Male Reproductive System III
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ductus Deferens, Accessory Glands, Urethra, and Penis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Identify the cut:
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
Magenta:
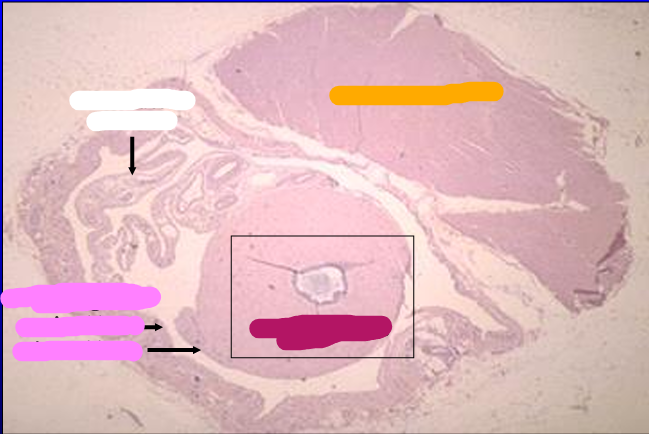
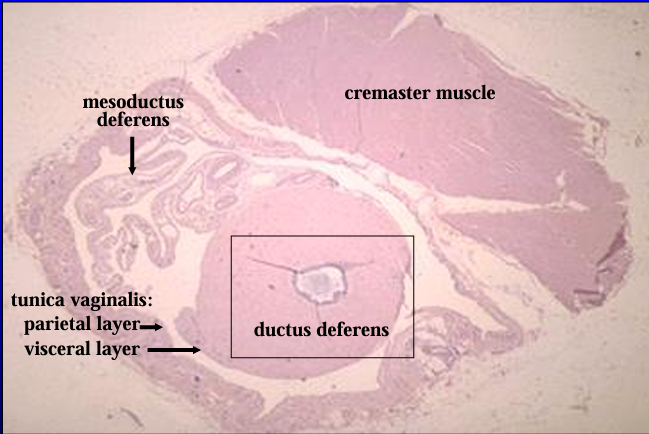
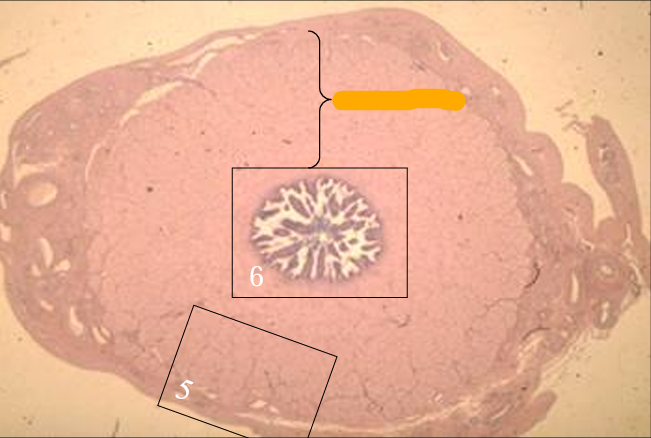
Cross-section of the canine spermatic cord. H-E stain.
The section includes the ductus deferens, mesoductus deferens and blood vessels, parietal and visceral layers of the tunica vaginalis, and cremaster muscle (striated skeletal muscle).
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
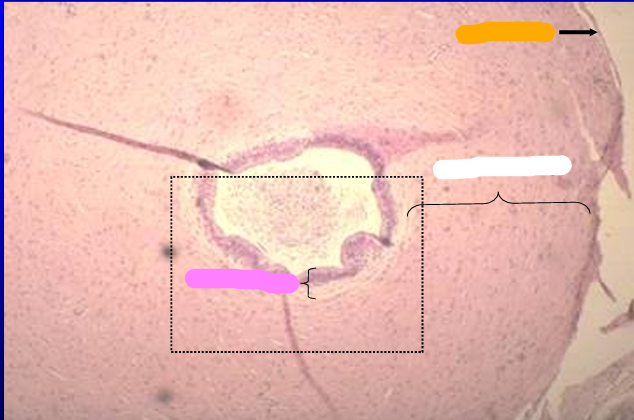
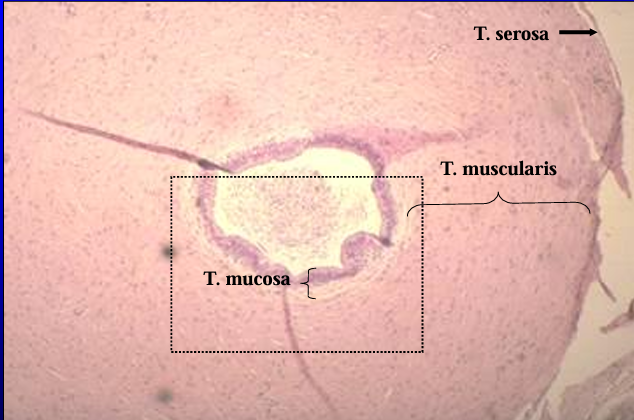
Canine ductus deferens.
The tunica mucosa, tunica muscularis, and tunica serosa are shown.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
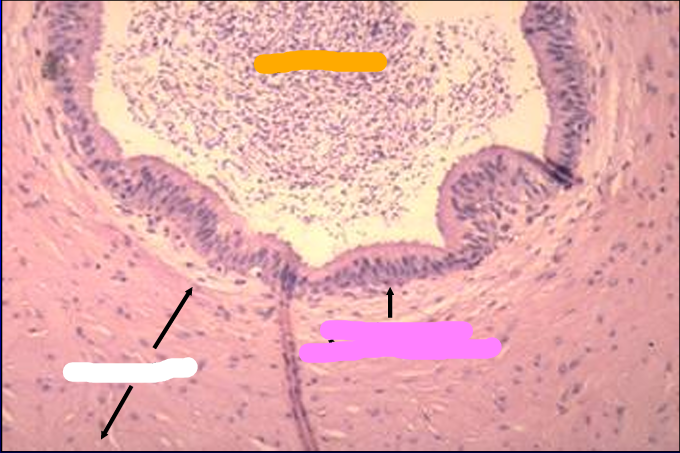
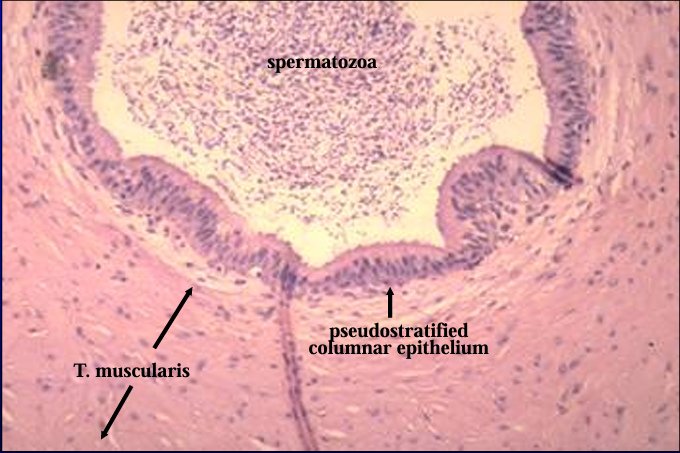
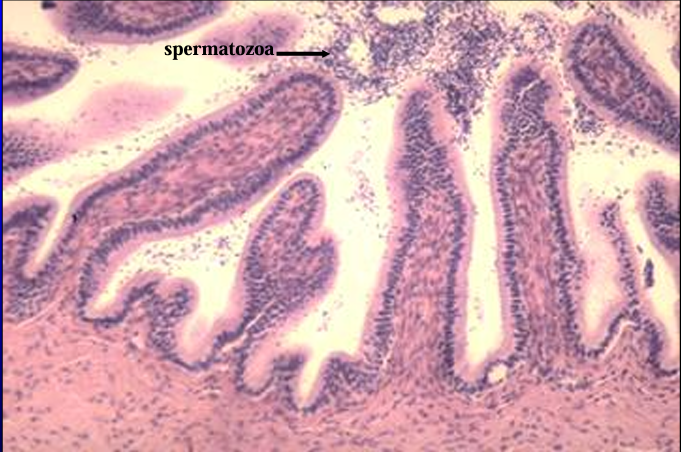
Canine ductus deferens.
Spermatozoa are present in the lumen.
The mucosa is lined by a pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
The tunica muscularis is a thick layer of smooth muscle.
