BICD 110-Midterm 1
1/190
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
191 Terms
What was the last eukaryote common ancestor?
LECA
Naked eye
~100um+
Light microscope
10nm to 1mm (higher resolution)
Electron microscope
0.1nm to 1mm (high resolution for smaller proteins)
atom
0.1nm
small molecule
1nm
globular protein
10nm
virus ribosome
100nm
bacterium
1um
animal cell
10 um
plant cell
100um
frog egg
1mm
Robert Hooke (1635-1703)
discovered (plant) cells, compound microscope (50x magnification), the cell is the most basic unit of life
Anthonie van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723)
discovered microorganisms (protists, bacteria, sperm cells), red blood cells, cell theory, single lens microscope 200-300x magnification, observed that fertilization process requires sperm cell to enter oocyte, observed ‘lumen’ in the salmon red blood cells- the nucleus
Cork micrograph drawing (Hooke)
“honeycomb”; “pores”, “cells”
gum swabs (Leeuwenhoek):
'“animacules” (tiny animals): can grow=independent form of life
Rudolphi/Link (1804)
cells have independent cell walls (not shared)
Dutrochet (1824)
“the cell is the fundamental element of organization”
Schleiden (1839)
every part of a plant is made up of cells, cells made from ‘crystallization process’ stole crystallization process
Schwann (1839)
both plants and animals are composed of cells and their products
Virchow(1855)
all cells arise only from pre-existing cells
What is tenet 1 of cell theory?
all living organisms are composed of one or more cells
What is tenet 2 of cell theory?
the cell is the most basic unit of life
What is tenet 3 of cell theory?
all cells arise only from pre-existing cells
What did basic stains allow Brown and Flemming to discover?
the nucleus, chromosomes, and different stages of cell division due to positive and negative charge
What did a “black reaction” in neurons allow C.Golgi to discover?
identify the ‘internal reticular apparatus’ called the golgi apparatus
electrons have a smaller wavelength than photons
high-resolution images
transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
thin: stained/shadowed with heavy metals
thick samples: fixed, dehydrated, embedded in resin, sectioned, and stained with heavy metals
scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
surface of sample is metal-shadowed
cryogenic electron microscopy(cryo-EM)
hydrated, unfixed, unstained samples are plunge-frozen leading to the formation of vitreous ice
What did Porter, Claude, and Fullham obtain?
First electron micrograph of a cell
What did George Palade discover?
ribosomes of the endoplasmic reticulum, rough endoplasmic reticulum, lumen of rough endoplasmic reticulum, vesicles moving proteins from the rough endoplasmic reticulum to the gogli complex, lumen of golgi vesicle, golgi complex
increase absorption of photon
decrease emission of photon at longer wavelength
violet
400nm
indigo
445nm
blue
475nm
green
510nm
yellow
570nm
orange
590
red
650
some organisms produce flourescent protiens (FPs) which the genes can be
fused to a gene of interest to produce a recombinant fluorescent protein and express in an organism/cell line of interest
transfection/transduction of cells resulkts in the expression of an
ectopical protein
results in an overexpression of the protein
(endogenous+exogenous protein)
Roger Tsein GRP in all colors which allows for
identification and localization of proteins via fluorescence microscopy
Identification and localization of proteins via ‘immuno-labeling’
antigen A→ primary antibody (antibody directed against antigen A), secondary antibodies (marker-coupled antibodies directed against the first antibodies
antibody with a probe covalently attached
generating antibodies to the specific protein of interest, immune system generates proteins called antibodies to the antigens
antibodies by injecting a model animal
with the protein of interest
monoclonal antibodies
generate antibodies from a cell line which can be purified
cells/tissues fixed
with common fixative like formaldehyde or glutaraldehyde which cross-links amino groups on adjacent molecules, tissue embeded in paraffin for sectioning
Permeabilized
with non-ionic deterghent that makes plasma membrane permeable to reagents
stained
with a ‘marker’ that is covalently attached to specific antibodies with heavy metals that stain different biomolecules to gain contrast or with small flourescent dyes that bind to membranes, DNA, or other structures
What is the first key concept of chemistry of life?
Molecular Complementarity (to stabilize the complex with molecule compounds that complement each other)
What is the second key concept of chemistry of life?
Polymerization, subunits need to come together
What is the third key concept of chemistry of life?
Chemical equilibrium( proteins can bind to each other at one dynamic rate, dissociate at another rate, reactants spatially controlled)
What is the fourth key concept of chemistry of life?
