Biology Final Review
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/80
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
1
New cards
Temperature
One of the things that allows for enzyme denature and one of the things that defines a biome
2
New cards
Species
Organisms that can produce viable and fertile offspring together
3
New cards
Logistic Growth
“S” graph. Graph of species that reaches carrying capacity.
4
New cards
Biome
Defined by temperature and precipatation
5
New cards
Predation
Predator/Prey Relationship
6
New cards
Sun
The giant yellow thing in the sky that provides heat and energy (sets the energy for the Earth)
7
New cards
C6H12O6
Thing that plants make which we turn into energy
8
New cards
Biotic
Alive
9
New cards
Primary Producer
Herbivore. Sets the energy for the ecosystem
10
New cards
Mutualism
Both organisms are happy
11
New cards
Photosynthesis
The process of plants turning carbon dioxide into oxygen
12
New cards
CO2
the thing that plants turn into oxygen via photosynthesis
13
New cards
Rain
water falling from the sky
14
New cards
10% Rule
Energy that stays as it goes up the food chain
15
New cards
Carrying Capacity
The environment can no longer sustain organisms because it has run out of resources
16
New cards
Community
a group of populations in one area (at least two or more different species)
17
New cards
Herbivore
animals that only eat plants
18
New cards
Exponential Growth
“J” graph. The environment has yet to reach carrying capacity and is still expanding.
19
New cards
Abiotic
Not alive
20
New cards
O2
What plants produce when they consume CO2. What humans breath in to create CO2
21
New cards
Tropic Level
What we call each level on the food chain
22
New cards
Population
Smallest group that can evolve. A group of one species in an area
23
New cards
H2O
Water
24
New cards
Commensialism
When one organism is happy and the other is neutral.
25
New cards
Control Ecological Footprint
Something we’d better do
26
New cards
Ecosystem
All the biotic and abiotic factors in one place
27
New cards
Carnivore
Organism that only eats meat
28
New cards
Cellular respiration
the process of converting glucose (food) into energy (ATP) using oxygen and releasing CO2
29
New cards
Rainforest
Very humid/rainy
Extreme biodiversity
Tigers, monkeys, snakes
Extreme biodiversity
Tigers, monkeys, snakes
30
New cards
Independent Variable
The thing you change in an experiment
31
New cards
Climate Change
The Earth is getting hotter and that’s bad
32
New cards
Dependent Variable
The variable that changes because of the changes of independent variable
33
New cards
Ozone Depletion
