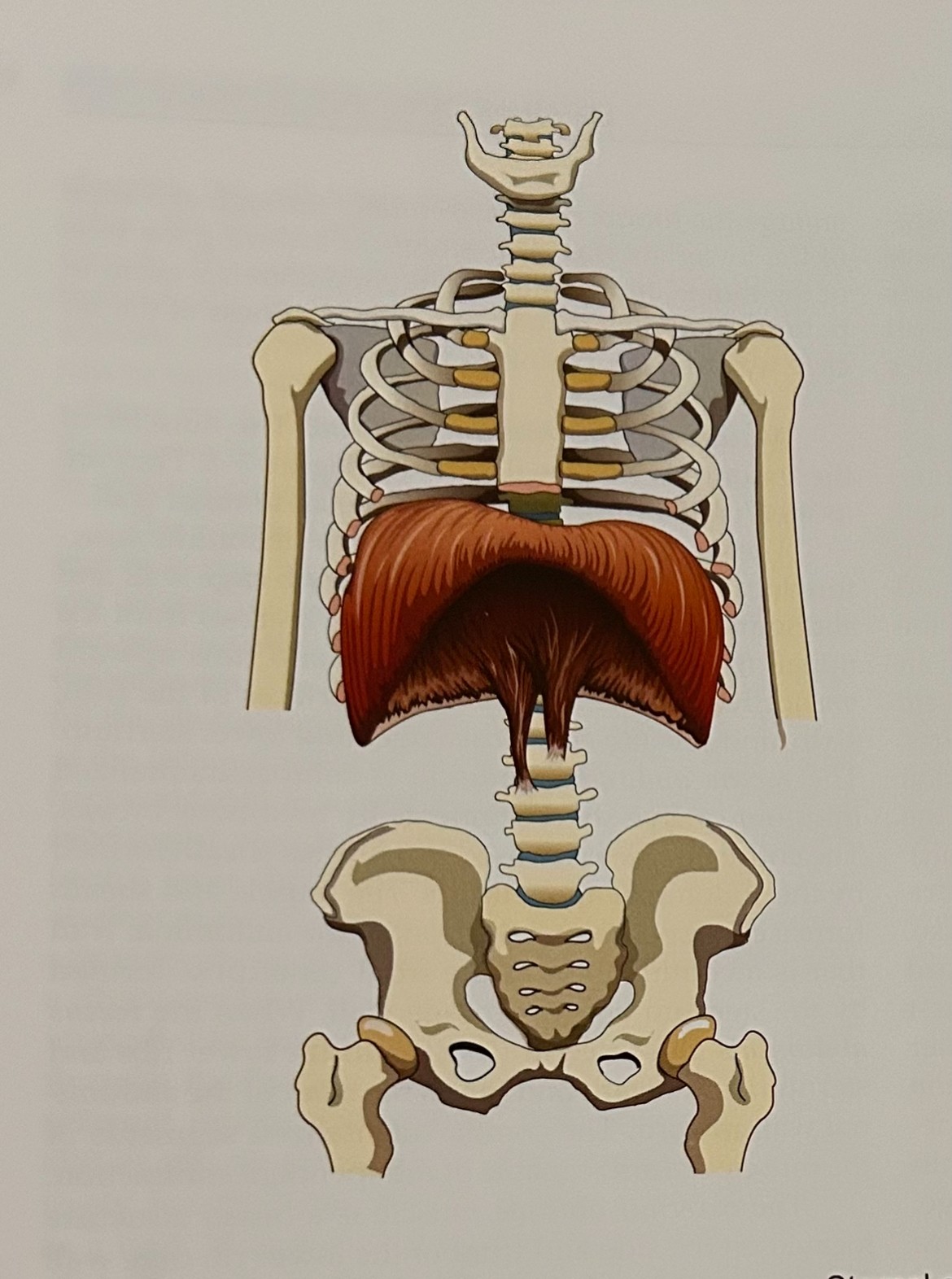
Diaphragm (Primary Inhalation):dome-shaped floor of thoracic cavity and roof of abdominal viscera, singular, attaches to sternum, lower ribs (11&12), lumbar vertebrae, and ventral tendon. Contains three passageways. The function is to raise the thoracic cavity and compress the abdominal viscera.
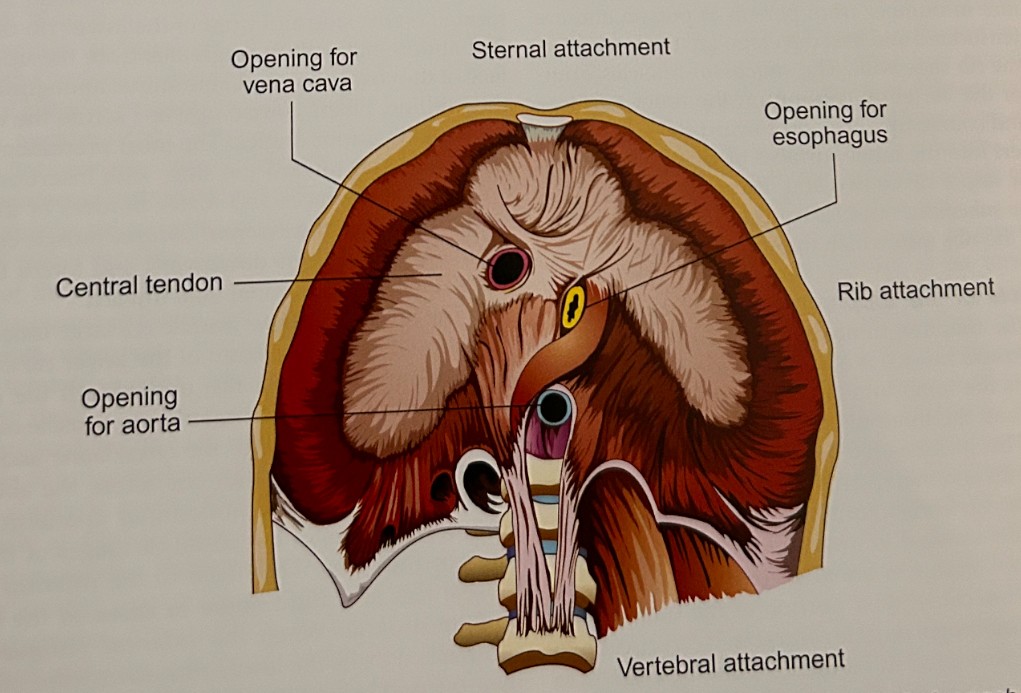
aortic hiatus: aorta carries oxygenated blood away from the heart.
esophageal hiatus: esophagus carrying food to stomach.
foramen vena cava: vein returning to heart. Inferior vena cava.
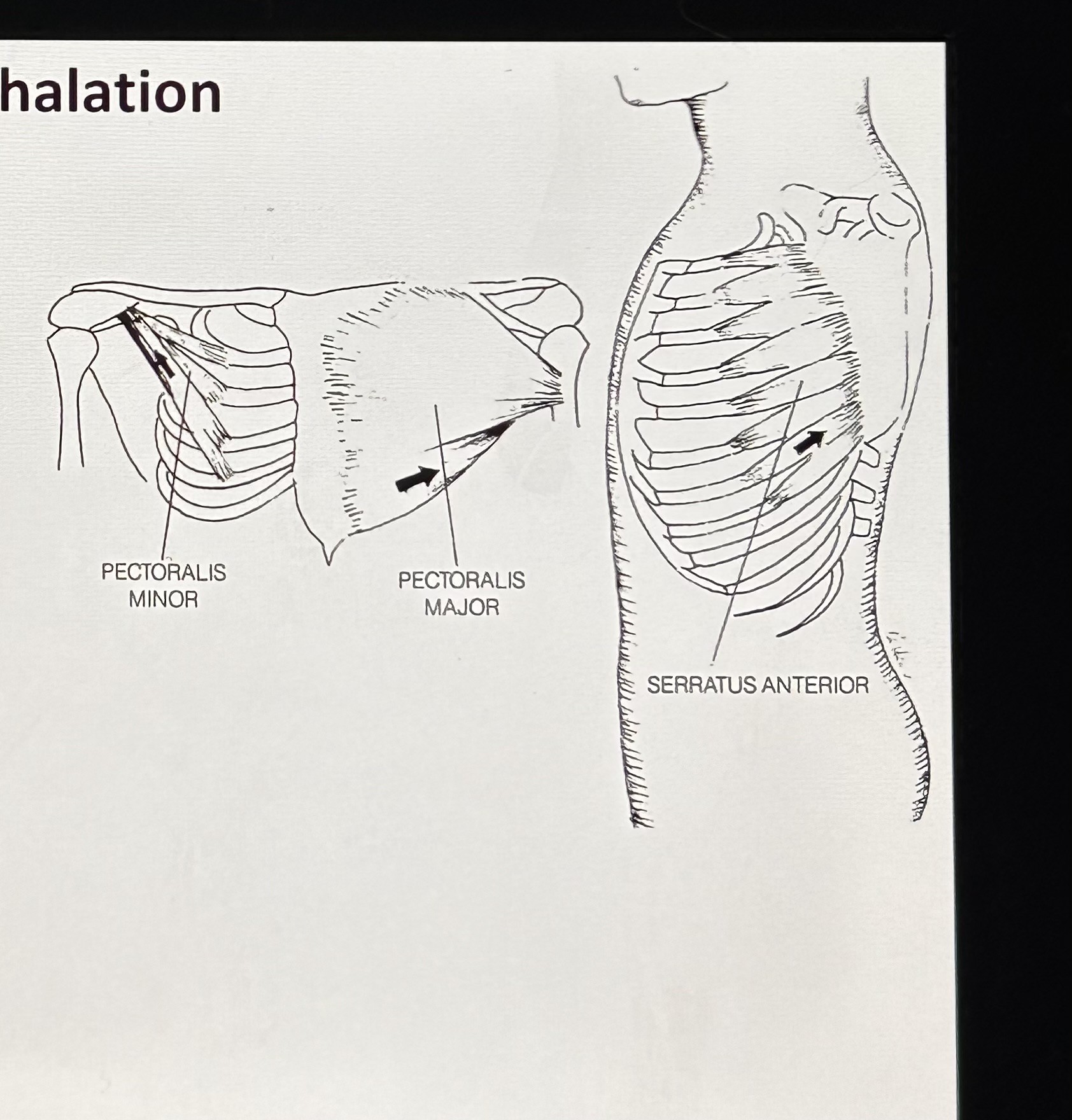
Pectoralis major (Secondary Inhalation): attaches to humerus (upper arm), clavicle, sternum, and costal cartilage. Function is to raise ribs and sternum.
