Archer Endocrine Study Set: Key Terms & Definitions
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
hypothalamus releases what
TRH
corticoid releasing hormone
pituitary gland releases what
TSH
follicle stimulating hormone
lutenizing hormone
oxytocin
ADH
glucocorticoids
affects mood, causes immunosuipression, breakdown fats and proteins, inhibits insulin
mineralocorticoids
aldosterone
-retention of sodium and water
-excretion of potassium
how to remember steroid hormones effect
SUGAR SALT AND SEX
Glucocorticoids mineralocorticoids androgens
Methylprednisolone
- Corticosteroid
- inflammation, allergy, autoimmune disorders
-suppress inflammation and normal immune response
norepinephrine
increases BP, pupil dialtion, increases contractility, inhibits GI system activity
epinephrine
increases metabolism, increase glucose levels in blood by inhibiting secretion of insulin
look for issue with ADH if patient has what
craniotomy, head injury, sinus surgery
Levothyroxine (Synthroid) nursing considerations
- must be taking on an empty stomach
- take at the same time every day
- life long therapy
Calcitonin
produced by thyuroid gland, stops bones from releasing more caclium into blood, opposes PSH
Glucagon
causes glycogenolysis of glucogen in the liver, released when BG is low
iodine
used to reduce the size and vascularity of the thyroid gland in hyperthyroidism
what drugs decrease serum calcium
biphosphonates such as alendronate and risedronate and calcitonin
calcitriol
A hormone produced from vitamin D that acts in essentially the same manner as parathyroid hormone.
-increases serus calcium
rapid acting insulin
insulin aspart insulin lisper
insulin lispro and aspart onset
15 min
when is patient at highest risk for hypoglycemia with insulin
at peak
insulin aspart peak
1-3 hrs
insulin lispro peak
30-90 mins
insulin lispro duration
5 hrs
insulin aspart duration
3-5 hrs
short acting insulin
regular
short acting insulin onset, peak and duration
30 min, 2-4 hrs, 5-12 hrs
intermediate acting insulin
NPH
NPH insulin onset, peak, duration
1-4 hrs, 4-12 hrs, 10-24 hours
long acting insulin name
glargine
glargine onset, peak, duration
1-4 hrs, none, 24 hrs
mixing insulin
glargine cannot be mixed
draw up regular insulin, then NPH
RN
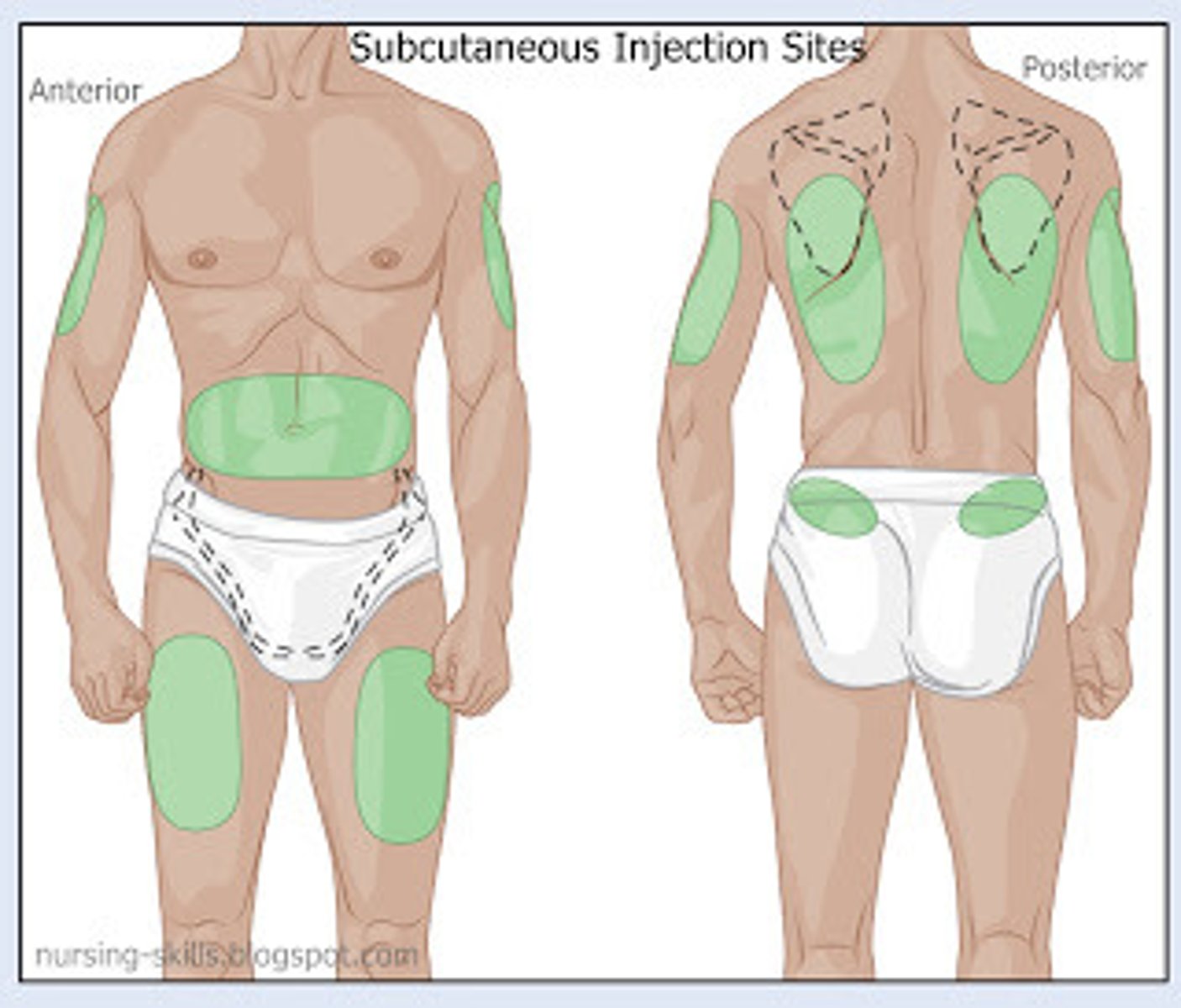
subcutaneous injection sites
abdomen, anterior thigh, flank, scapular, buttocks, outer aspect of the upper arm
how is glucagon administered
IM, used for emergency hypoglycemia treatment
Metformin nursing considerations
do not give to clients with renal or hepatic impairement
take with food
hold for 24 hr before and 48 hrs after any study withIV contrast
addison's disease side effects
fatigue weight loss hypoglycemia, confusion, bronze skin, hypovolemia, hyperkalemia, hypotension, hair loss, hyperpigmentation,