Identify the cut:
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Orange:
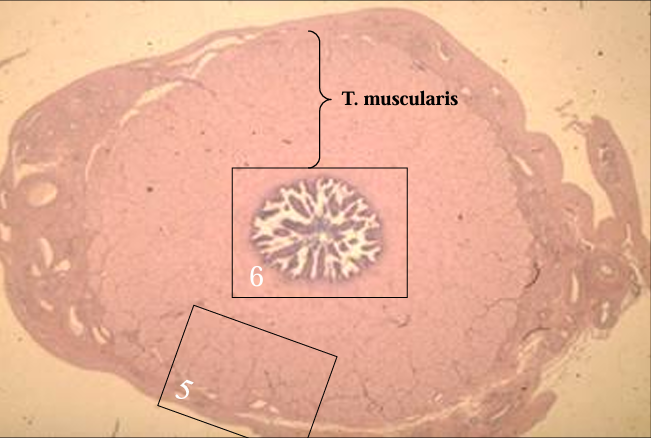
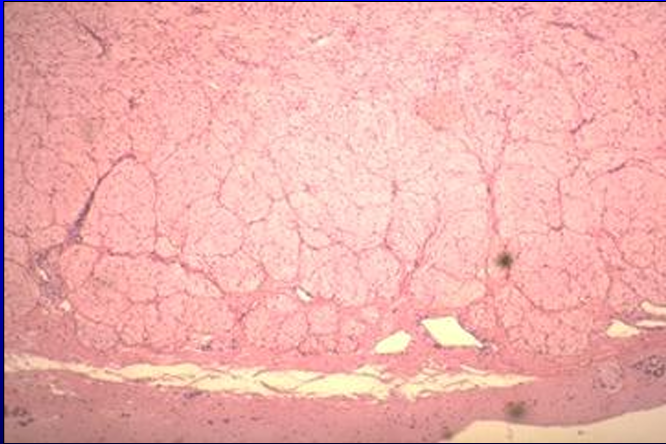
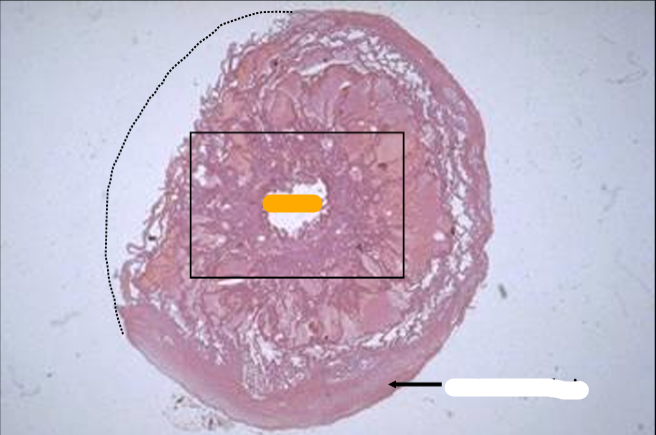
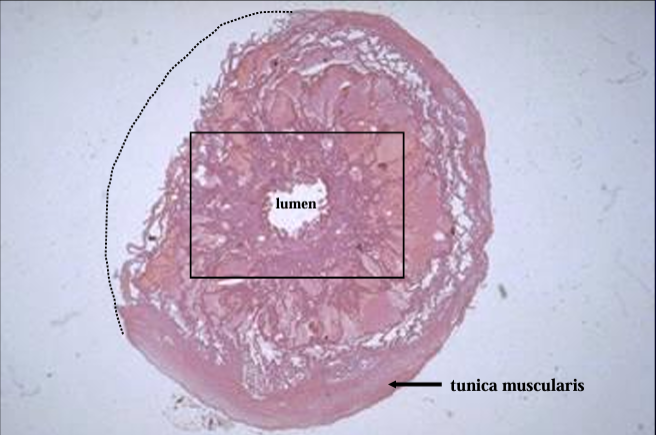
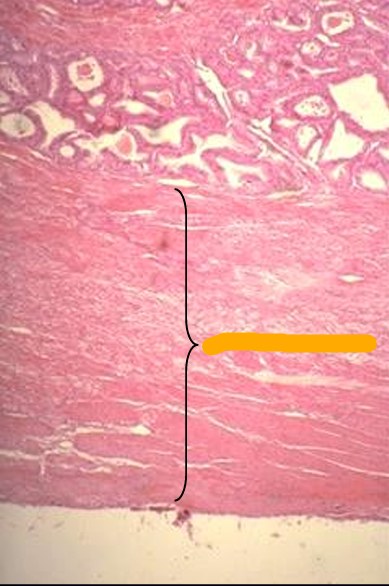
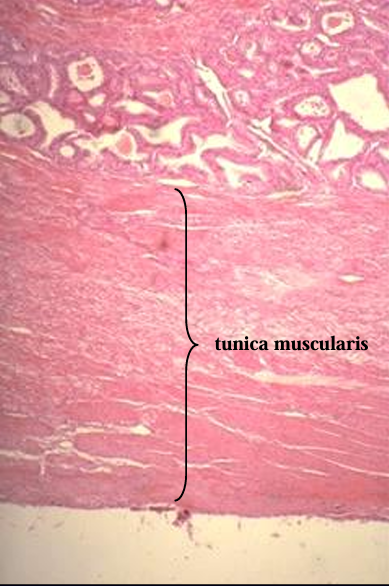
Cross-section of the equine ductus deferens, H-E stain.
Notice the thick tunica muscularis.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
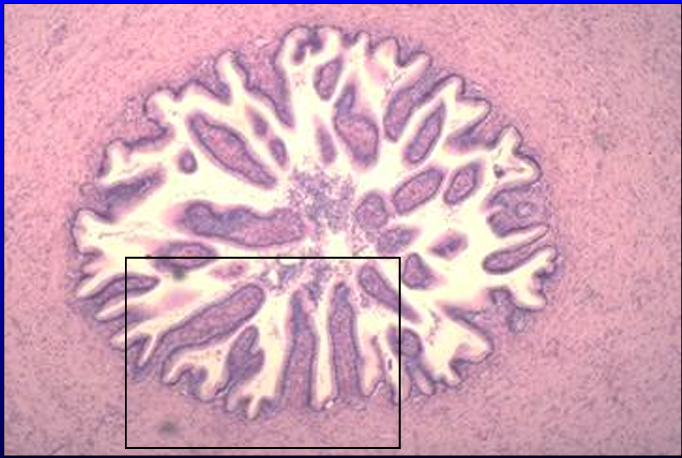
Equine ductus deferens.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Equine ductus deferens.
The mucosa is thrown into folds which project into the lumen.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Lined by:
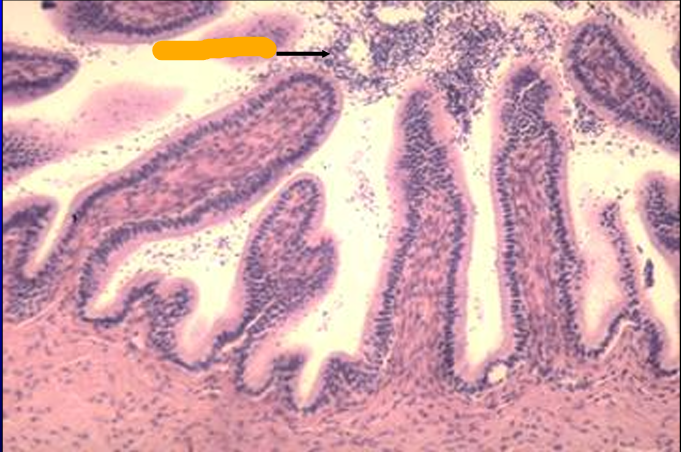
Equine ductus deferens.
The mucosa is lined by a simple columnar epithelium.
Spermatozoa are present in the lumen
Identify the cut:
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Orange:
White:
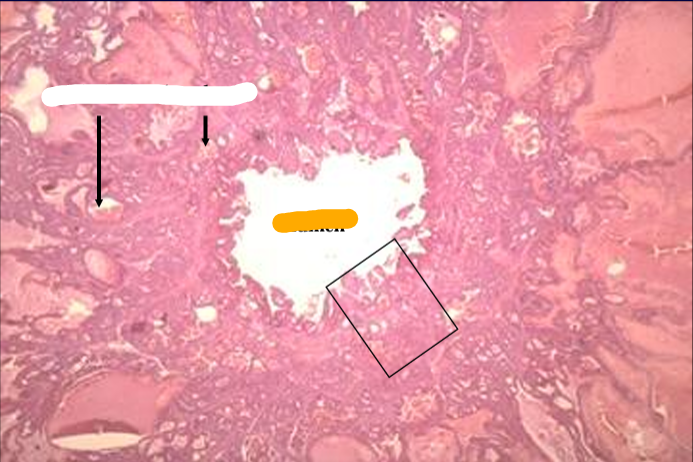
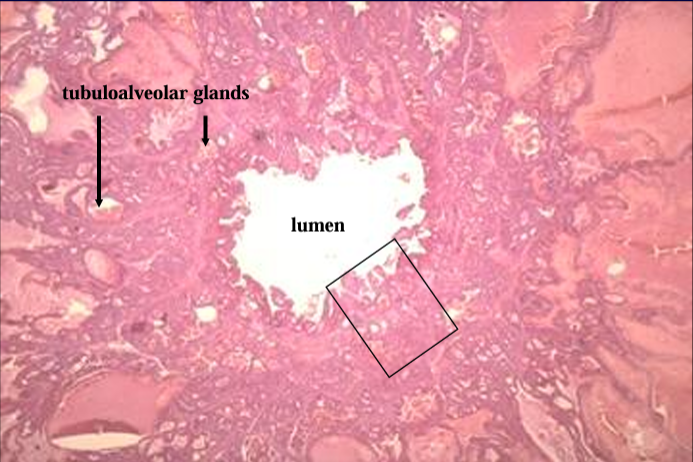
Cross-section of ampulla of equine ductus deferens, H-E stain.
The ampulla is an enlargement of the ductus deferens before it empties into the urethra. (The dotted line indicates a missing part of the section).
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
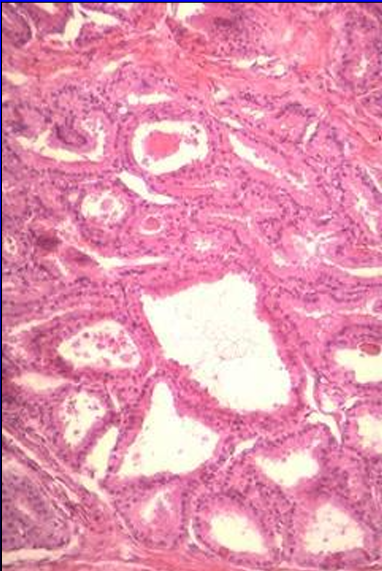
Ampulla of ductus deferens, equine.
The mucosa is characterized by the presence of tubuloalveolar glands.
The glands are filled with acidophilic secretory material.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
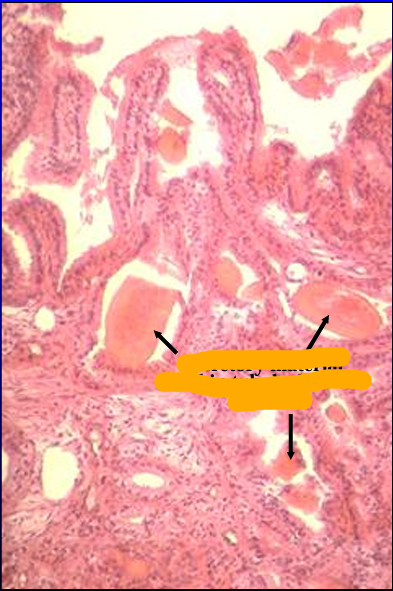
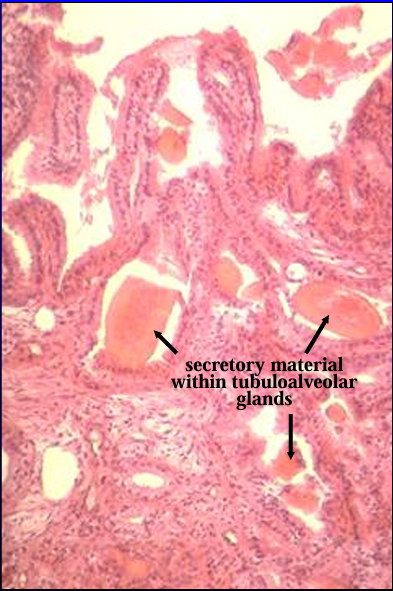
Ampulla of ductus deferens, equine.
The luminal surface is thrown into folds between which the ampullary glands open
Identify the structure:
Lined by:
Ampullary glands.
Ampullary glands are tubuloalveolar glands lined by a simple columnar epithelium.
They contain acidophilic secretory material.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
Ampulla of ductus deferens, equine.
The outer wall of the ampulla is provided with a layer of smooth muscle, the tunica muscularis, from which smooth muscle bundles penetrate the interior via the trabeculae.