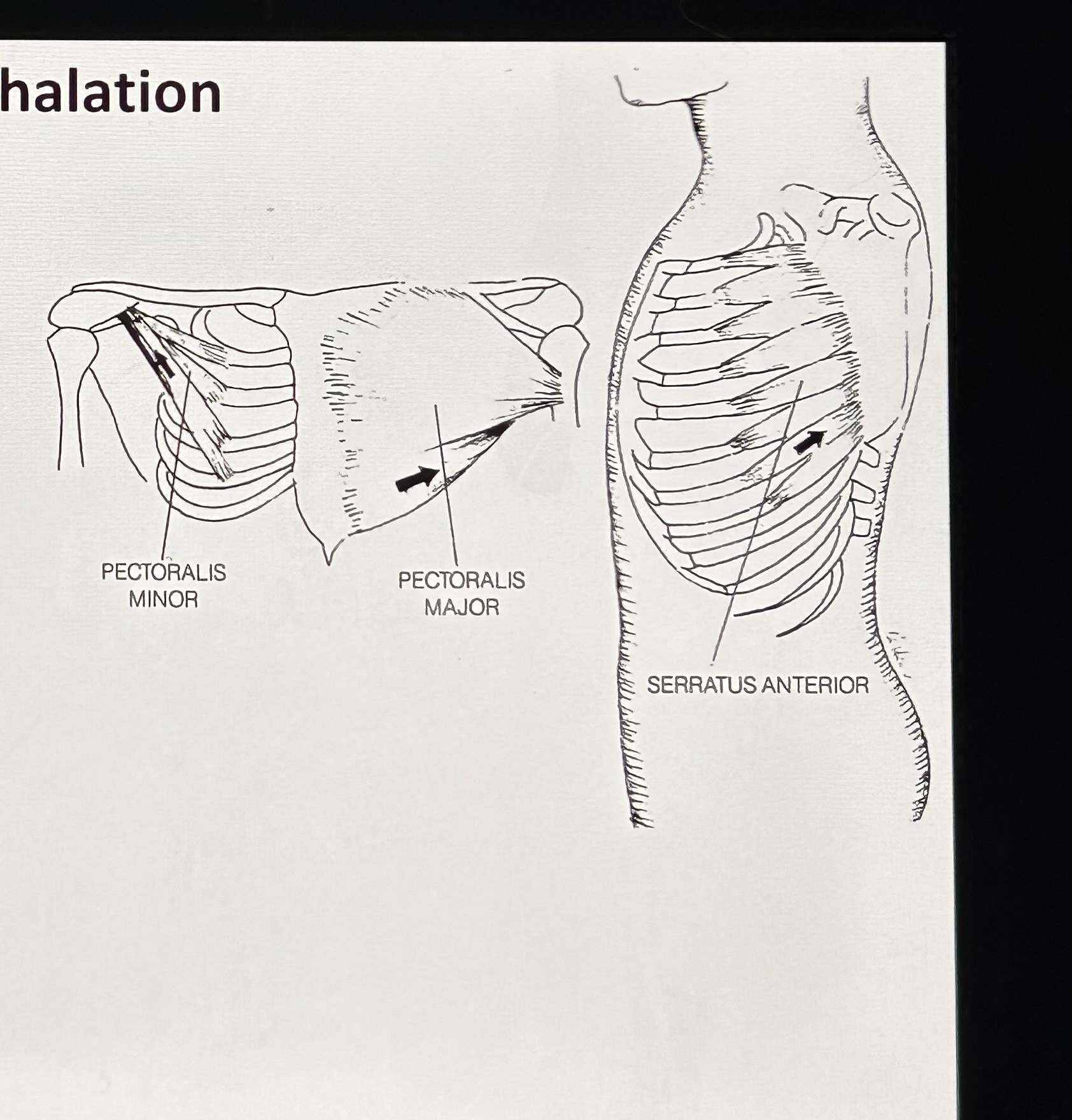
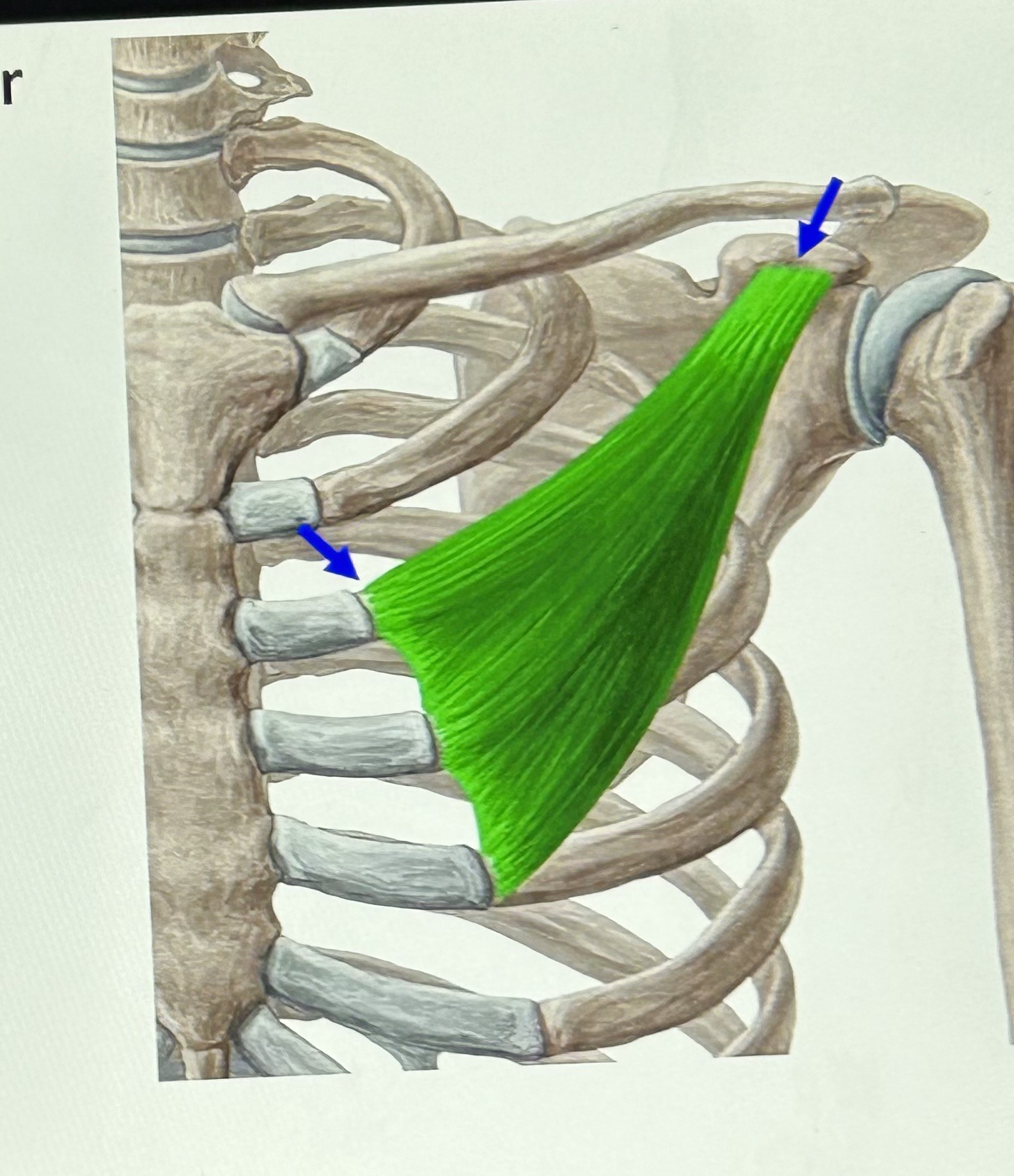
Pectoralis minor (Secondary Inhalation): attaches to scapula and ribs 2-5 and it raises some ribs.
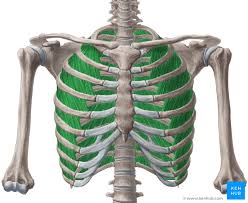
External intercostals (Primary Inhalation): attaches between ribs, fills most space except anteriorly where tendon attaches. Function is to raise the rib cage.
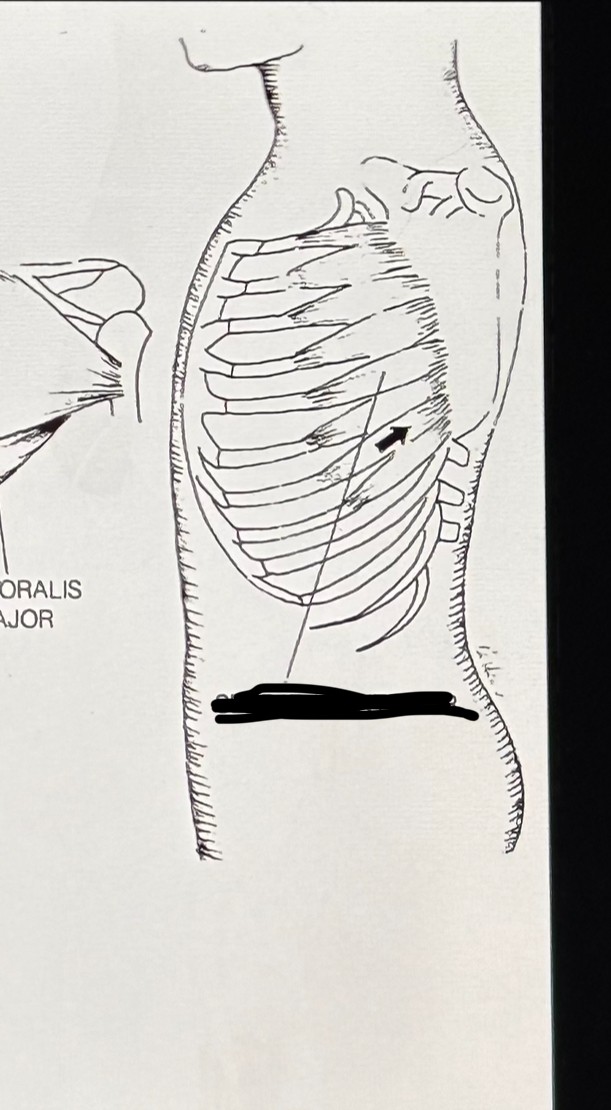
Serratus anterior (Secondary Inhalation): serraded edge, surface of scapula and ribs 1-9, raises ribs.
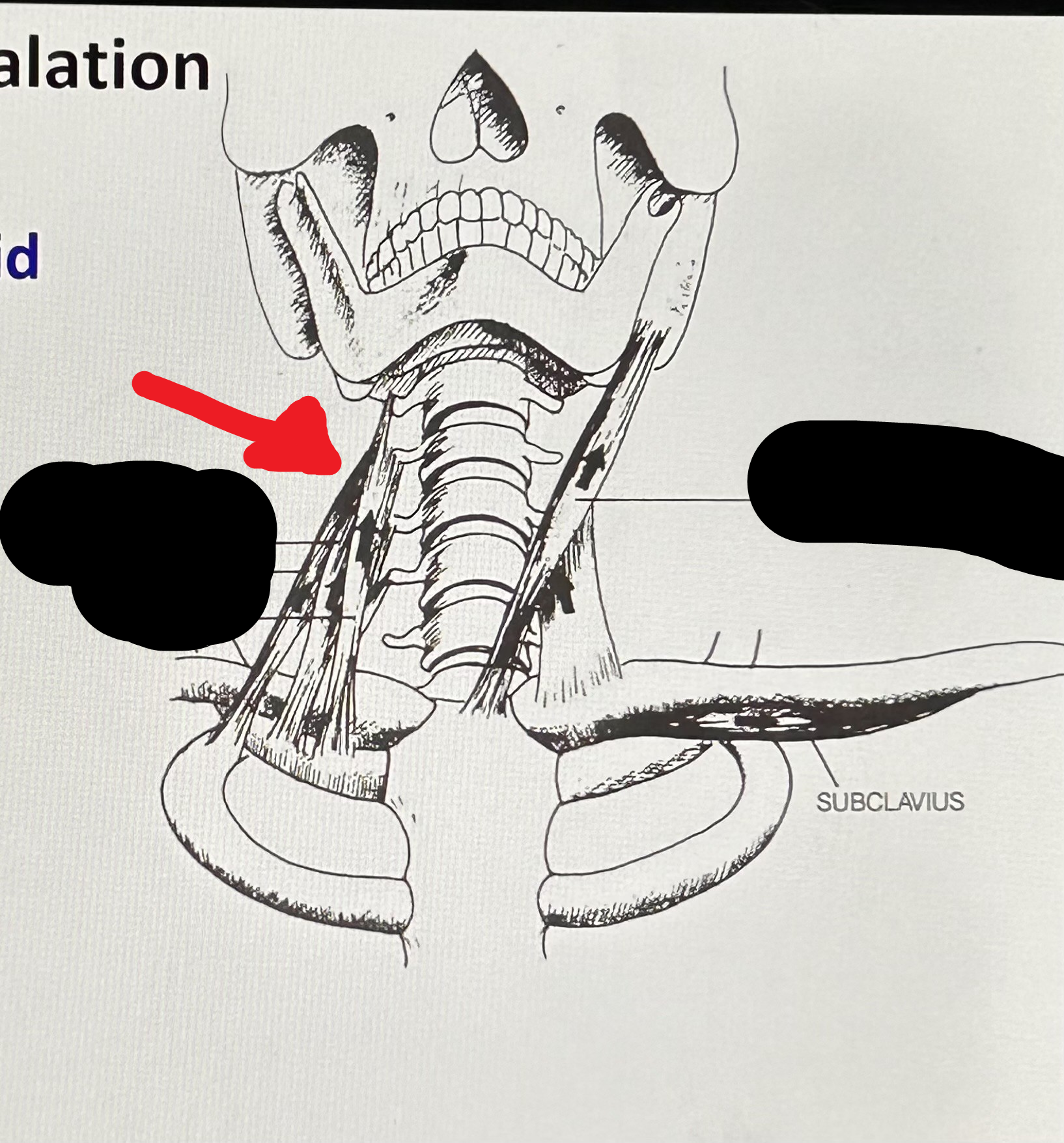
Scaleni (Secondary Inhalation): cervical vertebrae, 1st and 2nd ribs. It can raise some ribs.
