GenChem 1st MT
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
atoms
fundamental unit of matter, smallest particle
molecules
composed of atoms
ions
particles with charges
SOLID
- The molecules that make
up a solid re arranged in
regular, repeating
patterns.
-They are held firmly in
place but can vibrate
within a limited area.
LIQUID
-The molecules that make up
a liquid flow easily around
one another. They are kept
from flying apart by
attractive forces between
them.
-They assume the shape of
their containers.
GAS
-The molecules that make
up a gas fly in all
directions at great speeds.
-They are so far apart that
the attractive forces
between them are
insignificant.
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
ACCDG TO CHANGE INVOLVED DURING MEASUREMENT OF THE PROPERTY
no change in composition takes place during the determination or
measurement of these properties
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
ACCDG TO CHANGE INVOLVED DURING MEASUREMENT OF THE PROPERTY
a change in composition occurs during the determination or measurement
of these properties.
EXTENSIVE PROPERTIES
ACCDG TO DEPENDENCE ON AMOUNT OF MATTER
change their value when the amount of matter or substance is changed
INTENSIVE PROPERTIES
ACCDG TO DEPENDENCE ON AMOUNT OF MATTER
do not change their value when the amount of matter is changed
PURE SUBSTANCES
TYPES OF MATTER
composed of only one component
MIXTURES
TYPES OF MATTER
Composed of several components
ELEMENTS
TYPES OF P.S.
pure substances that are made up of only one kind of atoms. Possible examples: iron;
gold; mercury
COMPOUNDS
TYPES OF P.S.
pure substances made up of two or more kinds of atoms. Possible examples: salt; sugar;
water
HOMOGENEOUS MIXTURE
is a combination of two or more substances that cannot be distinguished
from each other. It has a uniform composition and exhibits the same properties in different parts of the
mixture.
EVAPORATION
is done by heating the solution to dry up the solvent and crystallized the
substance of interest. HOMO SOLID-LIQUID
Recrystallization
is a separation technique based on the difference in solubilities of
substances in an appropriate solvent at an elevated temperature. HOMO SOLID-LIQUID
Distillation
is a separation technique based on the difference of boiling points between two
liquid components. HOMO LIQUID-LIQUID
Simple distillation
is used when there is a large difference in the boiling points of the components of the
solution.
Fractional distillation
is used when there is a relatively small difference in the boiling points of the
components of the solution.
Vacuum distillation
is used for compounds with very high boiling points.
Steam distillation
is used for compounds that are heat-sensitive.
Chromatography
is a separation technique that relies on the differential partition of the components between its two components.
● The separation is determined by the two competing processes: the adsorption onto the stationary phase and the solubility in the mobile phase.
● Solutes that have high solubility in the mobile phase will go along with the mobile phase as it travels on the stationary phase.
normal-phase chromatography
the mobile phase is nonpolar and the stationary phase is polar.
reversed-phase chromatography
the mobile phase is polar and the stationary phase is nonpolar.
HETEROGENEOUS MIXTURE
is a combination of two or more substances that can be distinguished
from each other. It has a nonuniform composition and its properties vary in different parts of the mixture.
suspension
heterogeneous mixture whose solutes do not completely dissolve and its
particles settle into clumps or layers when left undisturbed. FLOUR-WATER, MUD-WATER, SAND-WATER, LEMONADE, DUST AND FOG, MILK OF MAGNESIA, CHALK-WATER
colloid
heterogeneous mixture whose solute-like particles are dispersed in a medium. PERFUME, CIGARETTE, INK, MILK, GELATIN, STYROFOAM, COLORED GLASS, CONDIMENTS
SOLUTION
homogeneous mixture where 2 substances are dissolved togther
Manual picking
HETERO SOLID-SOLID using your hands or tongs can be done in separating the components of
these kinds of mixtures.
Sieving
HETERO SOLID-SOLID exploits differences in particle size
magnetic separation or magnets
HETERO SOLID-SOLID can be used to attract materials
Filtration
HETERO SOLID-LIQUID is a process of separating solids from liquids by allowing the mixture to pass through
a filtering material.
residue
solid leftover from filtration
filtrate
liquid leftover from filtration
Sedimentation
HETERO SOLID-LIQUID Is the process in which suspended
solids will eventually separate from liquids by gravity.
Decantation
HETERO SOLID-LIQUID the removal of the liquid component from the solid sediment by pouring the liquid out of the container gently to avoid the solid particles to suspend again.
Centrifugation
is a process in which the suspension is rotated at very high speeds, allowing the components to separate into layers based on their densities or particle size.
ISOTOPES
Atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons and electrons but different
numbers of neutrons. NATURALLY OCCURRING
SAME SA BABA AKA ATOMIC NUMBER AKA PROTONS
Radioisotopes
Artificial Isotopes, can be produced from heavier elements. These isotopes are highly unstable such that when they decay, they release enormous amounts of radioactivity which can be harnessed to power up large scale processes in nuclear reactors.
iodine-113
thyroid disease treatment
Isotones
are elements that have the same number of neutrons. MASS NUMBER - ATOMIC NUMBER
SAME NEUTRONS, SUBTRACT ACCORDINGLY, DOES NOT HAVE TO BE SAME ELEMENT
Isobars
are elements that have the same mass number but different atomic numbers.
SAME MASS NUMBERS, SAME SA TAAS, DOES NOT HAVE TO BE THE SAME ELEMENT
Molecular Formula
most common way to represent molecules, symbols of each element are written down with a subscript indicating how many atoms are in
the compound
Empirical Formula
● gives the simplest whole-number ratio of each element in a compound
Structural Formula
used for more complex molecules such as organic compounds
inorganic compounds
lack carbon bonds
complete structural formula
all bonds and atoms are shown
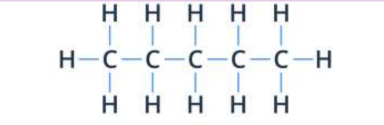
condensed structural formula
atoms connected to a specific carbon are represented like molecular formula
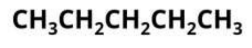
skeletal or line angle formula
hydrogens attached to each carbon will not be drawn: implicit hydrogens
cation
is formed when an atom loses one or more electrons resulting in a net positive
charge.
anion
is formed when an atom gains one or more electrons resulting in a net negative
charge.
Ionic Compounds
compounds that are made of cations and anions
assembled together in a crystal lattice
The bond that holds these ions together in the lattice is called the ionic bond.
Ionic bonds are formed when there is an electron
transfer between two or more atoms.
Binary compounds
are compounds that contain only two types of elements.
Covalent compounds
two or more nonmetals that are chemically bonded together.