Energy-’high energy’ phosphoanhydride bonds supports unfavorable reactions (chemical energy)
Thermal energy
noncovalent interaction lowest bond strength
van der waals
noncovalent interactions second lowest bond strength
hydrogen bonds
noncovalent interactions third lowest bond strength
noncovalent interactions
molecules interact fall apart but environmental heart→ unstable→ don’t want K+ to interact
Hydrolysis of ATP phosphoanhydride bonds
covalent bond third strongest bond
c-c<c=c
covalent bond more bonds equal more bond strength
weak interactions
additive interactions contribute to protein complex ability, in an aqueous enviornment Kd is a measure of affinity for the enzyme, more stable less molecules, low Kd high affinity, high Kd low affinity more molecules less stable
conformational selectivity
conformational change is followed by ligand binding
induced fit
binding of one molecule changes the conformation of the other (increases molecular complementarity)
hydrophobic effect
nonpolar substance is surrounded by highly ordered water molecules low entropy with hydrophobic aggregation the water molecules are released into bulk solution are less ordered being higher entropy a thermodynamically favorable process
‘emergent properties’
a property that an individual subunit does not have, but which arises from the collective/complex system
What is the ‘RNA world’ Theory?
nucleotides→ random non-enzymatic polymerization→ short oligomer pool→ recombination→ long oligomer pool→ folding and emergence of ribozymes→ encapsulation→ emergence of first RNA replicase