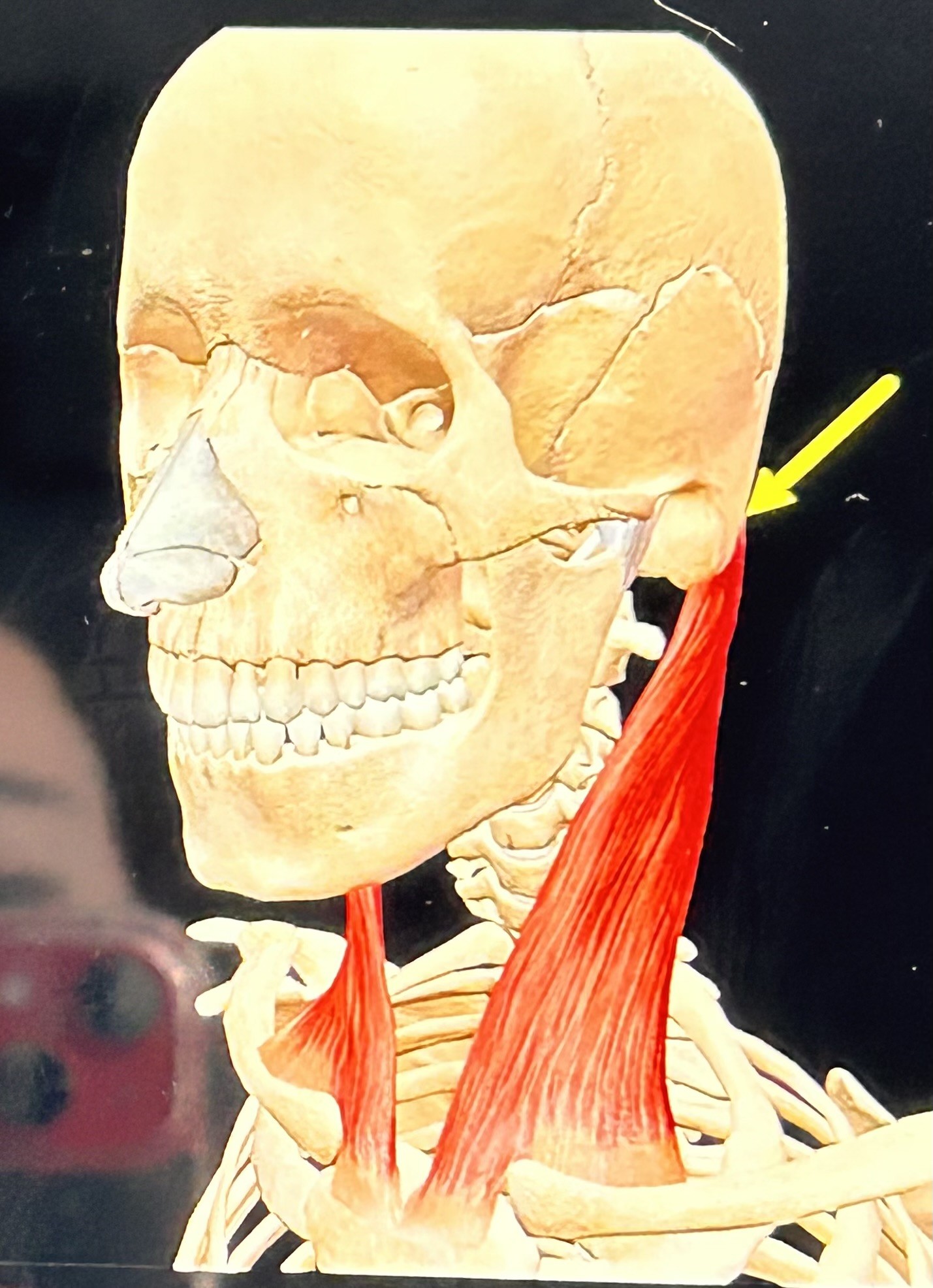
Sternocleidomastoid (Secondary Inhalation): attaches to mastoid, sternum, and clavicle. Raises ribs and sternum.
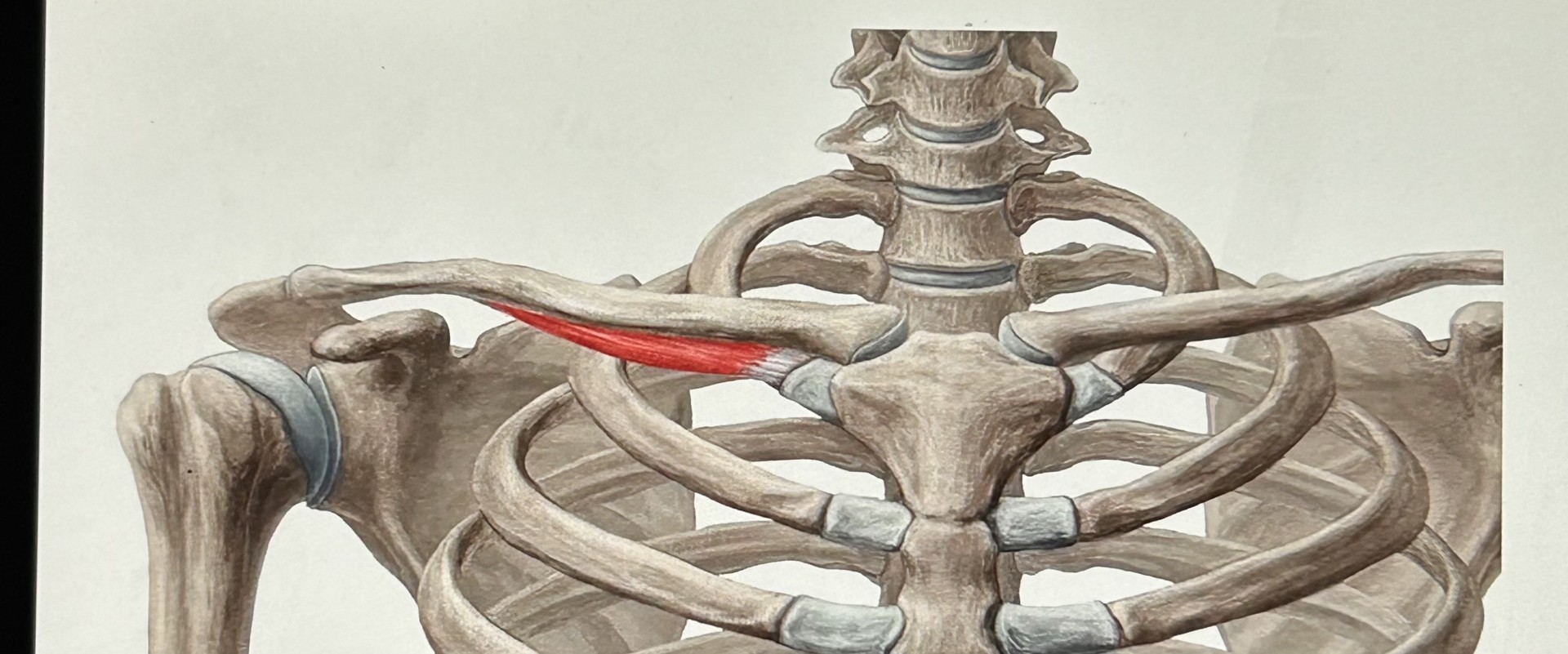
Subclavius (Secondary Inhalation): below clavicle, attaches to first rib. Raise first rib.
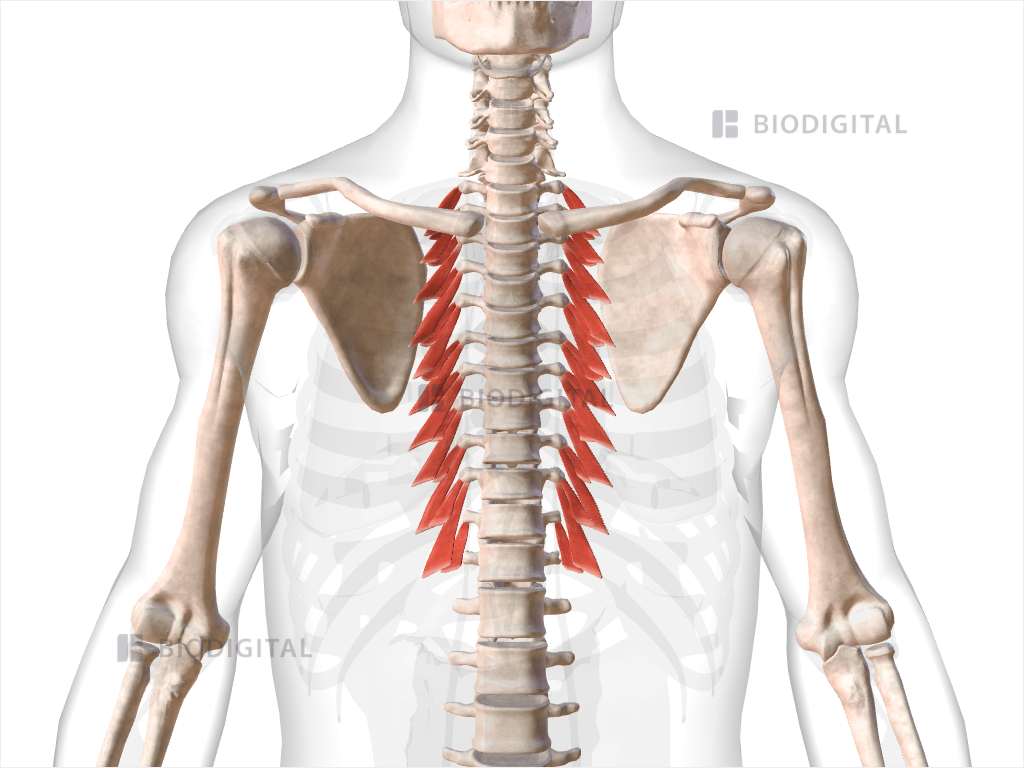
levatores costarum (Secondary Inhalation): 12 small muscles. 7th cervical - 11th, thoracic vertebrae, and rib below vertebral attachment. Raise rib cage (weak).
