CE11 - Lecture 2 - Rocks and Minerals
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Rock
A ______ is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized based in minerals included, chemical composition and its genesis.
Rocks
_______ are generally classified into three: Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic
Rock Formation
A mappable unit of rock consisting of an initially connected volume deposited in one interval of time.
A formation may contain an assortment of different kinds of rocks but there is a prevailing character in the mix of rocks.
The distinctive character of a formation may relate to the engineering properties.
Soils
______ are formed by weathering of rocks.
The ______ physical property is dictated primarily by the minerals that consists the weathered rock.
Weathering, erosion, transportation, and deposition
________ are process involved in breaking down rocks and transferring to another place until it settles in a place.
Outcrop
Any rock can be brought up to the surface and part of it becomes an ________ and be exposed to weathering and become sediments.
Sedimentary Rocks
_________ come from sediments which may come from any kind of rock. The rocks just need to be exposed and this usually means that these rocks are brought above surface.
Igneous rocks
___________ come from magma. Magma can form from metamorphic rocks (since it is only at great depths where metamorphic rocks form can you reach temperature to melt rocks naturally).
Minerals
_________ are naturally occurring inorganic compound with a definite composition. They make up rocks, although most of the rocks will have several different ________ in it. Only a small set of _______ are rock-forming: mostly silicates
Mineral Properties
Each mineral has a unique combination of diagnostic physical features.
Color
Mineral Property - some minerals may have variations of _______ so it is not a reliable way to describe minerals by itself

Streak
Mineral Property – color of the mineral in its powdered form

Luster
Mineral Properties - the way mineral reflects light (Metallic, Dull, Pearly, Vitreous (glassy))
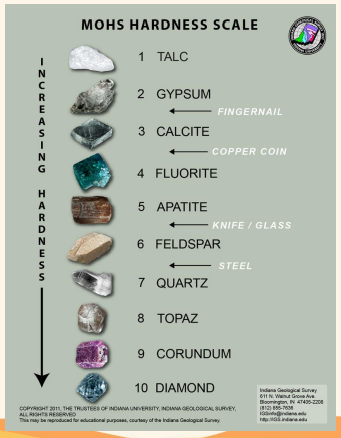
Hardness
Mineral Properties - measures the ability to scratch or be scratched.
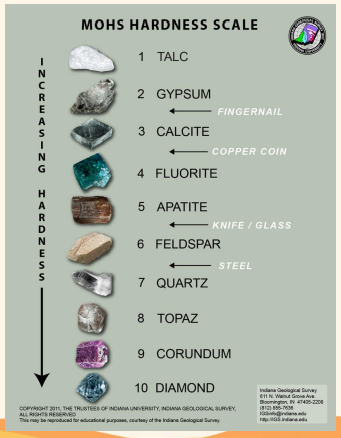
Mohs Scale of Hardness
___________ is used to determine how hard a mineral is by scratching it against reference minerals.
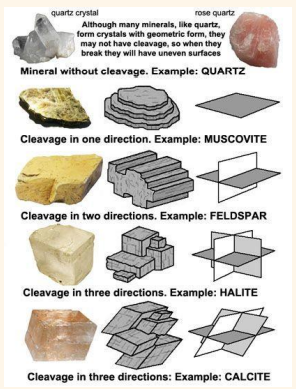
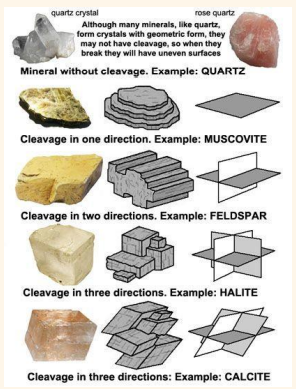
Cleavage
Mineral Properties - The way a mineral breaks along a plane easily and smoothly based on its lattice. The plane of breakage is called the _________ plane.
Fracture
Mineral Properties - The way a mineral breaks if there are no cleavage planes.
Density
Mineral Properties - Mass/Volume of a mineral. Specific weight (Weight/Volume) is simply the______ multiplied by g.
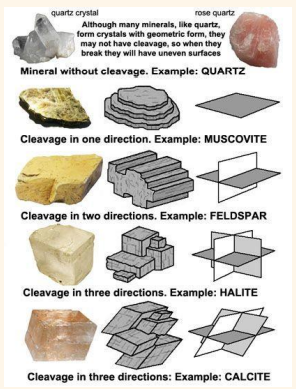
Mineral Identification
Identification of minerals contribute to identification of rocks and their properties.
Uses of Minerals
Since minerals are found in rocks, a lot of the characteristics of minerals matter in our usage of rocks.
Some minerals are mined to be used as additives or to be processed to make construction materials like gypsum, cement, and aggregates (sand and gravel used in concrete making).
Certain minerals that decay or become weak in certain conditions may be dangerous for certain sites/projects.
Mineral Formation via:
Precipitation, Metamorphism, Weathering, Organically
Mineral Formation
Most minerals forming the rocks are from the process of magma cooling. As magma rises, it cools, and minerals can crystallize.
Only small crystals are formed
If cooling is fast (minutes to years), minerals may not have time to become ordered, and __________
Larger crystals can form
If cooling is slow (decades to millions of years), higher level of ordering may be achieved, and ________
No crystals were formed
If cooling is too rapid (seconds), the rock will be glassy, meaning ___________
Mineral Groups
Minerals are grouped based on the predominant anion or anion complex.
