metal-ceramic and dental ceramics restorations
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
definition of ceramics
an inorganic compound w nonmetallic properties composed of metallic and nonmetallic elements
what are some examples of metallic and nonmetallic elements in ceramics
Al2O3 (alumina), SiO2 (silica), SiC (silicon carbide), TiN (titanium nitride)
ceramic components and how they are joined
compounds, metallic and nonmetallic elements are joined by covalent and ionic bonds → crystalline structure
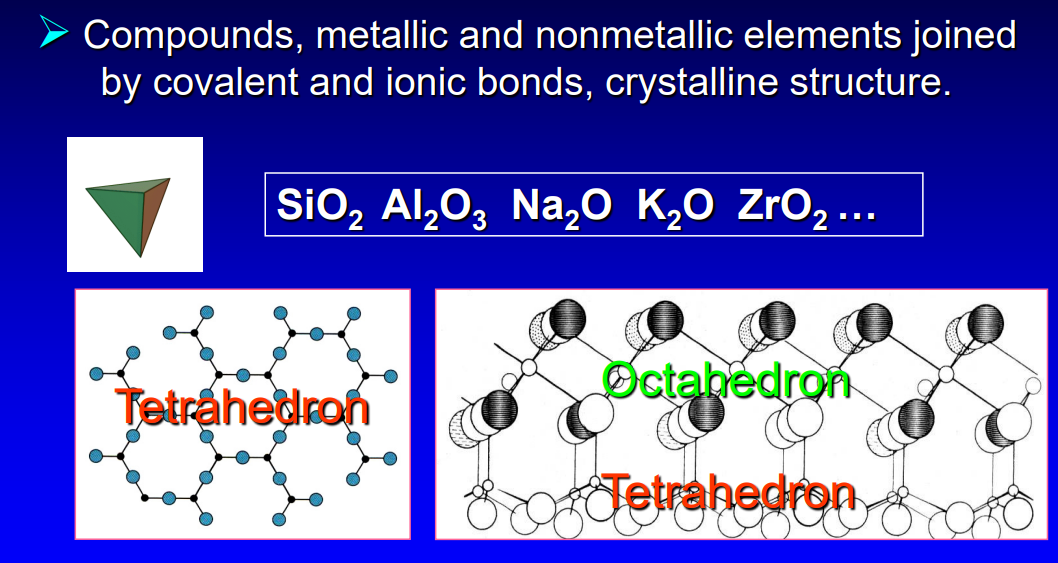
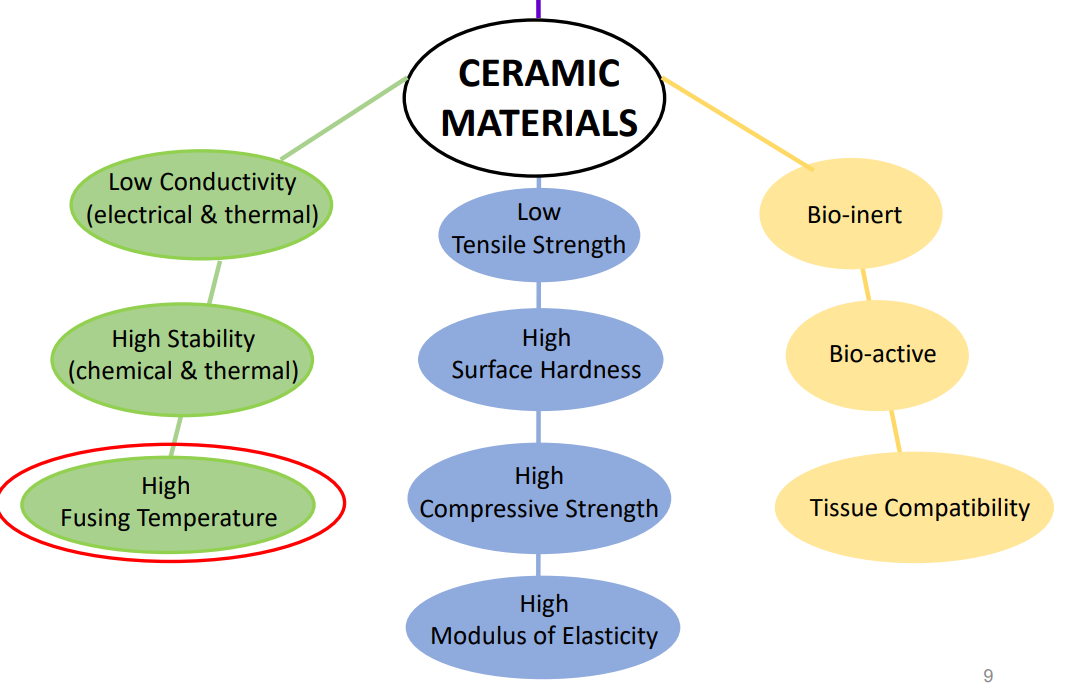
did ceramics have a higher or low conductivity, stability, and fusing temp
conductivity: low
stability: high
fusing temp: high
do metals and alloys have a higher or low conductivity, stability, and fusing temp
conductivity: high
stability: low
fusing temp: low
do ceramics or metals/alloys have a higher tensile strength
metal and alloys
true or false: ceramic materials have high surface hardness
true
true or false: ceramic materials have high compressive strength
true
true or false: ceramic materials have low modulus of elasticity
false
historical perspective of dental ceramics
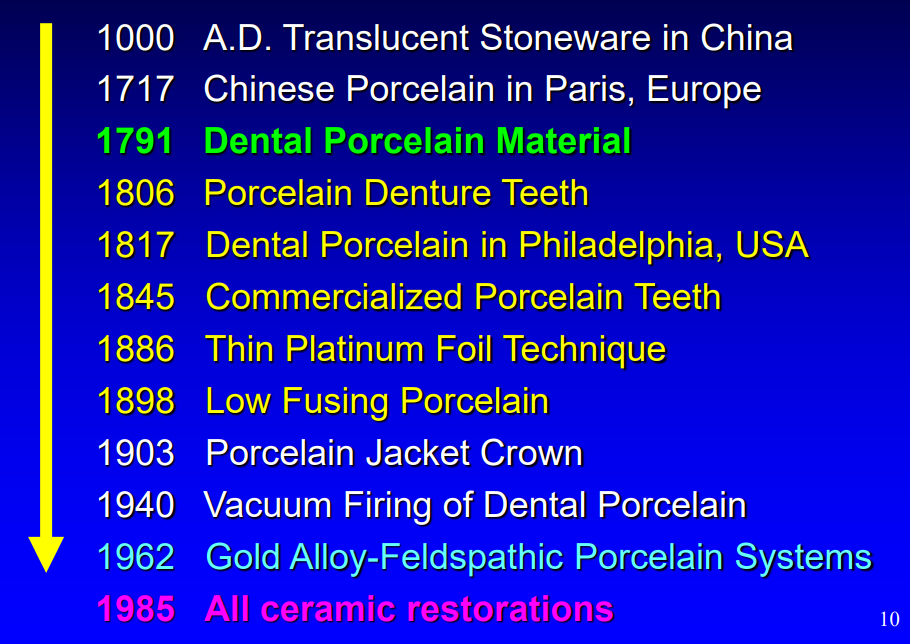
dental porcelain definition
refers to specific compositional range of ceramic materials made by mixing kaolin, quartz, and feldspar, and fused at high temperature to form enamel like substance
decorative porcelain, a white translucent stoneware, was first developed in…
Jingdezhen, Jiangxi province, China circa 1000 A.D.