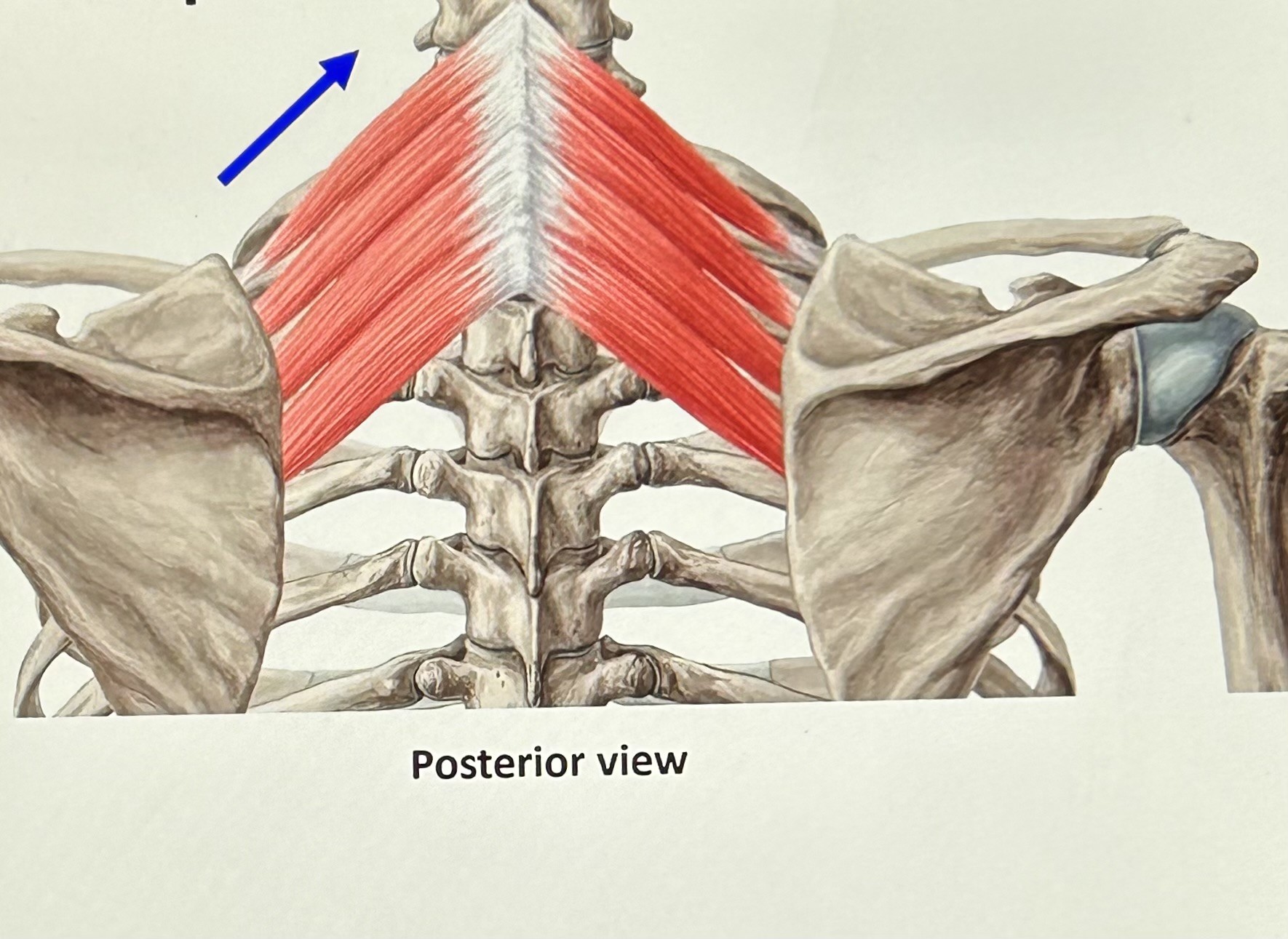
serratus posterior superior (Secondary Inhalation): 7th cervical to the first three thoracic vertebrae and upper ribs. Function: raise ribs (strong).
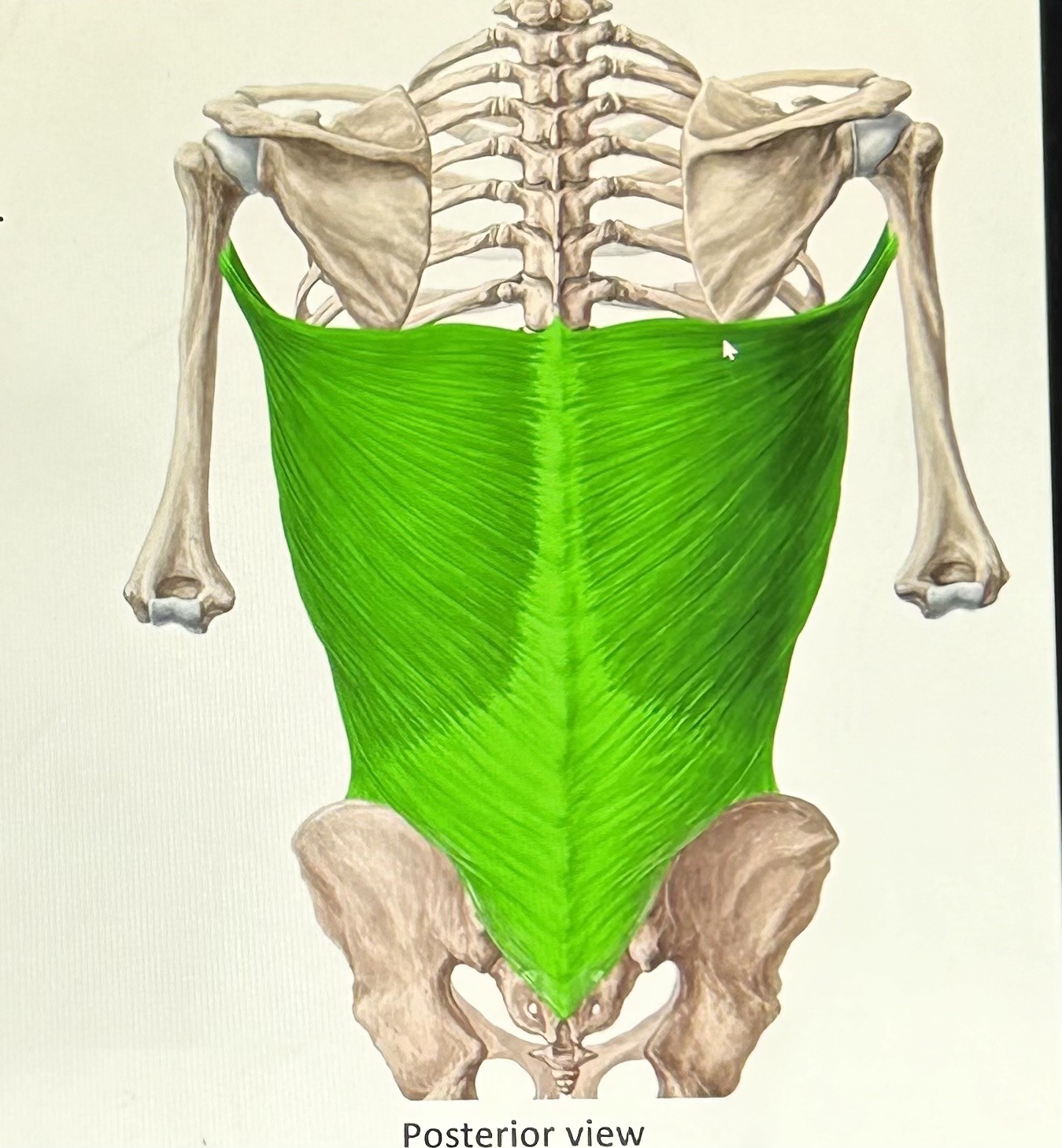
latissimus dorsi (exhalation): humerus, lumbar fascia, and ribs 10-12. Function raise lower ribs.
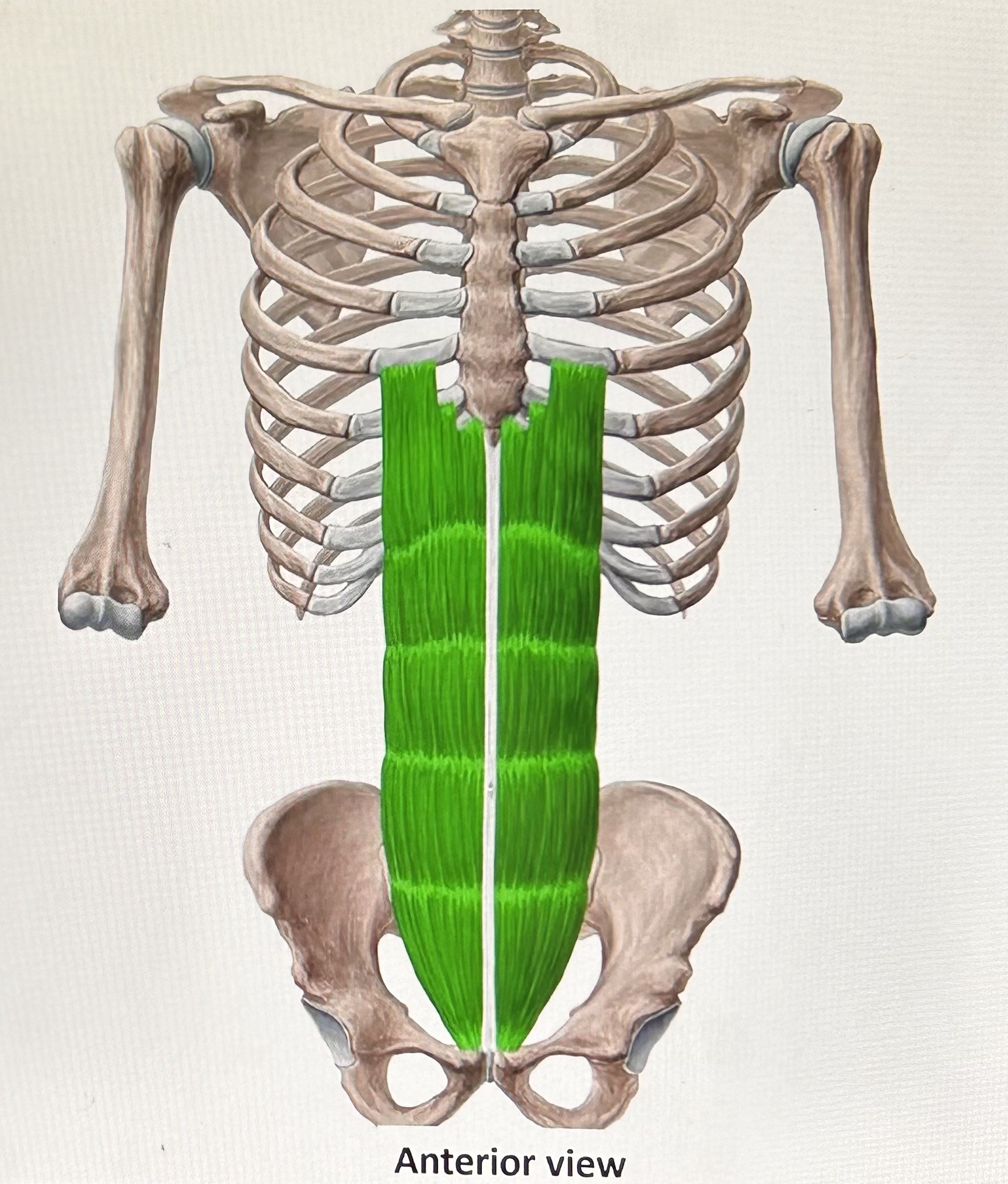
rectus abdominis (exhalation): (abs) fibers run vertical, enveloped in abdominal aponeurosis (layer of connective tissue). Attaches to pubic bone, sternum, and ribs 5-7 (cartilage). Function: pull sternum and ribs to compress the
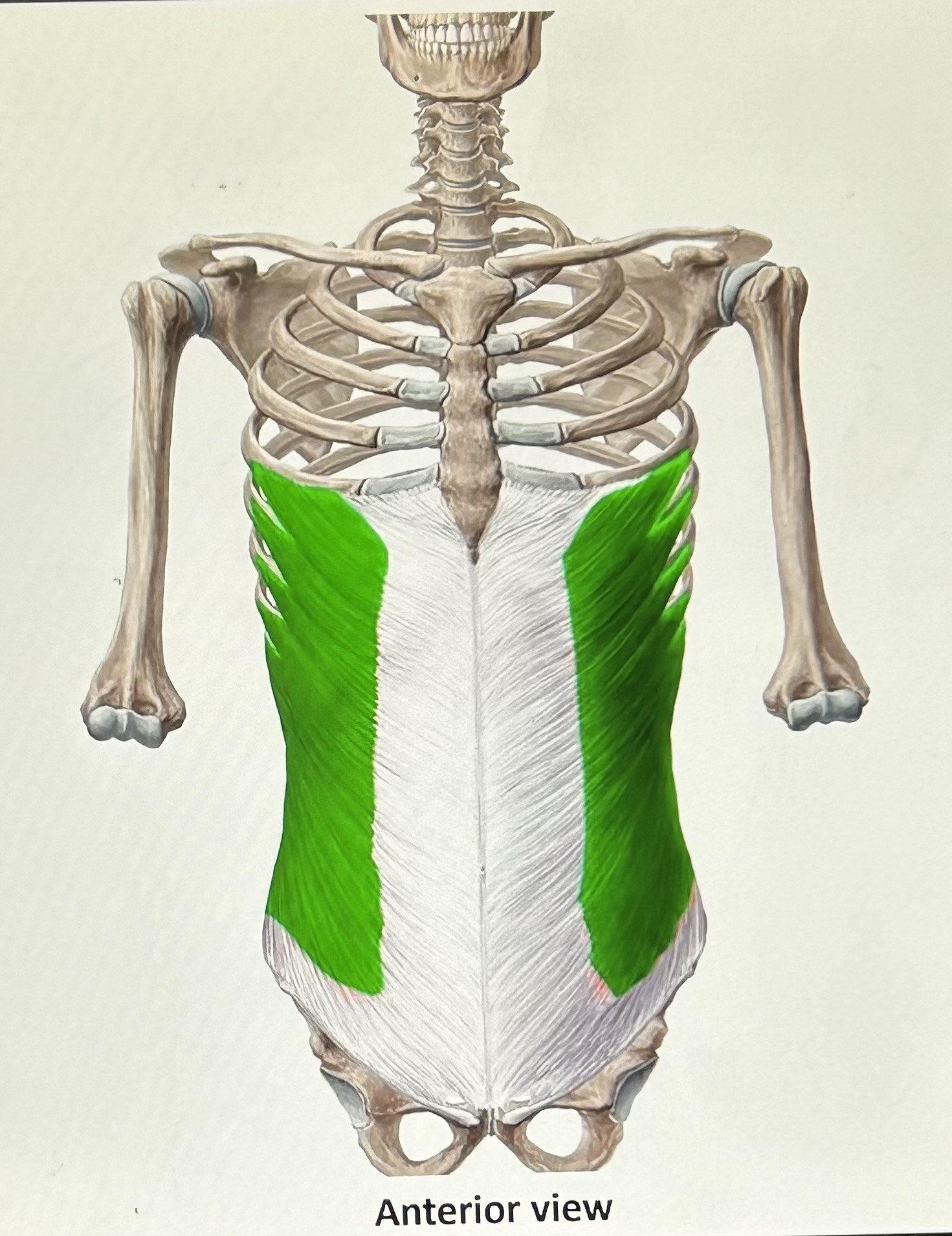
