Gram Negative Respiratory Pathogens
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
what are the 3 main respiratory pathogens?
Neisseria meningitidis
Haemophilus influenzae
bordetella pertussis
Genus Neisseria location of pathogenesis, morphology; they inhabit _____ surfaces. Their oxygen requirements classify them as _____ _____. They are catalase _____

two main pathogenic species of the neisseria group
N. meningitidis and N. gonorrhoeae
____ ____ is closely related to Neisseria and is normal flora of the _____. it is now a common cause of ___ ____ in children
Moraxella catarrhalis; URT; otitis media
The ___ ___ of neisseria is important in transmission, as this state is asymptomatic. N. gonorrhea can be asymptomatic more often in women
carrier state
in what population(s) is N. meningitidis most common and what are some reasons for its resilience?
6-24 months, college students, military recruits
- decreased general resistance
- exposure to new capsule serotypes
- increased transmission of secretions
N. meningitidis mode of transmission
large respiratory droplets at close range
how does N. gonorrhea spread? where does it attach? does it remain localized? Symptoms? what condition does it lead to in women?

what makes vaccines hard for N. gonorrhea? To what kinds of drugs has resistance been seen?
variable LPS/LOS; B-lactams and tetracyclines
Describe the process of meningococcemia following N. meningitidis infection
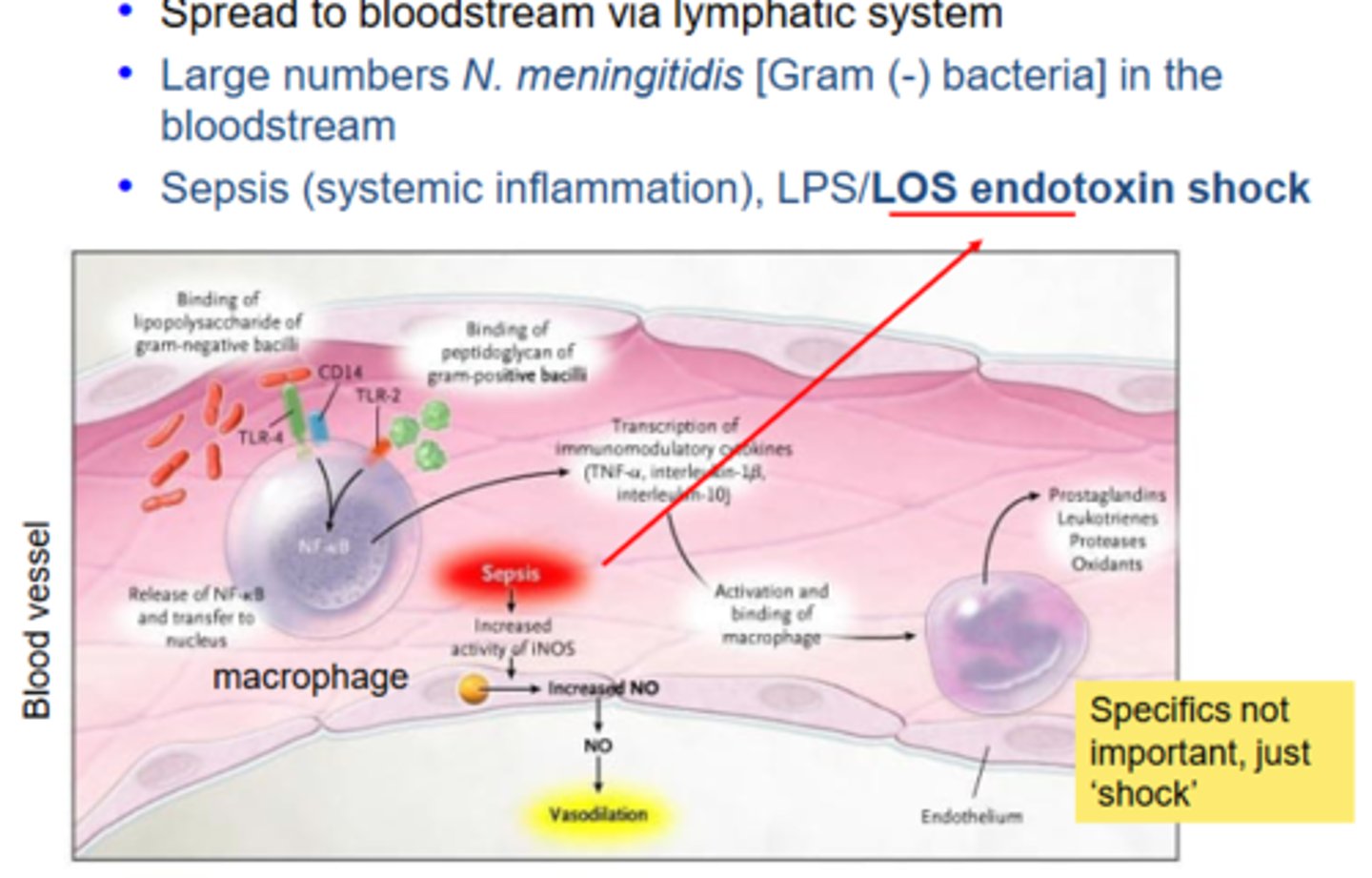