ceramic materials were the first material to be the subject of…
laboratory research (circo 1700 A.D.)
porcelain was the first material to be…
artificially made by man and used in dentistry in the late 1700s
De Chemant obtained French and English _________ for his formulation of dental porcelain in 1791
patents
who developed a practical formulation of porcelain denture teeth
Alexis Duchateau, a pharmacist, and Nicholas de Chemant, a dentist
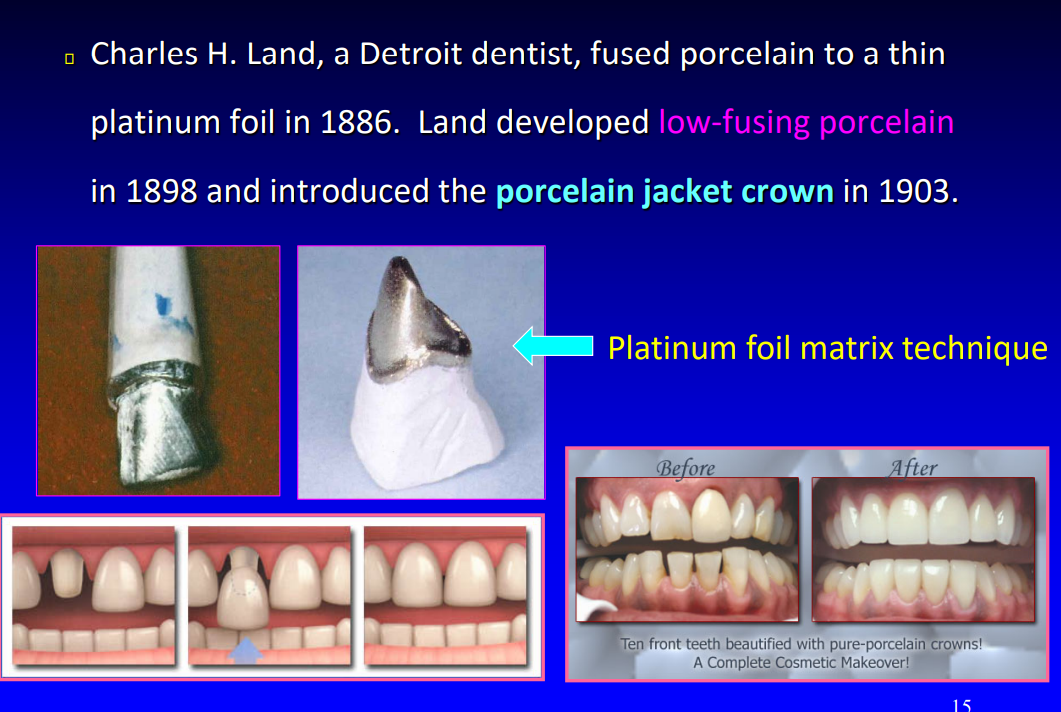
Charles H Land, a detroit dentist, fused porcelain to a thin platinum foil in 1886, this developed into what in 1903
low-fusing porcelain and introduced porcelain jacket crown
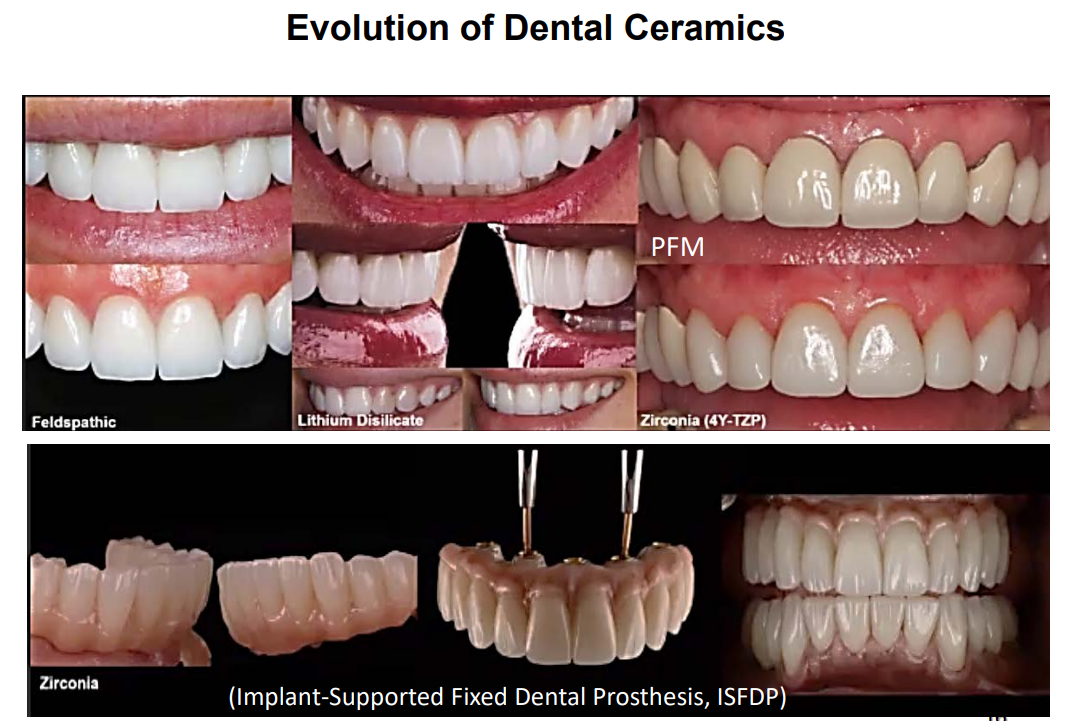
evolution of dental ceramics pic
what are the 4 classifications for dental ceramics
fusing temp
application
fabrication technique
crystalline phase
do metal or ceramic have a higher melting temp, why
ceramic bc of the covalent bond
ultra low fusing temp
<850 C
low fusing temp
850-1100 C
medium fusing temp
1100-1300 C
high fusing temp
>/= 1300 C