External oblique (exhalation): (fibers angle downward) attaches to the ilium, lower ribs, and abdominal aponeurosis. Function: compress viscera and lower ribs.
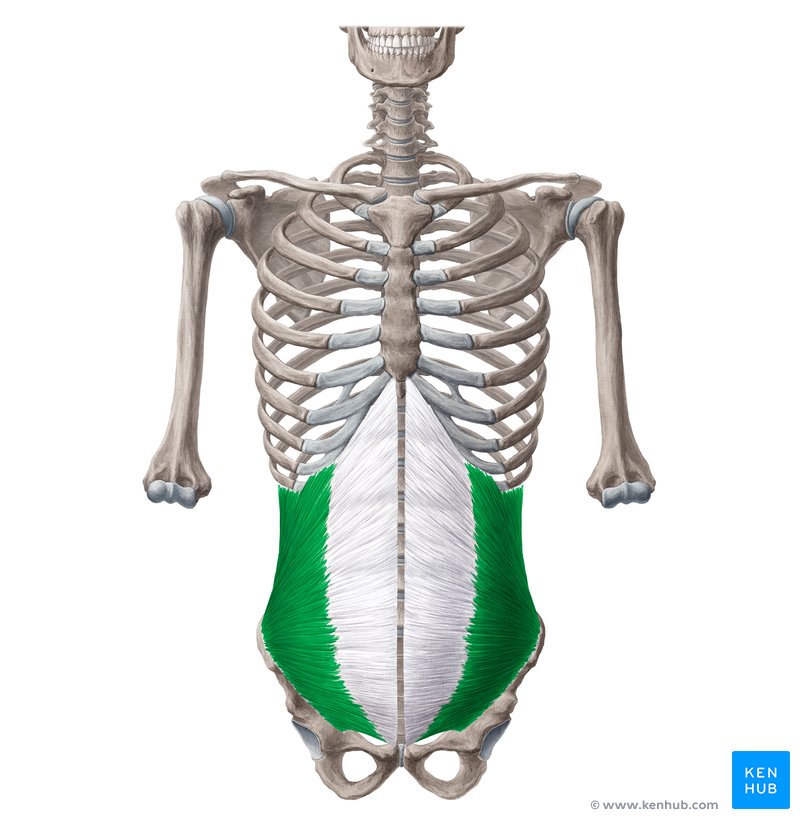
internal oblique (exhalation): (fibers create rainbow shape) attaches to ilium, inguinal ligament (groin), abdominal aponeurosis, and lower ribs. Function: lower ribs and compress viscera.
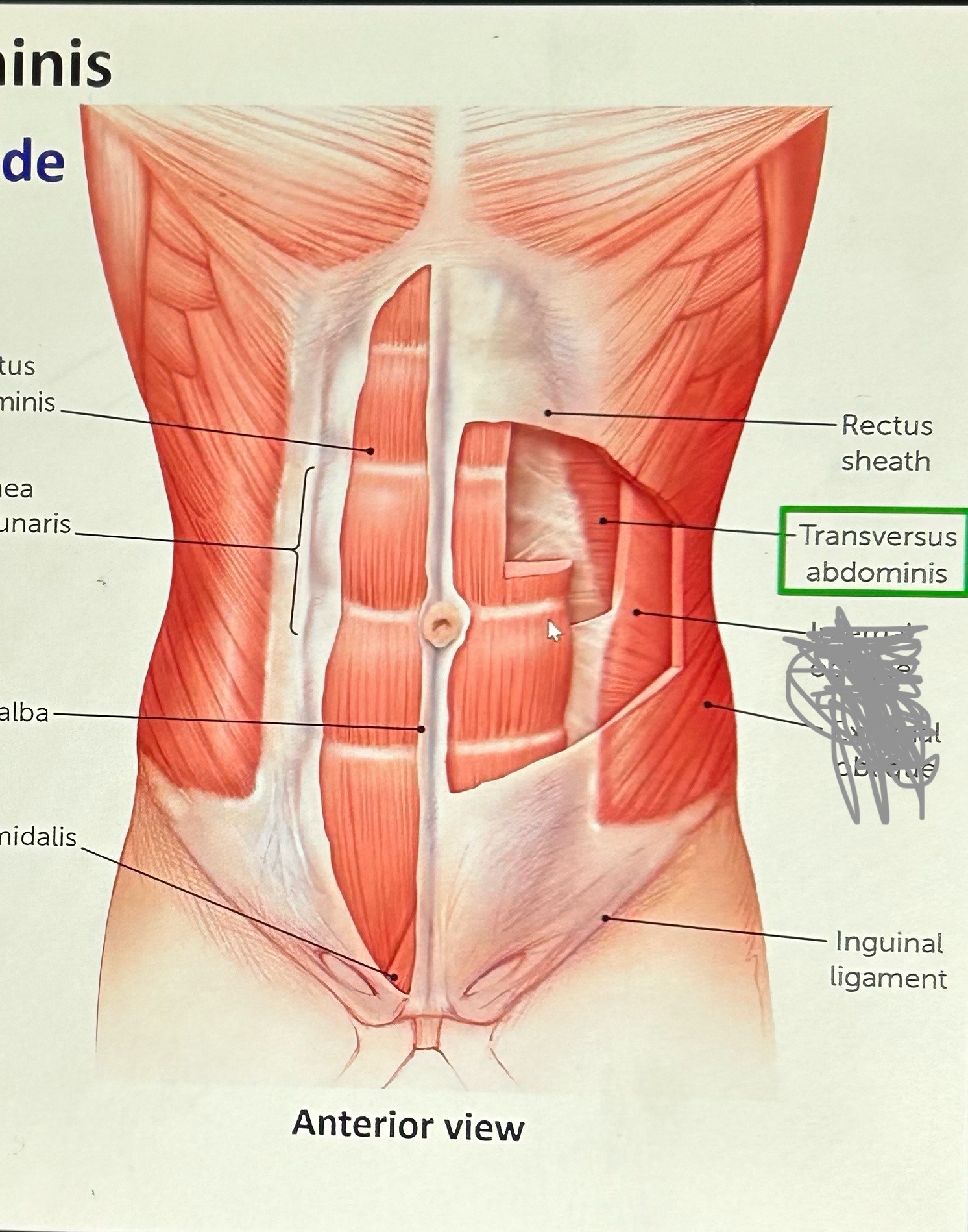
transversus abdominis (exhalation): fibers side-to-side. Attaches too lower ribs, lumbar fascia, ilium inguinal ligament and abdominal aponeurosis. Function: compress viscera and lower ribs.