Smooth muscle contraction during ejaculation causes the release of the secretion into the lumen
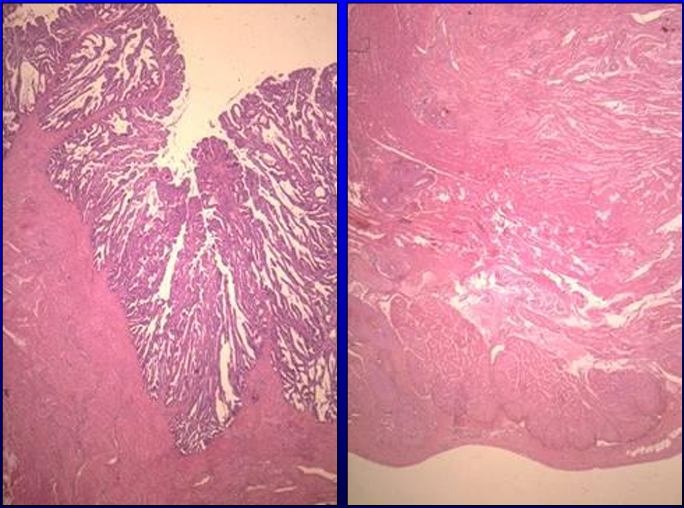
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Section of equine seminal vesicle, H-E stain.
The equine seminal vesicle is vesicular (bladder-like) and is provided with an inner glandular mucosa (seen A) and a thick outer muscular wall (seen in B).
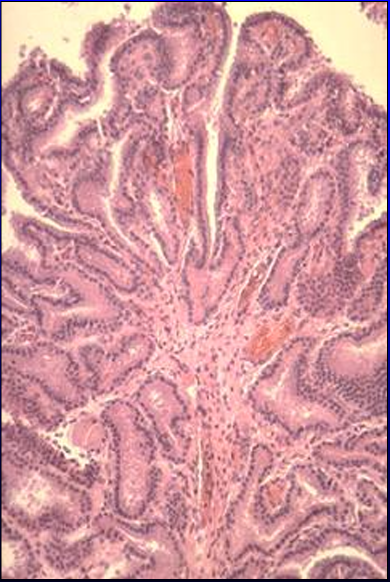
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Mucosa of equine seminal vesicle.
The mucosal surface is thrown into folds.
Tubuloalveolar glands are located in the deeper part of the mucosa
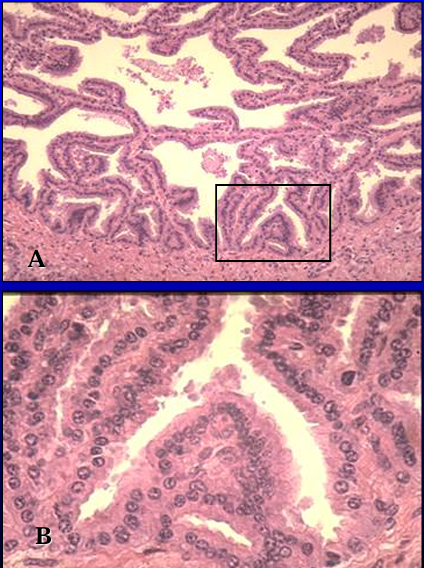
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Lined by:
Equine seminal vesicle.
The vesicular glands are tubuloalveolar glands lined by a simple columnar epithelium.
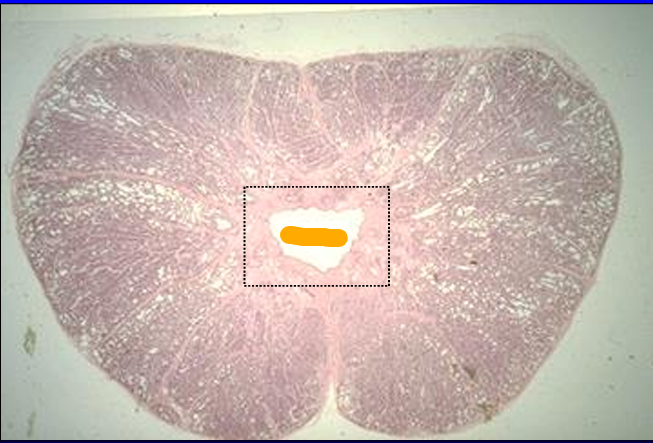
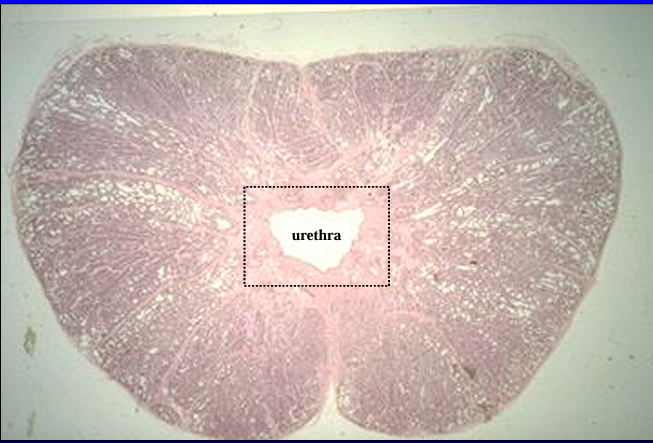
Identify the cut:
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
Cross-section of the canine prostate.
This section shows the prostatic body surrounding the urethra (center)
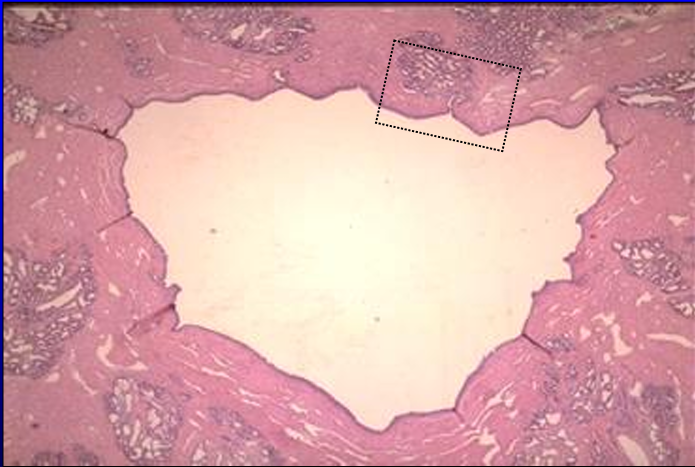
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Canine prostate gland.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
Lined by:
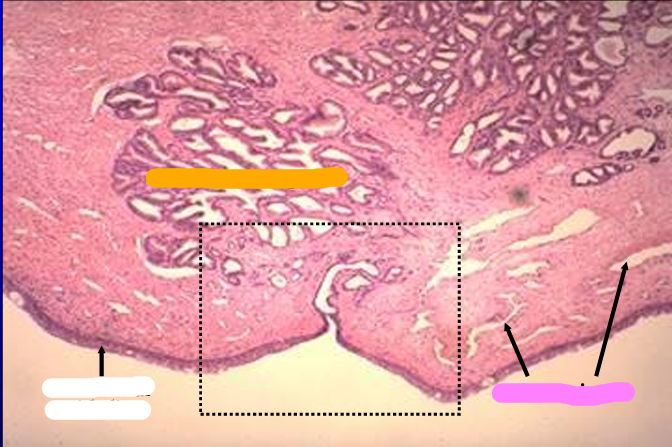
Canine prostatic urethra.
The prostatic urethra is lined by a transitional epithelium.
The lamina propria contains erectile tissue (represented by the venous sinuses which are empty and collapsed in this section) and tubuloalveolar glands.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
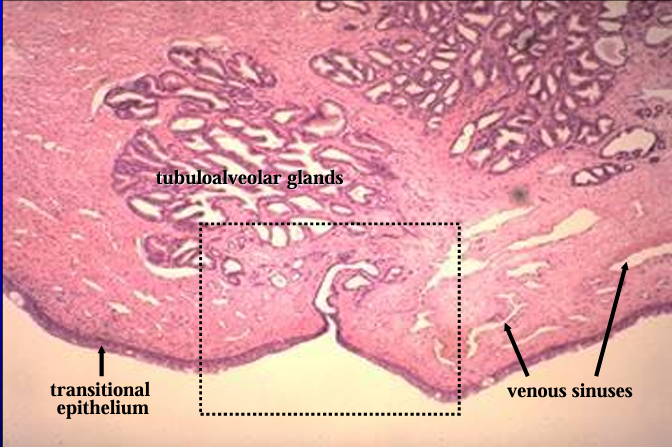
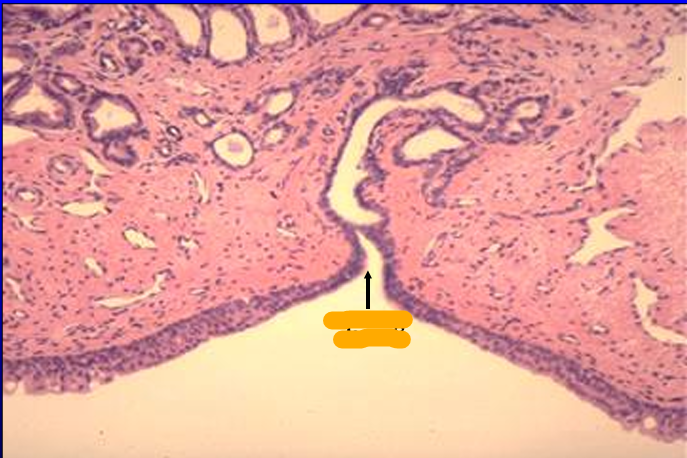
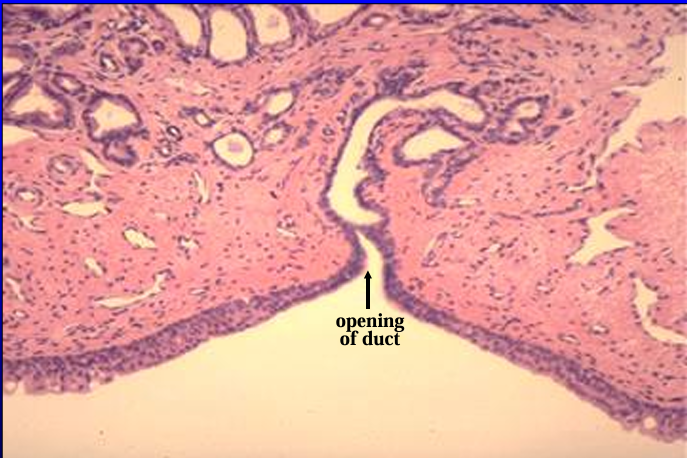
Canine prostatic urethra.
Observe again the transitional epithelium and the venous sinuses in the lamina propria.
A duct of the prostate gland is seen opening into the lumen of the urethra.
