ULTIMATE ANATOMY EXAM 2
1/1048
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
1049 Terms
above
spinal nerves C1-C7 pass ______ corresponding vertebrae
below
spinal nerves T1-S5 pass ______ corresponding vertebrae
C7 and T1
spinal nerve C8 passes through which two vertebrae?
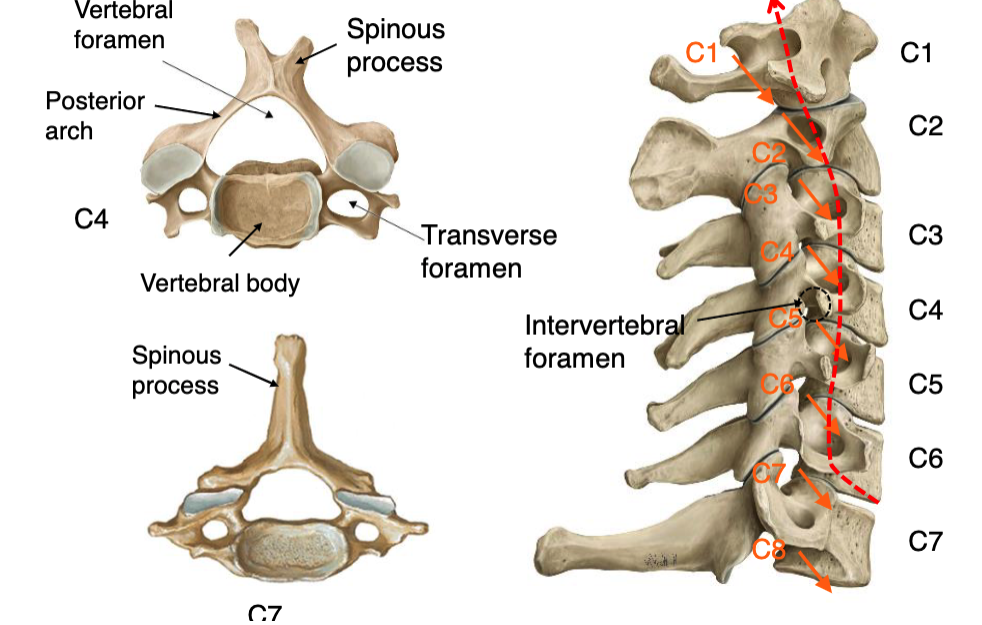
transverse foramen
the vertebral artery passes through what space in the vertebrae?
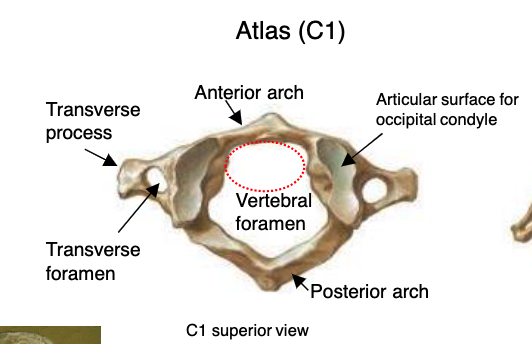
atlas (C1)
vertebrae that functions to support the skull
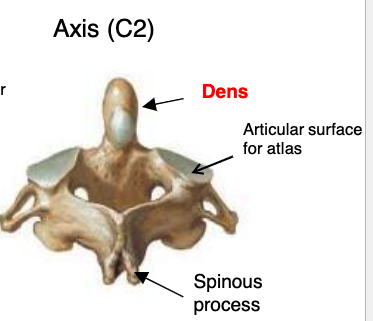
axis (C2)
vertebrae that functions to provide rotation on the head on the neck
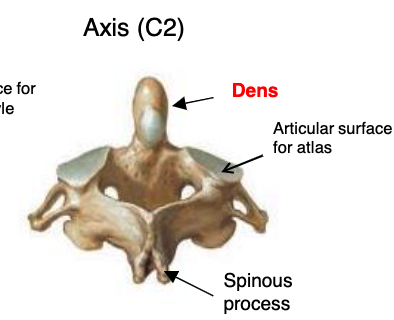
dens
what specialized structure allows for rotational movement of the head?