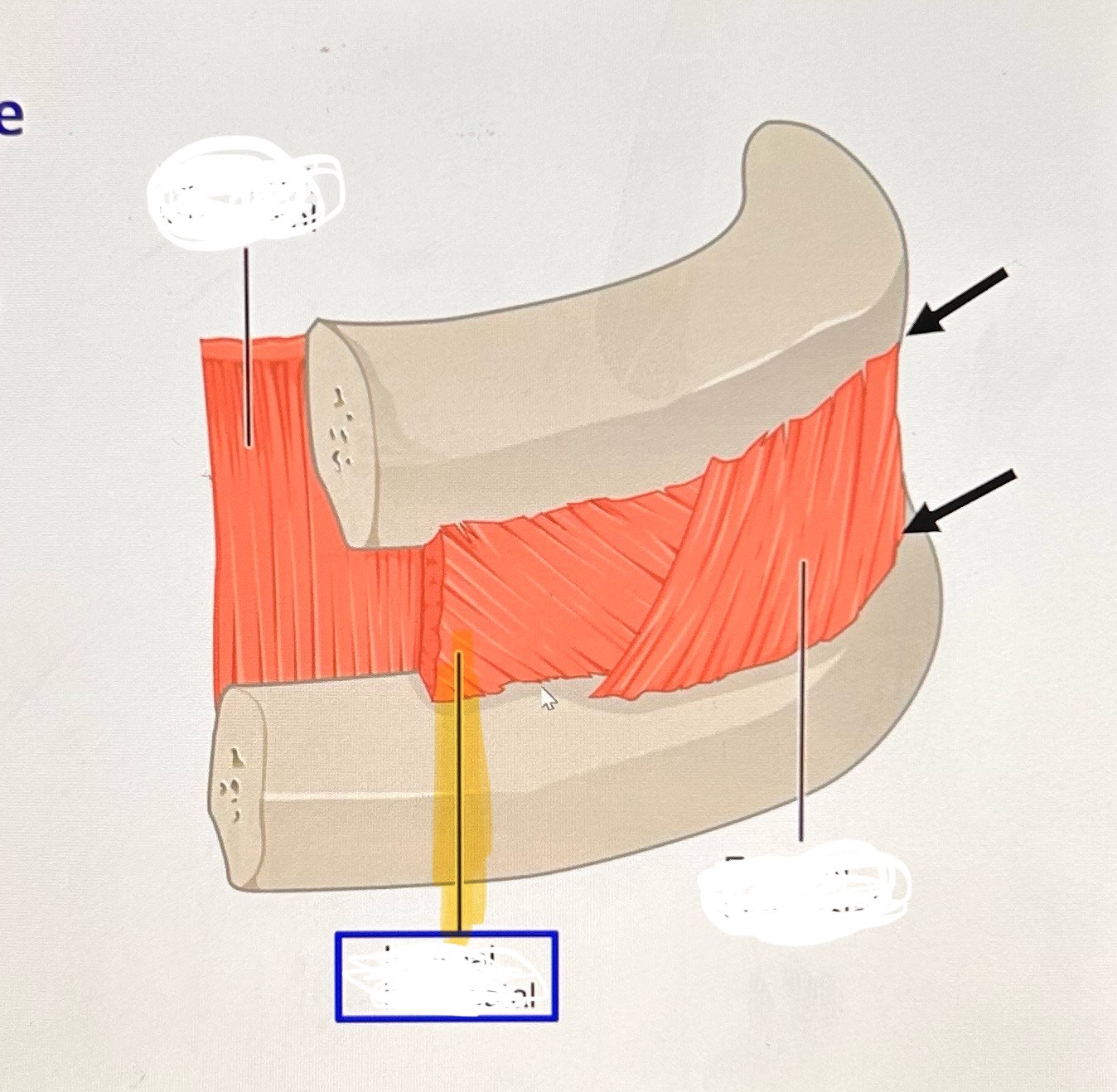
internal intercostals (exhalation): deep, attaches to upper and lower border of ribs, fills space between except posterior (back) portion. Function: lower the rib cage (increases alveolar pressure cuz ribs cover 75% of lung surface).
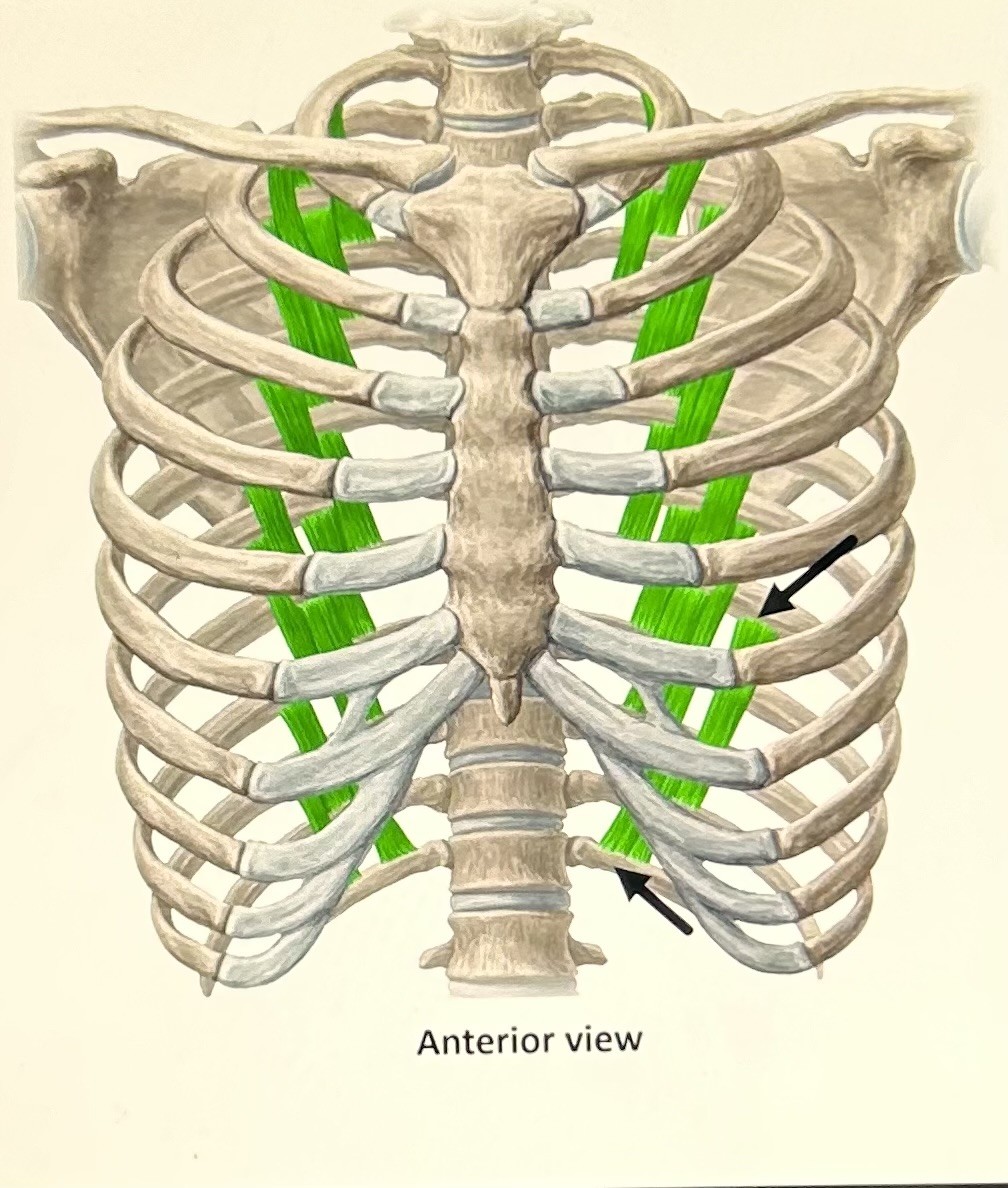
subcostals (exhalation): below ribs, attaches to ribs near vertebral column. Attaches to one rib or more higher, but varies in people. Functions: pull down ribs.
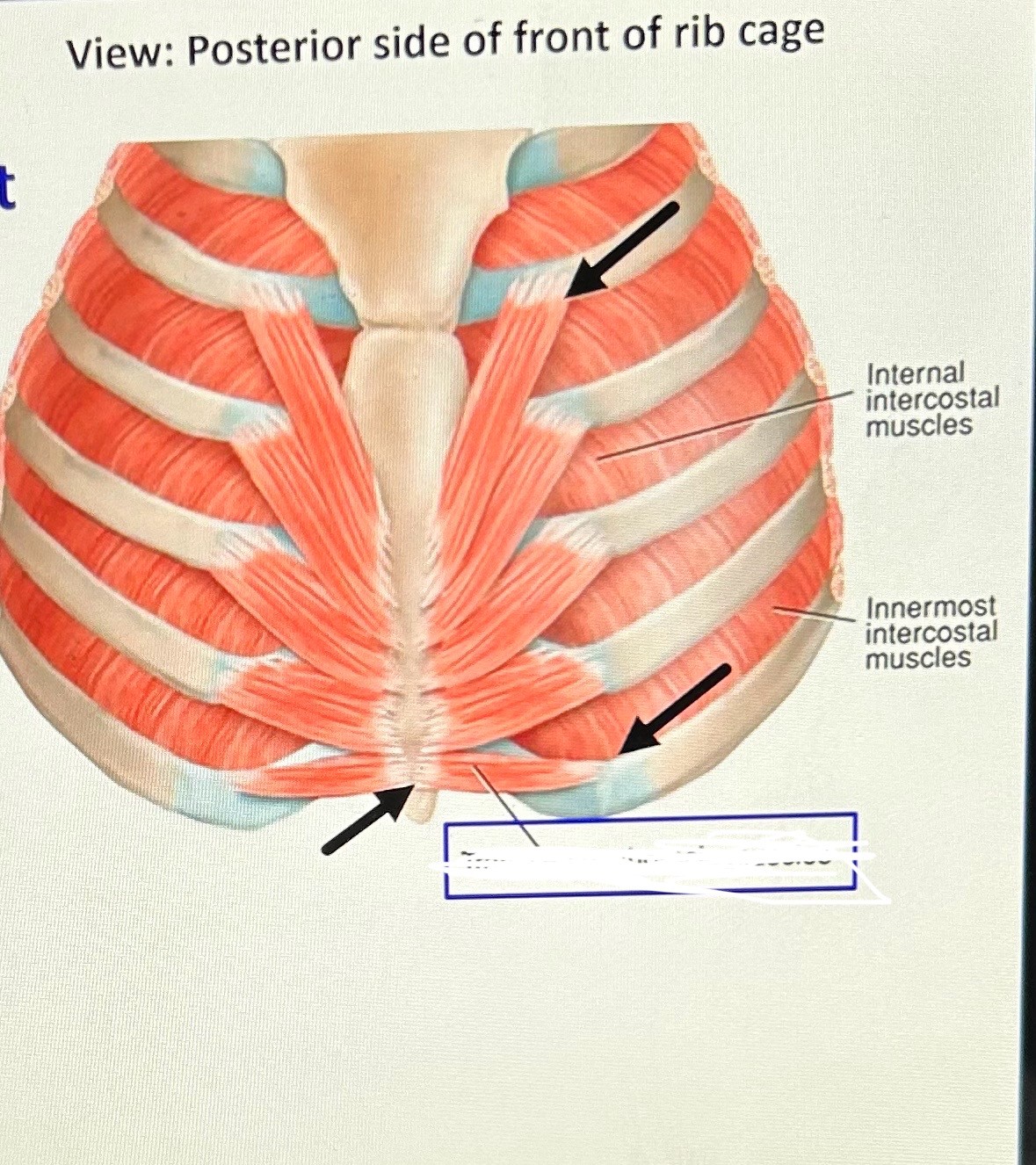
transversus thoracis (exhalation): attaches to lower sternum and ribs 2-6. Function pull ribs down.