insulin is produced -> hypoglycemia (think of these effects)
treatment addison's disease
think shock
-increase IV fluid admin
-increase sodium intake
-rreplacement therapy
-monitor vitalas
-educate ons signs of adrenal crisis
-I&O
-daily weight
Addisonian crisis treatment
Shock management
Fluid resuscitation using 0.9% NS and 5% dextrose
High-dose hydrocortisone IV push (tapper slowly or they will enter adrenal crisis)
cushing's disease side effects
potassium excretion, fluid retention, immunosuppresion, hyperglycemia, mood alteration, fat redistribution (buffalo hump), muscle waisting
high bp-> they are holding on to water
you can test with dextamethasone supression test or 24 hour urine collection
treatment of cushing's
avoid infection, adrenalectomy (remove gland)
conn's disease is caused by
caused by tumor on adrenal gland and makes too musch aldosterone
conn's disease symptoms
hypertension, hypernatremia, hypokalemia
pheochromocytoma
tumor of adrenal medulla secretes excessive epinephrine and norepinephrine
important pheochromocytoma nursing consideration
don't palpate because it can cause an increase in fight or flight hormones
Pheochromocytoma symptoms
tachycardia, palpitations, hypertension, diaphoresis, abdominal pain, chest pain, severe headache
diabetes insipidus (DI) can lead to what emergency
shock
DI side effects
large amounts of dilute urine, hypotension, tachycardia, headache, dry eyes, lack of concentration + memory, dehydration
lab values in DI
decreased USG and urine osmolarity
increased sodium
increased sodium osmolarity
hyperkalemia
treatment for DI
vasopressin, replace fluids, MONITOR NEURO STATUS
SIADH symptoms
weight gain but no edema (kidneys are helping body stay euvolemic), anorexia, nausea, vomitnig, low serum sodium (watch for seizures, irritability, confusion, hallucinations)
low urine output
body is euvolemic (water is retained)
lab values SIADH
concentrated urine
increased urine sodium, increased specific gravity, increase urine osmolality,
dilute blood
increased blood volume, decreased blood osmolality, hyponatremia, anemia
treatment for SIADH
monitor serum sodium, seizure precautions, fluid restriction, hypertonic fluids
what is the fluid of choice for SIADH
hypertonic saline
Hypothyroidism symptoms
constipation, weight gain, puffy face, bradycardia, intolerant of cold, dry skin
hyperthyroidism symptoms
sweating, exophthalmos, goiter, arrhythmia, muscle weakness, hungry, weight loss
first line treatment for hypertyrodisim
methimazole - antithyroid medication
thyroid storm
fever, super high heart rate, palpitaitons, SOB
give BB or adenosine to help high heart rate
WITH THYROIDECTOMY, WHAT TO WATCH FOR
keep trach set at bedside
watch for hypocalcemia
