storms
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
the storm track in the U.S. typically moves from
west to east
what does the U.S. storm track typically move from west to east
prevailing westerlies in the mid-latitudes
the first air to rise in an advancing storm typically creates
cirrus clouds
what are the largest storms on earth
hurricanes
what is the fastest storm on earth
tornadoes
why do we not typically have large storms near us
because of our cold ocean currents and high pressure systems
an air mass is a large bubble of air with similar…
temperatures, humidity, and moisture
what causes the characteristics of an air mass
it gets characteristics from where it forms
when air masses collide withother air masses it creates a
a front
air masses are grouped by
moisture and temperature
what are the different conditions of an air mass
Continental (dry), Maritime (wet), Polar (cold), Tropical (warm)
what are the different types of fronts
cold front, warm front, stationary front, occluded front
describe a cold front
cold air pushes under warm air rapidly, forcing it up rapidly, often bringing thunder storms. the cold air is attacking
describe a warm front
warm air pushes over cold air slowly, warm air is attacking
describe a stationary front
air masses meet but neither moves
describe a occluded front
cold front overtakes a warm front, lifting warm off the ground
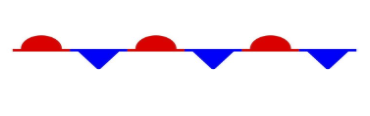
what type of front is this
stationary front
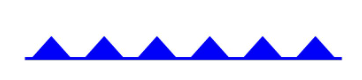
what type of front is this
cold front

what type of front is this
warm front
what type of front is this
occluded front
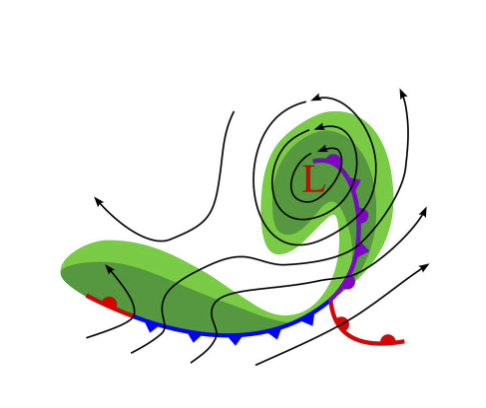
what are the common characteristics of a mid-latitude cyclones
low pressure, associated with rain/wet conditions, counter-clockwise spin, fronts are usually attached
what are the common characteristics of a mid-latitude anti-cyclones
high pressure, dry conditions, clockwise spin, does not encourage clouds/percipiptation/fronts
describe a thunderstorm
a violent convective storm
what are the conditions of a thunderstorm
thunder, lightning, unstable air, humidity, and large cumulonimbus clouds
what are the three stages of development of a thunderstorm
initial/cumulus stage, mature stage, dissipating stage
what is the scale used to measure the strength of tornadoes
enhanced fujita scale
before doppler radar, how was the strength of a tornado measured
damage surveys
which way do tornadoes rotate
counterclockwise in the northern hemisphere
what type of pressure system is associated with tornadoes
low pressure system
what gives tornades the fastest winds on earth
steepness of the pressure gradient
what provides energy for a tornado
thunderstorms, warm and moist air
at what stage in a thunderstorm are tornadoes more likely to occur
dissipating stage
what are the two other names for a hurricane
typhoon and tropical cyclone
what are the three parts of a hurricane
eye, eyewall, and spiral bands
where are hurricanes likely to form
5-10˚N (not on the equator)
which way do hurricanes rotate
counter-clockwise
why is the eye of the hurricane calm and clear
the air is sinking, and the winds are light. a pocket of high pressure
where did the largest natural disaster in the U.S. history occur in 1900
Galveston, Texas
the fastest winds in a hurricane are found in which part
eyewall
what is a storm surge
a rise in sea level due to low pressure and winds of a hurricane
where in the U.S. do hurricanes commonly occur
SE U.S. (gulf coast, atlantic coast)
what weakens hurricanes
entering land or cold water
what sustained wind speed must be met in order to be classified a hurricane
~74 mph
what scale is used to rank the relative strength of a hurricane
saffir-simpson scale
what causes hurricanes to form and where they travel
hurricanes form due to the ocean water and moist air and they travel westward and then bend right due to the coriolis effect and high pressure systems. tradewinds also push them east to west.