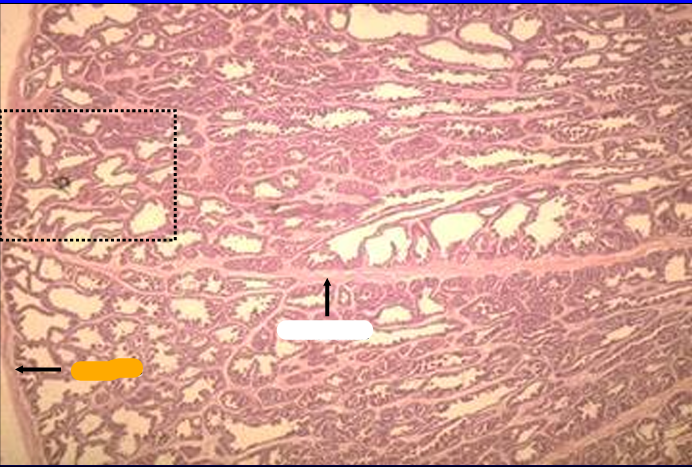
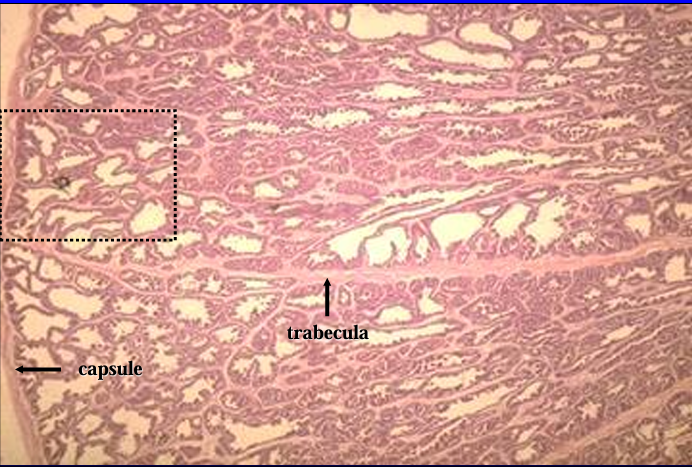
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Canine prostate gland.
The prostate gland is surrounded by a connective tissue capsule (left) from which connective tissue septa penetrate and subdivided the parenchyma into lobules.
The capsule and trabeculae also contain smooth muscle.
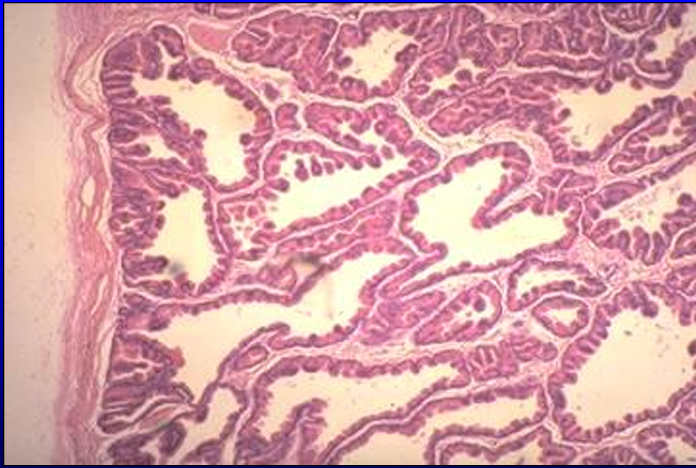
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Canine prostate gland.
The glandular tissue is composed of tubuloalveolar secretory units.
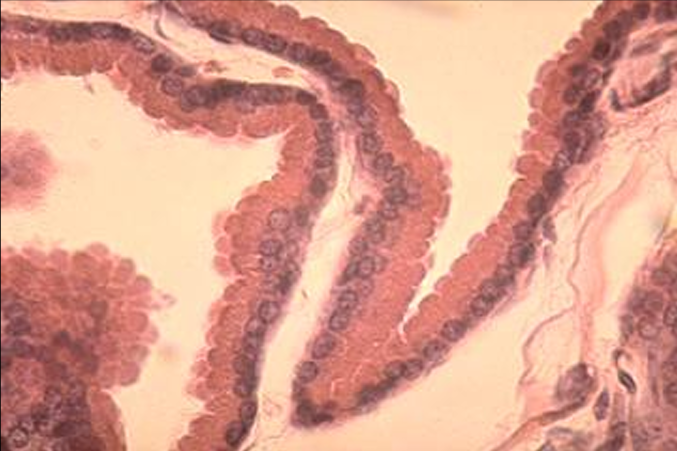
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Lined by:
Canine prostate gland.
The secretory tubules and alveoli are lined by a simple columnar epithelium.
Note the acidophilic apical portion of the secretory cells
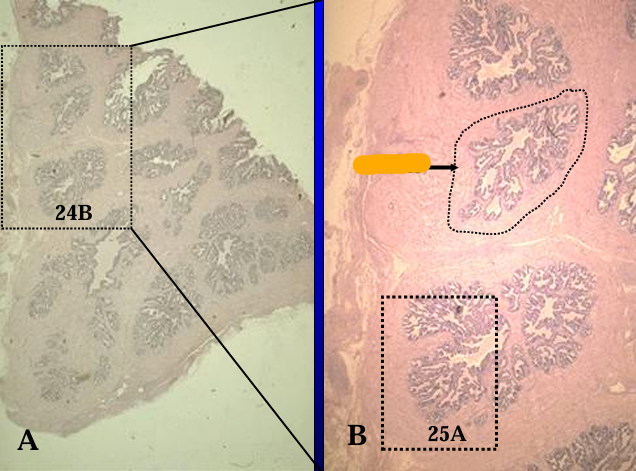
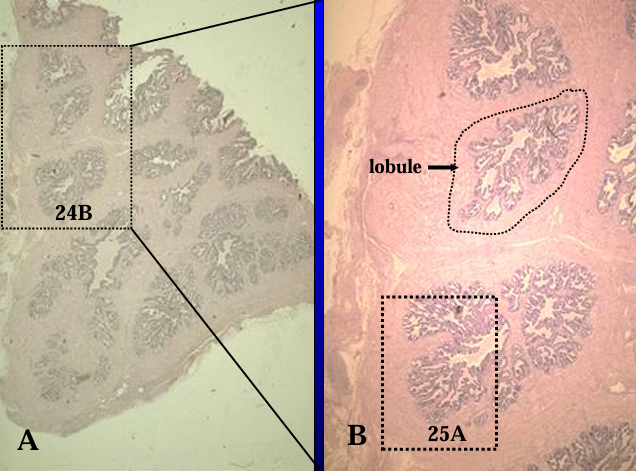
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
Section of the equine prostate gland.
The glandular tissue is tubuloalveolar and is separated by connective tissue septa into lobules
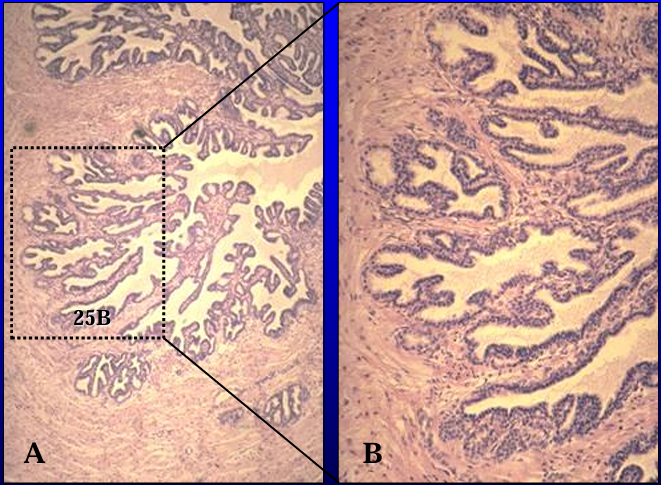
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Equine prostate gland.
The capsule and trabeculae also contain numerous smooth muscle fibers.
The tubuloalveolar secretory units are lined by a simple cuboidal epithelium
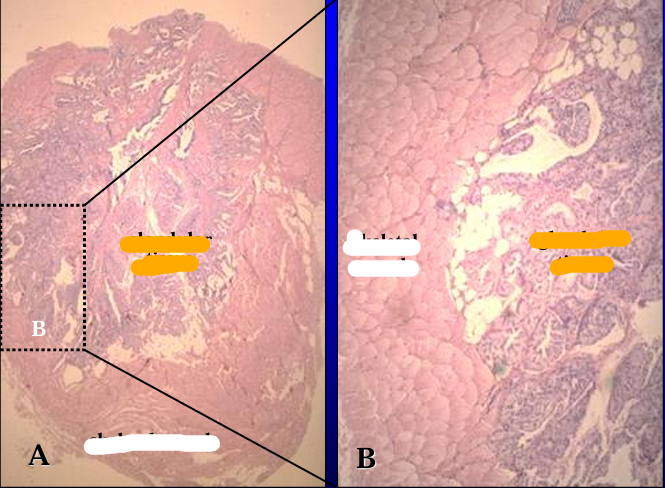
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Orange:
White:
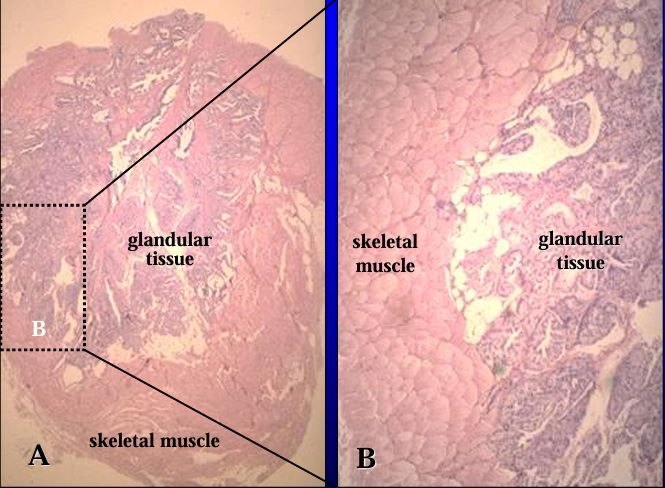
Section of the feline bulbourethral gland, H-E stain.
The gland is surrounded by striated skeletal muscle (bulbocavernosus m.) and is divided into lobules
Identify the structure:
Specie:
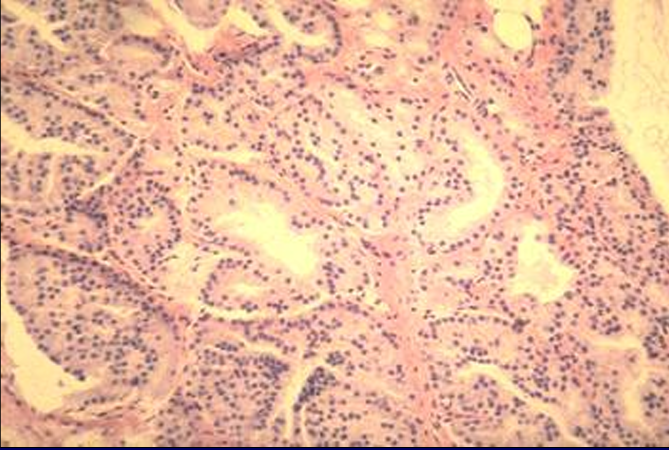
Feline bulbourethral gland.