what is the difference between these two crowns
1 porcelain crown w an inner metal lining
2 all ceramic crown w no metal lining
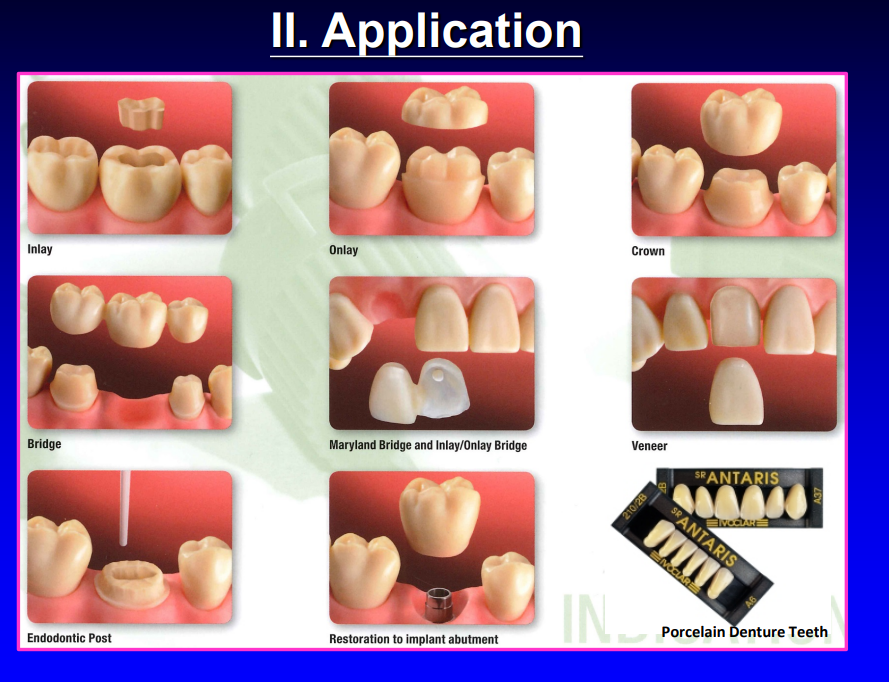
porcelain veneer application
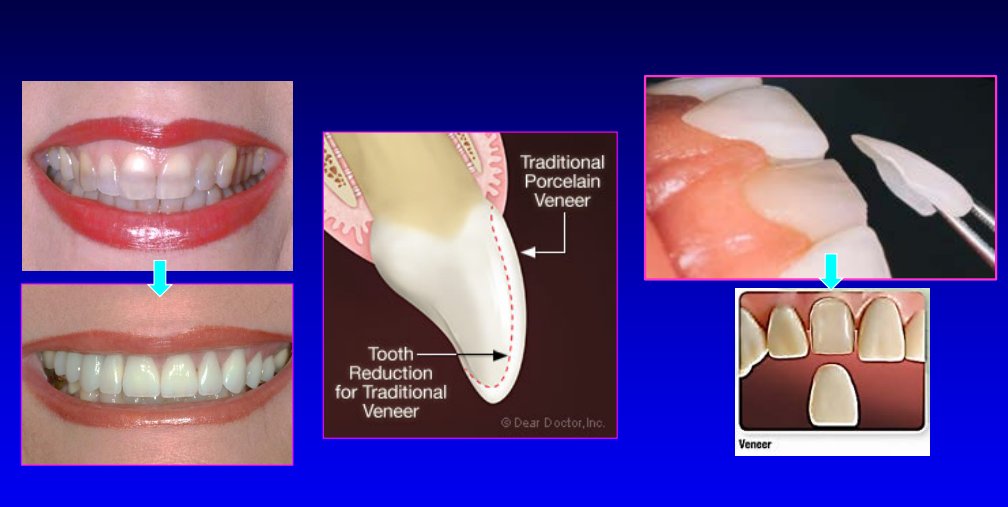
different indirect restorative applications
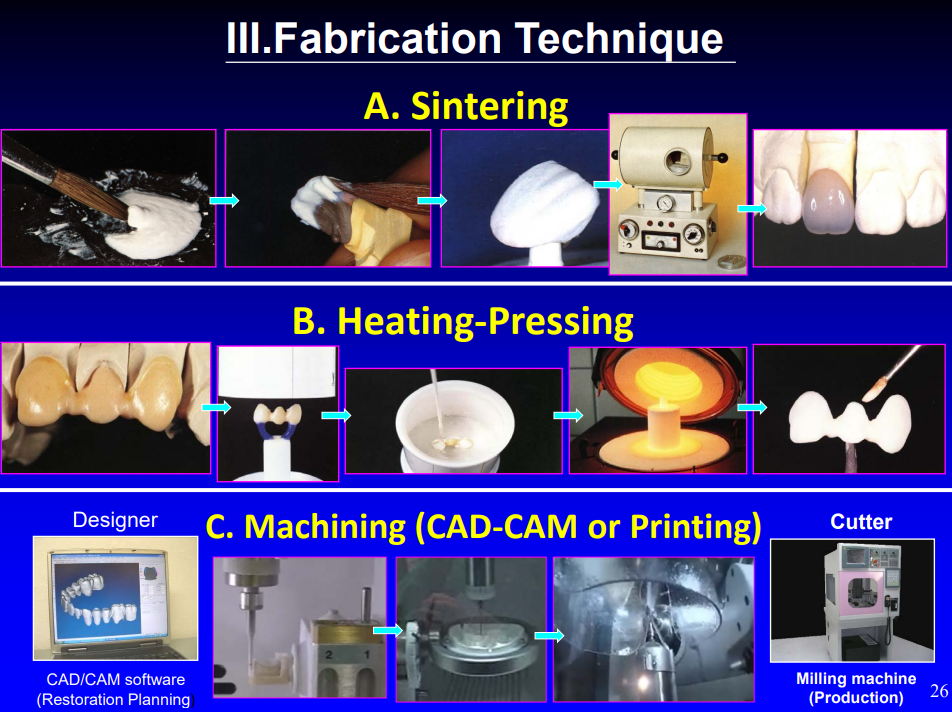
what are the three types of the fabrication technique
sintering
heat pressing
machining (CAD-CAM or printing)
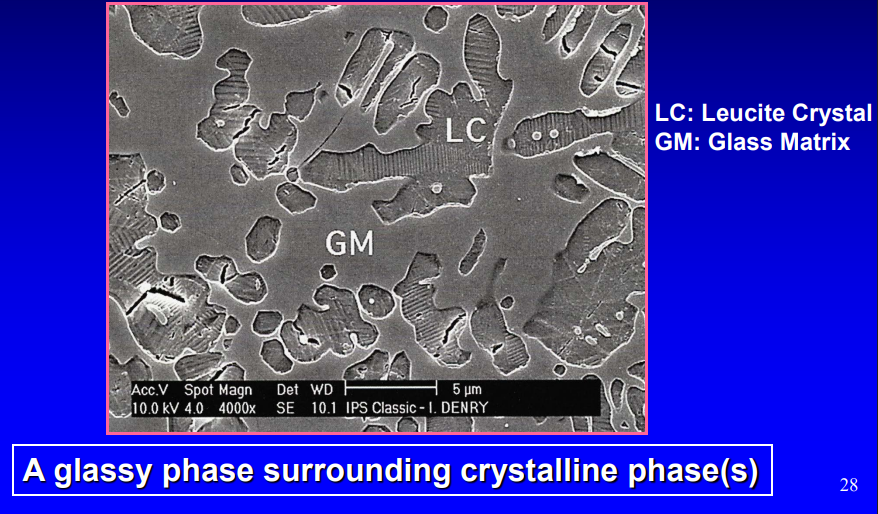
regardless of applications or fabrication technique, after firing, dental porcelains and ceramics are composed of at least what 2 phases
leucite crystal: ordered arrangement- strong
glass matrix- no structure
what are the four types of the crystalline phases
feldspar-based, sintering
leucite-reinforced, pressable
lithium disilicate, pressable
zirconia-based, machinable
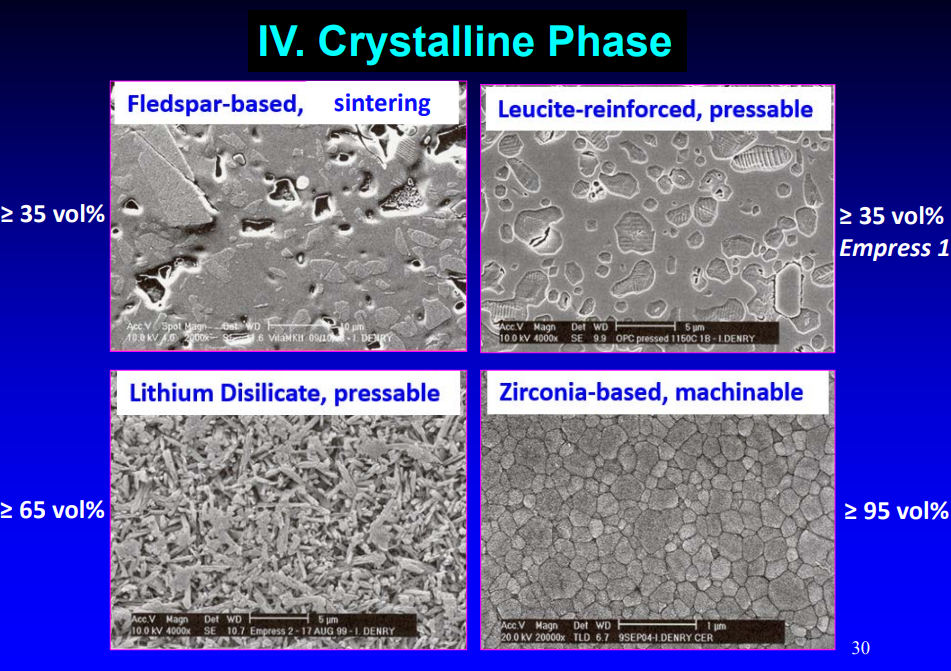
what is the crystalline percentage of feldspars
>/= 35 volume%

