1.2 The evolution of the atomic theory
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Atom
The smallest unit of matter; building block of all substances.
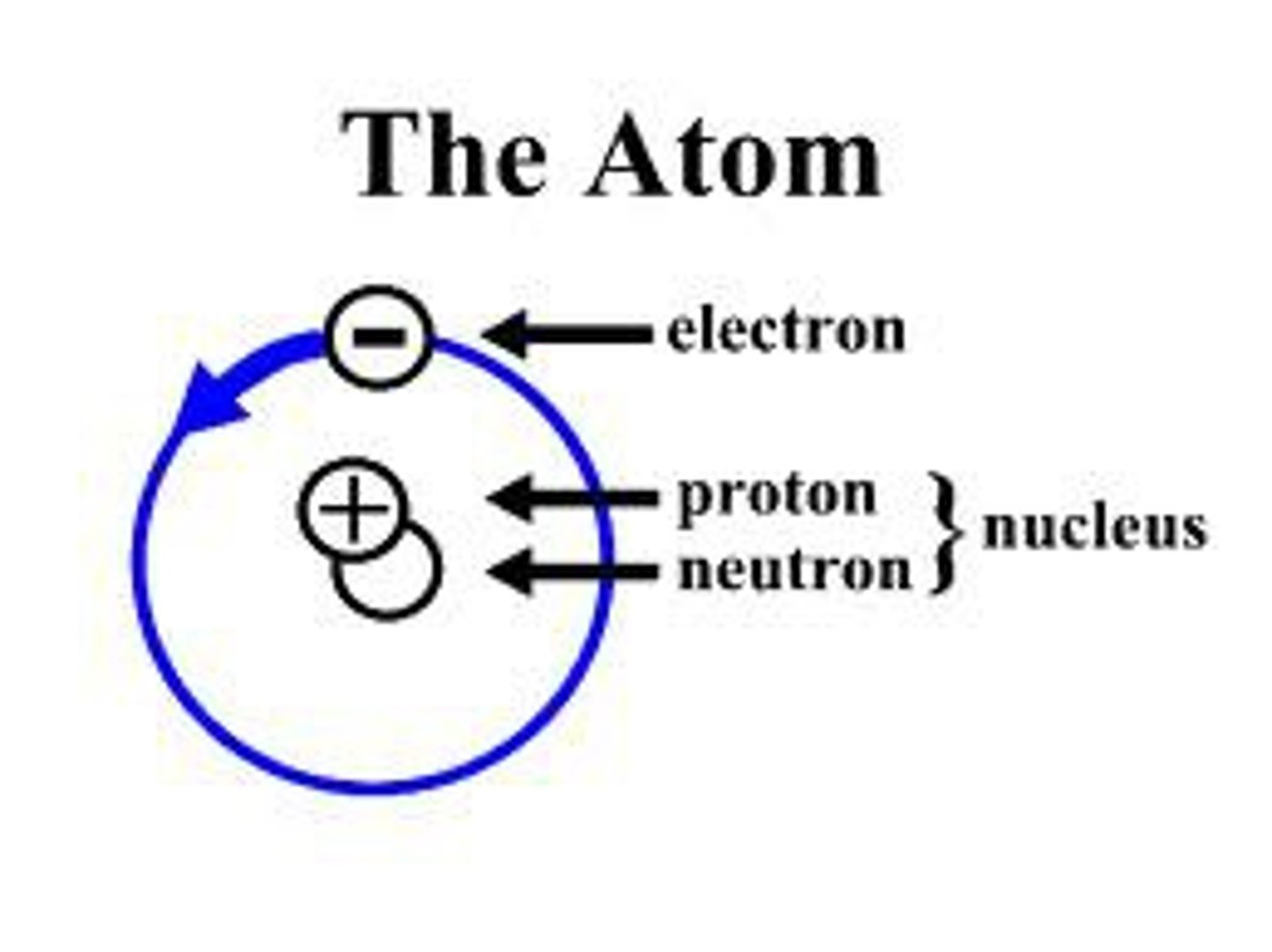
Electron
Negatively charged particle that orbits the nucleus.
Nucleus
The dense, positively charged center of the atom containing protons and neutrons.