The glandular tissue is also tubuloalveolar in type and the secretory units are lined by a simple cuboidal epithelium.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
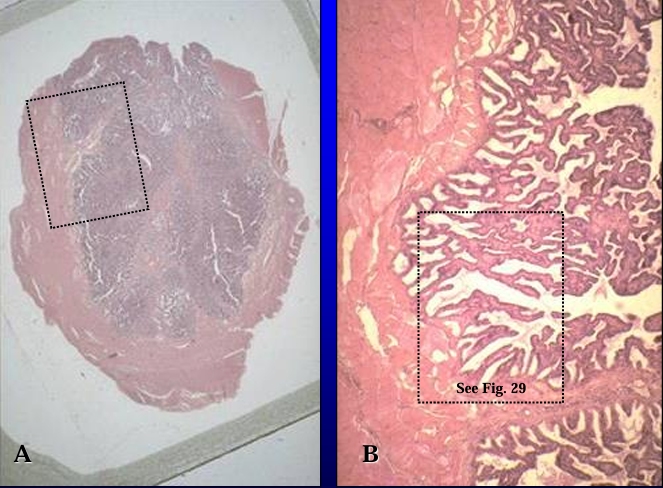
Section of equine bulbourethral gland, H-E stain.
Like the feline bulbourethral gland, the equine bulbourethral gland is also surrounded by skeletal muscle (bulbospongiosus m.) and is subdivided into lobules.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
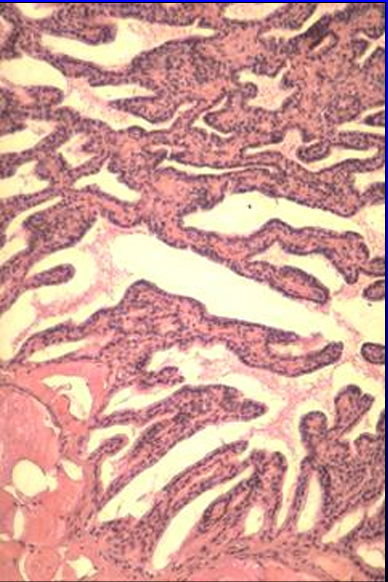
Equine bulbourethral gland.
The glandular tissue is also composed of tubuloalveolar secretory units lined by simple cuboidal epithelium
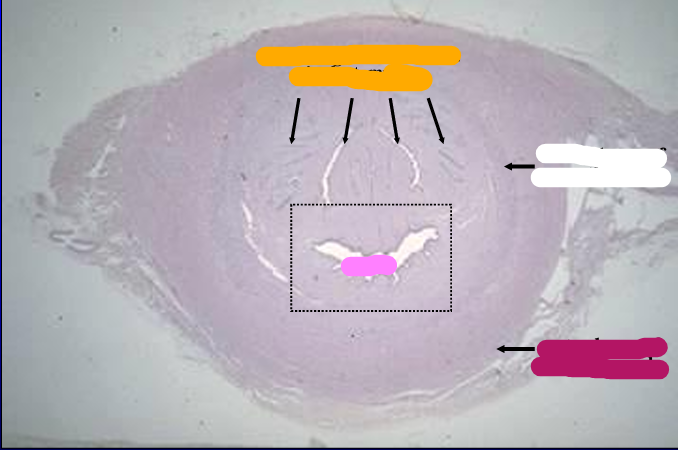
Identify the cut:
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
Magenta:
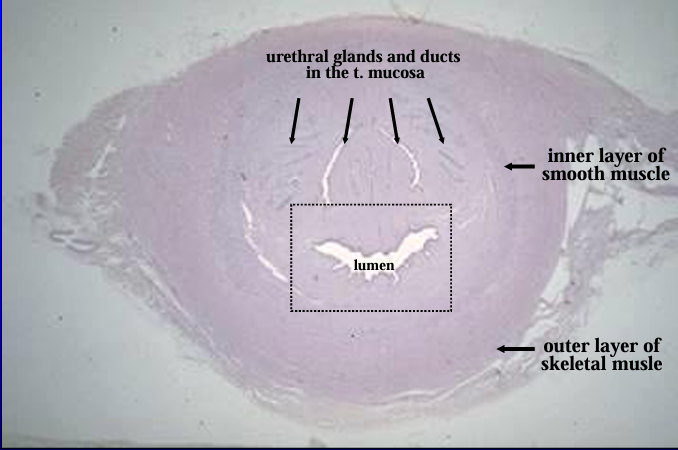
Cross-section of the equine pelvic urethra, H-E stain.
The section shows the lumen near the center
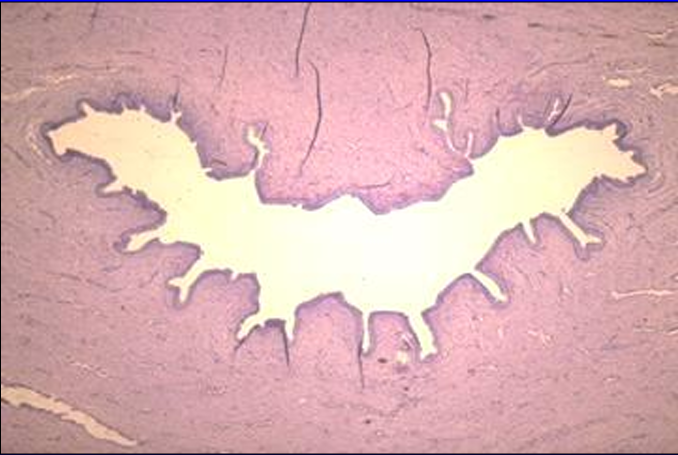
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Equine pelvic urethra.
The lumen is seen here at a slightly higher magnification.
The mucosa is thrown into folds and lined by transitional epithelium.
Erectile tissue is present in the lamina propria. (The venous sinuses present in the erectile tissue are collapsed in this specimen)
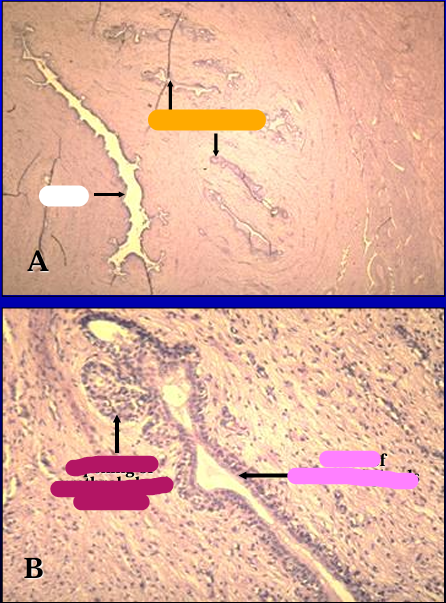
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
Magenta:
Equine pelvic urethra.
Urethral glands, in addition to erectile tissue, are present in the lamina propria.
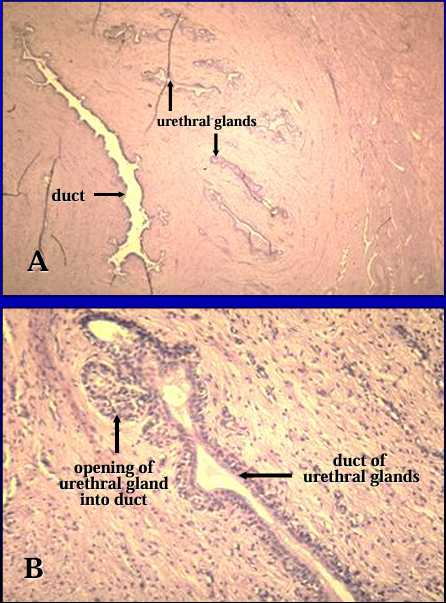
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
Equine pelvic urethra, another view.
The mucosa is lined by transitional epithelium and contains erectile tissue in the lamina propria. (The erectile tissue contains collapsed venous sinuses in this figure)
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
Equine pelvic urethra.
The thick tunica muscularis is seen at a higher magnification. It is composed of inner and outer layers of smooth muscle and an outer layer of circularly arranged striated skeletal muscle, the urethralis muscle.
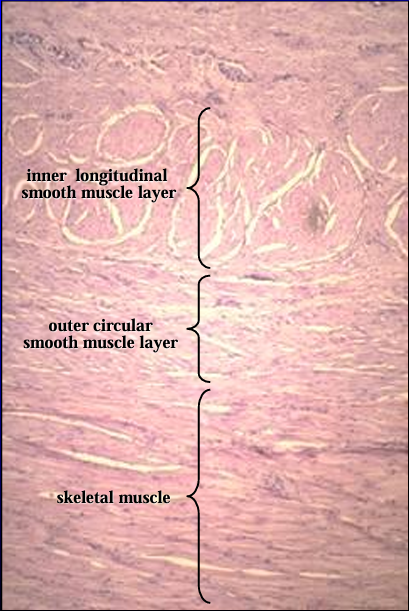
Identify the cut:
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Orange:
White:
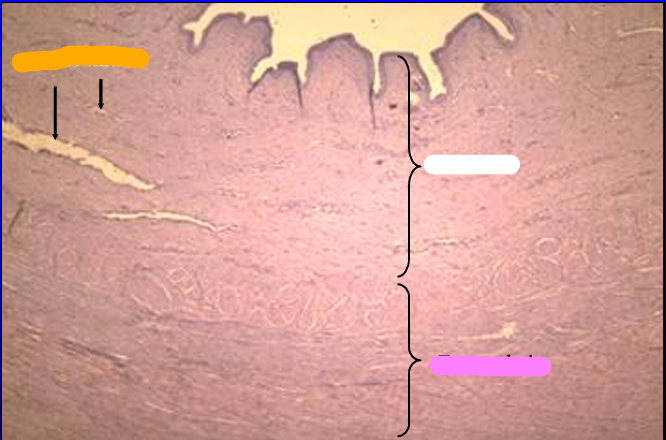
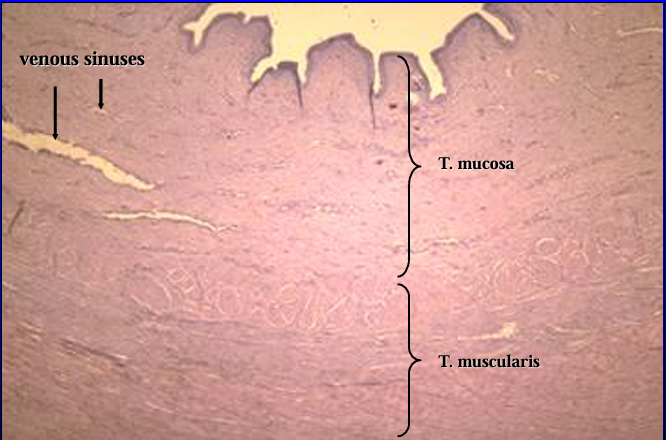
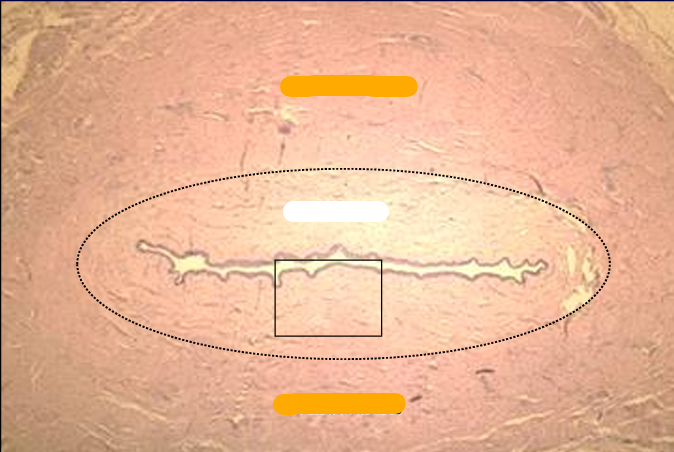
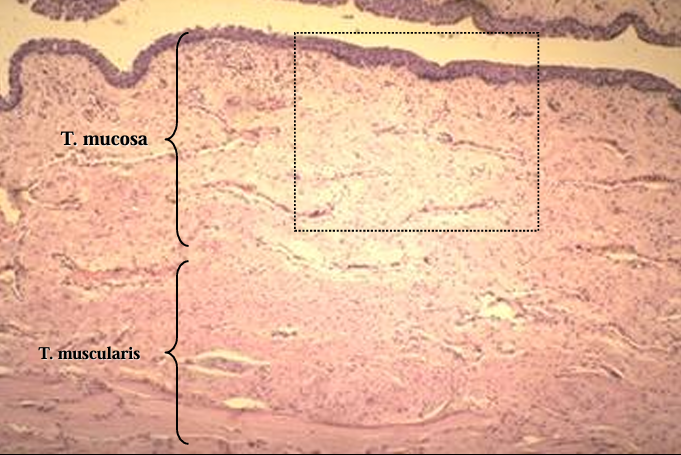
Cross-section of the canine pelvic urethra, H-E stain.
