Lecture 7: Learning and Memory
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
CLASSICAL CONDITIONING

Extinction
The weakening or disappearance of a learned behaviour when reinforcement is removed.

Desensitization
A process where repeated exposure to a stimulus reduces emotional or physiological response to it
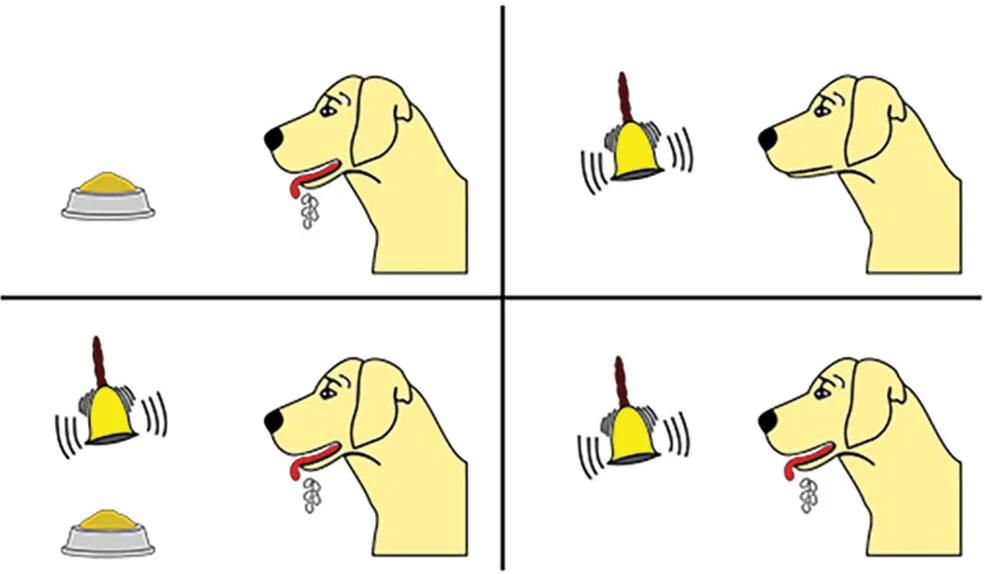
Pavlov’s Proposal (Classical Conditioning)
- There are brain regions that act in response to the unconditioned stimulus, the conditioned stimulus, and the unconditioned response
Pavlovs Dog Experiment (Classical Conditioning)
Unconditioned Stimulus = Steak → Dog salivates naturally
Conditioned Stimulus = Bell (paired with steak)
Eventually, Bell alone → Dog salivates (Conditioned Response)

Karl Lashley ENGRAMS
Reasoned that if memories were connections between brain areas, they could be severed with a knife

Engrams Findings
Trained rats on mazes, then cut to cortex
Cuts did not impair performance
Memory is not localized in one spot
Engrams: Equipotentiality
All parts of the cortex contribute equally to functioning behaviors (e.g., learning) and any part can substitute others

Engrams: Mass Action
The cortex works as a whole and more cortex is better
Modern Search for the Engram – Thompson (1930–2014)
LIP is where learning happens
Red nucleus is needed to show the response
Suppressing LIP = no learning

LIP
memory storage

Red Nucleus
Response Execution
OPERANT CONDITIONING
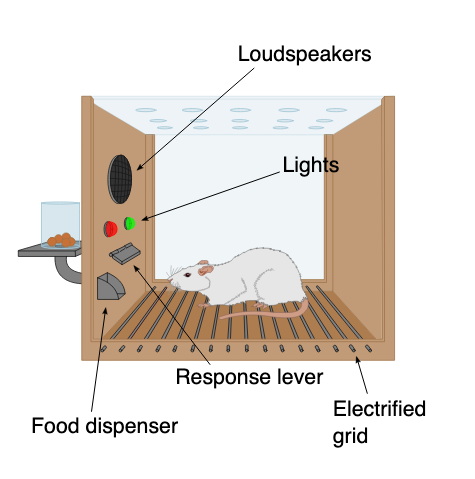
Operant Conditioning: Skinner Box
Conditioning chamber used to observe/manipulate behaviour.
Behavior is strengthened —> reinforcer, weakened—> punisher