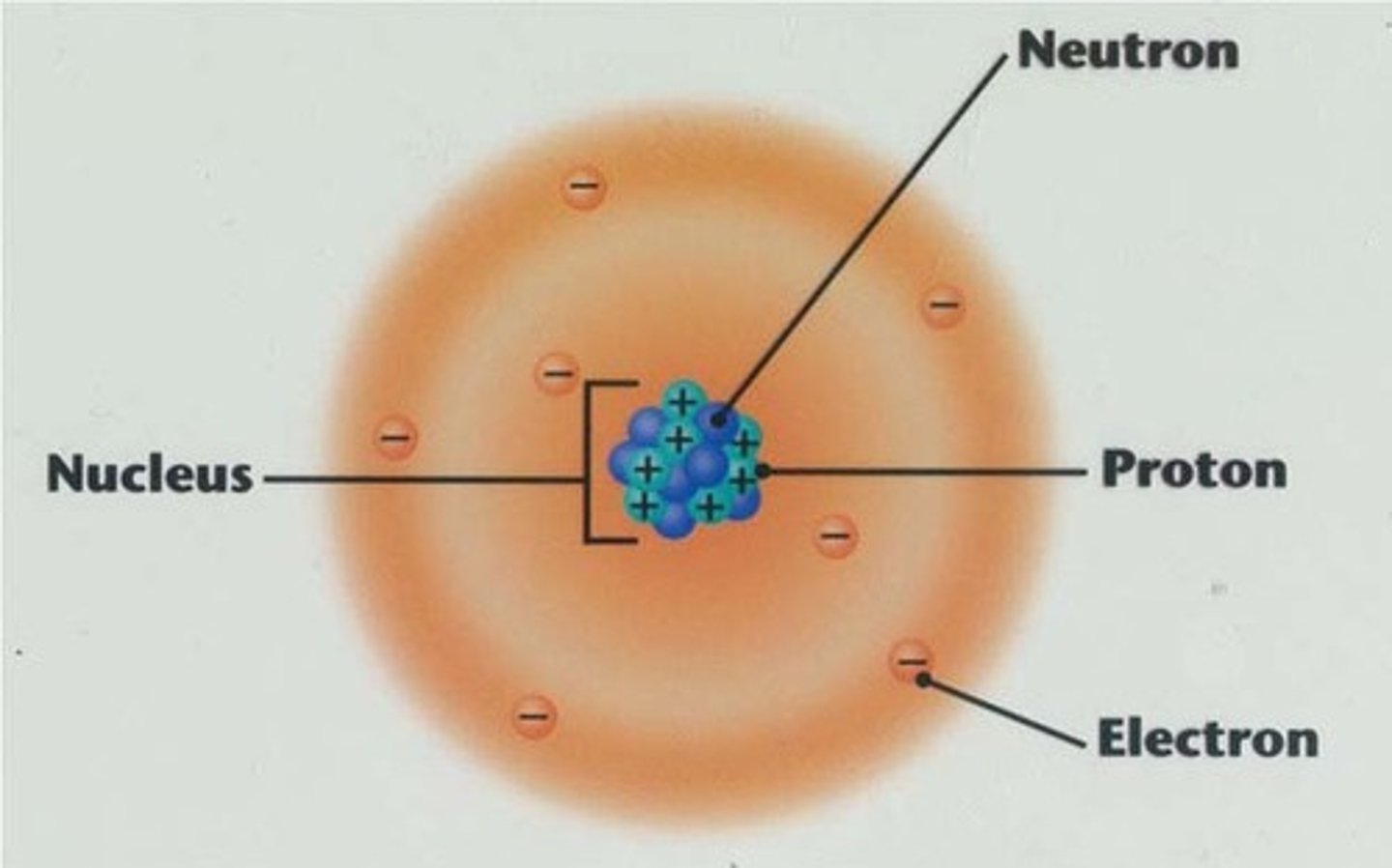
Proton
Positively charged particle found in the nucleus.
Neutron
Neutral particle found in the nucleus.

Atomic model
A scientific model that explains the structure and behavior of atoms.