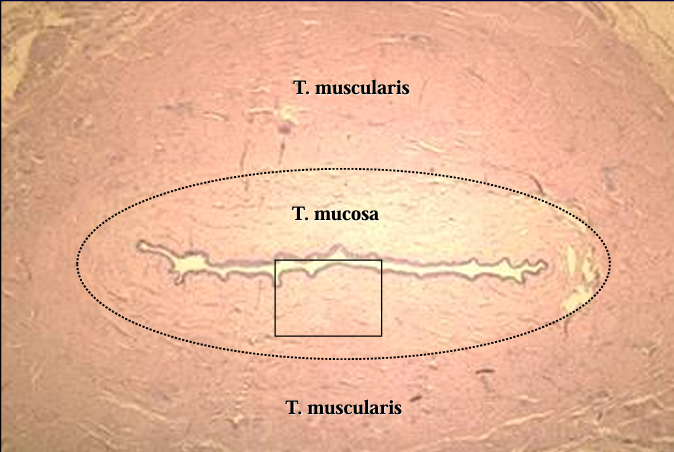
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
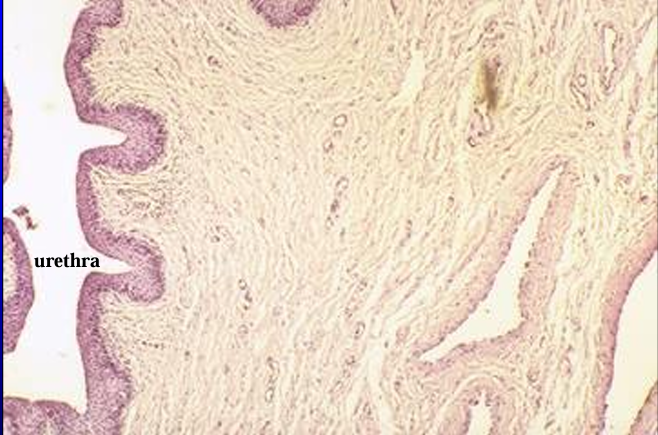
Canine pelvic urethra.
The mucosa and a part of the muscular layer are shown in this figure.
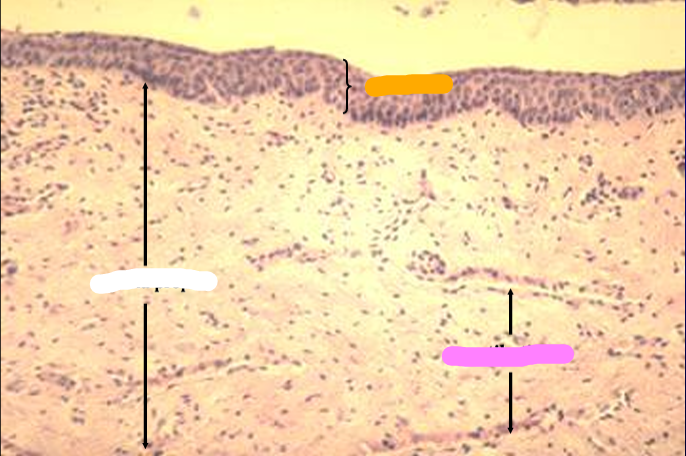
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
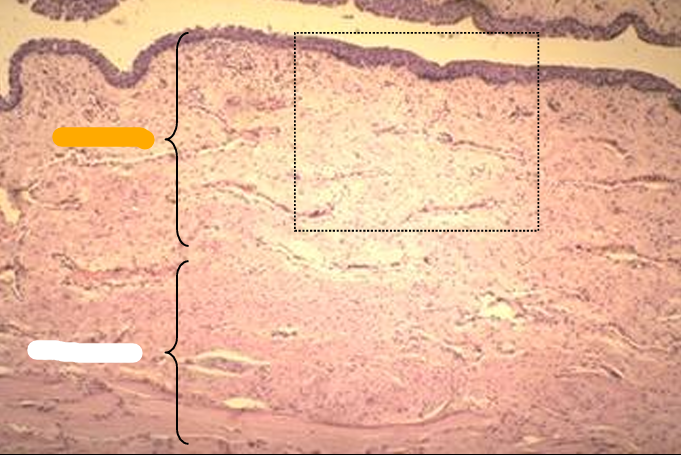
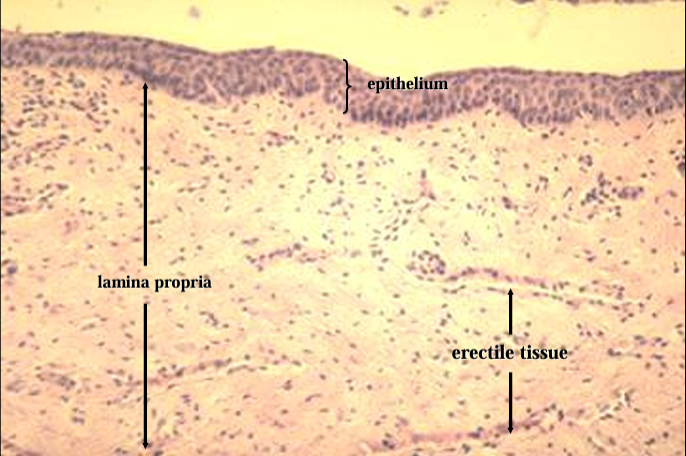
T. mucosa of canine urethra.
The mucosa is lined by a stratified cuboidal epithelium.
Erectile tissue (represented by collapsed venous sinuses in this slide) is present in the lamina propria
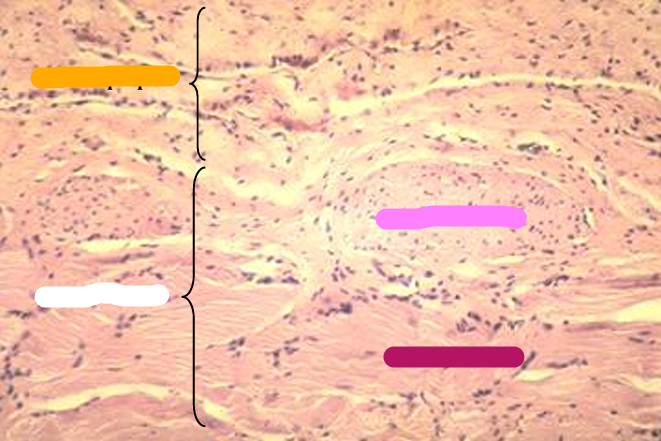
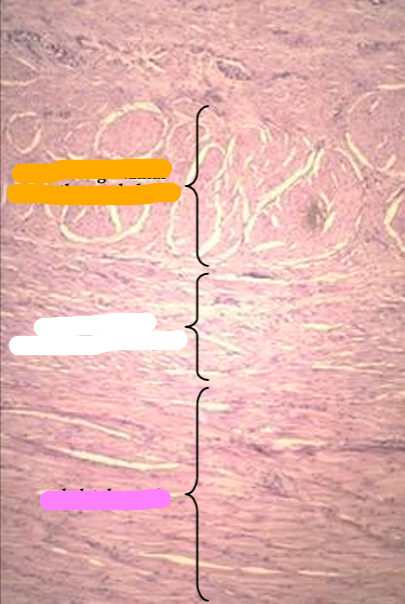
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
Magenta:
T. muscularis of canine pelvic urethra.
The tunica muscularis contains smooth muscle in the inner layer and striated muscle in the outer layer
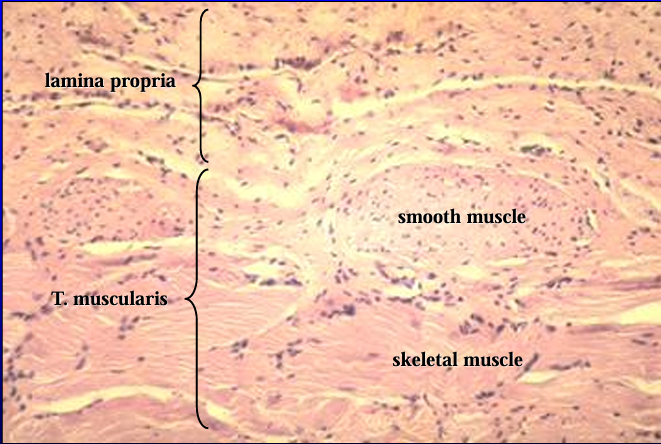
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Canine pelvic urethra.
The tunica muscularis and tunica fibrosa are shown.
The tunica fibrosa is the outer most layer and contains blood vessels, nerve fibers and fibrous connective tissue.
