Exam III: Chapter 16
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
Last updated 1:25 AM on 4/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards
signal transduction
taking one signal and making it into another
2
New cards
signaling cell
sends out a signal
3
New cards
extracellular signal molecule
how a signal is sent between cells
* proteins
* amino acids
* gas
* steroids
* fatty acids
* proteins
* amino acids
* gas
* steroids
* fatty acids
4
New cards
target cell
cell that receives the signal
5
New cards
receptors
recognize a signal and cause a reaction
6
New cards
intracellular signal molecule
how signals are sent within a cell and leads to a change in cell behavior
7
New cards
cell signaling
signal reception + transduction
8
New cards
hormone
actual signal sent to whole body through blood or sap
9
New cards
endocrine cells
make hormones in animals
10
New cards
endocrine signaling
blanket message to who body through blood or sap via hormone
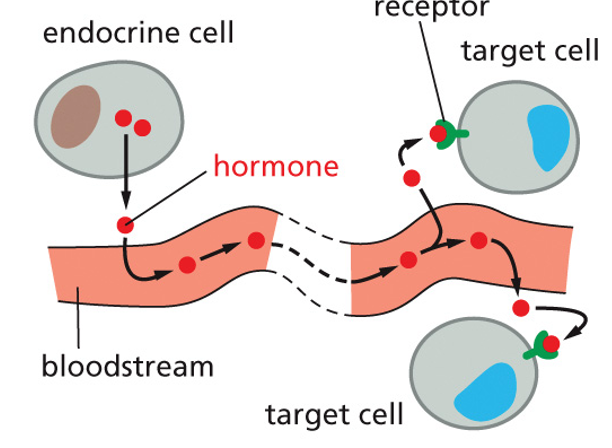
11
New cards
paracrine signaling
type of signal that is localized to a group of cells and travels through extracellular fluid
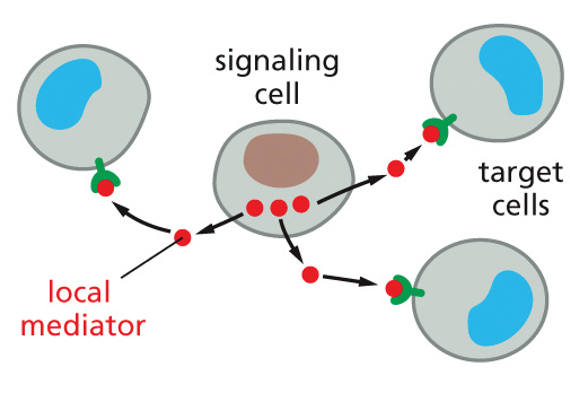
12
New cards
local mediator
signal that only work on neighboring cells- short range
13
New cards
autocrine signaling
when cells send signals to others in a localized area. must be the same type of cell and the original cell can receive its own signal
* used in cancer
* used in cancer
14
New cards
neuronal signaling
sending message through neurons/synapses and is long distance
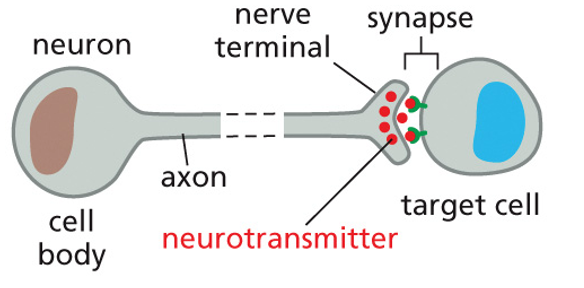
15
New cards
neurotransmitter
signal molecule for neuronal signalling
16
New cards
contact-dependent signaling
cells touch each other and send a message directly to one another. signal is in membrane and is touched to receptor
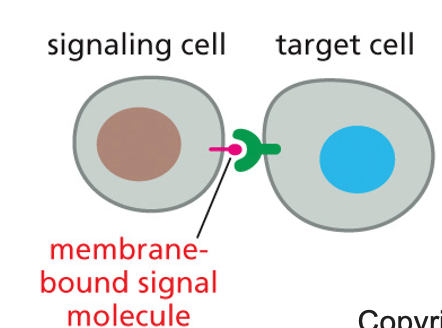
17
New cards
receptor
protein that responds to a certain signal