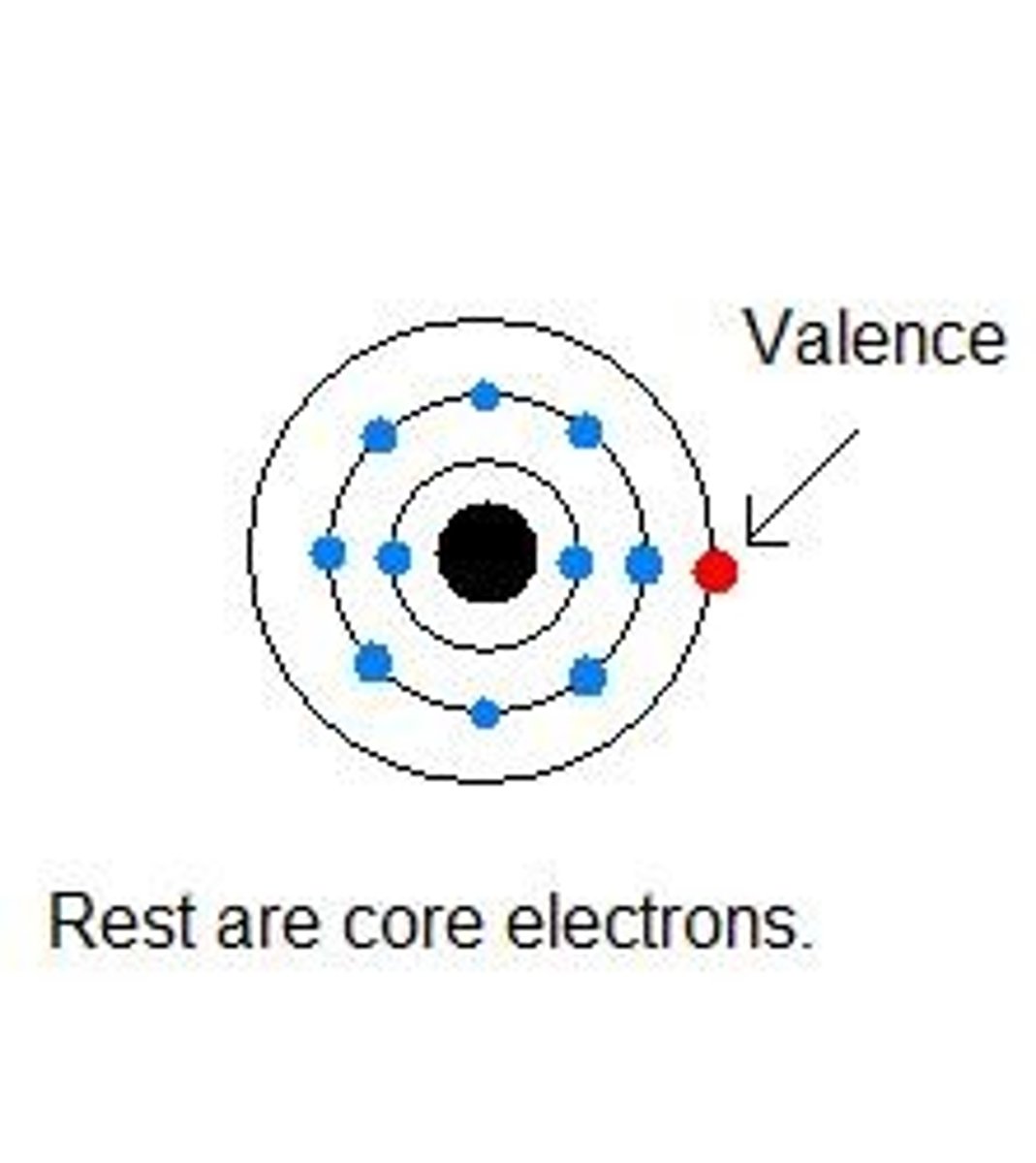
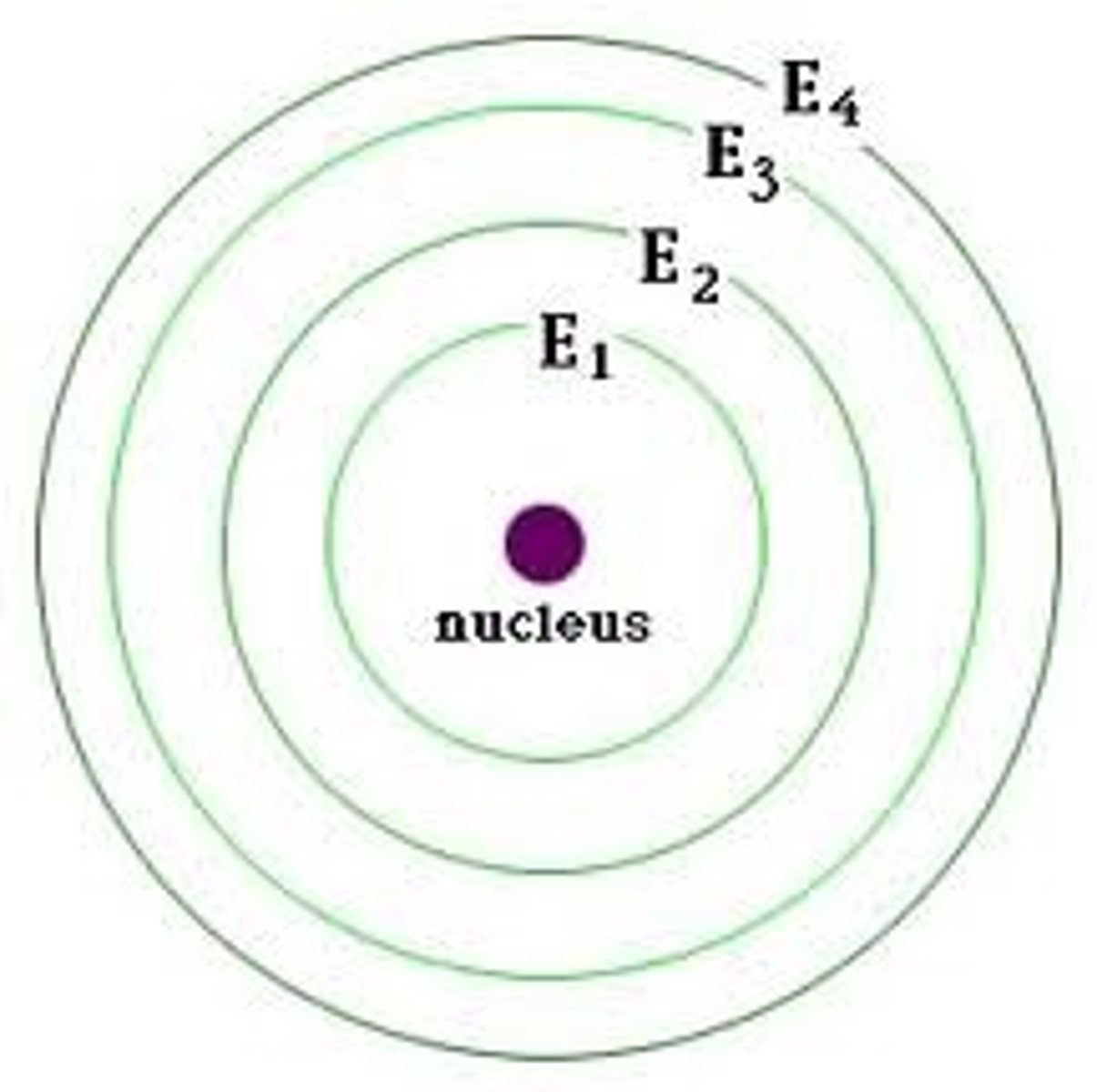
Energy level
A fixed region around the nucleus where electrons can be found.
Electron cloud
The region around the nucleus where electrons are likely to be found.