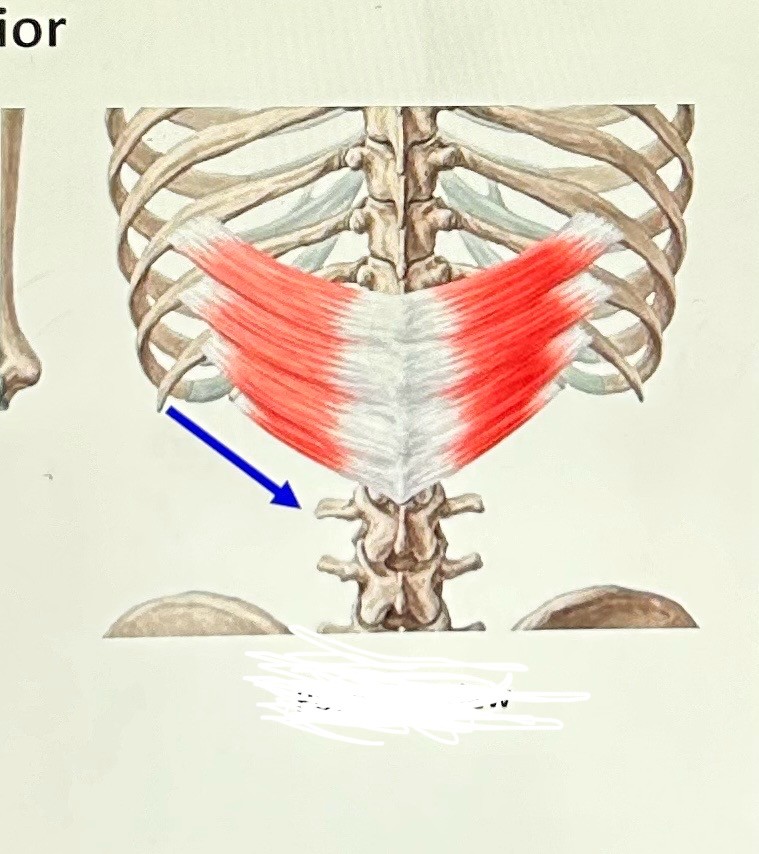
serratus posterior inferior (exhalation): attaches to back of ribs, lower thoracic and upper lumbar vertebrae, and lower ribs. Function: pull ribs down.
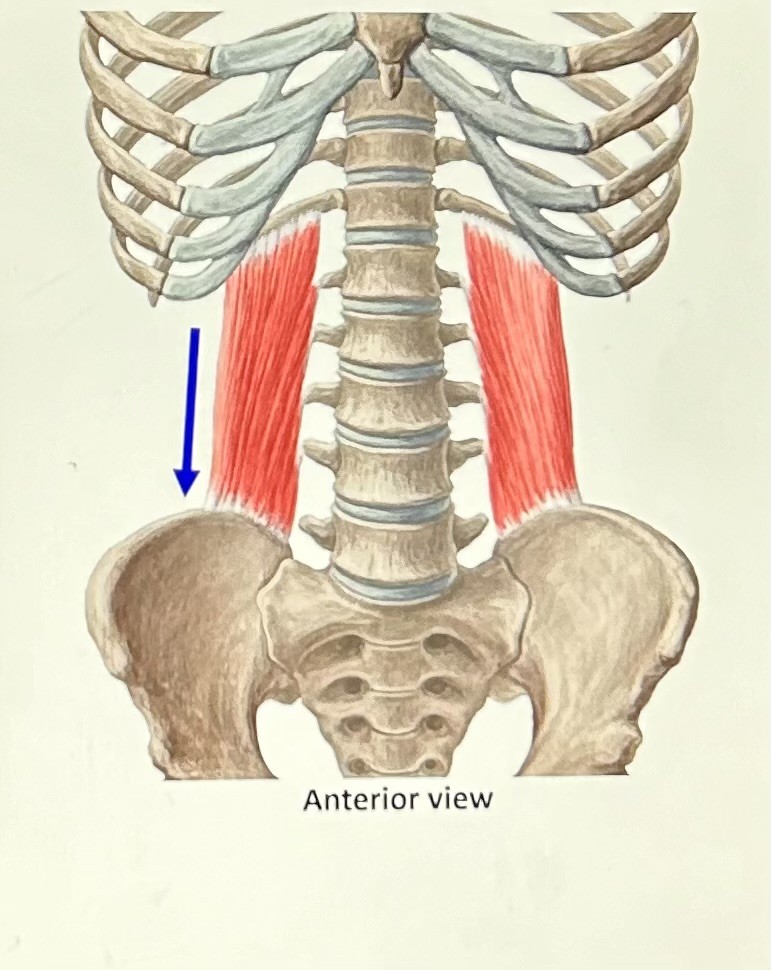
quadratus lumborum (exhaltion): quadrilateral, attaches to ilium and rib #12. Function: pull rib down.
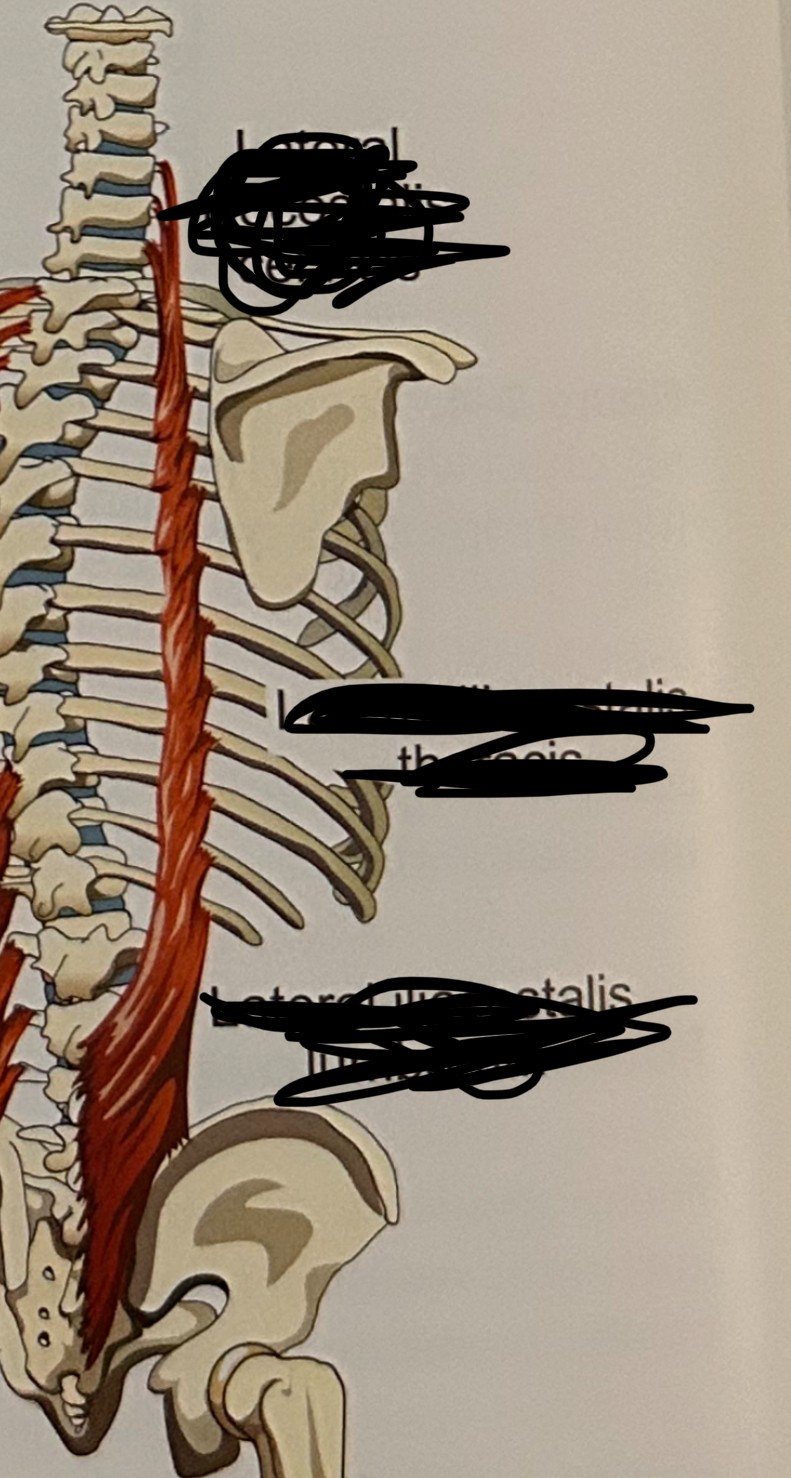
lateral iliocostalis (exhalation): (cervicis, thoracis, and lumborum)
speech sound
acoustic product of speaking
acoustic
of or for hearing
levels of observation and measurement
neural
muscular
structural
aeromechanical
acoustic (sound)
perceptual
neural
convert thoughts into words and coordinated muscle movements
muscular
they produce mechanical pulls on structures related to speech and swallowing
structural
respiration, phonation, articulation
aeromechanical
structural movements result in air movement, air pressure changes needed for heard speech
acoustic
speech is sound that can be heard
perceptual
speech can be experienced by speaker and listener, auditory and visually
medial
close to the middle
lateral
away from middle
coronal
cut at crown of head, so their is a front and back half vertically
transverse
side-to-side, horizontal cut into upper and lower section
sagittal
vertical cut into right and left sides
anterior
towards the front
posterior
towards the back
ventral
abdomen away from back bone, view from front
dorsal
towards back bone
inferior
closer to the feet
superior
closer to the head
superficial
towards surface
deep
away from surface
proximal
next to or toward midline
distal
distant away from midline
respiratory system role
power source of speech
biological role of respiratory system
breathing for life
upper respiratory tract
consists of three cavities: oral, nasal, and pharyngeal cavities.
lower respiratory tract
consists of: larynx, trachea, bronchus (bronchi), bronchioles, and alveolar air sacks.
lungs
located in rib cage
thoracic
is the space within the rib cage
mediastinum
heart, blood vessels and esophagus
visceral pleura
around each lung - most inner lining
parietal pleura
inside lining of thoracic cavity - outer layer of membranes
surface tension (pleural linkage)
pleural space contains fluid and creates tension between 2 pleural membranes
negative intrapleural pressure (pleural linkage)
negative pressure between two membranes created by a “vacuum” type seal. Based on Magdeburg principle
Magdeburg principle
refers to link created between two structures when there is negative air pressure or vacuum created between them (suction cups).