* extracellular receptor: very large or phillic signal
* intracellular “: small or phobic
* extracellular receptor: very large or phillic signal
* intracellular “: small or phobic
18
New cards
effector proteins
execute how a certain cell will respond to a signal
19
New cards
transmembrane receptor
senses a signal outside the cell and sends it to inside the cell in a new form
* can trigger a cascade of signals within the cell
* can trigger a cascade of signals within the cell
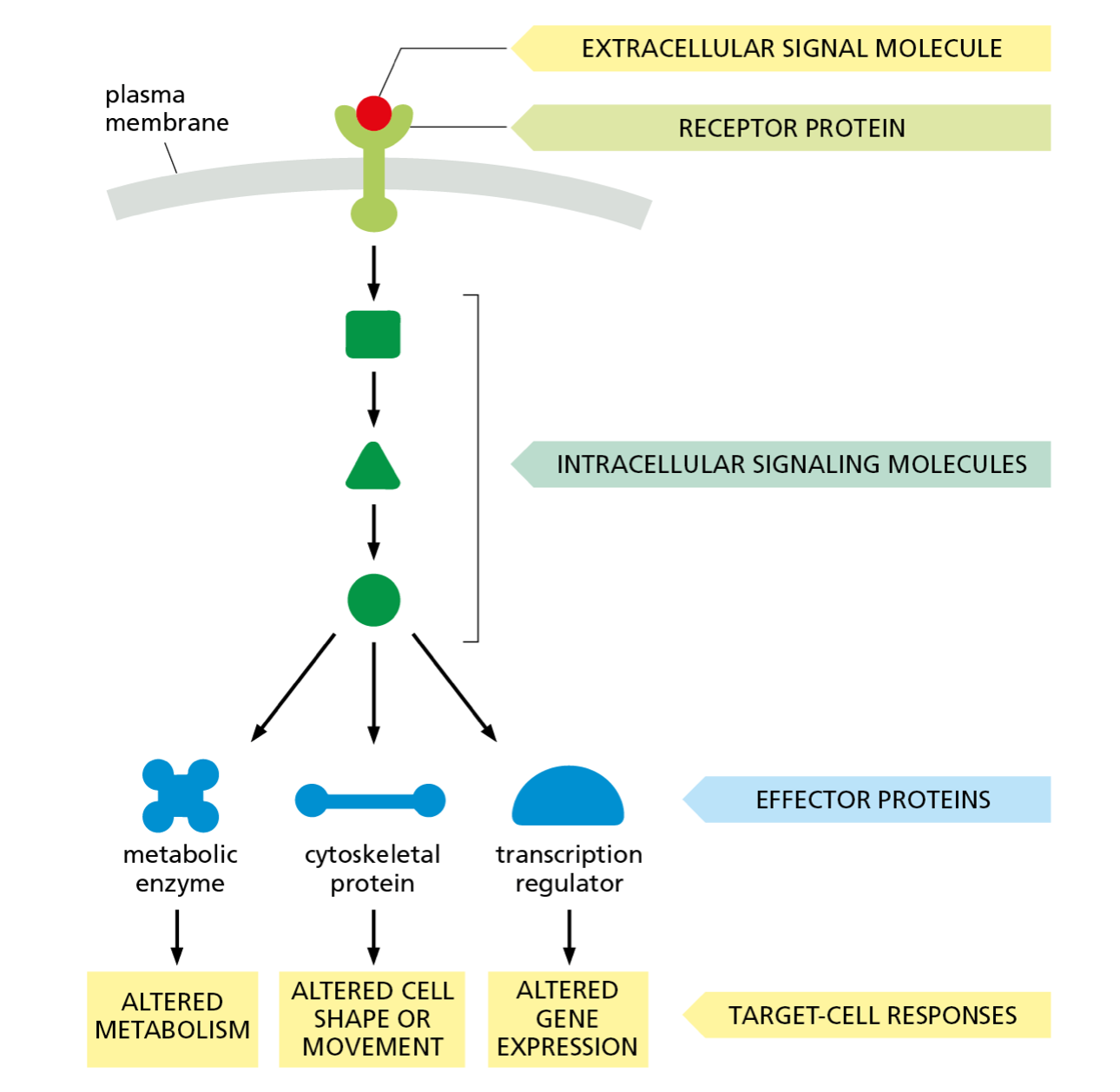
20
New cards
intracellular signaling pathway
many proteins that work together within a cell to send a message to a specific location
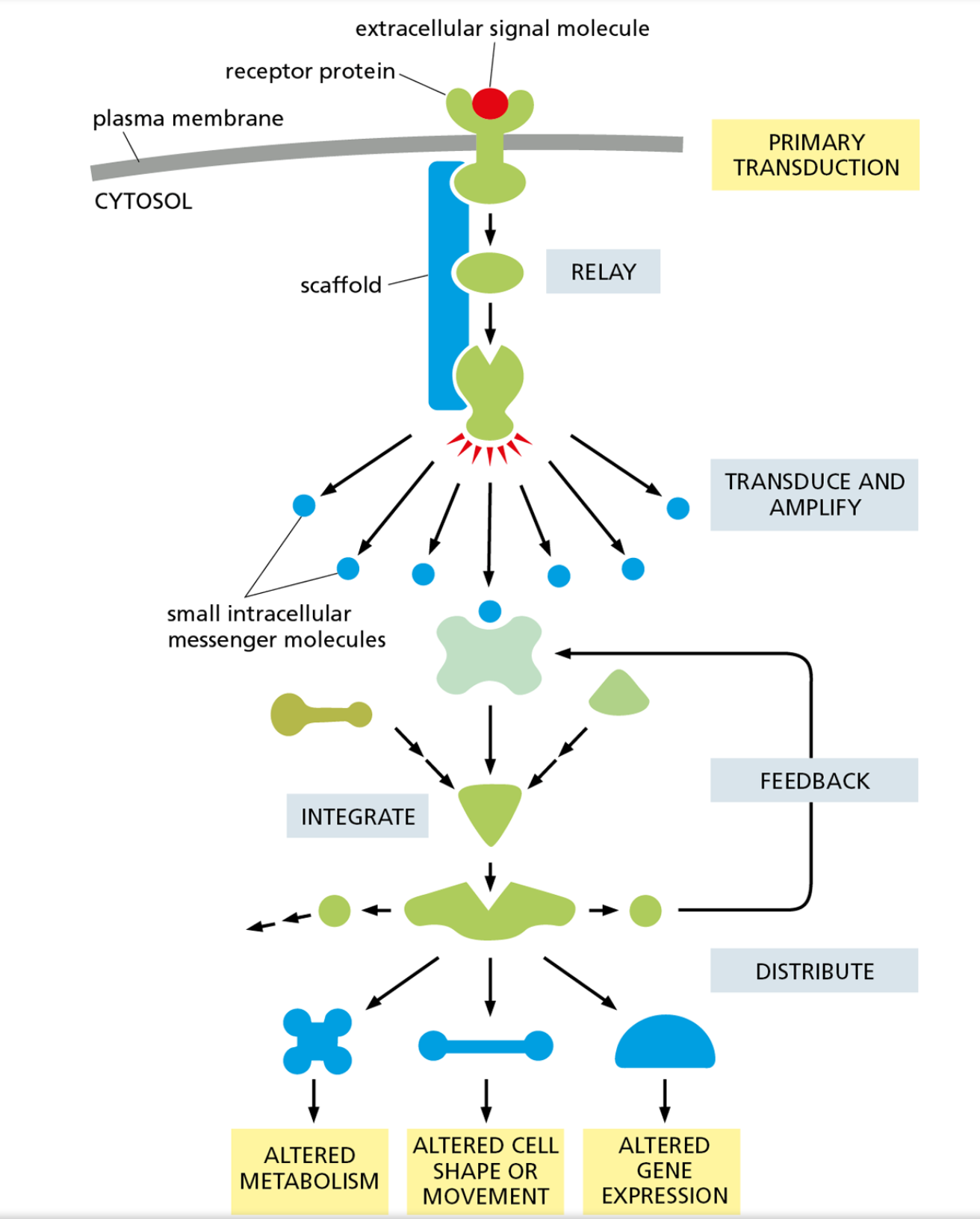
21
New cards
amplify
make a signal more prominent
22
New cards
relay
sending the signal to the next protein
23
New cards
integrate
combining multiple signals to only send out one
24
New cards
distribute
one protein sending a signal to multiple destinations
25
New cards
feedback
controlling what happens in the steps before them by sending a signal
26
New cards
feedback regulation
step in the signal pathway controlling cellular action by promoting or minimizing a signal
27
New cards
positive feedback
response from within pathway that increases activity on the pathway
* switch
* switch
28
New cards
negative feedback
response from within pathway that decreases activity on the pathway
* toggle
* toggle
29
New cards
molecular switch
signal put the protein from inactive to active conformation or vice versa
* need to be actively switched off
* controlled by phosphorylation or binding
* need to be actively switched off
* controlled by phosphorylation or binding
30
New cards
protein kinase
puts P group on DP
31
New cards
protein phosphatase
takes P group off TP
32
New cards
phosphorylation cascade
kinases activating each other
33
New cards
serine kinase
phosphorylate serine proteins
34
New cards
threonine kinase
phosphorylate threonine proteins
35
New cards