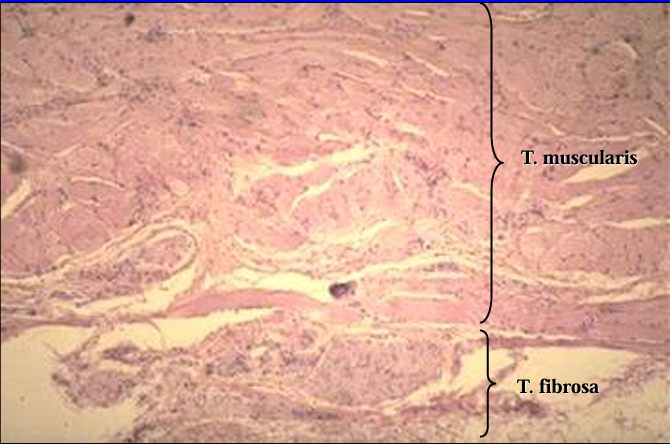
Identify the cut:
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
Pastel Orange:
White:
Pink:
Magenta:
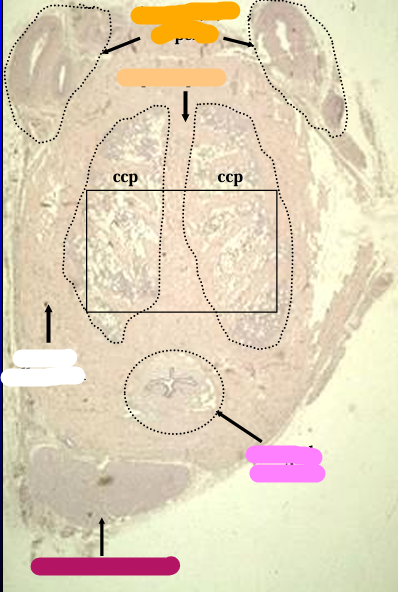
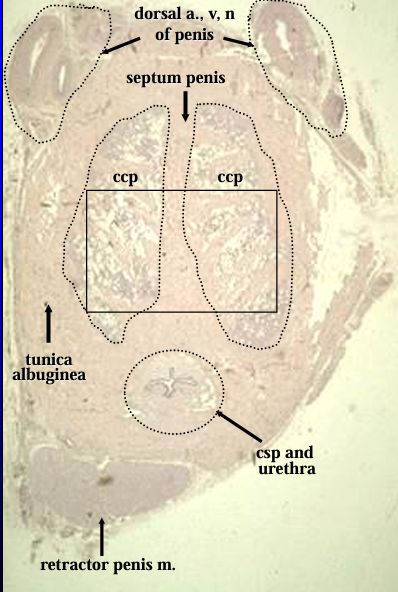
Cross-section through the body of the canine penis.
The dorsal artery, vein, and nerve of the penis are seen at the top of the figure.
The dense connective tissue that surrounds and divides the erectile body are the tunica albuginea and septum penis, respectively.
The erectile body (corpus cavernosum penis - ccp) is located on both sides septum penis ccp ccp of the septum.
Located ventrally are the urethra, surrounded by the corpus spongiosum penis (csp), and the retractor penis muscle.
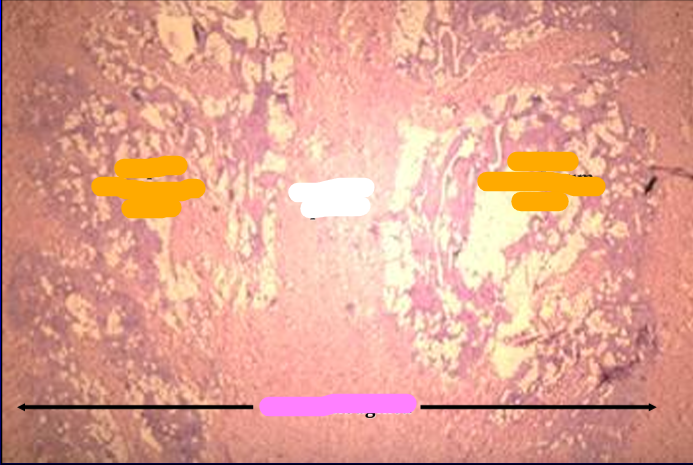
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
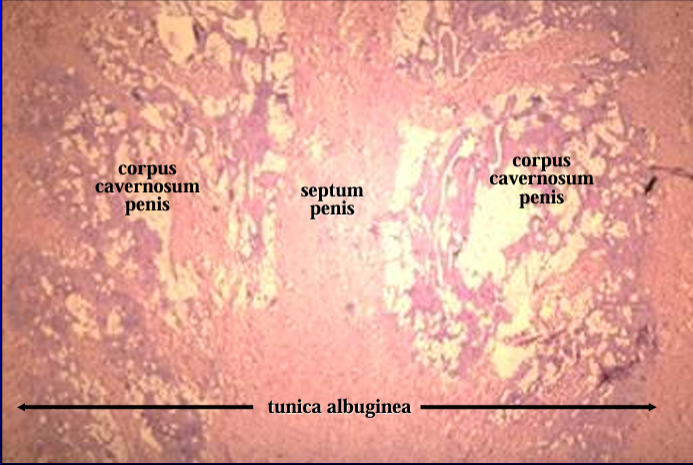
Canine penis.
The figure shows at a slightly higher magnification the tunica albuginea septum penis, and corpus cavernosum penis.
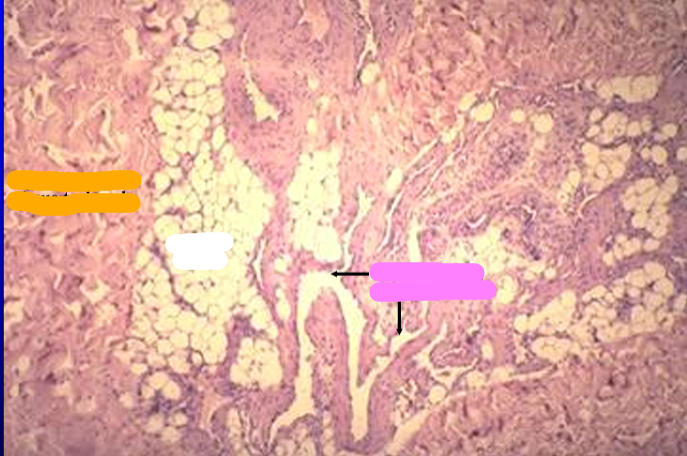
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
Canine penis.
The erectile body (corpus cavernosum penis) is seen at a higher magnification. It contains adipose tissue and anastomosing venous sinuses
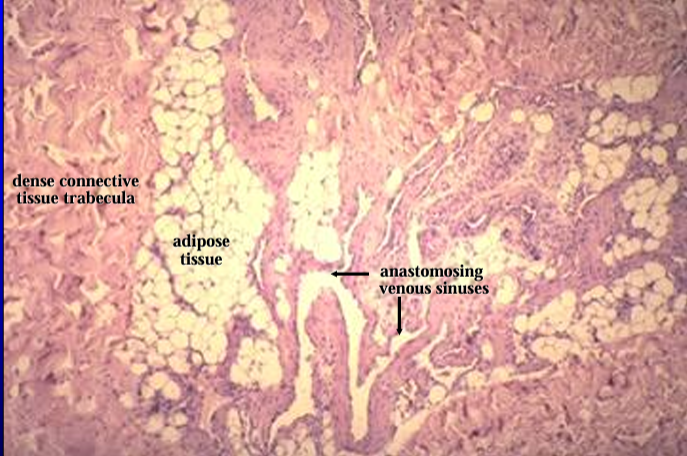
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
Magenta:
Corpus cavernosum, canine penis.
The corpus cavernosum is characterized by an abundance of smooth muscle which surrounds the cavernous sinuses
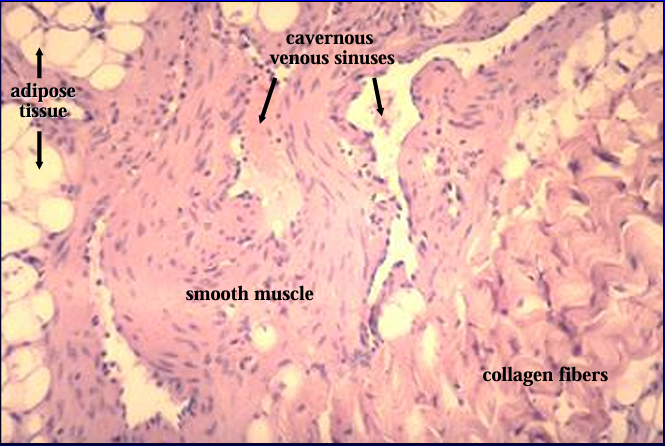
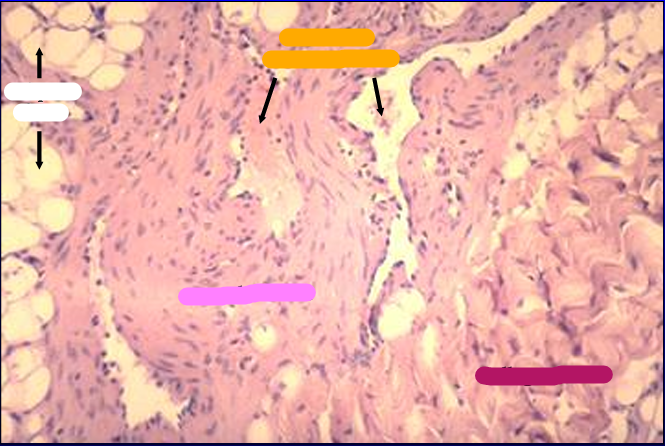
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Corpus cavernosum, canine penis.
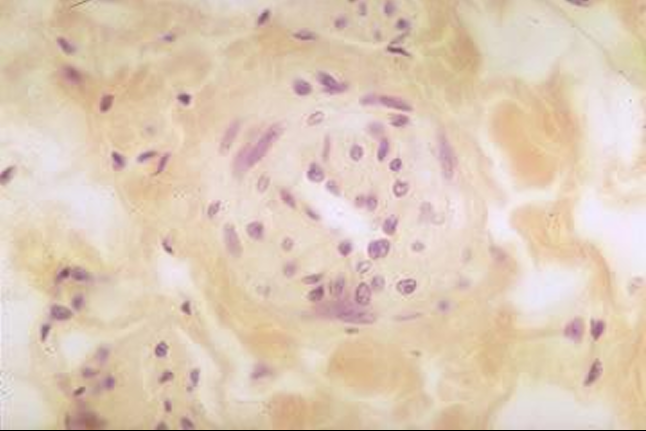
The figure shows a cross-section of a helicine artery (branch of the arterial blood supply to the corpus cavernosum penis).
