Physics - 2.2 - Forces on charged particles
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is an electric field?
A region around a charged object where it exerts a force on other charges and charged objects.
How can the strength of the field be shown on a diagram?
By how close the together the lines of force are.
What is gravitational field strength measured in?
Newtons per kilogram (N kg^-1)
What is electrical field strength measured in?
Newtons per coulomb (N C^-1)
What is a radial field?
A field where force extends or converges to a central point.
Why are radial fields not uniform?
Force decreases with distance from the source.
What are some rules for field lines?
They always touch the charged surface at 90 degrees and they never cross.
Why can charge flow through a conductor?
Because there are free charges in a conductor.
What happens if an electric field is applied to a conductor?
The charges will experience a force, causing the free electric charges in the conductor to move.
What fields are used in particle accelerators?
Electric and magnetic fields are used in particle accelerators.
What is a hazard due to electric fields?
Microchips can easily be damaged by electrostatic discharges.
What happens when a charge is moved against the direction of force in an electric field.
Work is done.
What happens to the work done to move a charge?
It is stored in the field as electrical potential energy.
The greater the electrical potential energy …
the greater the potential difference (between the two plates).
What does 1 volt equal?
1 joule per coulomb.
equation: W/Ew =
W/Ew = QV
How can the velocity of a charge moving in an electric field be found?
If the work done on the charge is known then the velocity can be found.
W = QV = Ek = ½ mv²
What is a magnetic field?
A region in which moving charges experience magnetic force.
How would a field line diagram look for a magnet?
Arrows pointing from north to south poles.
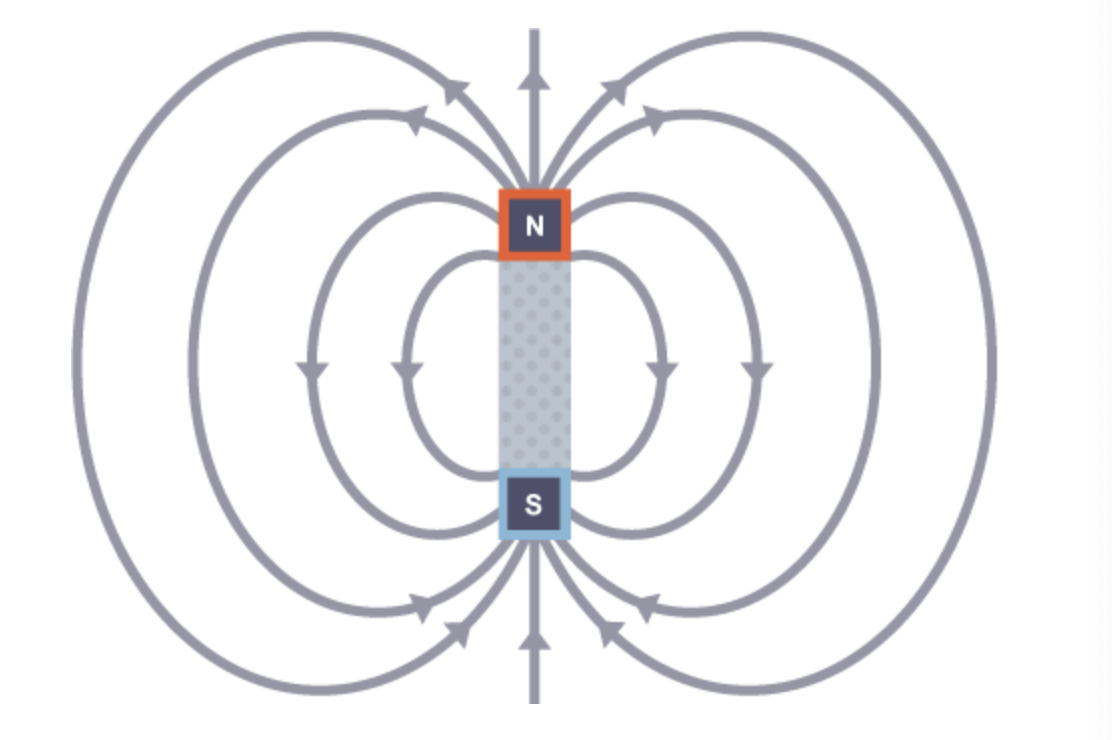
What rule can be used for determining magnetic field direction?
The left hand rule.
Left hand rule: What do the direction of fingers tell you?
Field lines.
Left hand rule: What does the direction the thumb points tell you?
The direction of the flow of electrons.
What field does a stationary charge produce?
An electric field.
What fields does a moving charge create?
An electric and magnetic field.
What happens when an electron moves through a magnetic field.
It experiences a force and the movement of the electron itself creates a magnetic force. The two magnetic fields interact and so the electron changes direction.
Right hand rule: What does the thumb direction show?
The direction of force experienced by the electron.
Right hand rule: What does the middle finger show?
The direction of electron flow (current)
Right hand rule: What does the forefinger show?
The magnetic field direction.
What happens if the charge is positive, how can the left and right hand rules be used?
The directions are reversed.
What are particle accelerators?
Tools that are used to separate the nuclei of atoms.
How do particle accelerators separate nuclei?
They accelerate charged particles (ions) to give them enough energy to separate the nucleus.
What are the two main types of particle accelerator?
Linear accelerators and circular accelerators.