what is the crystalline percentage of leucite
>/= 35 volume% Empress 1

what is the crystalline percentage of lithium disilicate
>/= 65 volume%

what is the crystalline percentage of zirconia
>/= 95 volume %

of the two types of all-ceramic systems, which is silica based and which is non-silica based
silicate ceramics- silica based
oxide ceramics- nonsilica-based
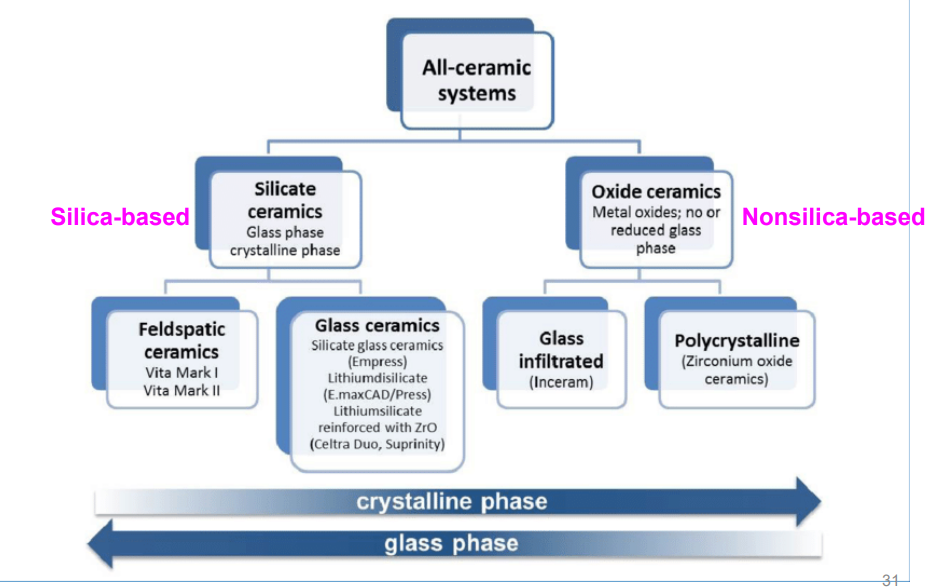
what are the types of ceramics that fall under silicate ceramics (2)
feldspatic ceramics
glass ceramics
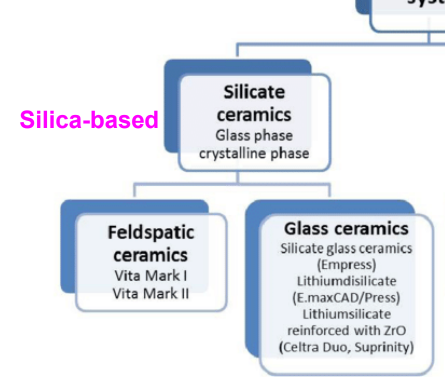
what are the types of ceramics that fall under oxide ceramics- no or reduced glass phase
glass infiltrated
polycrystalline
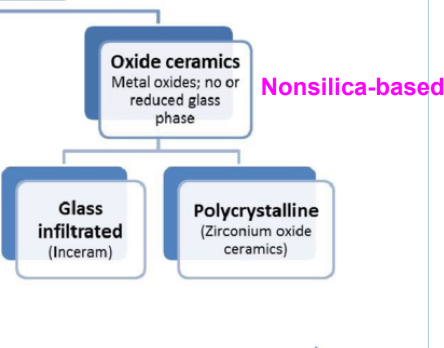
what do you etch Feldspathic porcelain ceramic with
9.5% hydrofluoric acid gel for at least 1 min
what are the two over-arching types of ceramic restorations
metal-ceramic restoration
all ceramic restoration
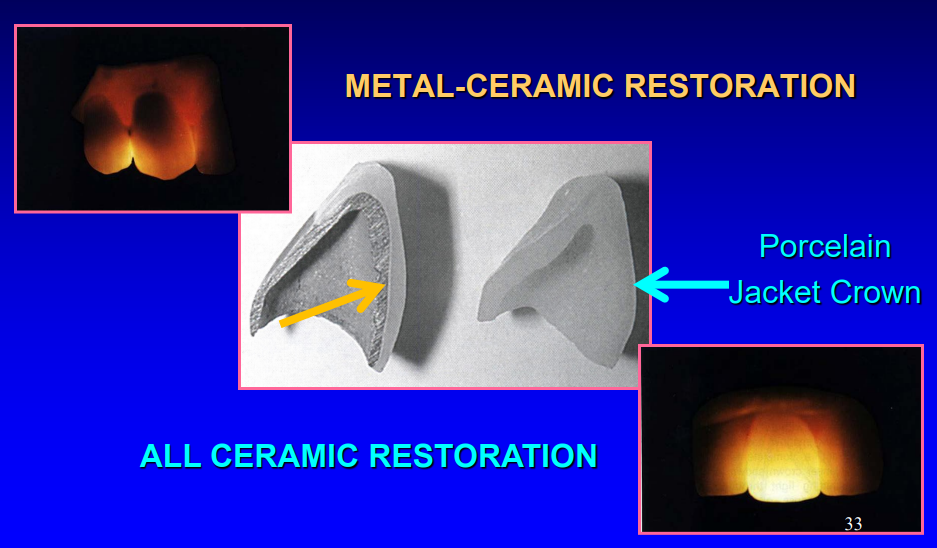
what are the three types of metal-ceramic restorations
porcelain-fused to metal (PFM)
ceramometal restoration
metal-ceramic restoration
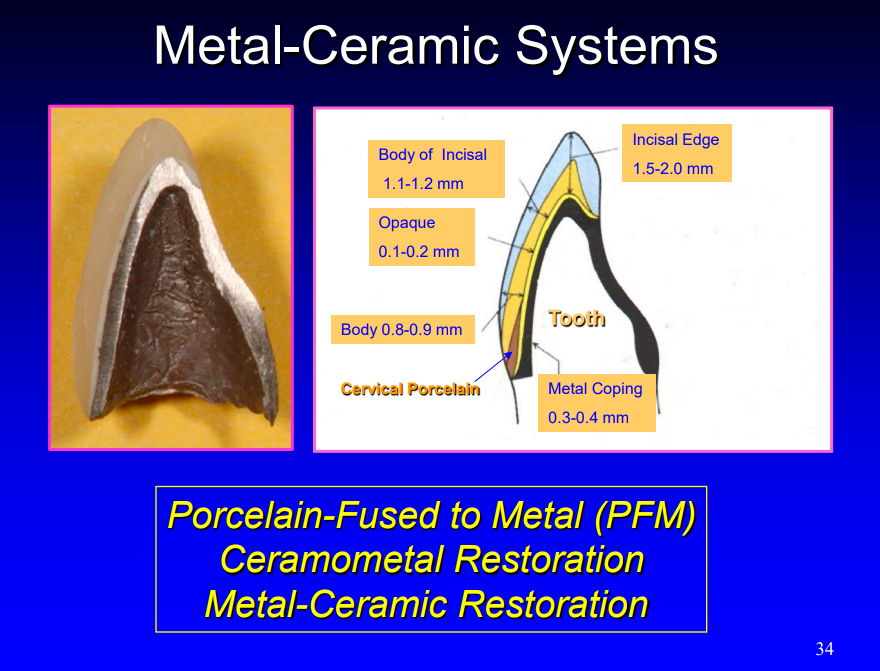
when referring to porcelain-fused to metal, what are the melting temperature and thermal expansion properties of the alloy and ceramic before bonding (high/low for each)
melting temp for alloy: low
melting temp for ceramic: high
thermal expansion for alloy: high
thermal expansion for ceramic: low
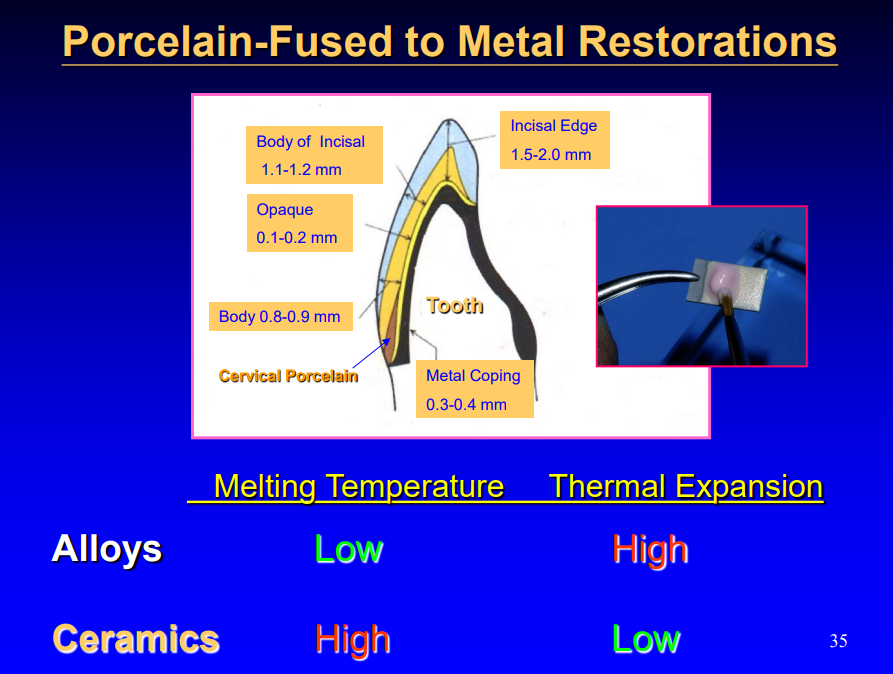
history of porcelain-fused to metal restorations
when heat treated, these produce high expansion ceramics suitable for metal bonding