Relaxation of the smooth muscle in these arteries result in dilation and increased blood flow to the cavernous tissue at the time of erection
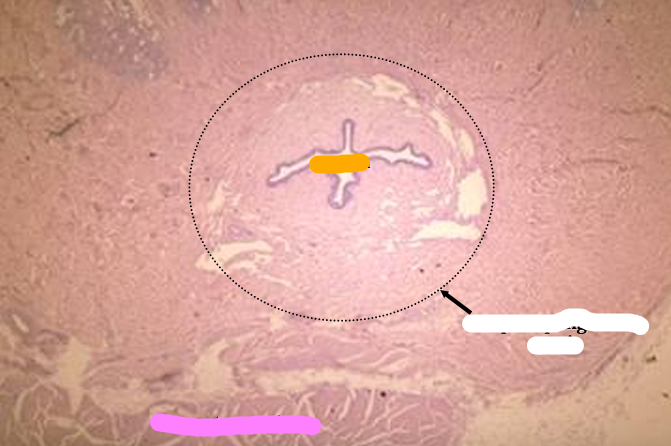
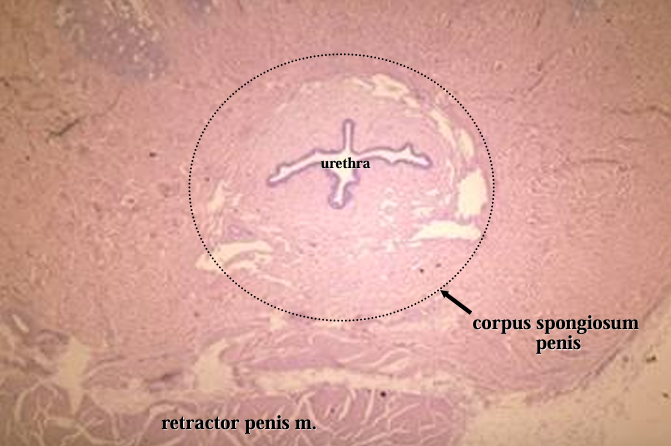
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
Canine penis.
The penile urethra, surrounded by the corpus spongiosum penis, and the retractor penis muscle (bottom of screen) are shown
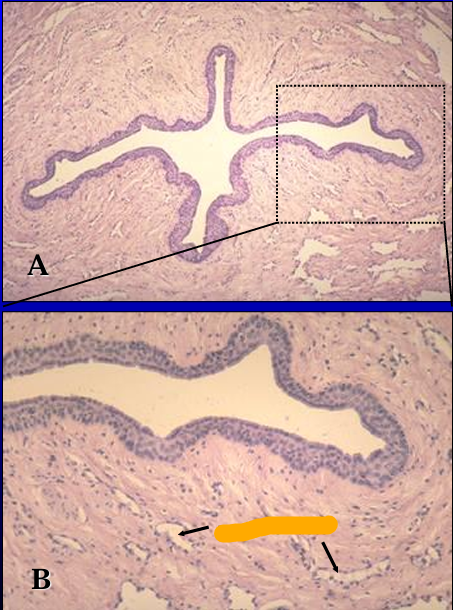
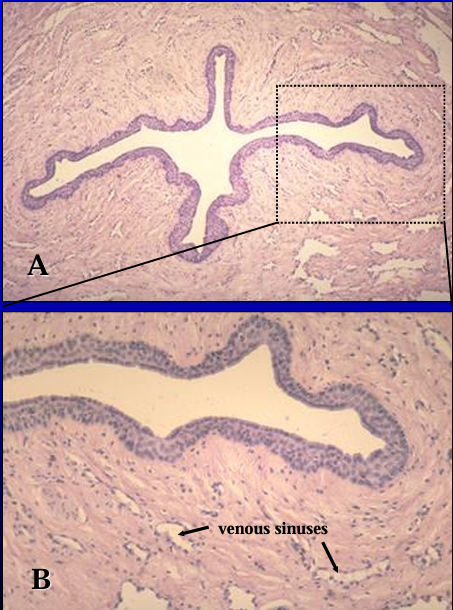
dentify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
Corpus spongiosum, canine penis.
The penile urethra and its erectile body, the corpus spongiosum penis, are seen in Figures A and B.
The urethra is lined by a stratified cuboidal epithelium.
Erectile tissue (represented by the venous sinuses) is present in the lamina propria.
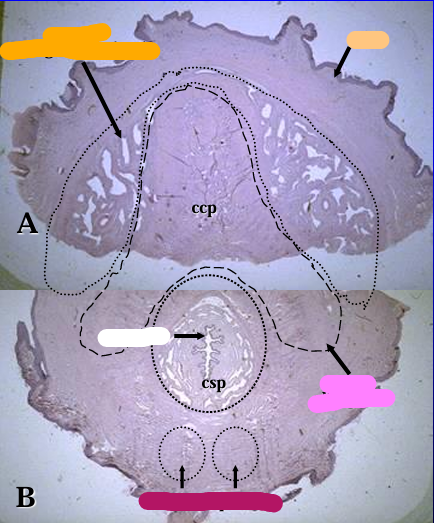
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
Pastel Orange:
White:
Pink:
Magenta:
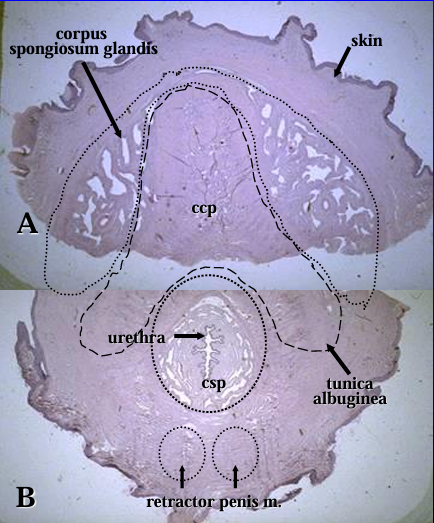
Equine penis.
Figure A is a cross-section through the dorsal part of the penis and shows the corpus spongiosum glandis (beneath skin layer), and part of the corpus cavernosum penis (ccp)surrounded by the tunica albuginia.
Figure B is a cross section through the ventral part of the penis and shows a part of the corpus cavernosum and the penile urethra surrounded by the corpus spongiosum penis (csp).
*(Figures A and B represent two parts of a cross section of the equine penis. Because of the large size, the cross section was divided into a dorsal part -A and a ventral part - B)
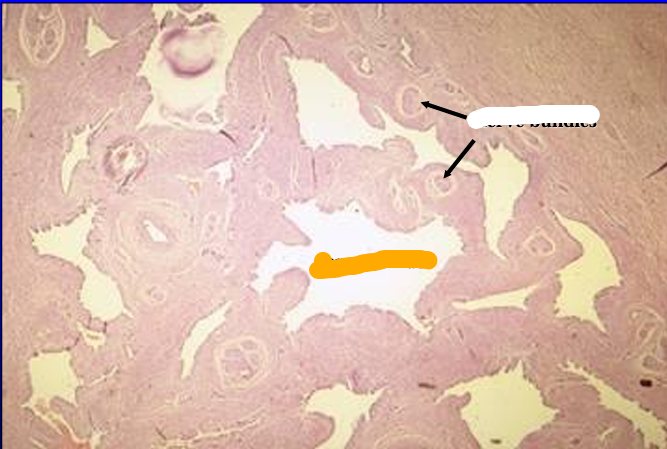
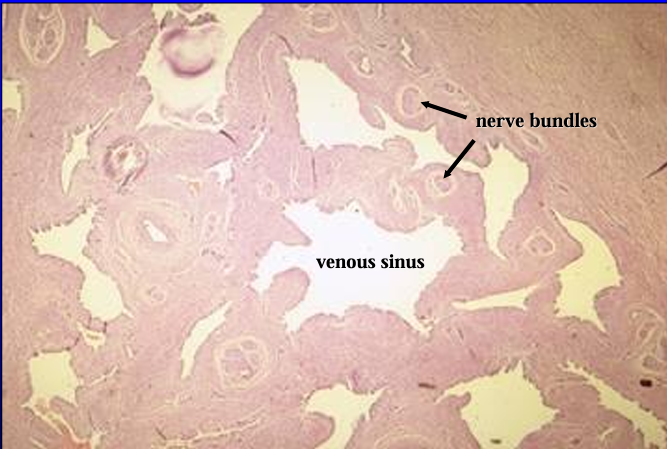
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Equine penis.
The corpus spongiosum glandis (erectile body of the glans penis) is seen at a slightly higher magnification.
Numerous nerve bundles are present in the connective tissue separating the venous sinuses
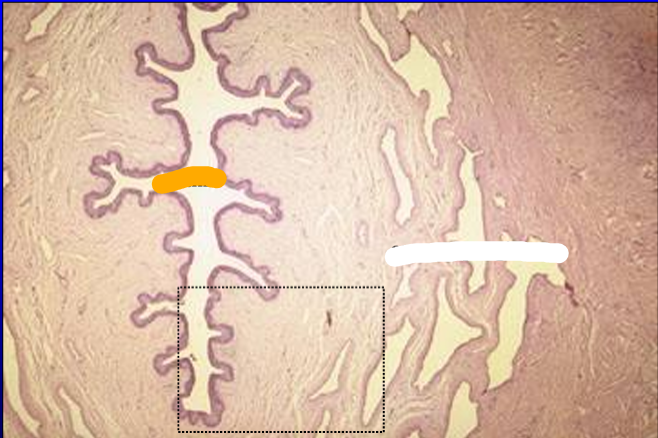
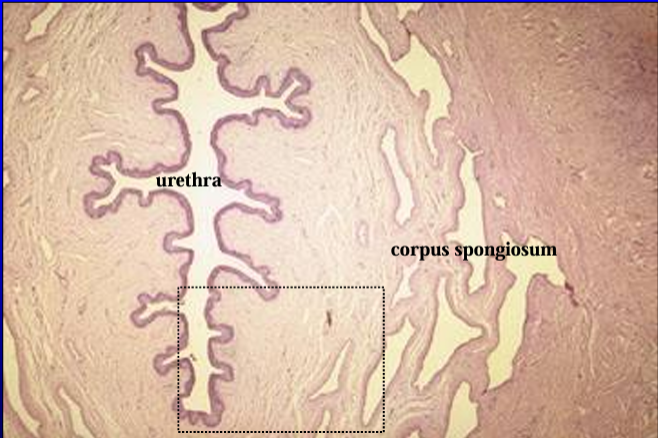
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Equine penis.
The penile urethra and the corpus spongiosum penis are shown.
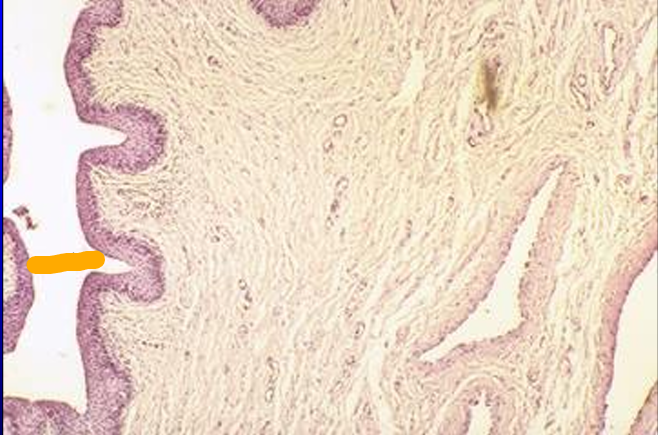
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
Penile urethra, equine penis.
The epithelium lining the penile urethra at the level of this section is in transition from stratified cuboidal to stratified squamous.
Erectile tissue is present in the lamina propria