N. meningitidis can spread to the meninges via the ____ _____. it can lead to permanent ___ ___, including ____ _____, ___ ____, and ___ ____
choroid plexus; neurological damage; neuromotor disabilities, seizure disorders, learning difficulties
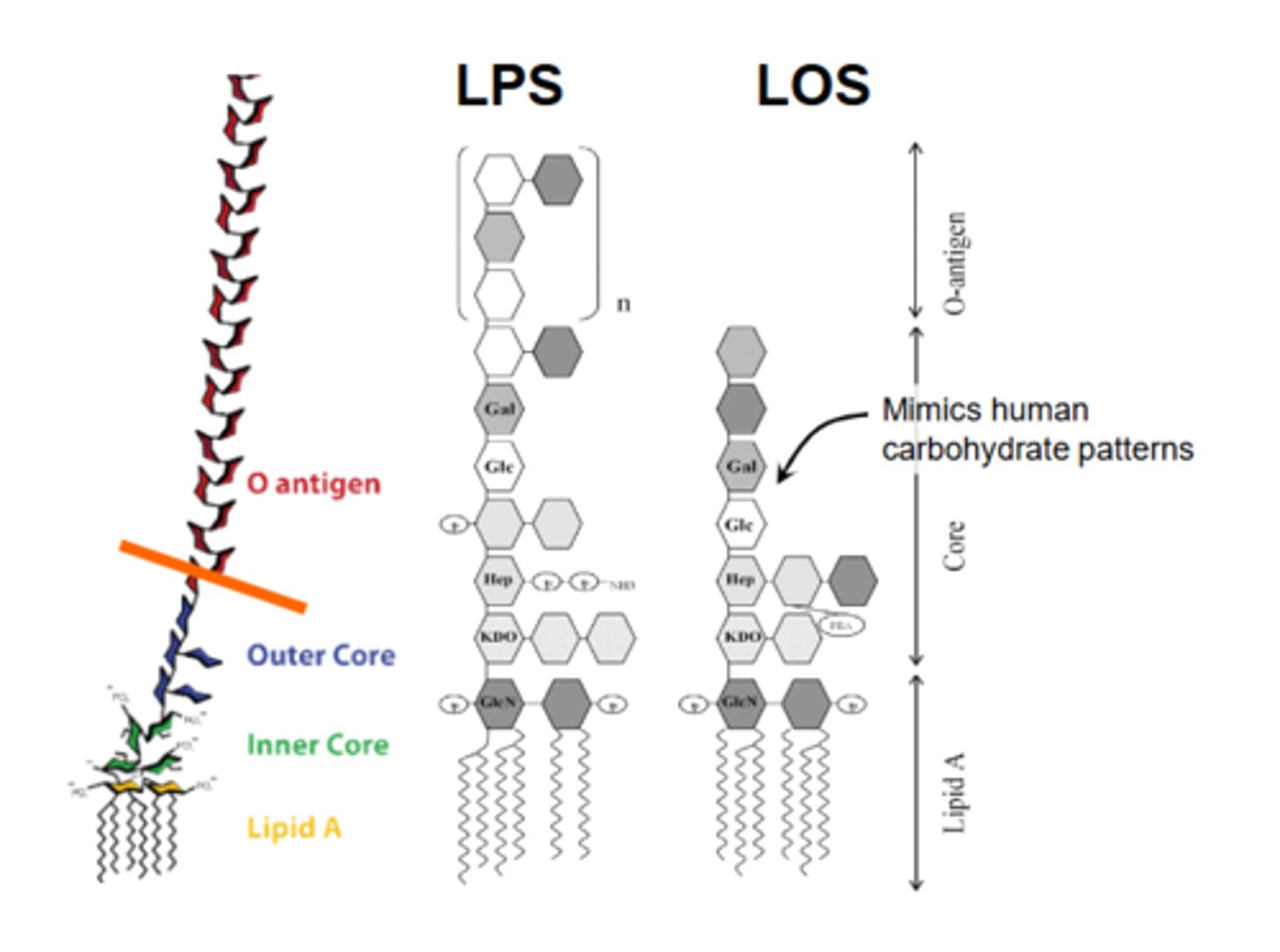
N. meningitidis cell envelope has a variant ____ with LPS (____) - __________, and no ___-____. It also has a ____ endotoxin

visualize the structural difference between LPS and LOS
what major virulence factor of N. meningitidis is used for vaccine?
polysaccharide capsule
_____ are a very distinctive feature on a Gram negative coccus
pili (fimbriae)
N. meningitidis has NO ___-toxins.
exo
exo-ENZYME of N. meningitidis