Positive and Negative REINFORCEMENT
Adding something good to increase behaviour ( treat).
Removing something bad to increase behaviour (no curfew→ good grades).
Positive and Negative PUNISHMENT and REINFORCEMENT
GIVING (positive)
Positive Punishment
Spanking a child
Positive reinforcement
Giving a child a sticker
TAKING AWAY
(negative)
Negative punishment
Taking away child’s screen time
Negative reinforcement
Excusing a child from completing their chores

Continuous Reinforcement
- The desired behaviour is reinforced every single time it occurs

Intermittent Reinforcement
- Reward or consequence only sometimes after a desired behavior, rather than every time. (slot machine)
Neural Basis of Positive Reinforcement
Involves the:
dopamine system
nucleus
(VTA)
which are activated when a rewarding stimulus is received, reinforcing the behaviour.
STATISTICAL LEARNING

Statistical Learning
The ability to perceive and learn regularities
■ E.g, in language, such as the speech sounds that comprise a word
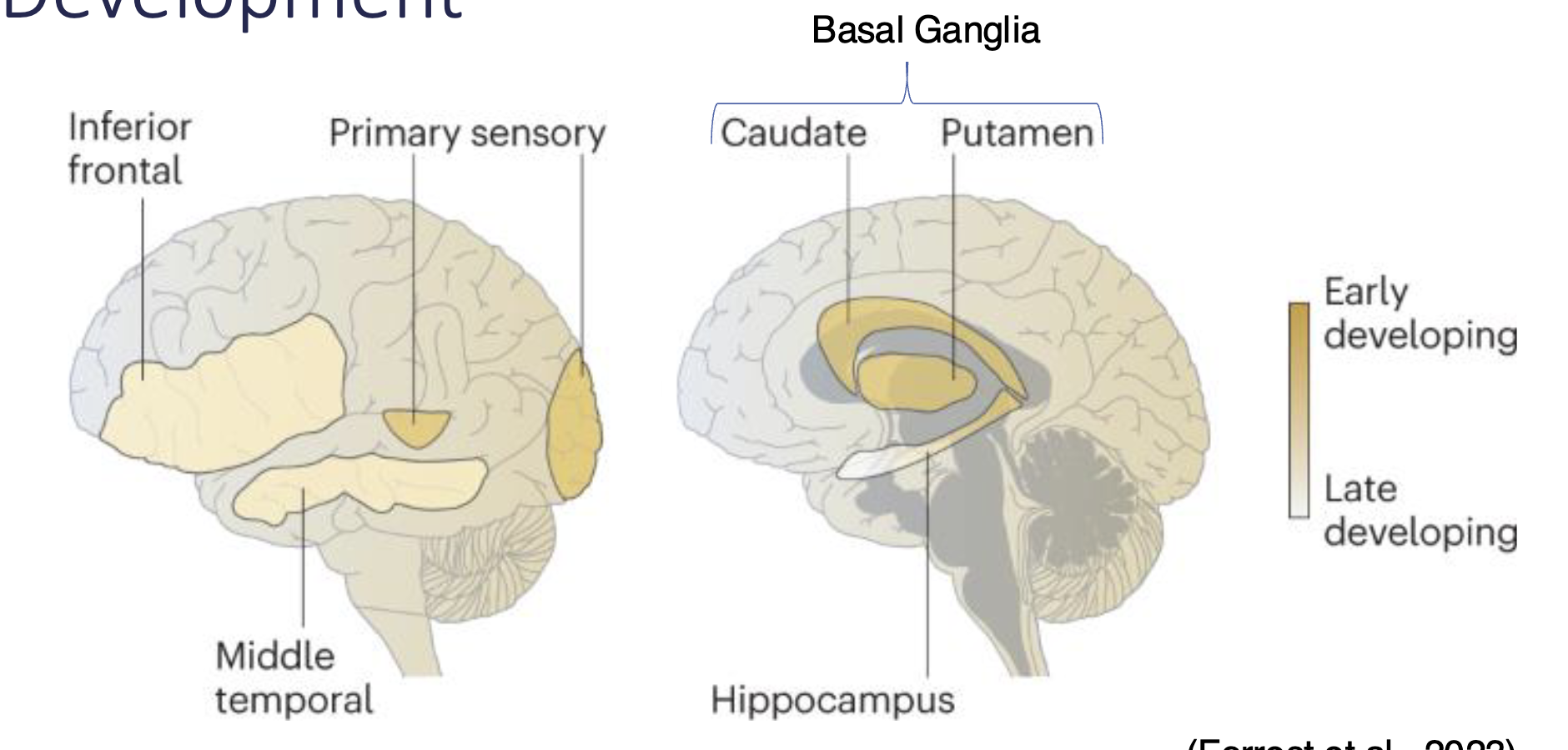
Changes in Statistical Learning Across Development
Basal ganglia & primary sensory areas = early-developing regions
lit up regions are active during language task
PERCEPTUAL LEARNING

