Structural Oraganisation in Animals
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What are tissues?
Tissue are a group of similar cells having the same origin and performing a specific function.
study of tissues
histology
coined the term tissues?
in plants: N.Grew
in animals: Bichat
4 types of animal tissues?
Epithelial Tissues
Connective Tissues
Muscular Tissues
Nervous/ Neural Tissues
2 types of epithelial tissues
simple epithelial tissues (one single layer)
compound epithelial tissues(multiple layers)
types of simple Epithelium?
Squamous Epithelium
Cuboidal Epithelium
Coulumnar Epithelium
Ciliated Epithelium
Pseudostartified Epithelium
Glandular Epithelium
Characteristic of Epithelium?
Epithelium is made up of one of more layers of cells that covers or lines the external and internal surfaces of various body parts.
Structure of Epithelium
variously shaped cells
arranged closely
little intercellular material
has a basment mebrane
what is basment membrane?
Epithelium usually lies on a noncellular basment membrane which provides:
elastic support
supplies nutrients and O2 from C.T. to above lying C.T
It has two parts:
Basal Lamina : Outer thin layer (near epithelial cells)
Fibrous or Reticular Lamina: Inner thicker layer.
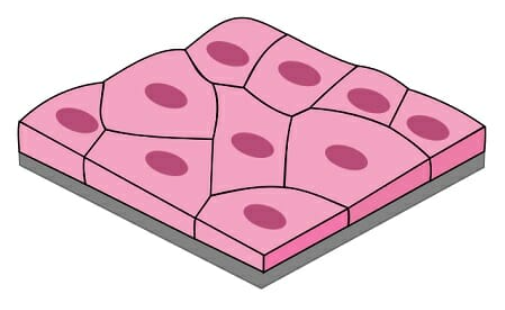
Structure of Simple Squamous Epithelium Tissue
thin layer
flattend cells
closely fitted cells
polygonal shape
flat and central buldge nucleus
Location of Simple Squamous Epithelium Tissue
innermost linning of blood vessles(endothelium)
air sacs (alveoli) of lungs (pneumocytes)
lymph vessles
ceolmic cavity
loop of henle and walls of bowans capsule of nephron
Functions of Simple Squamous Epithelium Tissue?
filtration
exchange of gasses
exchange of fluid materials between blood capillaries and tissue fluid
covering/ lining of organ

Structure of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Tissue
cube like
cental rounded nuclei
free surfaces may bear microvilli
Location of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Tissue
tubularpart of nephron
ducts in glands
thyroid follicle
gonads (germinal epithelium)
Functions of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Tissue
microvilli presnt is responsible for reabsorption of useful materials
secretion and excreation by glands
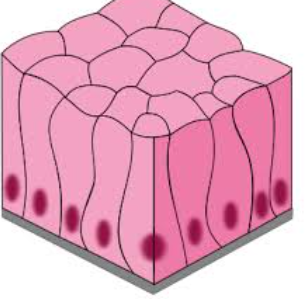
Structure of Simple Columnar Epithelium
tall and slender cells
nuclei is at base; elongated
may bear microvilli
may produce mucus- goblet cells
also contain underlying supporting connective tissue called mucus or mucosa membrane.
Location of Simple Columnar Epithelium Tissue
lining of stomach
lining of intestine
Function of Simple Columnar Epithelium
absorption
secretion
Structure of Ciliated Epithelium
bear cilia on their free surface
cilia can vary from few to numerous
the cilia remains in rythmic motion and create a current to transport the materials which come in contact with them.
Two types of Ciliated Epithelium
Ciliated Cuboidal Epithelium( e.g. bronchioles)
Ciliated Columnar Epithelium ( inner lining of hollow organs like fallopian tube)
Function of Ciliated Epithelium
move mucus or particles in a specific direction over the epithelium
in respiratory tarct responsible for expelling mucus and particles trapped in it towards pharynx.
in fallopian tube responsible for passage of ovum.
Structure of Psuedostratified Epithelium
columnar
unequal
goblet cells also occur
Location of Psuedostratified Epithelium
urethra of human male
large ducts of certain glands( salivary and partoid gland)
trachea and large bronchi
Location of Glandular Epithelium
unicellular - alimentary canal, goblet canal
multicellular - salivary, sweat,sebaceous lands
exocrine - gastric, intestinal, oil, mammary, tear
endocrine - adrenal.hypothalamus,pituitary,thyroid