OChem Unit 1 Chad's Prep
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Organic Chemistry
the study of carbon containing compounds
Organic compounds
carbon containing compounds
Inorganic compounds
generally defined as carbon-lacking compounds
Valency
the number of bonds a compound makes
Tetravalent
valency of 4
Trivalent
valency of 3
Divalent
Valency of 2
Monovalent
Valency of 1
Octet rule
atoms aim to have 8 ve- in their shell
Lone pair
a pair of unshared/non-bonding e-
Covalent bond
sharing of e-
Formal charge
associated with any atom that doesn’t xhibit the appropriate number of ve-
FC Equation
(Number of ve-) - (dots and lines)
+FC
Missing e-
-FC
Excess e-
Sigma (σ) bonds
Present in all bonds, end to end overlap along internuclear axis
Internuclear axis
imaginary line connecting the nuclei of two bonded atoms
Valence bond theory
a bond is simply the sharing of e- density bw 2 atoms as a result of constructive interference of their atomic orbitals
e- density
how likely an electron is to be found at a specific point in space
Pi (π) bonds
Can only occur bw p orbitals, occrus above and below the internuclear axis, and is any additional bond
sp Hybridization
2 e- groups and bond angles of 180
sp² Hybridization
3 e- groups and bond angles of 120
sp³
4 e- groups and bond angles of 109.5
ve-
e- involved in chemical bonding
Wave (Ψ) function
takes into account the wave-like behavior of an e- that is in the magnetic field of a p+
Ψ²
represents the probability of finding an e- in a particular location
Orbital
a region of space that can be occupied by an e-
Atomic orbital (AO)
a region of space filled with respect to the nucleus of a single atom
Molecular orbital theory
uses mathematics as a tool to explore the consequences of AO overlap
Bonding MO (π, σ)
the result of constructive interference of the original two AOs
Antibonding MO (π*, σ*)
the result of deconstructive interference (explains why it’s higher in E)
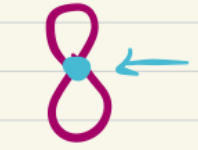
Nodes
locations where Ψ = 0, no possibility of finding an e-
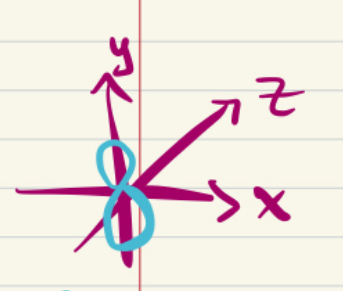
2py orbital
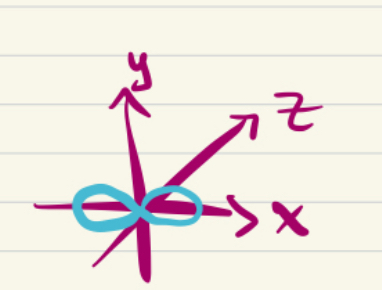
2px orbital
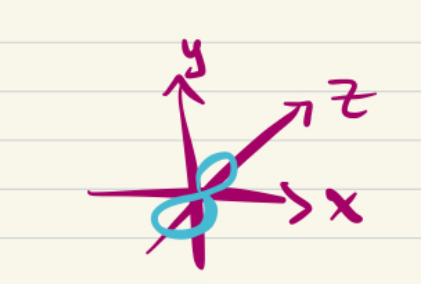
2pz orbital

1s orbtial
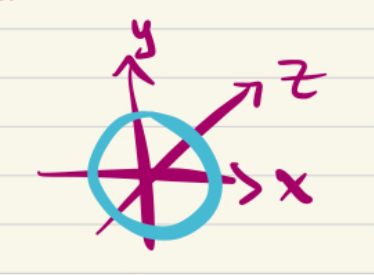
2s orbital
Aufbau Principle
lowest E obrital filled first
Pauli Exclusion Principle
each orbital can acomodate a max of 2 e- hat have opposite spin
Hund’s Rule
1 e- is placed in each degenerate orbital first, before e- are paired up
Degenerate orbitals
orbitals with the same E level Ex: 2s and 2p)
Constructive interference
overlap with orbitals of the same phase, produced a wave with larger amplitude
Destructive interference
overlap with differencing pases, cancelling each other out, and always produced a node
Diatomic
molecule composed of 2 atoms
Heterodiatomic
molecule composed of 2 different atoms
Homodiatomic
molecule composed of 2 of the same element
LUMO
“Lowest unoccupied Mo”: MO with the highest E in the molecular orbital diagram that’s empty
HOMO
“Highest occupied MO”: MO with the highest E in the MO diagram with e-
Bond order (BO)
the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons divided by two.
Fronteir MOs
LUMO and HOMO, usually the ones involved in chemical RXNs
Needs to donate e- → donate highest E ones in the LUMO
Needs to receive e- → receive in LUMO (most stable E spot)
Non-polar covalent
Difference of EN 0-0.5(small difference in EN)
Polar Covalent
Difference of EN 0.5-1.7
Ionic
Difference of EN 1.7< (larger difference in EN)
Dipole moment
measure of polarity
Molecular dipole moment
the vector sum of all bond dipoles in a molecule, indicating its overall polarity
δ Partial charge
representing partial charges in a polar bond
Dipoles that cancel
Linear in opposite directions, and symmectrical MGs (trigonal planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral)
C-C and C-H
Non-polar bonds
Dispersive forces
Temporary dipole moment, random movement of additive, random e- movement, and the more e- → the more polarizable the molecule
Dipole-dipole forces
Permanent dipole, polar
Hydrogen-bonding
H- O, N, F
Ion-dipole forces
IMF bw an ion and the partial charge of a molecule
Constitutional isomers
compounds that have the same molecular formula but difffere in the way the atoms are connected (usually differ in surface area)
Branching
Gives you a more compact structure
smaller SA → lower dispersive forces
Less branched
Higher BP, usually lower MP
More branched
Lower BP, usually higher MP
Solubility
“like dissolves like” in terms of polarity.
Ex: A molecule with the least amount of non-polar bonds →greatest solubility with a nonpolar molecule
A molecule with the greatest amount of polar bonds → greatest polarity and would have the greatest solubility in a polar molecule