IgA1 protease - protects against IgA1 on the mucosal surface and aids in colonization
how is the susceptibility of N. meningitidis to antibiotics?
good
Summarize the 2 N. meningitidis vaccines
Old ACY/W vaccine - purified capsule polysaccharide, works well in adults, still recommended for persons over 55
New ACY/W Conjugate vaccine - capsule polysaccharide conjugated to protein (to diptheria toxoid)
The US now sees mostly type ____ capsule strains, where there is now a recently available vaccine
B
4 components of the 4CMenB vaccine

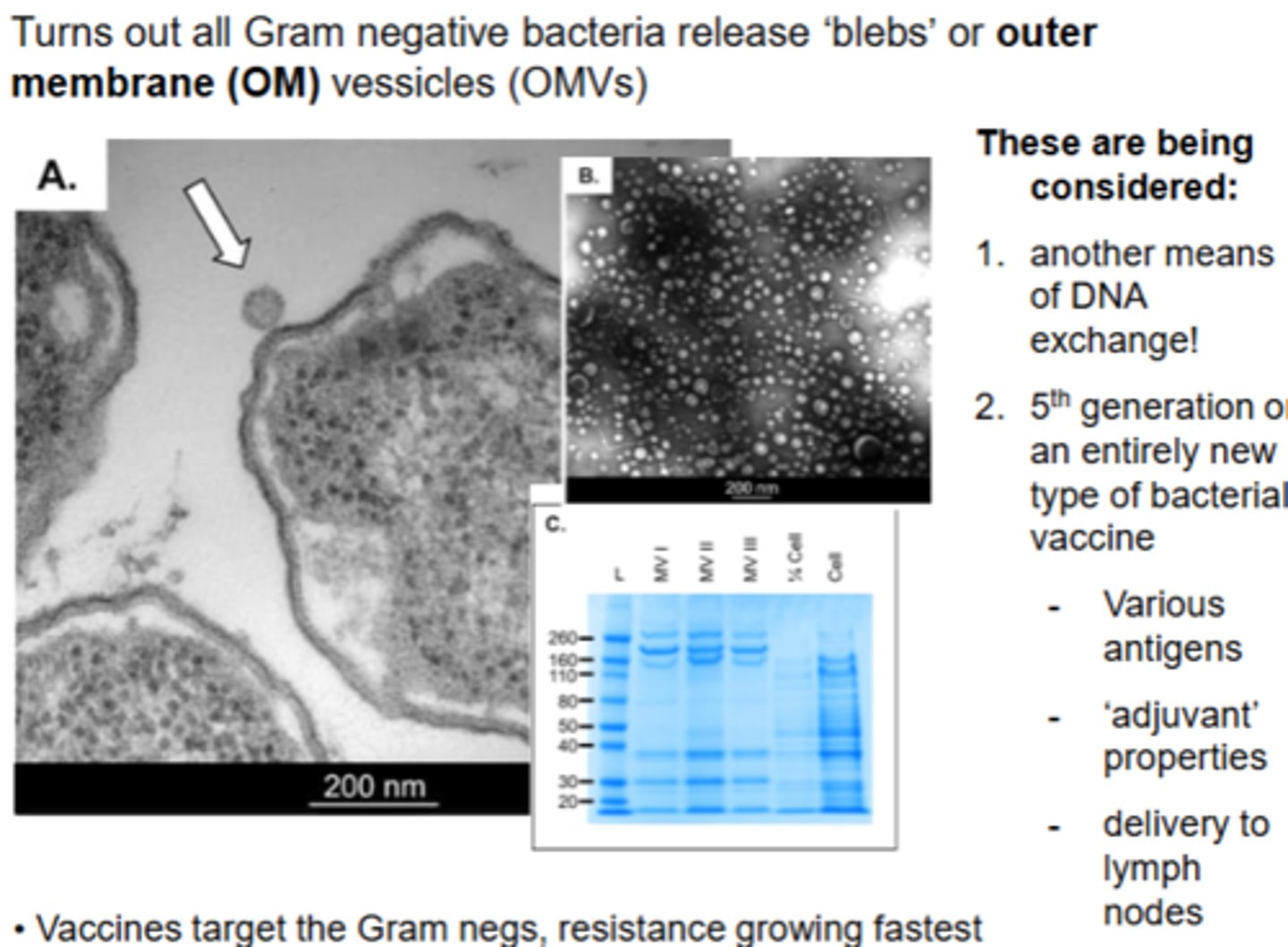
It turns out all Gram negative bacteria release "____", or ___ ___ _____. These are being considered in what ways?
Describe the morphology and location of Haemophilus sp.