Perceptual Learning
Learning to recognize and respond to stimuli through experience (identifying faces/voices better over time).
RELATIONAL LEARNING
Relational Learning
Involves learning the temporal and spatial relationships among objects and events
( where you parked based on landmarks).
SUBTYPES OF MEMORY

Short-Term Memory
Holds a limited amount of info for a brief time (15–30 s)

Working Memory
A more active form of short-term memory that manipulates and processes info (e.g., doing mental math).

Process of Consolidation
The transformation of short-term memories into long-term ones, mainly involving the hippocampus and strengthened through repetition and sleep.
Long- Term Memory
Memory of facts and events that can be consciously recalled

Long term Memory: Explicit
Refers to the conscious recollection of facts, events, and personal experiences

Long term memory: Episodic
Stores personally experienced events

Long- term Memory; Semantic
stores general knowledge
\

Long Term Memory: Procedural/ IMPLICIT
Unconscious memory for tasks/ skills (typing, driving, bike).
Flashbulb Memories
Vivid, detailed memories of emotionally significant events
Eg: big accident
HIPPOCAMPUS

Hippocampus – Role in Memory
Vital for declarative/episodic memory
Active during:
Memory formation
Memory recall
Imagining future events

Hippocampus – Visual Spatial Memory
More years as a taxi driver = larger hippocampal volume
Shows its role in navigation and memory mapping
Place Cells & Time Cells (located in HIPPOCAMPUS)
Fire in response to spatial locations and temporal information

Grid Cells (HIPPOCAMPUS)
Located in ERC hippocampus
Helps with navigation and spatial awareness
BASAL GANGLIA
Basal Ganglia - Role in Memory
Involved in implicit learning
Supports learning of patterns, habits, and motor skills
Basal Ganglia Anatomy
■ Striatum
– Dorsal striatum
Ventral striatum
DISORDERS OF MEMORY

Retrograde Amnesia
Can't remember what happened BEFORE brain injury
HM study : Retrograde Amnesia
Severe anterograde amnesia (no new episodic memories)
Some retrograde amnesia
Working memory intact
Inability to form new explicit/episodic memories
Procedural learning remained intact

Anterograde Amnesia
Can't form new memories

Infantile Amnesia
The inability of humans to remember episodic experiences that occurred during the first few years of life ( 0–3 yrs)
→ Immaturity of hippocampal systems

What is Severely Deficient Autobiographical Memory (SDAM)?
can remember facts but can’t relive or recall personal past events, even tho they r healthy.

Aphantasia
Inability to visualize images in the mind’s eye.

Korsakoff’s syndrome
Caused by thiamine (vitamin B1) deficiency, often from alcoholism
Brain damage, especially in the dorsomedial thalamus
Main sign: confabulation (making up stories without knowing)