Democritus' Atomism (5th Century BC)
All matter is made of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms, constantly in motion and too small to see.

Dalton's Solid Sphere Model (1803)
Atoms are tiny, indestructible spheres with no internal structure; each element made of identical atoms.

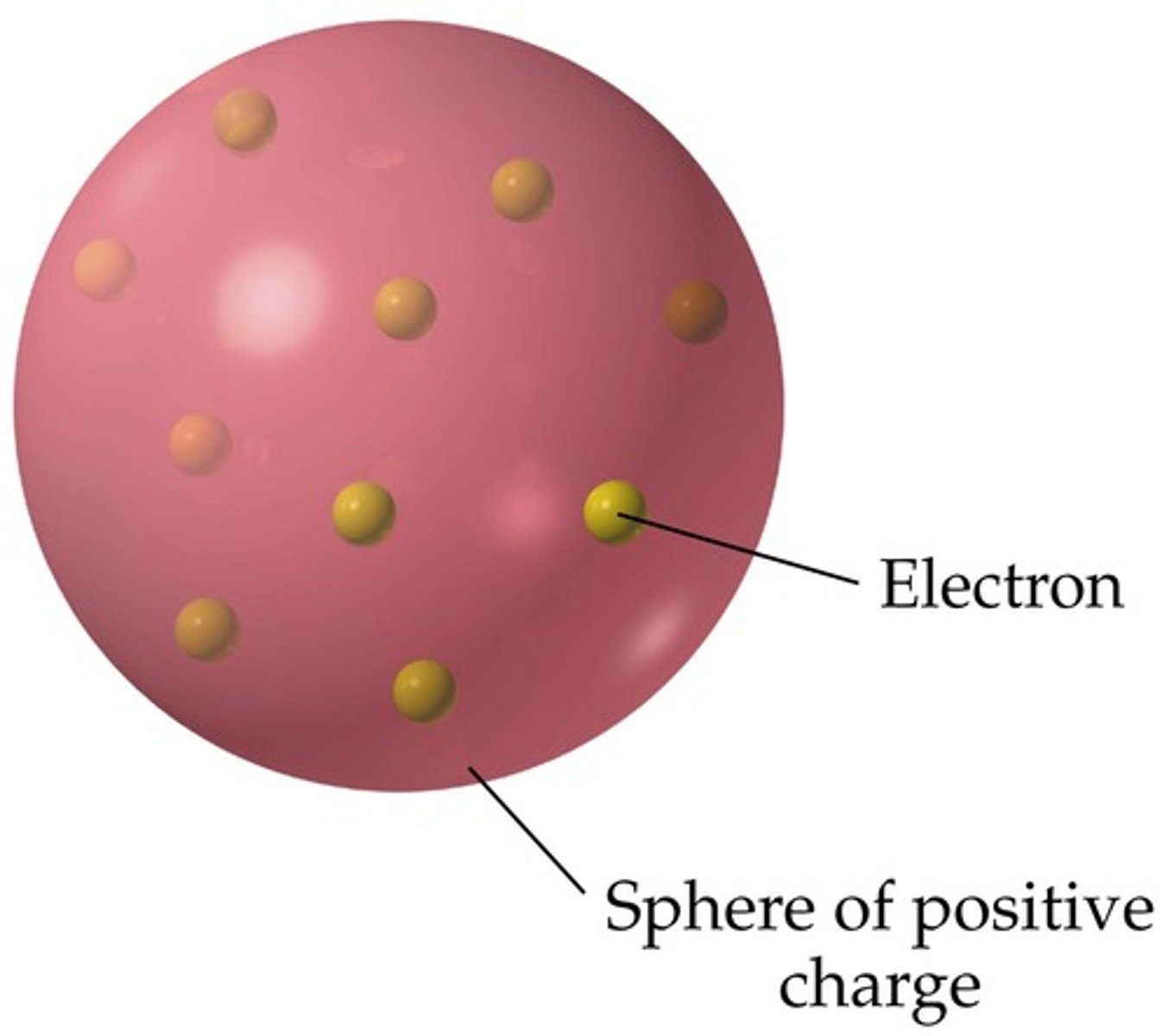
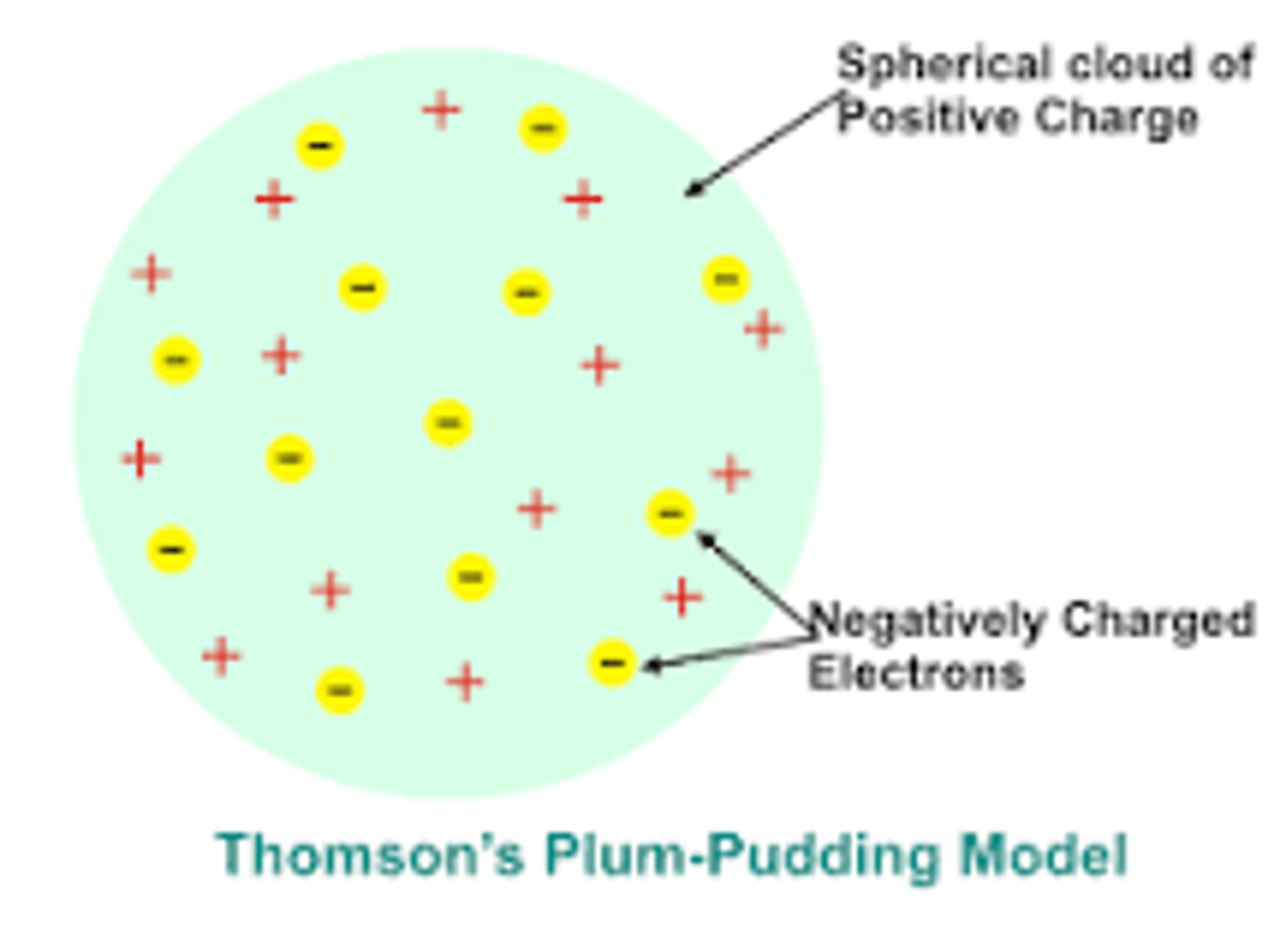
Thomson's Plum Pudding Model (1904)