Thyroidectomy complications
hypocalcemia = tetany (chvostek's/trusseau's) (because they can remove the thyroid )
paresthesia
thyrotoxicosis (thyroid storm)
throat swealling (glottal edema)
hemorrhage/hematoma
vocal cord paralysis (hoarseness)
dmg to parathyroid glands
Hypoparathyroidism symptoms
symtoms of hypocalemia
-Muscle cramps
-Tetany
-Chvostek sign (facial muscle contraction when tapping facial nerve)
-Trousseau sign (carpal tunnel spasm with BP cuff tight)
-Circumoral tingling (around lips)
-Tingling of hands and feet
-seizures and parkinsons or dystonia
-Cognitve changes
-Cataracts
-Hyperactive DTRs
how to treat hypoparathyroidism
calcium replacement and phosphate binders (calcium carbonate or tums)
-activated vitamin D
hyperparathyroidism tretament
take out gland
-only 2/4
can cause rebound hypoglycemia if you take out too much
type 1 diabetes symptoms
frequent urination, fatigue, irritability, extreme hunger, weight loss, increased thirst, blurred vision
diabetic ketoacidosis signs
polydipsia, polyphagia, polyuria, high serum potassium, kussmaul respirations (metabolic acidosis)
-difficulty breathing, feeling weak, dry flushed skin, high ketones in urine
DM type II symtpoms
blurred vision, frequent urination, excessive thirst and dry mouth, slow wound healing, tingling and numbness in hands and feet, sexual issues, recurrent fungal infections, sfatigue
why is perfusion bad in DM
sugar in blood makes blood thick and sticky, harder to get into capillaries
aspart
rapid acting insulin
cannot be given iv
only insulin that can be given IV
regular (short-acting)
store insulin
refrigerator
not in direct heat
only cloudy insulin
NPH
dka treatment
HOURLY BG AND K+ CHECKS
evaluate abg
prevent shock
NS to start then when glucose lowered to 250/300 use D5W to prevent hypoglycemia
lower glucose slowly
Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome (HHNS)
extremelly high blood glucose levels, blood becomes hyperosmolar, kidneys start producing more urine due ot hyperosmolarity of blood, polyuria leads to dehydration which leads to shock, no KETONES in urine
exercise with diabetes
eat before exercises, exercise when blood sugar is at its highest
basal/bolus system
long acting agent given once per day and rapid-acting agent given with meals to cover carbs eaten
Hypoglycemia symptoms
Tachycardia
Irritable
Restlessness
Excessive hunger
Diaphoresis (clammy)
how to treat hypoglycemia
1. have a snack-about 15 grames of carbs
-4-6 oz of sugar drink
-8-10 pieces of candy
2. wait 15 mins and check BG again
3. if still <70, have another 15 grams of carbs
4. after the BG rises, eat a snack with complex carb/protein to keep BG up
-crackers with peanut butter
what is client with hypoglycemia is unconscious
if IV access-push D50W
if no iv- iM glucagon