when referring to porcelain-fused to metal, what are the melting temperature and thermal expansion properties of the alloy and ceramic after bonding (high/low for each)
melting temp for alloy: high
melting temp for ceramic: low
thermal expansion for alloy: high
thermal expansion for ceramic: low
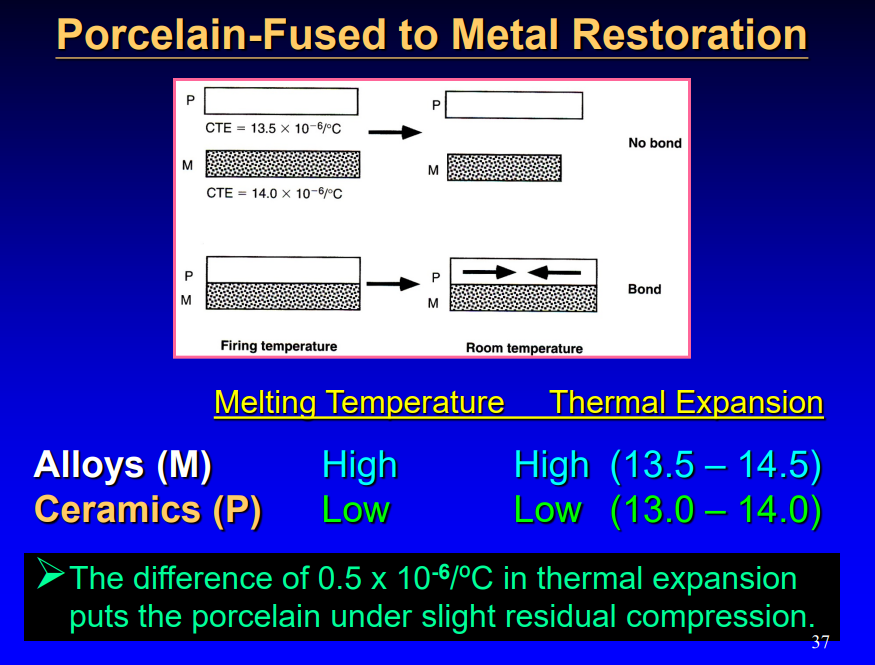
the properties of ceramics are customized for dental applications by precise…
control of the type and number of components (kaolin, quartz, feldspar) used in their production
dental porcelain fuses at a relative _________(high/low) temperature to form a hard substance much like enamel in appearance
relatively low temp
___________ is accomplished w various colored fusible materials
staining
what are the three triaxial porcelain compositions
quartz
kaolin (clay)
feldspar
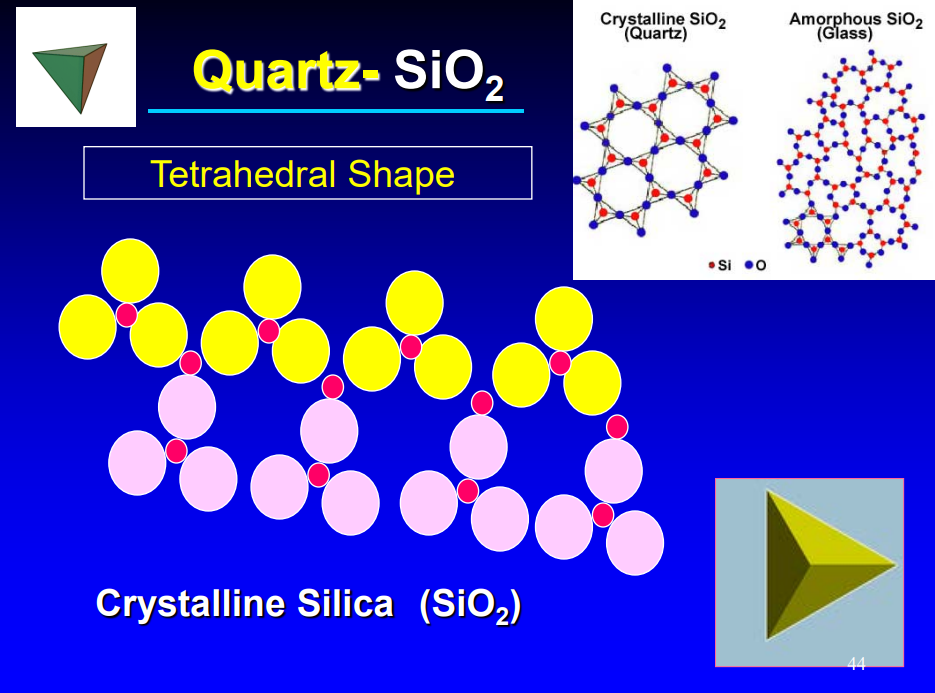
what is quartz
silica (SiO2)
what is kaolin (clay)
a hydrated aluminosilicate