Atom is a positively charged sphere with electrons embedded like "plums" in pudding.
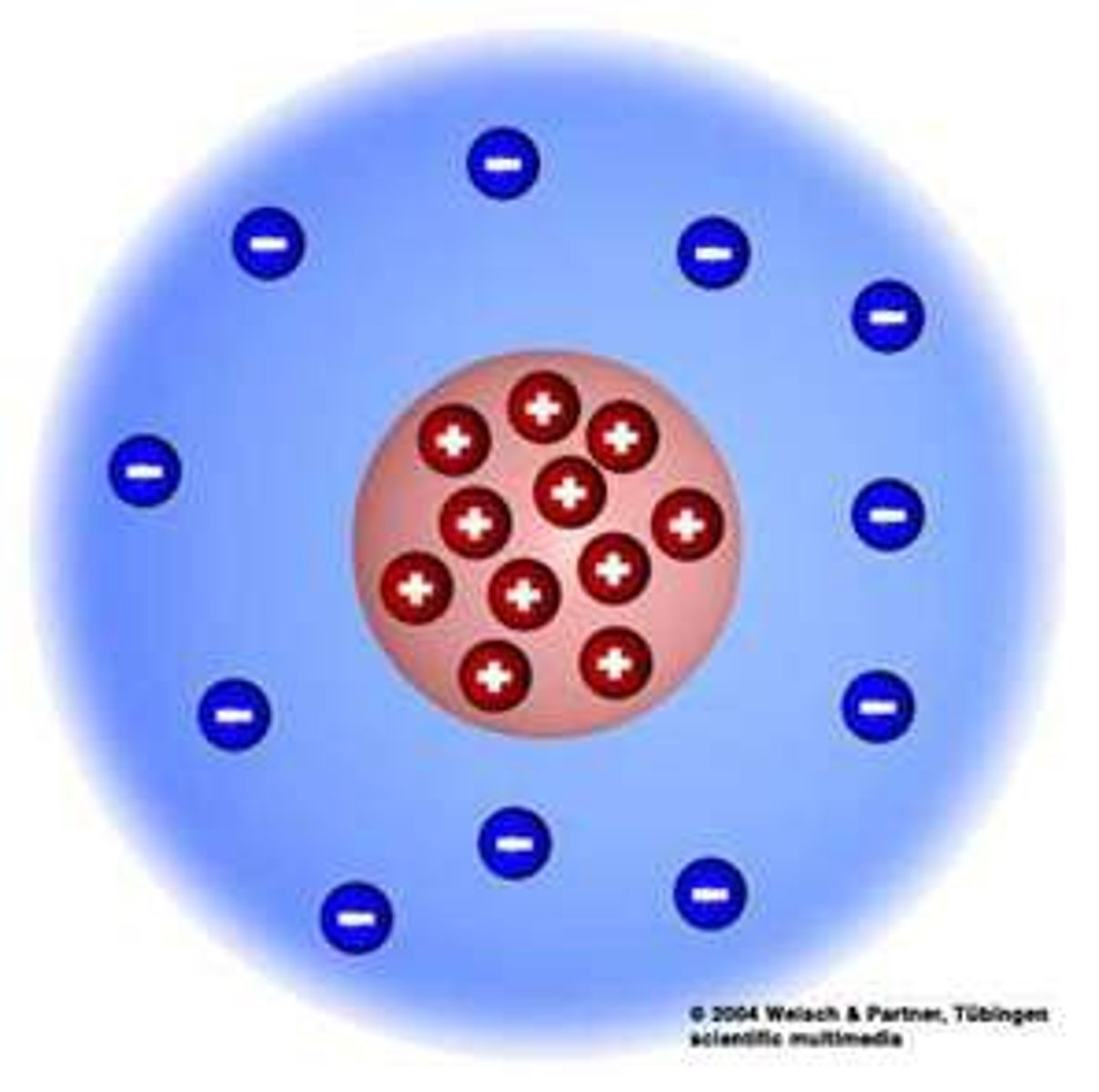
Rutherford's Nuclear Model (1911)
Atom has a tiny, dense, positively charged nucleus with electrons moving around it.