Holes in the ozone layer that we made that let UV light through (O3)
34
New cards
Hypothesis
If… then… statement
35
New cards
Antibiotic
Thing used to treat bacterial infections
36
New cards
Large intestine
absorbs the water from the stuff you digested
37
New cards
Asexual reproduction
Mode of reproduction in which offspring is produced by one parent rather than two. Lacks genetic variation.
38
New cards
Lytic
when a virus infections a bacteria cell,
39
New cards
Mouth
First stop in digestion.
40
New cards
Endergonic
Absorbs energy
41
New cards
Enzyme
type of protein, organic catalyst
42
New cards
Active site
Site where the reaction between the enzyme and substrate takes place
43
New cards
Allopatric Speciation
When new species evolve after being geographically seperated
44
New cards
Analogous Structure
Similar function, different structure (ex: birds wing and insects wing)
45
New cards
Carbohydrate
macromolecule, short term energy
46
New cards
Fossils
evolution evidence, physical remains of ancient life
47
New cards
Stabilizing Selection
the middle is “selected”
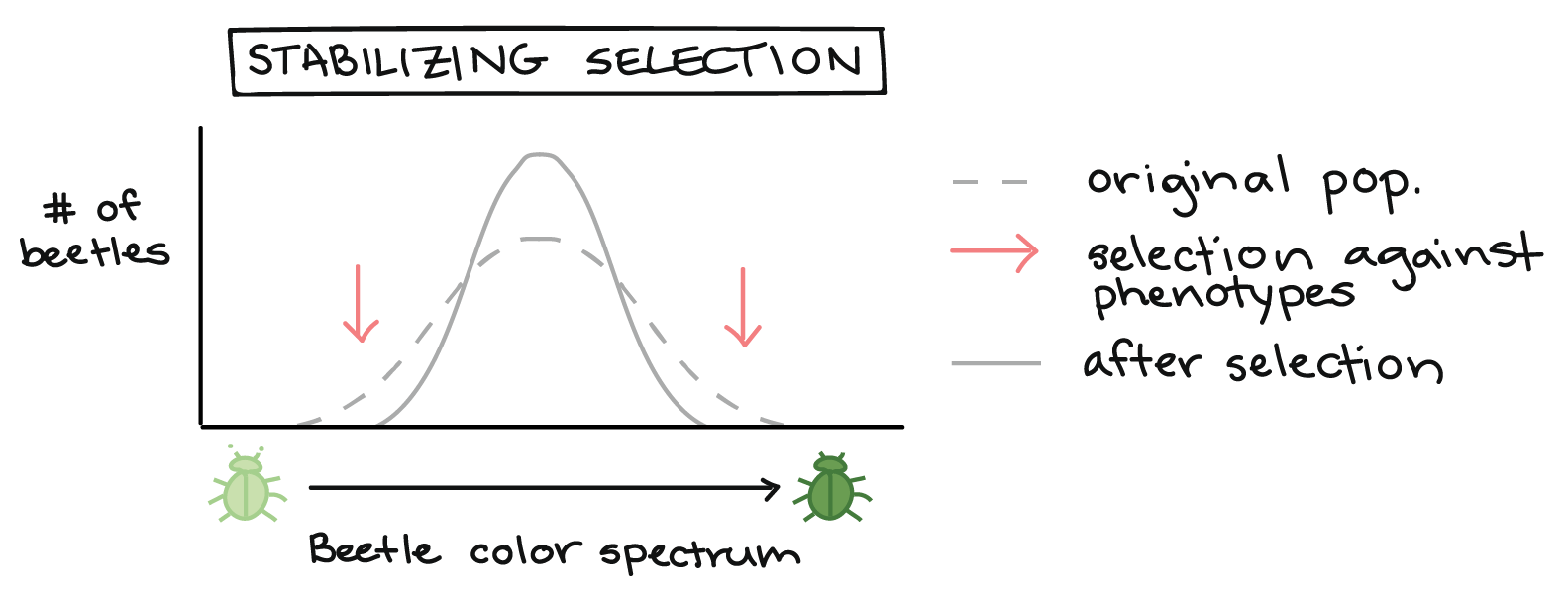
48
New cards
Ribosome
part of a prokaryote cell where proteins are made
49
New cards
Bacteria
type of prokaryote cell. can be both good and bad
50
New cards
Plasmid
part of prokaryote cell that carries extra piece of DNA and carries the genes for antibiotic resistance
51
New cards
DNA
double stranded genetic material
52
New cards
When was the Earth formed
4\.6 billion years ago
53
New cards
Catalase
type of enzyme that turns H2O2 into oxygen and water
54
New cards
Stomach
3rd step of digestion. Uses mechanical and chemical digestion. Food is broken down by churning, pepsin (breaks down proteins), and gastric juice (pH of 2)
55
New cards
Darwin
Cool scientist guy who came up with the idea of natural selection
56
New cards
Substrate
thing the enzyme bonds to to make a reaction
57
New cards
Flagella
part of most prokaryotic cells that helps with movement
58
New cards
Lemark
first person to state that organisms change over time, believed that one would acquire a characteristic and pass it onto their kid
59
New cards
pH
used to measure the acidity of a solution. Also one of the two reasons an enzyme denatures
60
New cards
Conjugation
Passing DNA between each other with a really long tube (sex pilus). Doesn’t make a new cell. Creates genetic variation
61
New cards
Competitive Inhibitor
interferes with substrate for active site
62
New cards
Binary Fission
Form of asexual reproduction for prokaryotes
(1→2→4→8, etc).
(1→2→4→8, etc).
63
New cards
Capsid
protein outer shell of virus
64
New cards
Protein
Things like amino acids and enzymes.