what is feldspar
a mixture of K and Na aluminosilicates

feldspar is a ______ (high/low) fusing component
low- 125-1170 C
what is the funx of quartz
binder
what is the funx of kaolin
opacifier and viscosity control

what is the funx of feldspar
strength and binder

what is the shape of quartz
tetrahedral shape
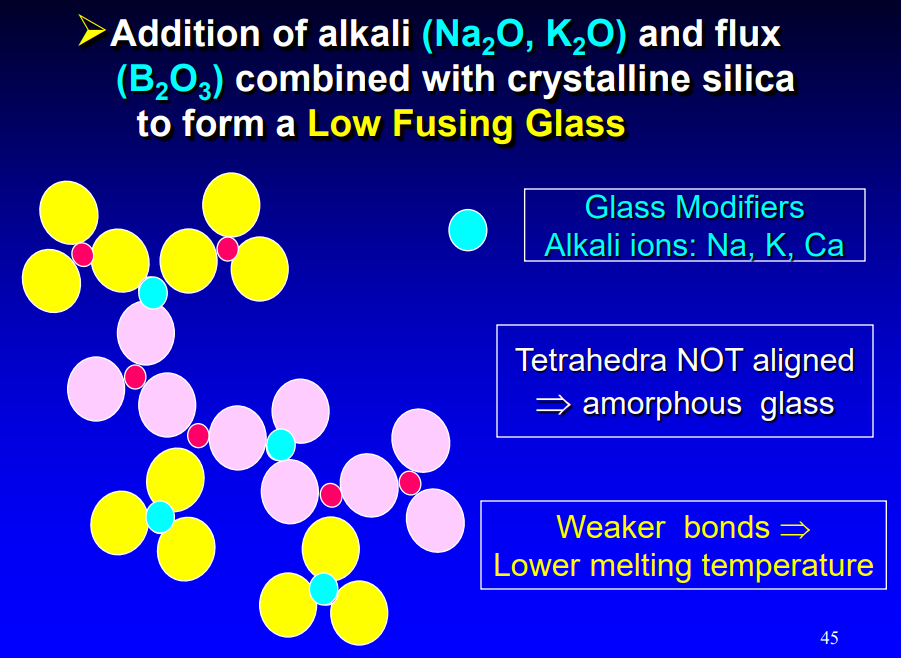
the addition of alkali (Na2O, K2O) and flux (B2O3) combined w crystalline silica forms a…
low fusing glass