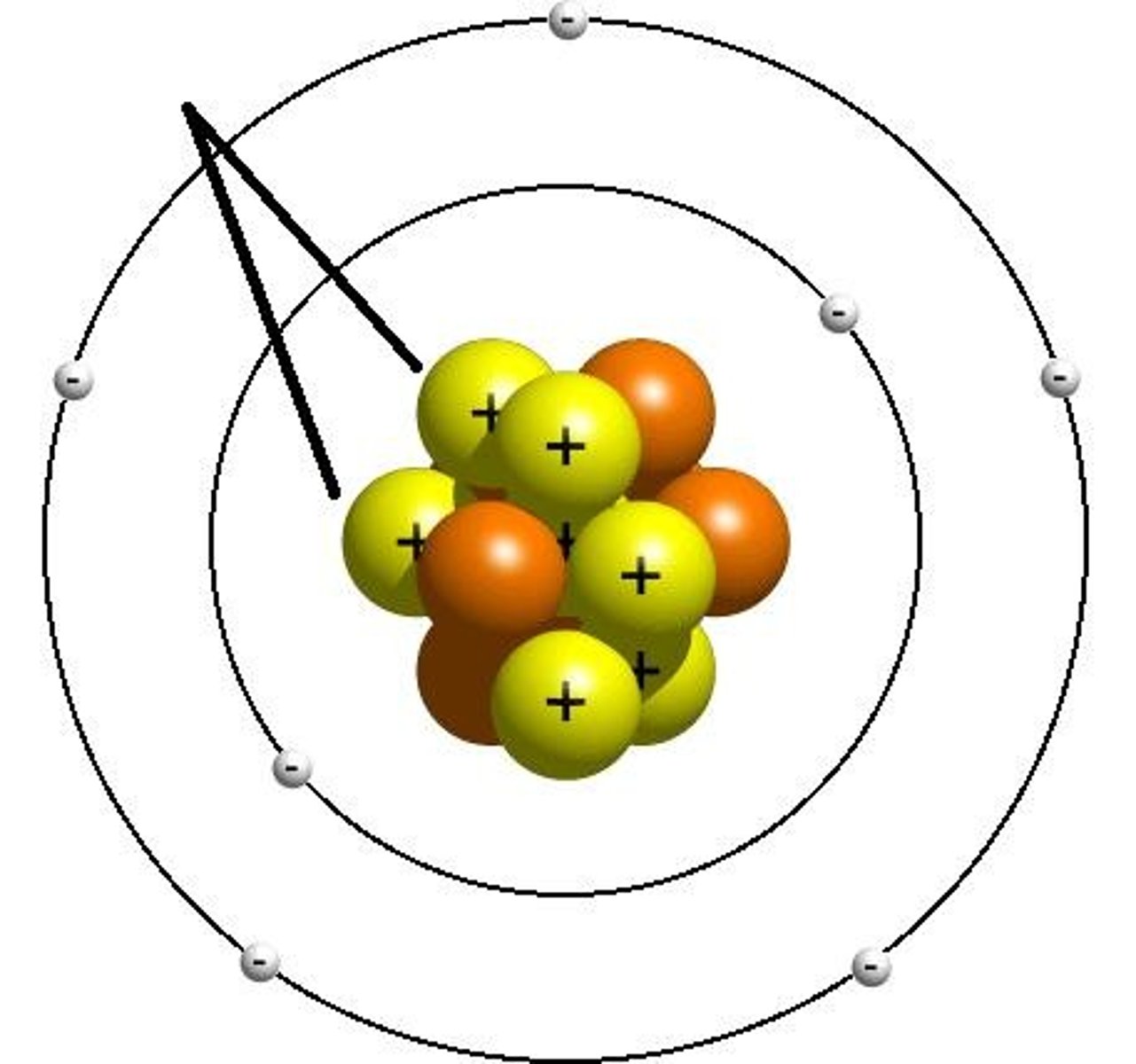
Bohr's Planetary Model (1913)
Electrons orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels (shells) and can jump between them by absorbing or emitting energy.