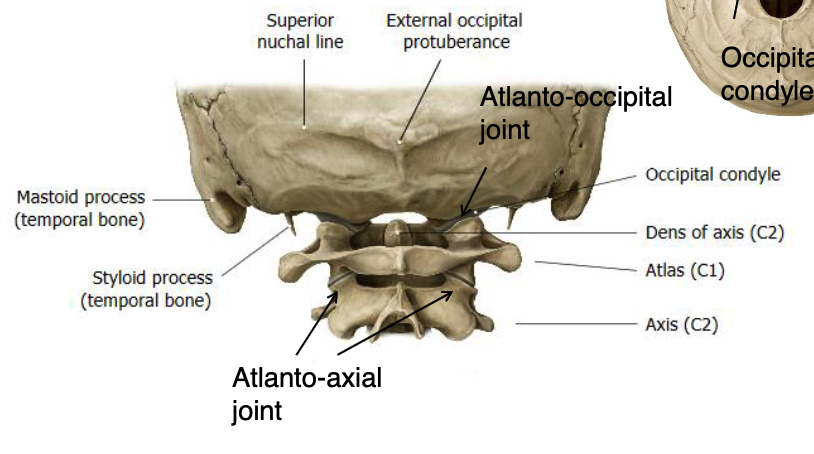
atlanto-occipital joint
joint primarily for flexion/extension and lateral bending of skull of C1:
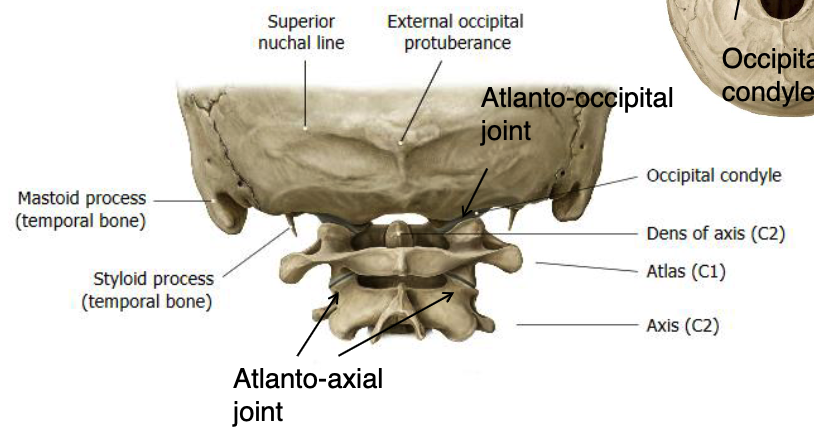
atlanto-axial joint
joint primarily rotation with some flexion/extension, lateral bending of C1 on C2
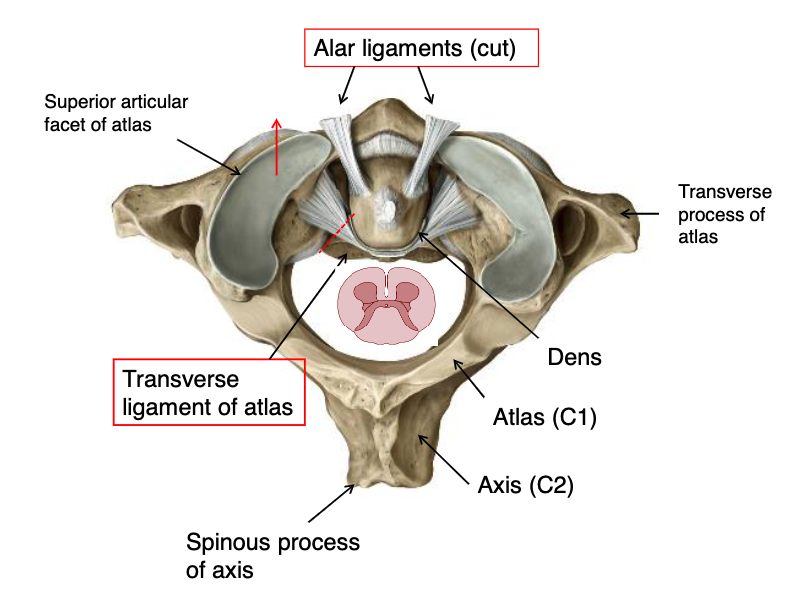
transverse ligament of atlas
what structure prevents anterior displacement of the skull and atlas together?