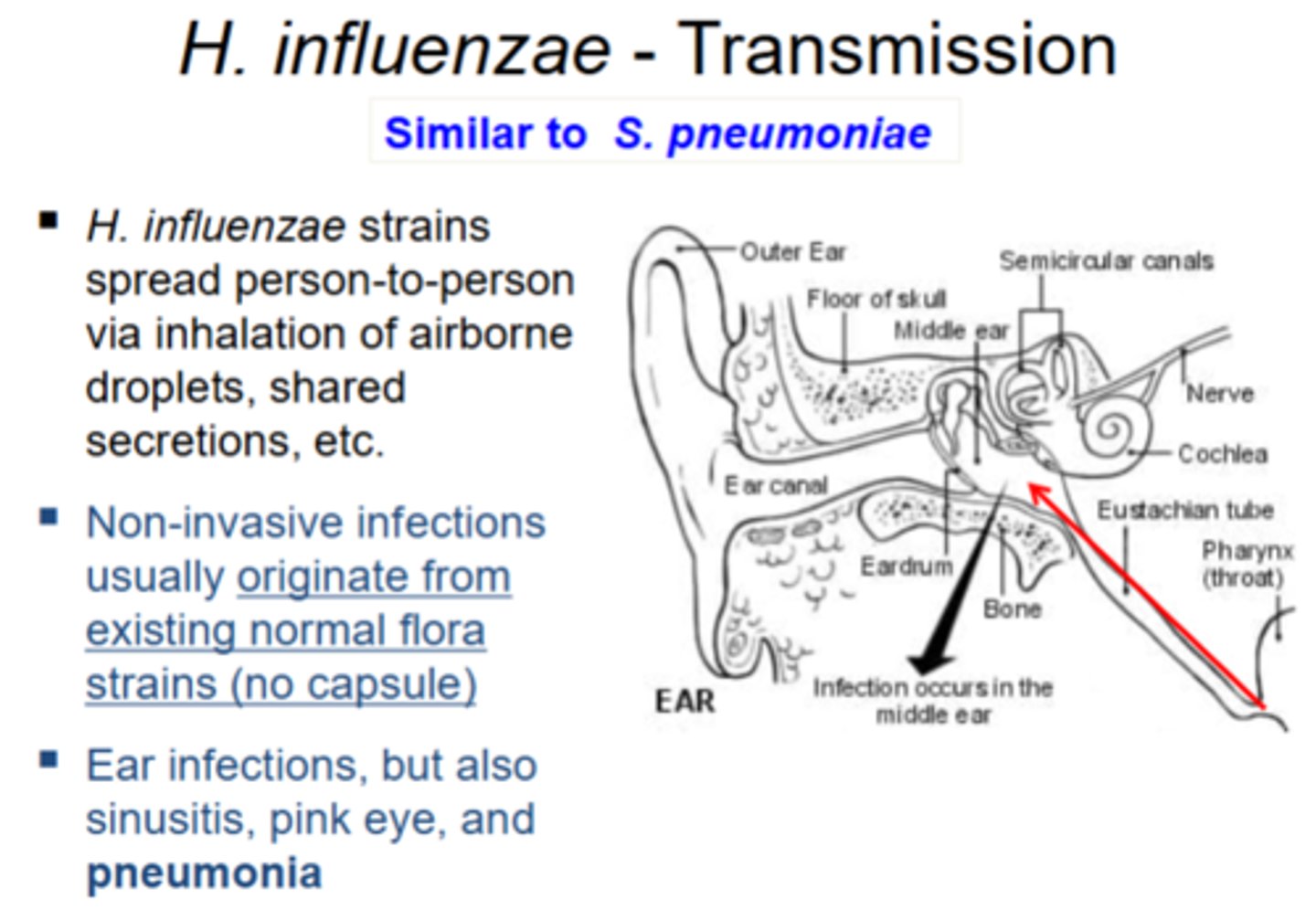
Describe the transmission of H. influenzae
2 common invasive infections caused by H. influenzae

Virulence factors of H. influenzae

H. influenzae does not produce _____, but it does produce the exo-enzyme _____
exo-toxins; IgA protease
Describe the H. influenzae vaccine

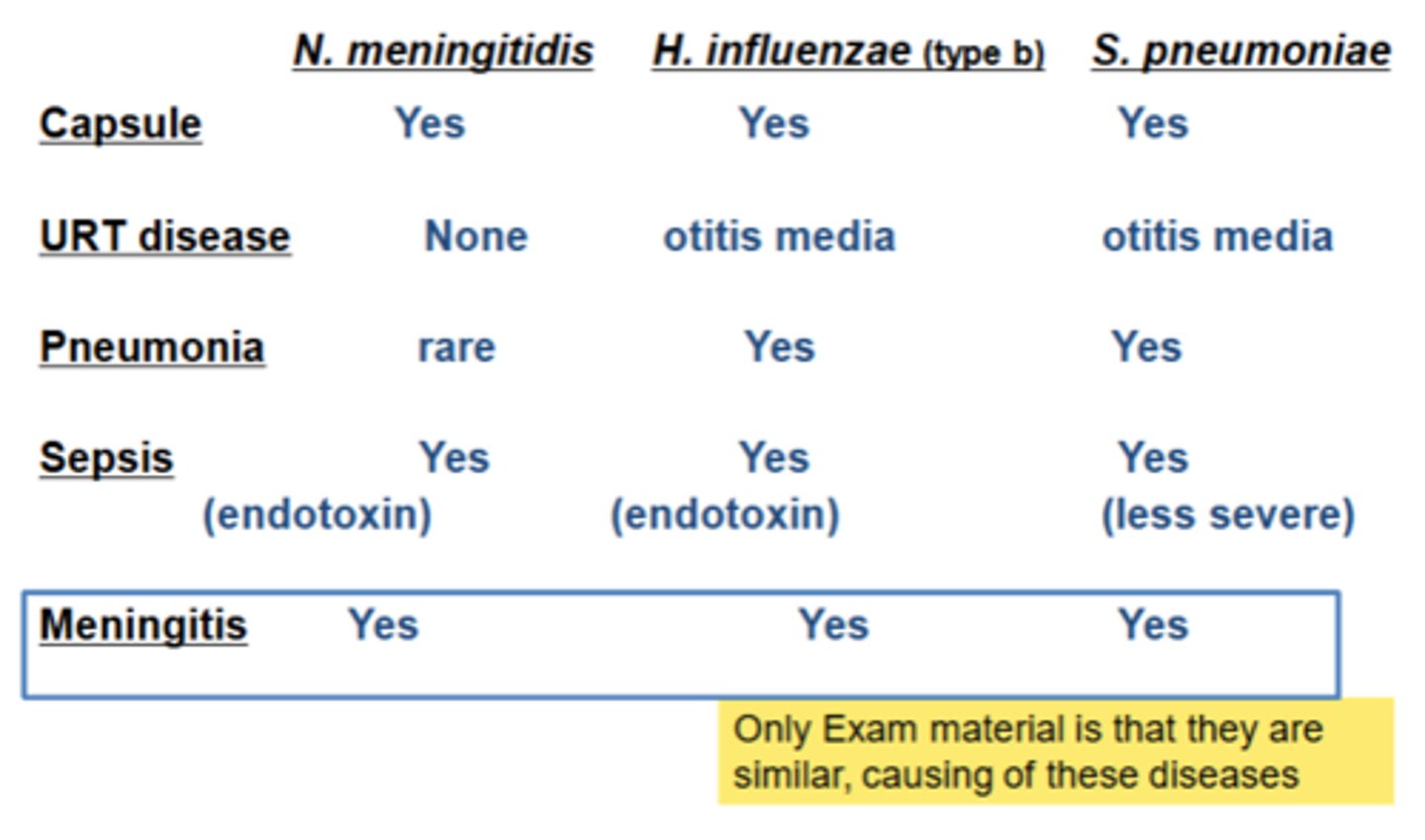
What are the "Triplets" and what diseases can they all cause?