65
New cards
Behavioral Isolation
Signals that attract mates aren’t attractive
66
New cards
Exergonic
reaction that releases energy
67
New cards
sympatric speciation
new species evolves w/o geographic separation
68
New cards
Lipid
long term energy storage (fats)
69
New cards
Activation Energy
The amount of energy it takes to make a reaction (enzymes lower it)
70
New cards
Vestigial Structure
something your ancestors used that you have no use for (ex: appendix)
71
New cards
Directional Selection
one extreme is “selected”
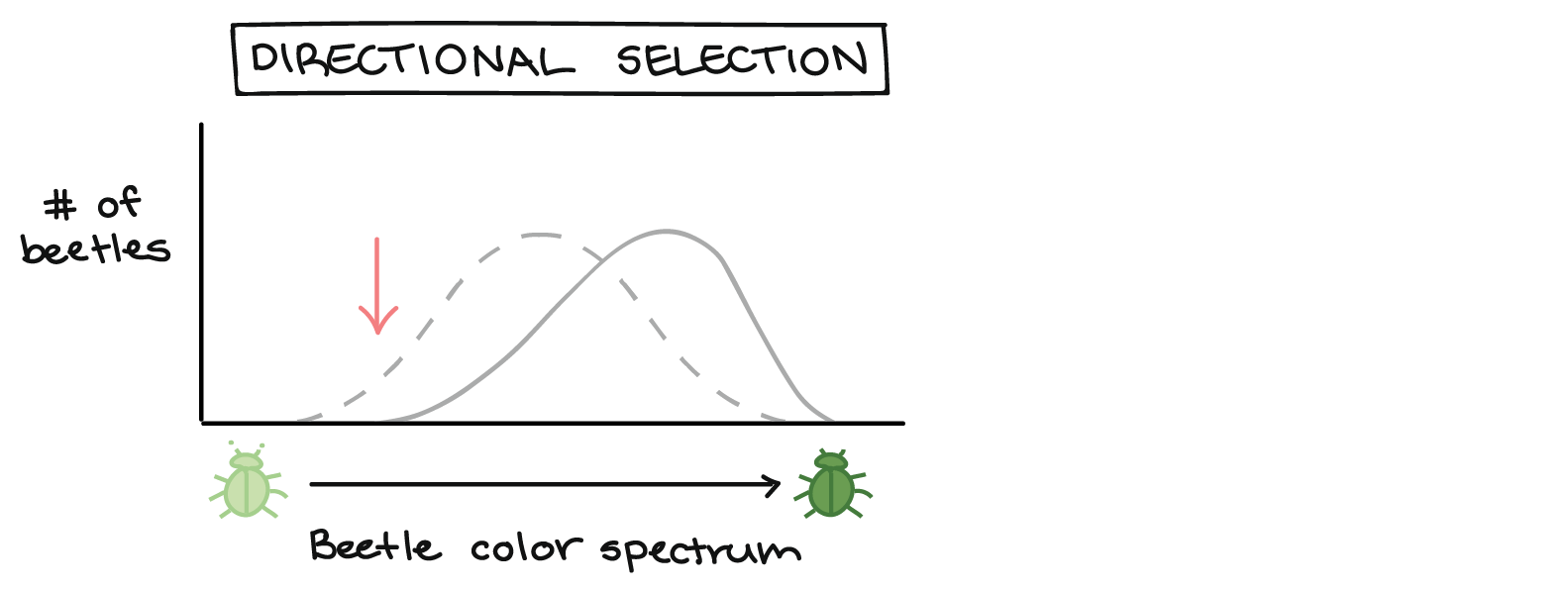
72
New cards
Transformation
Picking up random DNA in the environment
73
New cards
Homologous Structure
inherited from a common ancestor (ex: arms of all mammals)
74
New cards
Peptidoglycan
thing that makes up the cell wall. antibiotics love it
75
New cards
Genetic Drift
Random change due to chance (ex: if a brick fell out of the sky and kills the only blonde in a population, the population would lose the blonde gene)
76
New cards
Natural Selection
proposed by darwin as a mechanism of evolution
77
New cards
Capsule
helps prokaryotic cells stick to stuff
78
New cards
Noncompetitive Inhibitor
binds elsewhere on enzyme causing a shape change in the active site so that the enzyme can’t bind to the substrate
79
New cards
Biochemical Evidence
organisms that use the same basic biochemical molecules
80
New cards
Constant
Something that never changes in an experiment
81
New cards
\