Step 1 of building a cell
create a barrier which separates in from out, interior biochemical environment differs from the exterior, protection of endogenous macromolecules and processes
Amphiphatic phospholipids spontaneously assemble into a bilayer structure
bilayer advantages: self assembly (hydrophobic effect), fluidity, barrier
Fatty acid composition of the bilayer fluidity
cis c=c bond introduces a rigid kink which prevents tight packing in a membrane bilayer whereas the reduced form is straight without kinks and the oxidized form has rigid kinks
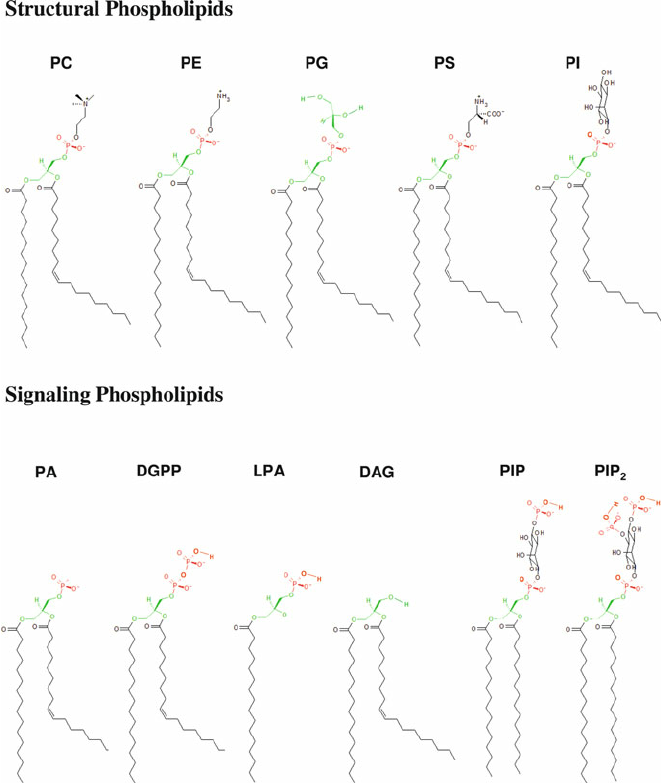
PC
methylation, phospholipid
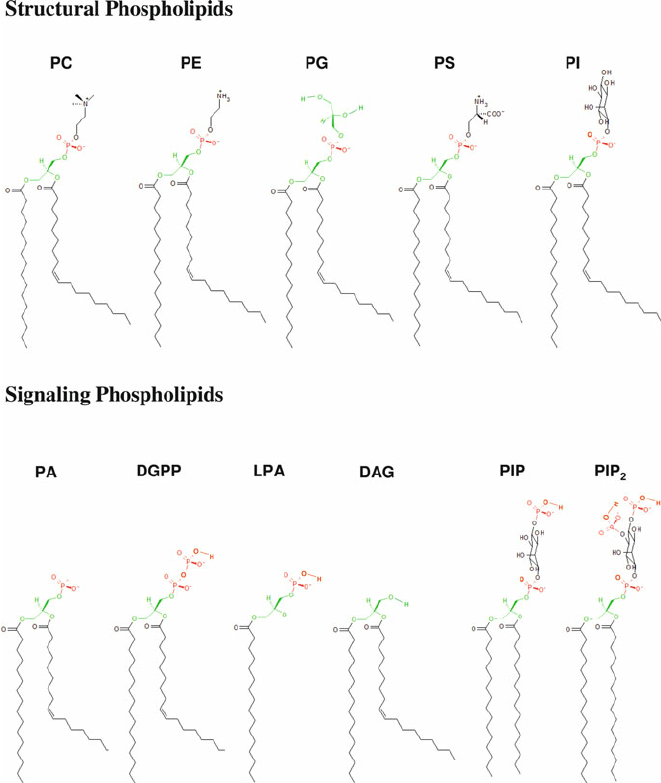
PS
Serine, phospholipid
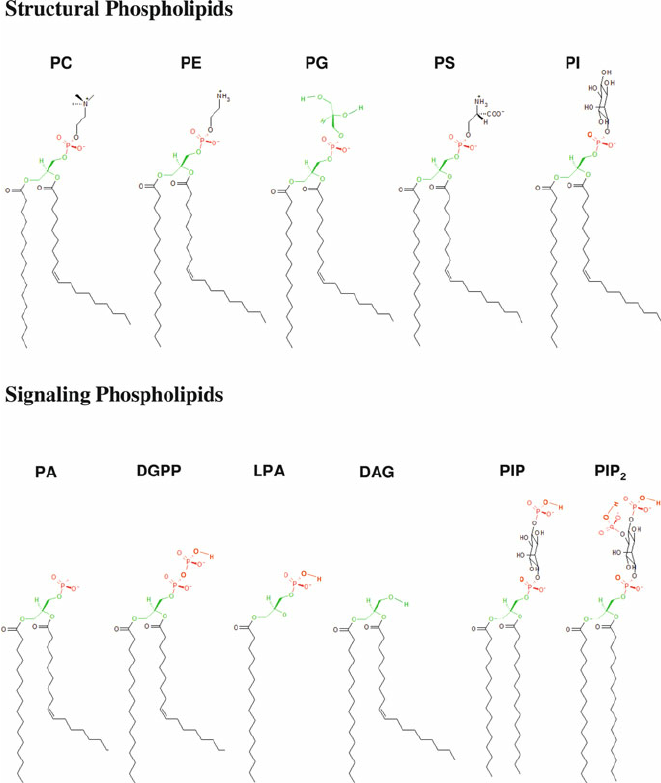
PE
ethanol, phospholipid
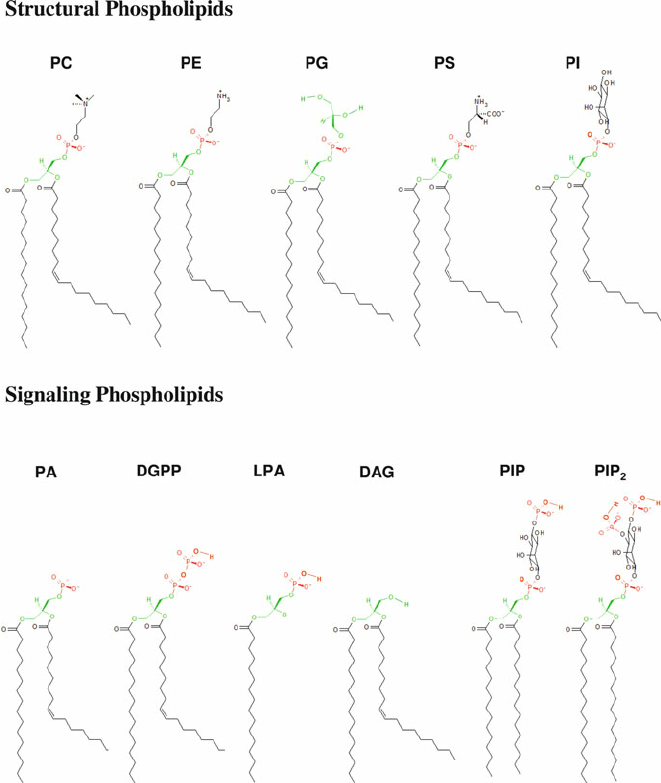
PI
oleoid- hydroxy groups to phosphate Ser knows where Golgi is, phospholipid
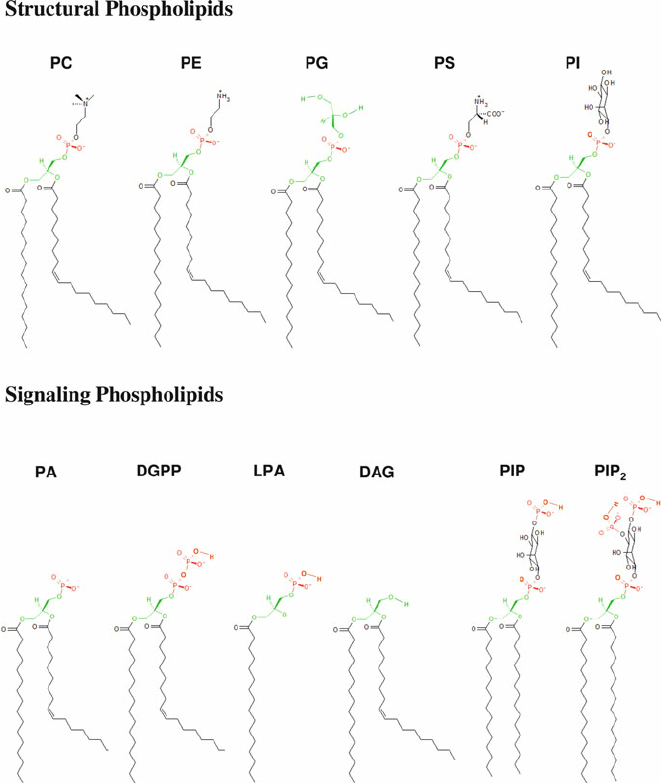
PG
phospholipid
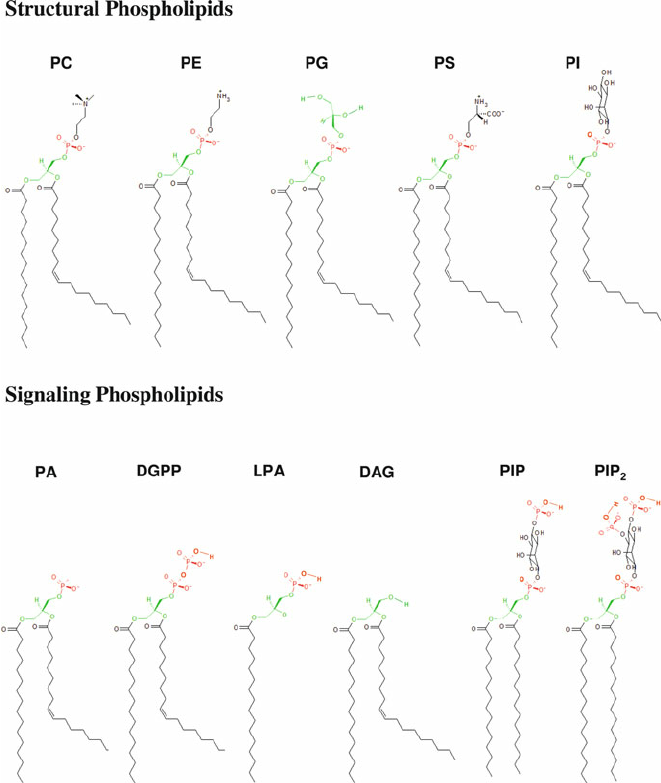
SM
Sphingomyel cholestrol lover, phospholipid
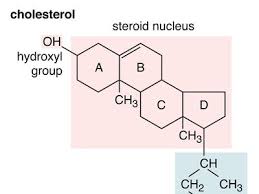
cholesterol
phospholipid
Cerebroside
sphingolipids with carbohydrates
LPS
lipids have specific carbohydrates
Homeoviscous Adaptation
cells dynamically change their membrane lipid composition to control membrane fluidity
decrease transition temperature
unsaturated bonds, shorter acyl chains
increase transition temperature
saturated bonds, longer acyl chains
cholesterol fluidity impact