Describe the morphology of Bordetella
small gram-negative coccobacilli
Describe the habitat of B. pertussis
Nasopharynx of humans only in disease
No carrier state, some asymptomatic infections
NOT normal flora
What population is most susceptible to B. pertussis and why
newborns; they lack the maternal Ab
Describe the route of clinical disease of B. pertussis
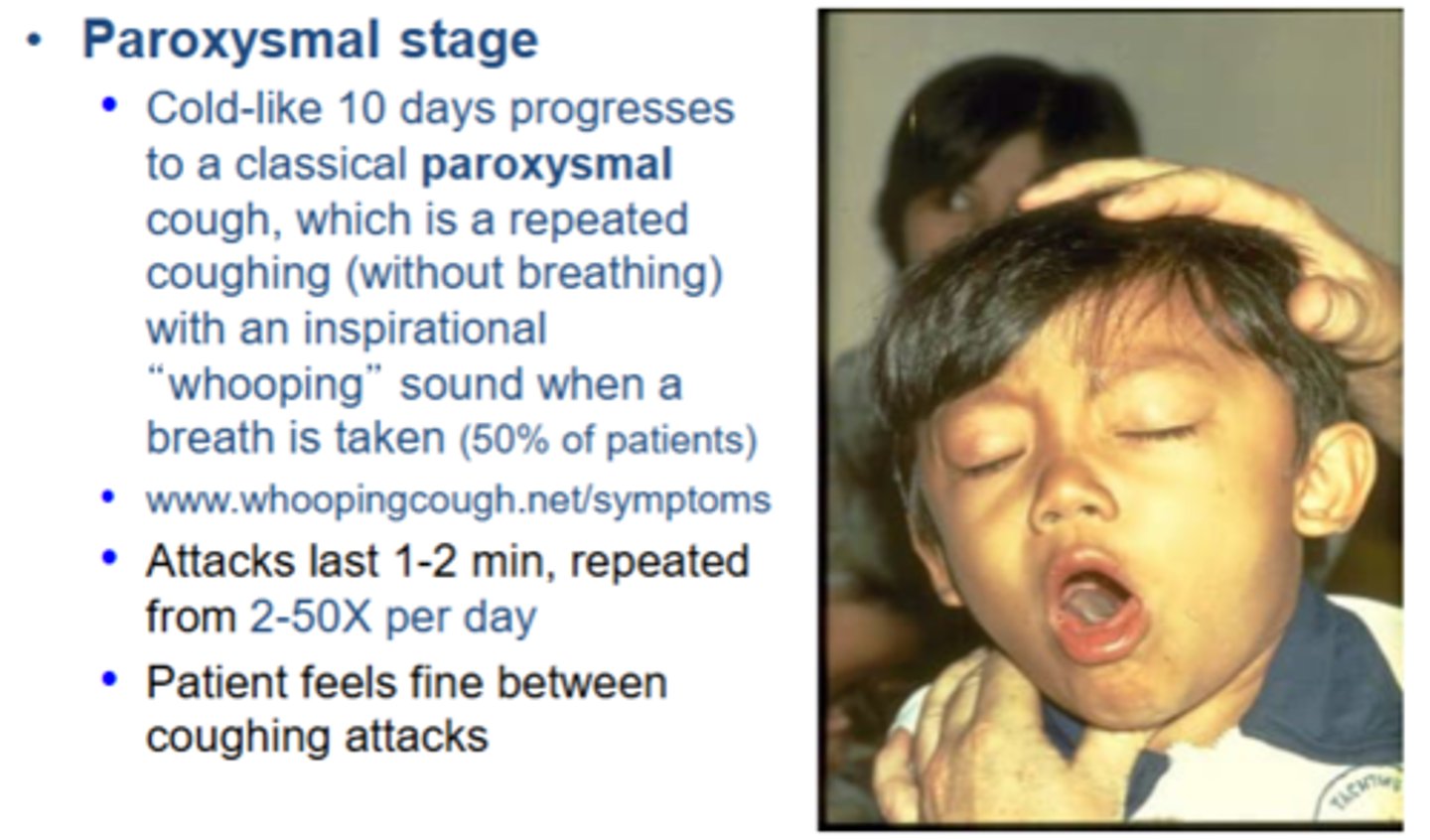
Describe the paroxysmal stage of B. pertussis
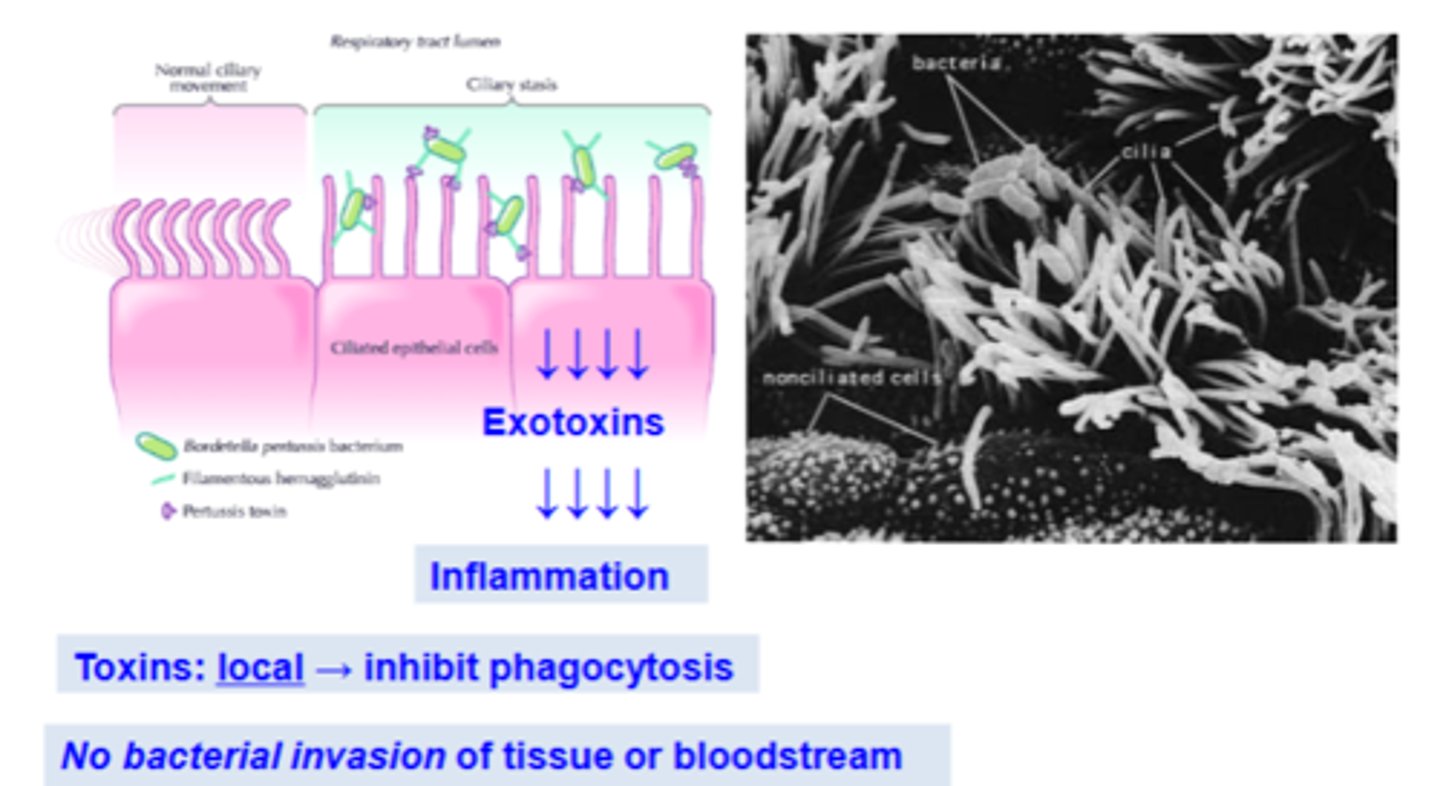
Describe the virulence factors of B. Pertussis

what are the 3 secreted extracellular toxins of B. pertussis
Pertussis toxin
adenylate cyclase toxin
tracheal cytotoxin
Describe pertussis toxin
inhibits monocyte and neutrophil activation and killin
MAJOR COMPONENT of the acellular vaccine
Describe the tracheal cytotoxin
- peptidoglycan monomer
- inhibits ciliated epithelial cells
- triggers inflammation
what vaccine includes immunity to B. pertussis
DTaP; specifically the aP portion - acellular pertussis