tyrosine kinase
phosphorylate tyrosine proteins
36
New cards
GTP binding protein
protein active or inactive dependent on if GDP or GTP bound
37
New cards
trimeric GTP-binding proteins
send message from G-protein-coupled receptors
38
New cards
monomeric GTPase
\
39
New cards
guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEF)
help take a GDP and replace with GTP
40
New cards
GTPase activating proteins (GAP)
help swap GTP for GDP
41
New cards
RTK
receptor tyrosine kinase
42
New cards
enzyme coupled receptor
transmembrane protein with receptor on the extracellular side and enzymatic tails on the cytosolic side
43
New cards
tyrosine phosphatase
removes RTK’s phosphate groups to deactivate
44
New cards
Ras
GTP binding protein with one phospholipid tail hooked in the plasma membrane
45
New cards
Ras-GAP
helps Ras go from GTP to GDP
46
New cards
GEF
helps Ras go from GDP to GTP
47
New cards
MAP kinase kinase kinase
puts phosphate group on MAP kinase kinase
48
New cards
MAP kinase kinase
puts phosphate groups on MAP kinase
49
New cards
MAP kinase
phosphorylates many types of proteins and transcription factors
50
New cards
MAP
signals for cell division/replication
51
New cards
PI 3-kinase
will phosphorylate inositol phospholipid
52
New cards
protein kinase B
prevents Bad molecule from signaling
53
New cards
AKT
another name for PKB
54
New cards
Tor
proteins which signals to prevent protein degradation and encourage protein synthesis
55
New cards
Notch
protein that signals for cell to become neural cell
56
New cards
Delta
signal that attaches to Notch
57
New cards
signal transduction
1) reception
2) primary transduction
3) relay
4) amplification
5) divergence
2) primary transduction
3) relay
4) amplification
5) divergence
58
New cards
receptor
what a signal will attach to
59
New cards
hydrophobic signaling
signaling using fatty acids, gas, steroid, cholesterol based
60
New cards
eicosanoid
small fatty acid signals for pain