lowers membrane permeability, adjusts membrane fluidity: low temp increases fluidity high temp decreases fluidity
hydrophobic molecules
all pass through the bilayer
small uncharged polar molecules
some pass through
large uncharged polar molecules
slightly pass through
ions
do not pass through the bilayer
phosphorylation
kinases catalyze transfer of phosphoryl group to amino acid side chain from ATP, serine, theorenine, tyrosine
acetyl lysine
epigentic control, cytoskeleton dynamics
3-Hydroxyproline
crosslinking of collagens, requires ascorbic acid
3-methylhistidine
urinary excretion reliable index of muscle protein breakdown
y-carboxyglutamate
high affinity binding of calcium ions
O-glcNAc-threonine
sending out more hydrogen bonds causing it to be more sticky , placeholder for S/T phosphorylation sites
primary structure
linear sequence of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
secondary structure
local alpha helices or beta sheets, held together by hydrogen bonds, 3.6 amino acids per turn, R groups project outward, prolines don’t participate
tertiary structure
peptide three-dimensional shape
quaternary structure
association between multipeptide complexes
supramolecular complexes
can be very large, consisting of tens to hundreds of subunits
the more disordered the protein the more
exceptional conformational flexibilities that contribute to their multiple functions
coiled coiled motif
two alpha helices wound around each other, alpha helix heptad repeat sequence with a hydrophobic residue at positions 1 and 4