plural space
potential/space between two membranes same as pleural cavity (filled with fluid)
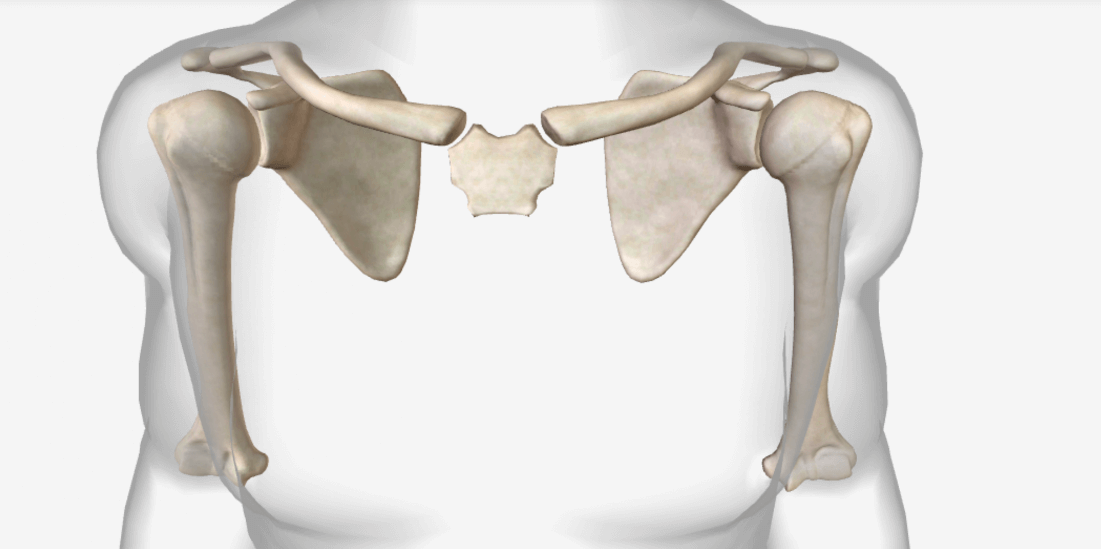
pectoral girdle: contains clavicle and scapula
vertebral column
32 or 33 vertebrae (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, fussed sacrum, and fused coccyx)
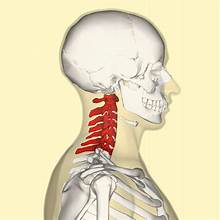
cervical vertebrae (7)
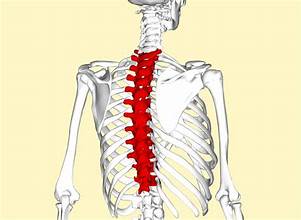
thoracic vertebrae (12)
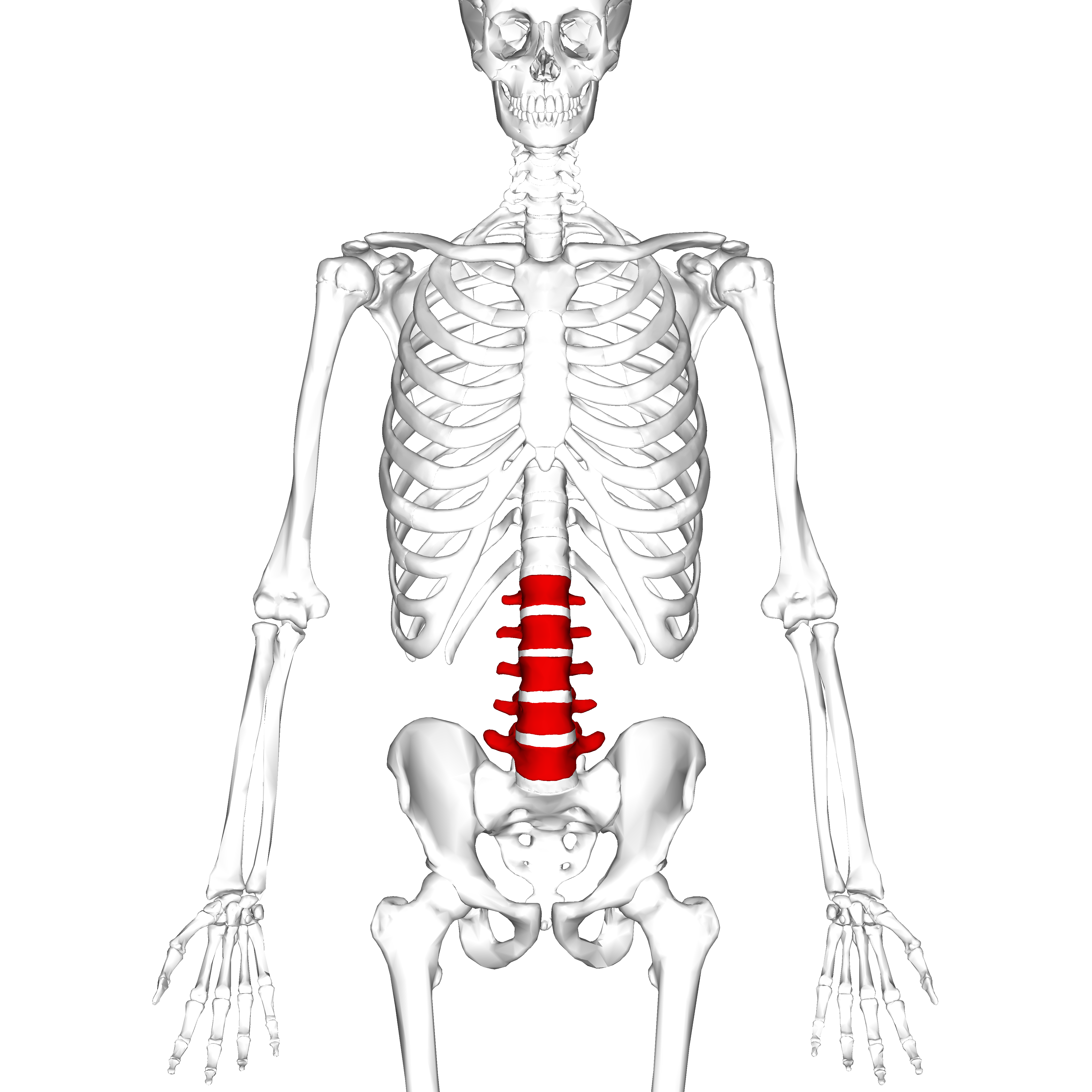
lumbar vertebrae (5)
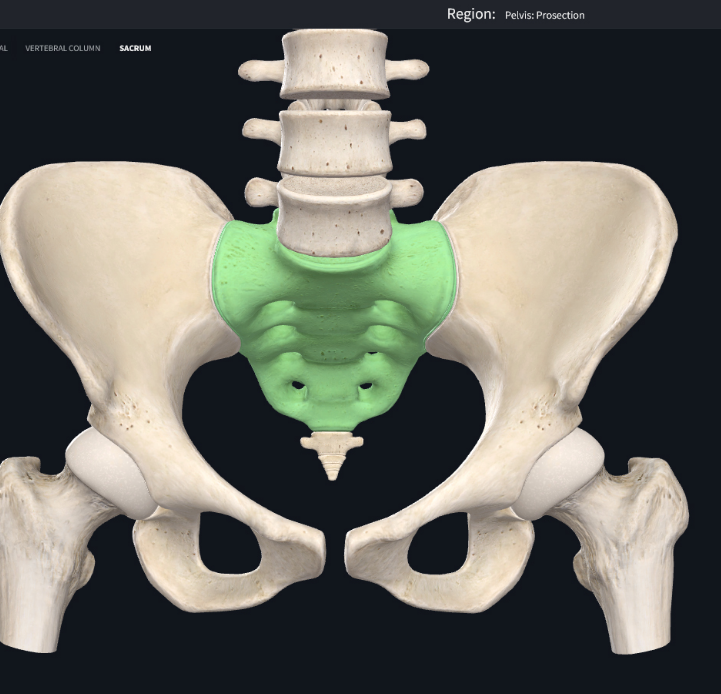
fused sacrum vertebrae (5)
fused coccyx
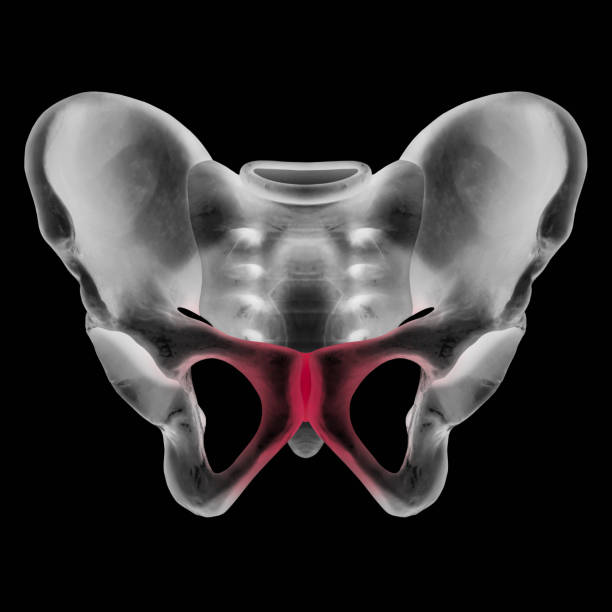
pelvic girdle
basic floor for abdominal viscera (ilium, ischium, and pubic bone)
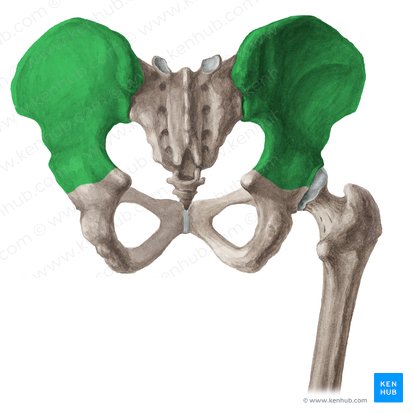
ilium (groin)
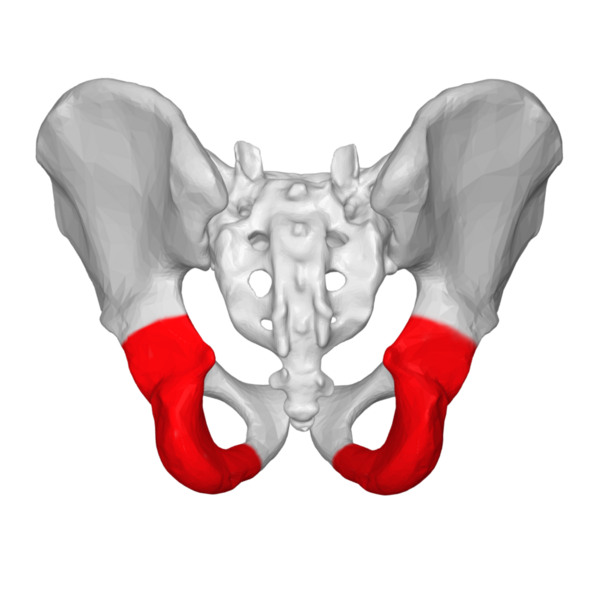
Ischium (seat bones)
pubic bone (maturation)
transverse expansion
side-to-side
anteroposterior expansion
front-to-back
boyle’s law
volume and pressure of gases are inversely proportional
alveolar air pressure
pressure inside of lungs
Inhalation pressure changes
as size of thoracic cavity increases, volume increase, thus pressure decreases
Exhalation pressure changes
as size of thoracic cavity decrease, volume decreases, thus pressure increases
vital capacity (vc)
maximum useable volume of air that can be inhaled from rest and exhaled to end of breath
resting volume
amount of air exhaled from resting position. Air still remains in lungs at 40% of vc
tidal volume
amount of air inhaled or exhaled during respiration during resting
inspiratory reserve volume
amount of air that can be inhaled beyond any one tidal line
Expiratory reserve volume
amount of air that can be exhaled beyond any one tidal line
residual volume
amount of air left in lungs after max exhalation
elastic recoil
elastic recoil after stretched out system rebounds to natural shape
What happens during inhalation?
rib cage raised against gravity
viscera compressed by diaphragm
alveolar air sacs inflated against surface tension
What happens during exhalation (quiet breathing)?
gravity pulls rib cage down
alveolar air sacs recoil
abdominal viscera rebounds pushing diaphragm upward
relaxation pressure
alveolar pressure that results from passive forces of exhalation when muscles relax
vital capacity for quiet breathing
uses additional 10-15% of vc (or 50-55% vc)
vital capacity for conversational speech
uses additional 20-25% of vc (or 60-65% vc)
vital capacity for loud speech
uses additional 40%+ of vc (or 80%+ vc)
loudness
amount of cm h2o displaced in u-shaped water manometer at different speech loudness levels
loudness level for soft speech
3-6 cm h2o
loudness level for conversational speech
7-10 cm h2o
loudness level for loud speech
11-80 cm h2o
speech prosody
fluctuations in loudness within an utterance
pitch
high or low pitch due to stretched or contracted vocal folds
duration
holding a stressed syllable longer than the rest
How much area of the lung surface does the rib cage contract?
75%
How much area of the lung surface does the diaphragm contract?
25%
Duration of inhalation and exhalation for breathing for life:
40% inhalation and 60% exhalation
Duration of inhalation and exhalation for speech breathing
10% inhalation and 90% exhalation