* cause smooth muscle contraction, inflammation, platelets
* are prostaglandin
* are leukotrienes
* cause smooth muscle contraction, inflammation, platelets
* are prostaglandin
* are leukotrienes
61
New cards
arachidonic acid
20 C phospholipid tail
* ecoisinoid’s linear precursor
* ecoisinoid’s linear precursor
62
New cards
cycloxygenase
folds arachidonic acid into eicosanoids
63
New cards
COX1
constitutive enzyme that acts as cycloxygenase
64
New cards
COX2
inducible enzyme that acts as cycloxygenase
65
New cards
PGG2 and PGH2
two eicosanoids that can be blocked with asprisin
66
New cards
aspirin
drug that prevents cycloygenase activity
67
New cards
leukotriene
lipid that makes inflammation
68
New cards
lipoxygenase
fold arachidonic acid into leukotrienes
69
New cards
leukotriene
eicosanoid responsible for inflammation
70
New cards
prostaglandin
eicosanoid that increases membrane permeability
71
New cards
acetylcholine
neurotransmitter that initiates:
* saliva production
* skeletal contraction
* decreased heart rate
* saliva production
* skeletal contraction
* decreased heart rate
72
New cards
endothelial
blood vessel cell
73
New cards
acetylcholine receptor
where acetylcholine binds to on endothelial cell membrane; initiates Ca2+ influx
74
New cards
Ca2+
cofactor for NO synthase
75
New cards
arginine
NO is created from this amino acid via NO synthase
76
New cards
soluble guanyl cyclase
takes NO and makes cGMP from GTP
* i.e. SGC
* i.e. SGC
77
New cards
cGMP
activates protein kinase G (PKG)
78
New cards
protein kinase G
phosphorylates myosin light chain kinase (MLCK)
79
New cards
MLCK
causes smooth muscle contraction
* can be phosphorylated by PKG to inactivate
* can be phosphorylated by PKG to inactivate
80
New cards
MLCP
causes smooth muscle relaxation
* can be activated by PKG
* can be activated by PKG
81
New cards
smooth muscle relaxation
following factors all allow for blood vessel dilation and ….