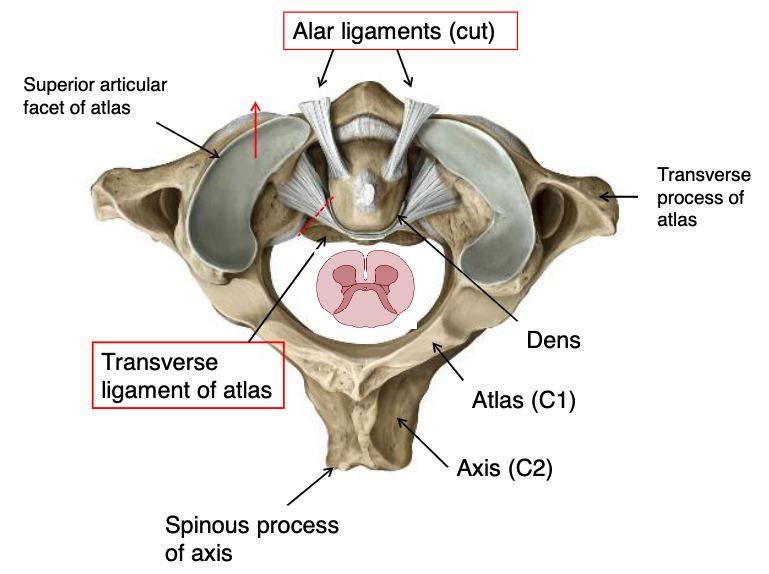
alar ligaments
what structure prevents excessive lateral rotation of the skull and atlas, attaches to dens and foramen magnum?
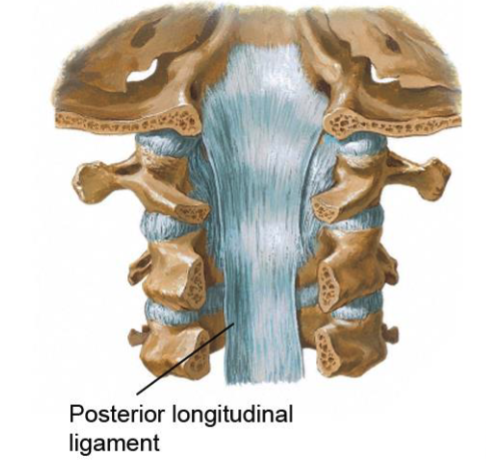
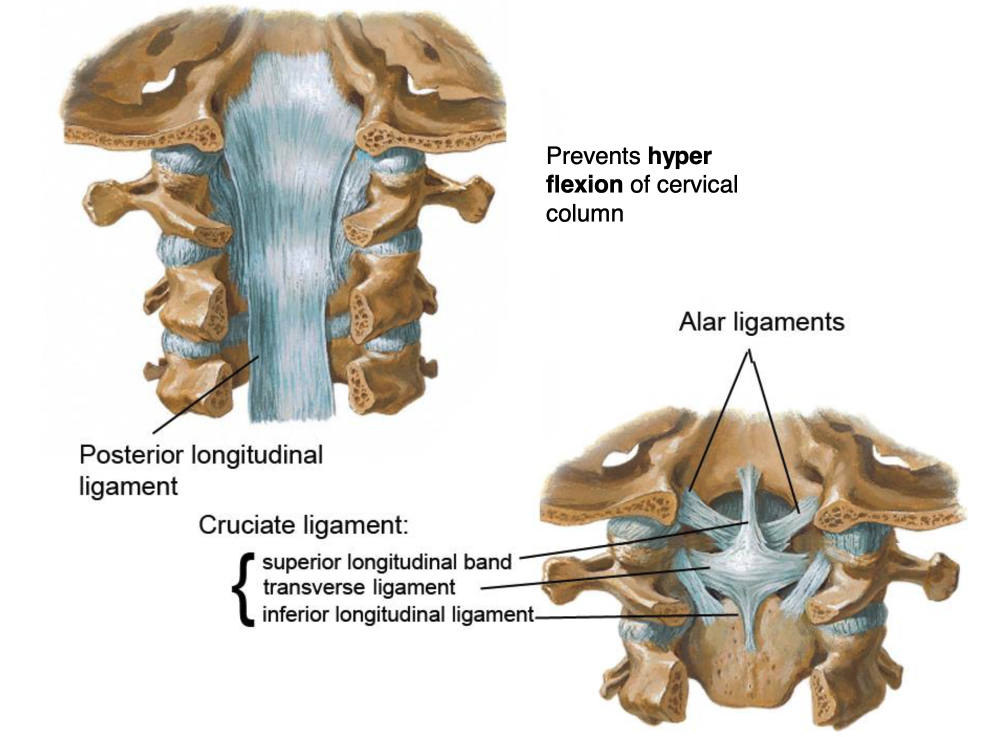
posterior longitudinal ligament
this structure prevents hyper flexion of cervical column:
posterior longitudinal ligament
Identify the structure.
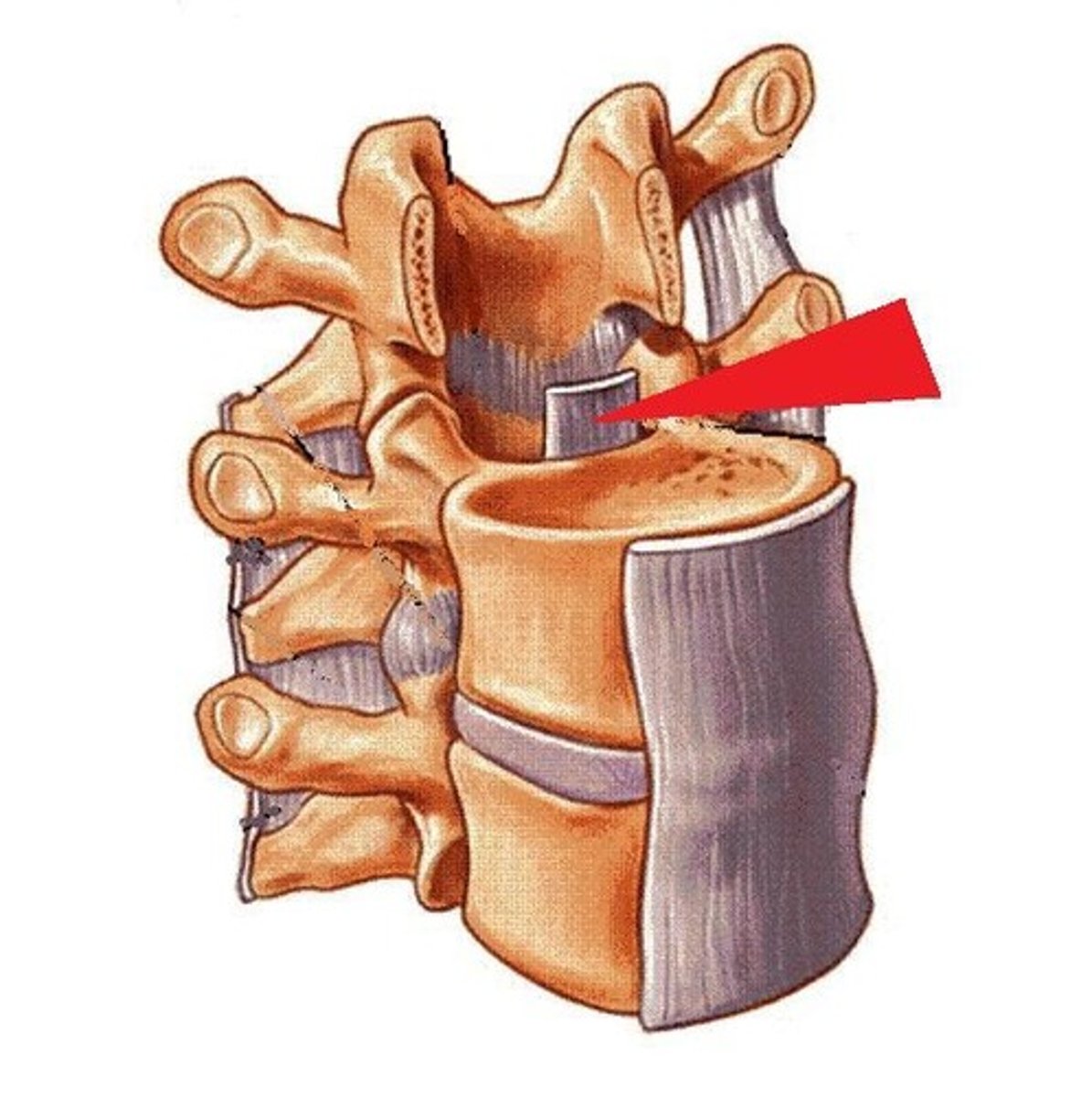
superior longitudinal band
inferior longitudinal band
transverse ligament
these three structures make up the cruciate ligament:
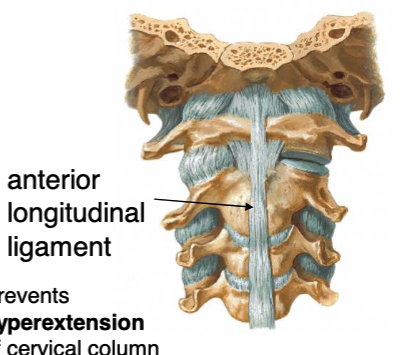
anterior longitudinal ligament
this structure prevents hyper extension of cervical column:
anterior longitudinal ligament
Identify the structure.
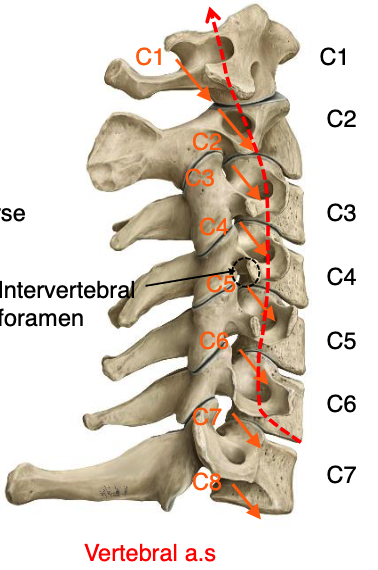
C1-C6
through which vertebrae does the vertebral artery run through transverse foramena
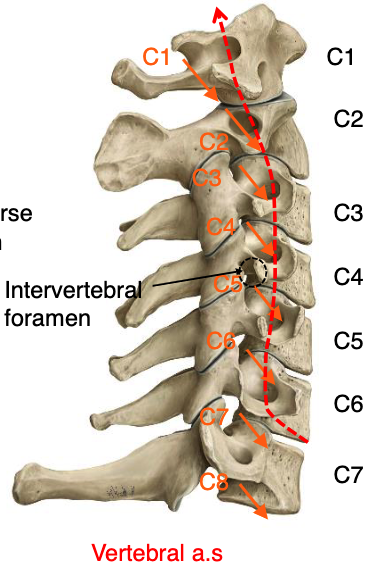
vertebral a.
what structure passes through the transverse foramena of vertebrae C1-C6?