what are glass modifiers
alkali ions: Na, K, Ca
if the tetrahedra is not aligned…
will be disorders → amorphous glass → weaker bonds → lower melting point
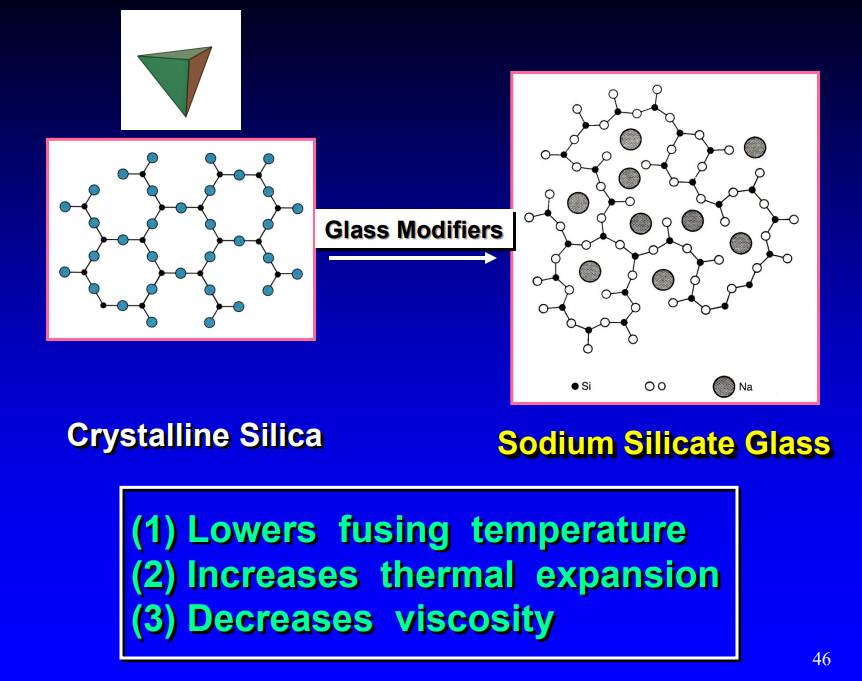
when adding glass modifiers to crystalline silica, you get…
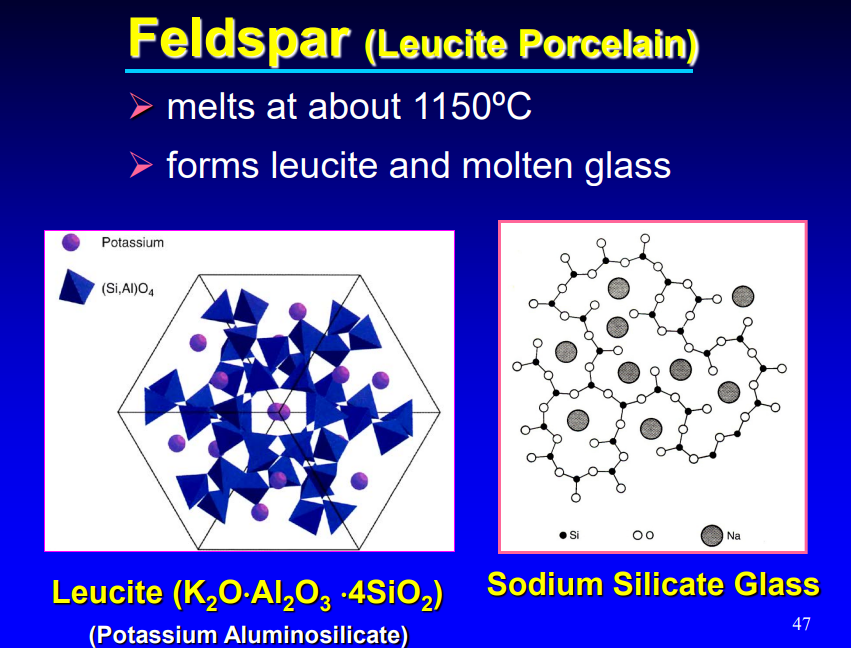
sodium silicate glass
how do properties change when glass modifiers as added to crystalline silica to form sodium silicate glass
lowers fusing temp
inc thermal expansion
dec viscosity
what does feldspar melt at
~1150 C
feldspar can form…
leucite and molten glass
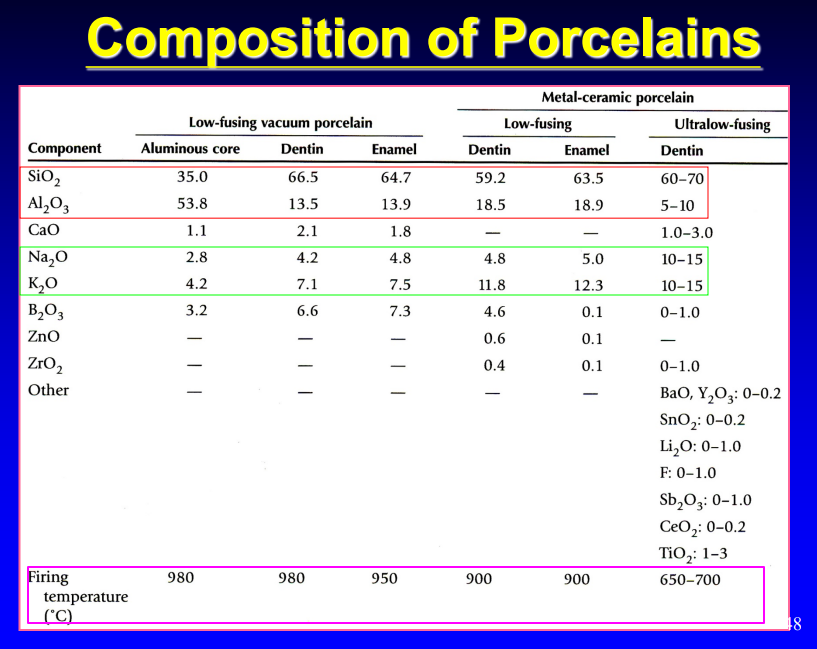
composition of porcelains
red box: major composition
green box: feldspathic material
the feldspars are colorless, thus _______ and ________ are added for color
pigments and opacifiers

how are pigments made
grinding together metallic oxides w feldspar and glass
fusing the mixture in the furnace
regrinding to a fine powder
what is the manufacturing process (generally) to form dental porcelain (frit)
feldspar + alumina + silica + opacifiers + pigments
heat treated in furnace (allows leucite crystal growth)
quenching
grind pigments to powder
frit

what is the processing portion of dental porcelain
shade selection
porcelain powders are mixed w water to produce a plastic mass of material which can be molded and carved before firing
in the processing phase of metal-ceramic restoration, what do you apply w a brush
apply opaque w brush to oxidized alloy
apply body and enamel w brush to opaquing alloy
apply incisal or enamel over body porcelain
what are important opacifying oxides for dental ceramics
TiO2 and SnO2
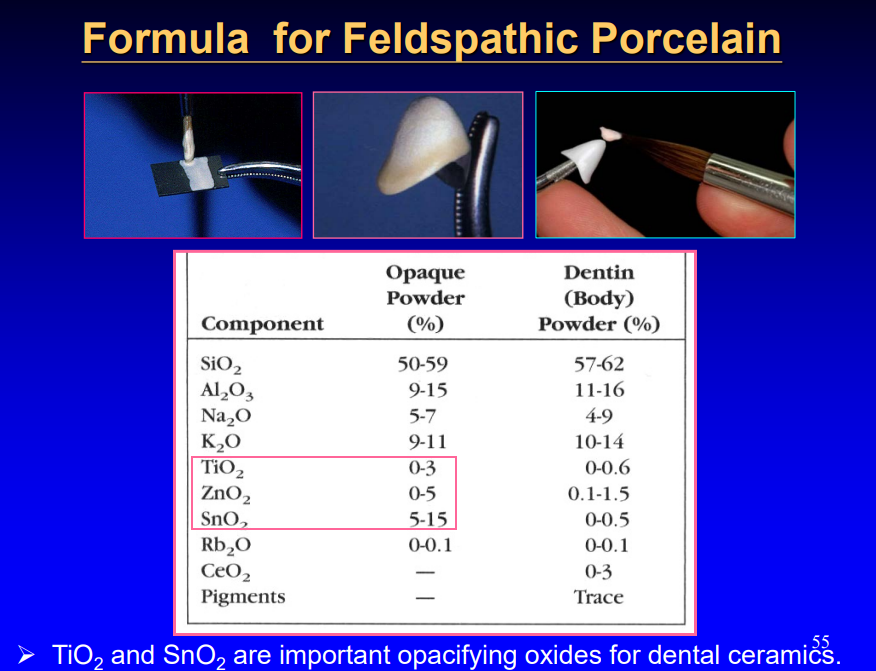
when processing there is a 13% oversize to accomodate for what
shrinkage
in processing, the technician fuses the porcelain powder and simply…
remelts the drits w/o causing any significant inc in rxn between components