* deactivated MLCK
* activated MLCP
* open Ca2+ channel
* open K+ channel
* deactivated MLCK
* activated MLCP
* open Ca2+ channel
* open K+ channel
82
New cards
phosphodiesterase
causes cGMP breakdown to deactivate PKG
83
New cards
viagra
signal recognition particle and competitive inhibitor of phosphodiesterase
84
New cards
steroid
cholesterol derivative hormone
* cortisol
* cortisol
85
New cards
gene transactivation
activating gene transcription based on signal
1. cortisol diffuses through plasma membrane
2. cortisol binds to intracellular receptor protein
3. activated complex enters nucleus
4. complex attaches at target gene to start transcription
1. cortisol diffuses through plasma membrane
2. cortisol binds to intracellular receptor protein
3. activated complex enters nucleus
4. complex attaches at target gene to start transcription
86
New cards
intracellular receptor protein
binds to cortisol to enter the nucleus
87
New cards
NO pathway
1. acetylcholine binds to Ac receptor in endothelial
2. Ca2+ influx
3. NO synthase activated
4. arginine made into NO
5. NO diffuses to smooth muscle cell
6. NO activates guanylyl cyclase (SGC)
7. GTP made into cGMP
8. cGMP binds to PKG
1. MLCK deactivated
2. MLCP activated
3. Ca2+ increases
4. K+ increases
9. muscle relaxation
\
88
New cards
eicosanoid pathway
1. phospholipase A2 makes arachadonic acid
2. 2 pathways
1. COX1/COX2 fold chain into prostaglandin
2. lipoxygenase folds chain into leukotriene
\
89
New cards
phospholipase A2
cuts out arachidonic acids from phospholipid
90
New cards
G protein coupled receptor
7 pass protein
1. signal binds to receptor
2. conformation change in alpha, beta, gamma subunits
3. GDP replaced by GTP with GEF’s help
1. GTP bound to alpha subunit
4. activated g-protein target protein
5. GAP and g-protein alpha subunit cut GTP into GDP
1. signal binds to receptor
2. conformation change in alpha, beta, gamma subunits
3. GDP replaced by GTP with GEF’s help
1. GTP bound to alpha subunit
4. activated g-protein target protein
5. GAP and g-protein alpha subunit cut GTP into GDP
91
New cards
arrestin
adaptin that binds to phosphorylated g-protein to prevent function
92
New cards
kinase
phosphorylates
93
New cards
glycogen
… breakdown
1. epinephrine binds to GPCR
2. adenylyl cyclase activated
3. ATP made into cAMP
4. cAMP activates PKA
5. PKA activates glycogen phosphorylase with ATP
6. glycogen phosphorylase breaks glycogen into glucose
\
1. activates PKA inhibits glycogen synthase alpha
2. synthase alpha becomes synthase beta
1. epinephrine binds to GPCR
2. adenylyl cyclase activated
3. ATP made into cAMP
4. cAMP activates PKA
5. PKA activates glycogen phosphorylase with ATP
6. glycogen phosphorylase breaks glycogen into glucose
\
1. activates PKA inhibits glycogen synthase alpha
2. synthase alpha becomes synthase beta
94
New cards
protein kinase a
PKA = phosphorylase kinase
* ATP to ADP
* 4 cAMP: 2 subunits
* ATP to ADP
* 4 cAMP: 2 subunits
95
New cards
CREB
PKA is also used for … activation
1. GPCR activates adenylyl cyclase
2. adenylyl cyclase takes ATP to cAMP
3. cAMP activates PKA
4. PKA moves to nucelus
5. PKA activates transcription regulator
6. transcription regulator allows DNA transcription
1. GPCR activates adenylyl cyclase
2. adenylyl cyclase takes ATP to cAMP
3. cAMP activates PKA
4. PKA moves to nucelus
5. PKA activates transcription regulator
6. transcription regulator allows DNA transcription
96
New cards
deamplification
making a signal smaller
97
New cards
CREB
transcription factor
98
New cards
calmodulin
cofactor with Ca2+ that is always in the cytosol
* together activate caM-kinase
* goes onto phosphorylate others
* together activate caM-kinase
* goes onto phosphorylate others
99
New cards
Ca2+ channel
can open …
1. signal binds to GPCR
2. phospholipase C activated
3. cleaves IP3 from diacylglycerol
1. IP3 binds and opens Ca2+ channel
2. diacylglycerol docks PKC
1. Ca2+ binds to PKC to activate
1. signal binds to GPCR
2. phospholipase C activated
3. cleaves IP3 from diacylglycerol
1. IP3 binds and opens Ca2+ channel
2. diacylglycerol docks PKC
1. Ca2+ binds to PKC to activate
100
New cards
protein kinase c
PKC
* phosphorylates serines and threonine
* phosphorylates serines and threonine