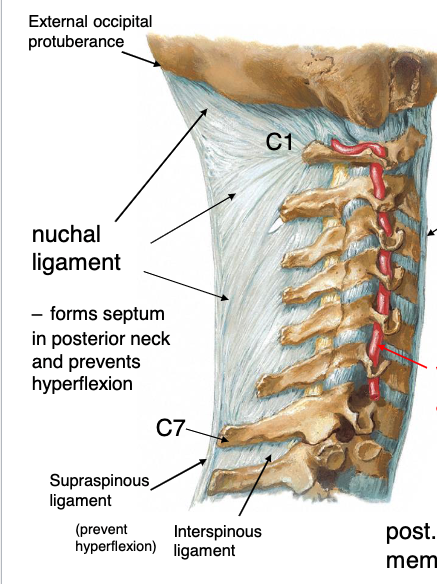
nuchal ligament
this structure forms septum in posterior neck and prevents hyperflexion, runs form external occipital protuberance to C7
nuchal ligament
Identify the structure
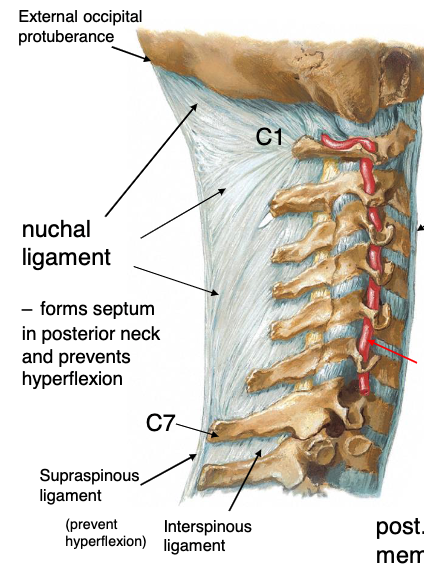
interspinous ligament
this structure replaces the nuchal ligament below C7 to connect the spinous processes:
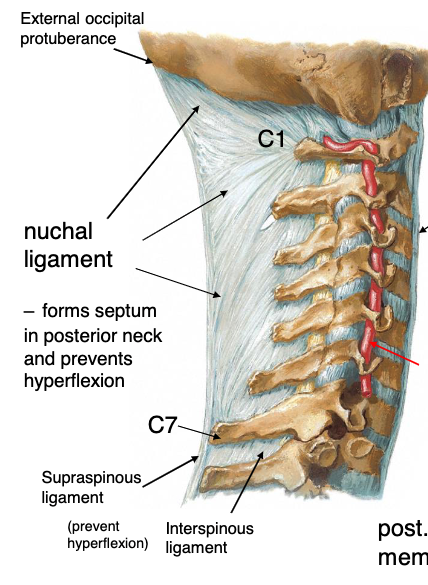
supraspinous ligament
this structure connects the tips of the spinous processes
supraspinous ligament
identify the structure
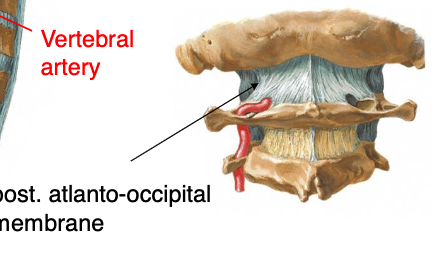
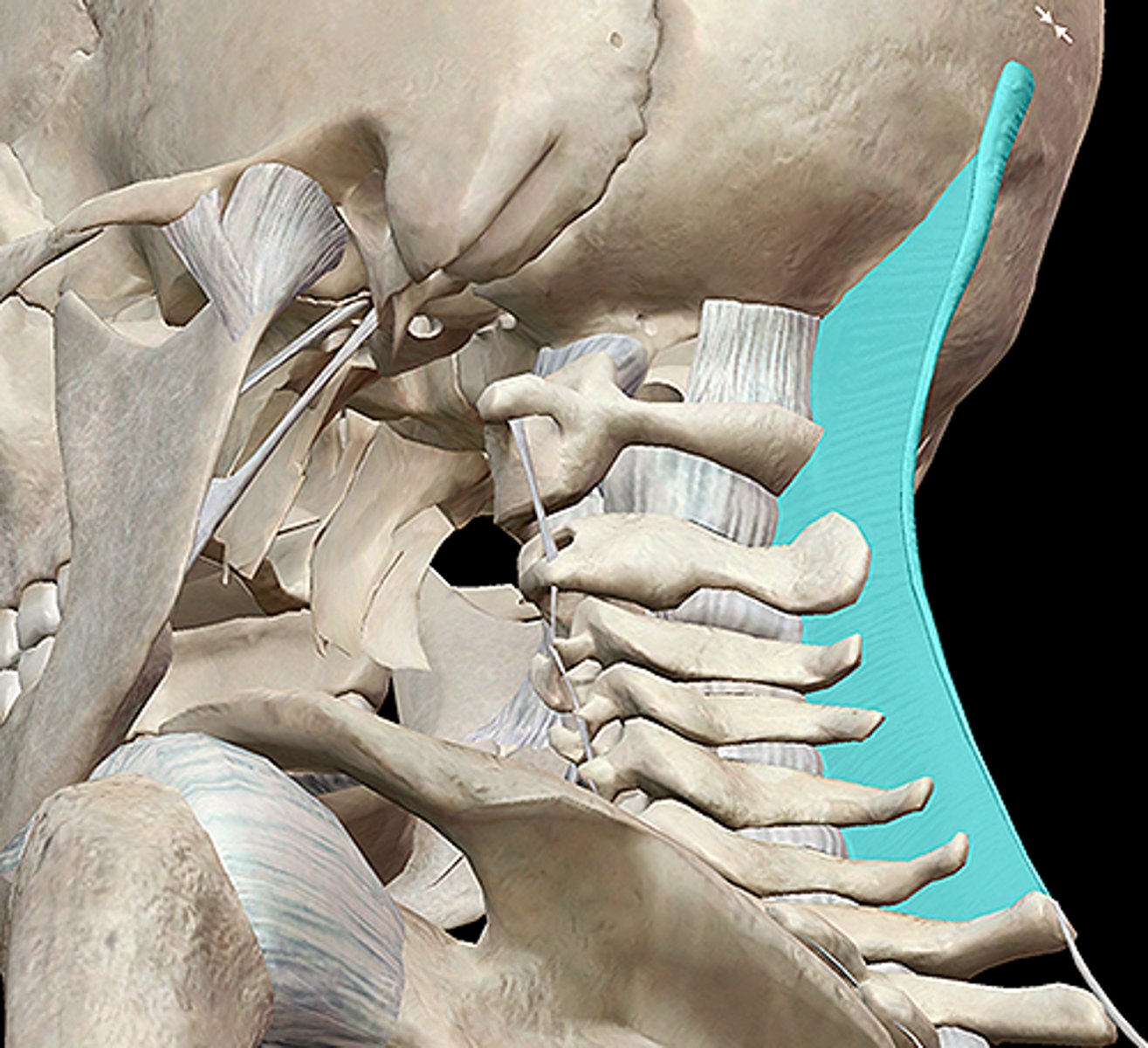
posterior atlanto-occipital membrane
the vertebral artery pierces what structure as it leaves the vertebrae and enters the skull?