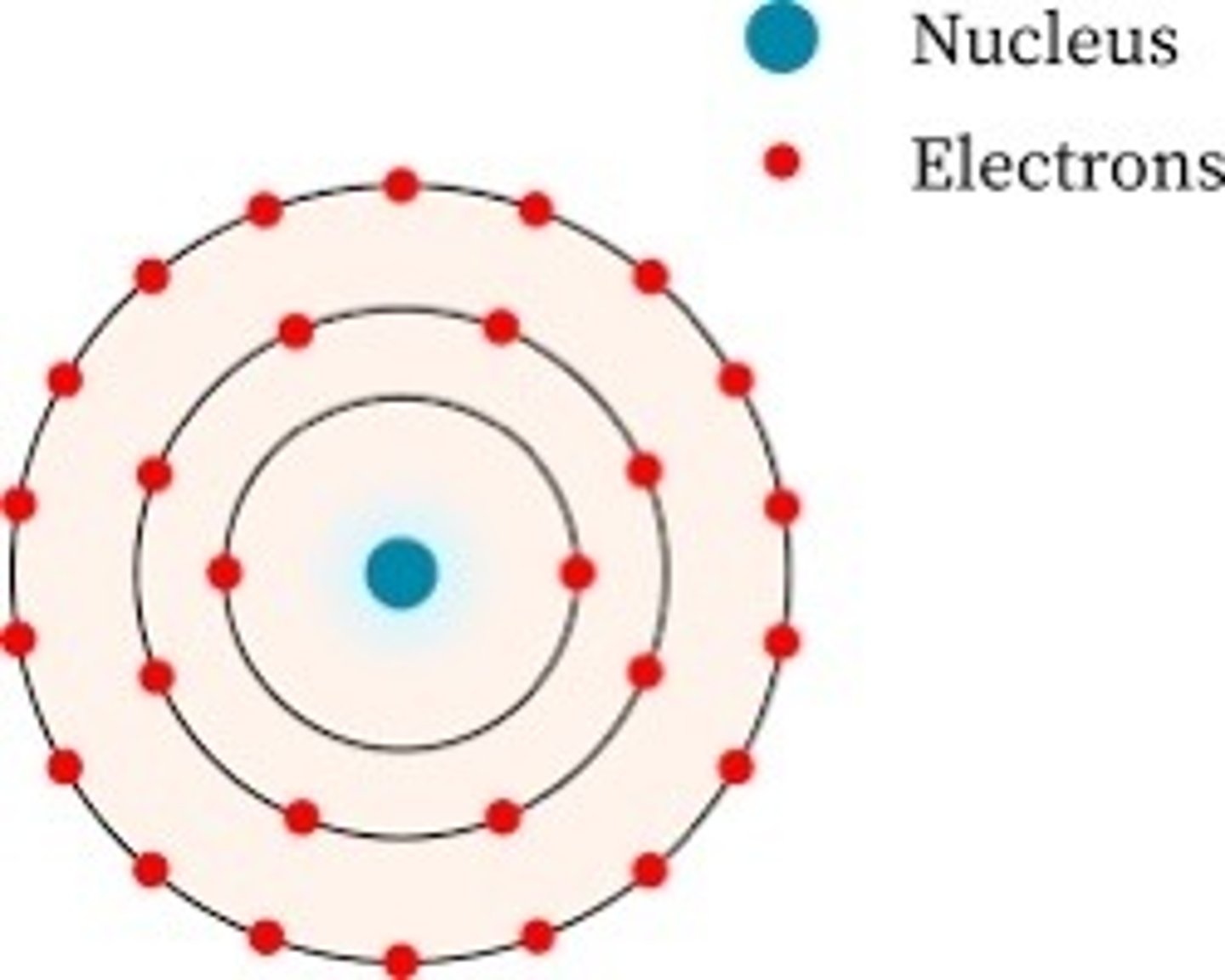
Quantum Model (Modern)
Electrons exist in a cloud around the nucleus, not fixed paths; described by probabilities.