what is the fusion process known as
sintering
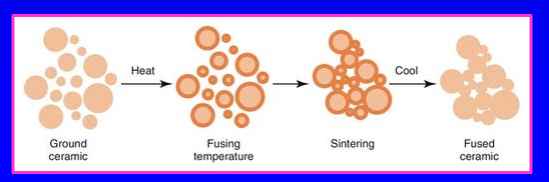
what is sintering
the outer layers of the grains of porcelain partly combine together; the process of heating closely -packed particles to achieve inter-particle bonding
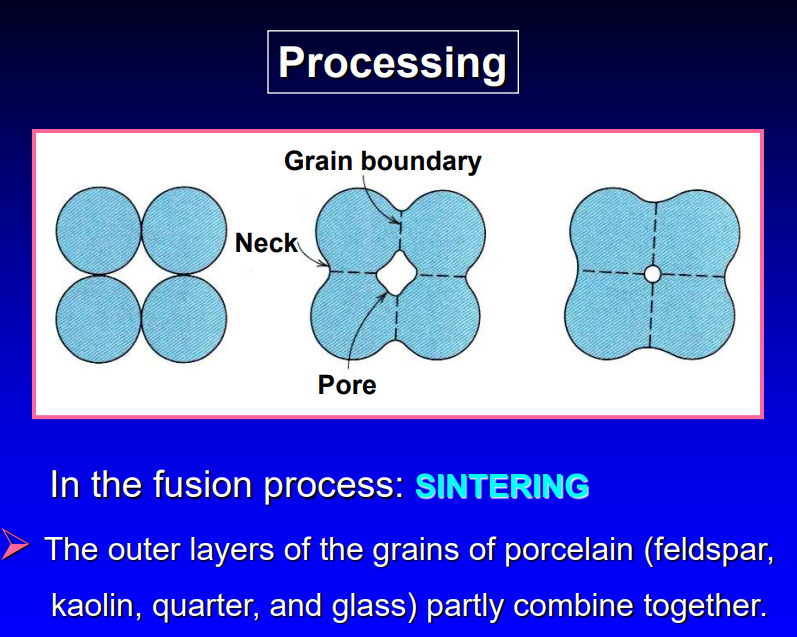
sintering image
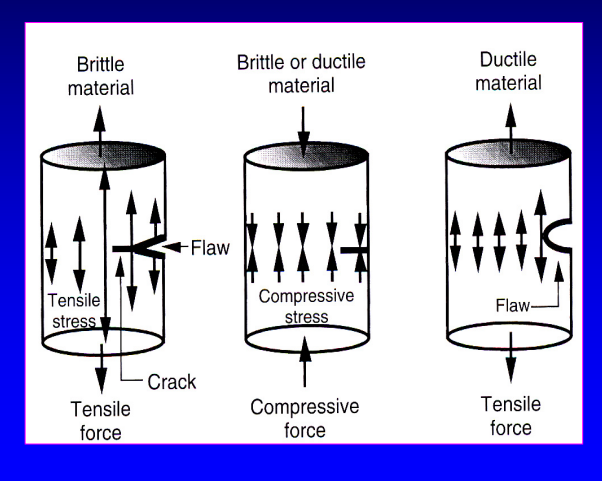
ceramic has a _________ (high/low) compressive strength and a _______ (high/low) tensile strength
high compressive and low tensile
what is glazing
a low-fusing, transparent glass that may be used as a glaze material; glaze give a crown an impervious, smooth surface and imparts greater translucency
requirements for a metal-ceramic system: the veneering porcelain must have a _____ fusing temp
low fusing temp
requirements for a metal-ceramic system: melting range of the alloy must be at least _____ higher than the firing range of the veneering porcelain
100 C
requirements for a mental-ceramic system: the alloy should have excellent _________
castability
requirements for a metal-ceramic system: the alloy substrate has adequate __________ and ______________
adequate stiffness and strength
requirements for a metal-ceramic system: the porcelain must wet the alloy surface readily during…
firing
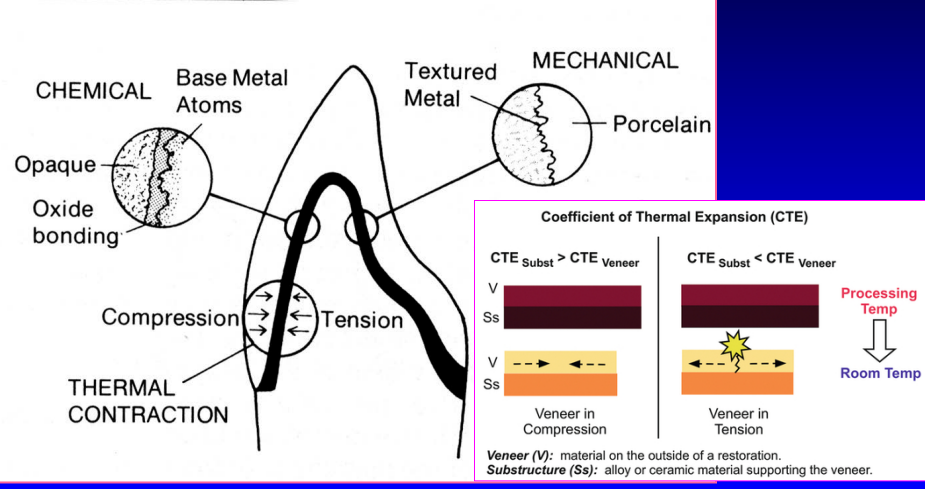
requirements for a metal-ceramic system: coefficients of thermal expansion of the metal is slightly ______ (higher/lower) than that of porcelain
slightly higher
requirements for a mental-ceramic system: a stronger bond between the __________ and __________ is essential
between veneering porcelain and metal substrate
what are the three methods of bonding porcelain to metal
chemical
thermal contraction
mechanical
bond strength of gold alloy w. vs w/o minor element added
higher w added minor elements
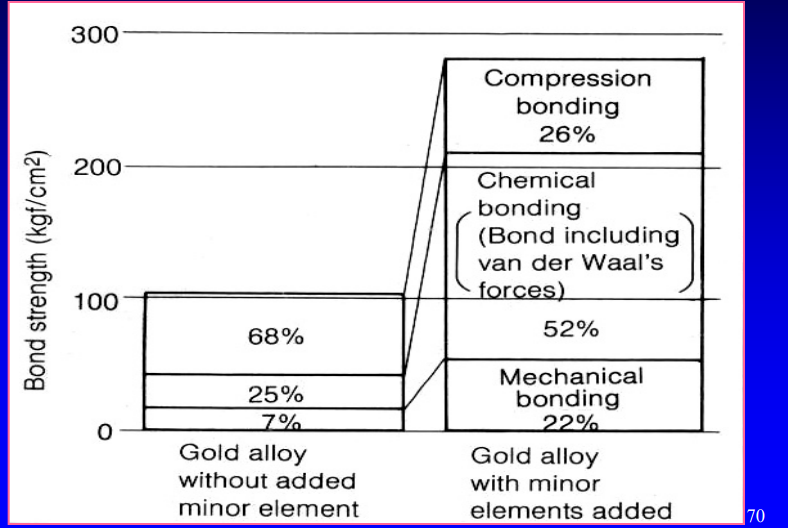
in obtaining surface oxide, you introduce base metal elements into precious metal alloys to form…
thin oxide
in obtaining surface oxide, direct oxide production the constituents of the alloy such as…
base metal alloys
in obtaining surface oxide, surface coating of metals w oxidizable metals such as…
In and Sn
advantages of metal-ceramic restorations
adequate marginal integrity
predictable strength
disadvantages of metal-ceramic restorations
compromised esthetic results
potential biocompatibility problem w some base-metal alloys