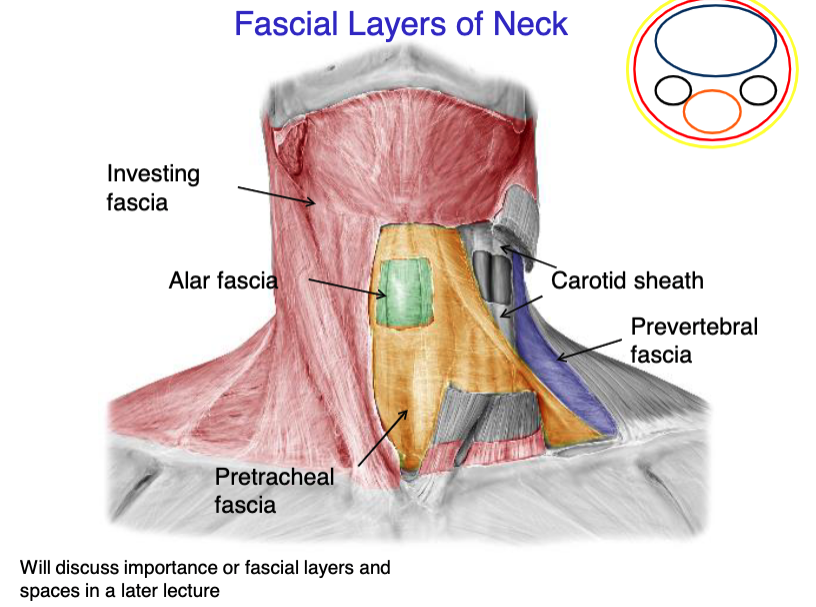
investing fascia
this fascial layer of the neck encloses the trapezius and the SCM
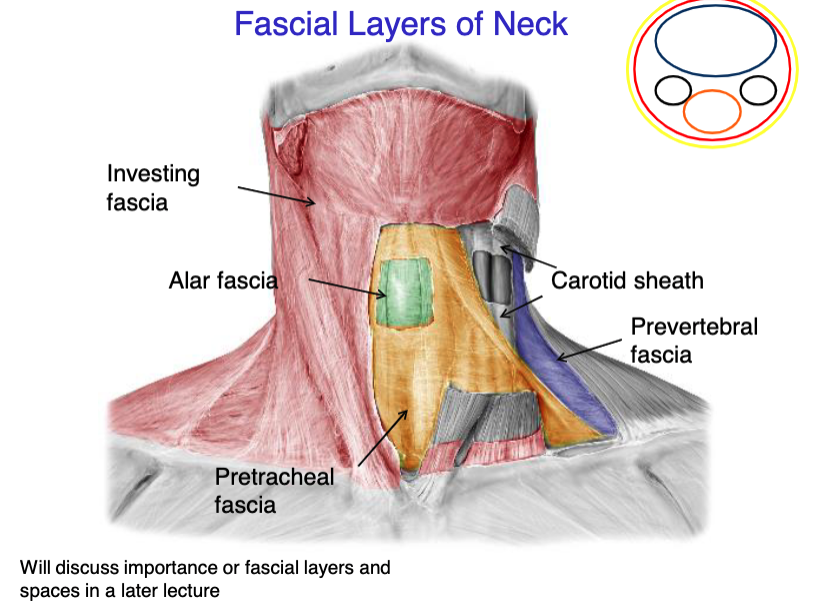
superficial fascia
this fascial layer of the neck encloses the platysma muscle
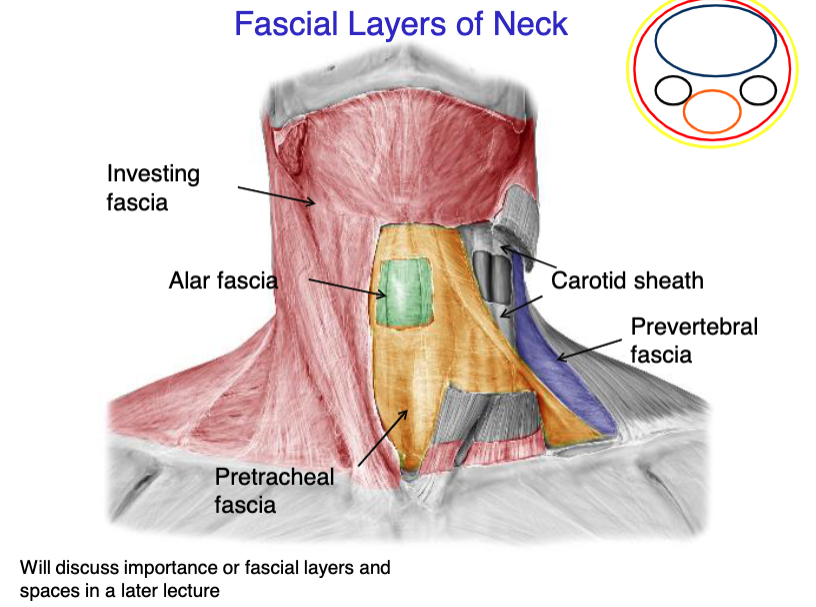
pretracheal fascia
this fascial layer of the neck encloses the trachea, thyroid, parathyroids and esophagus
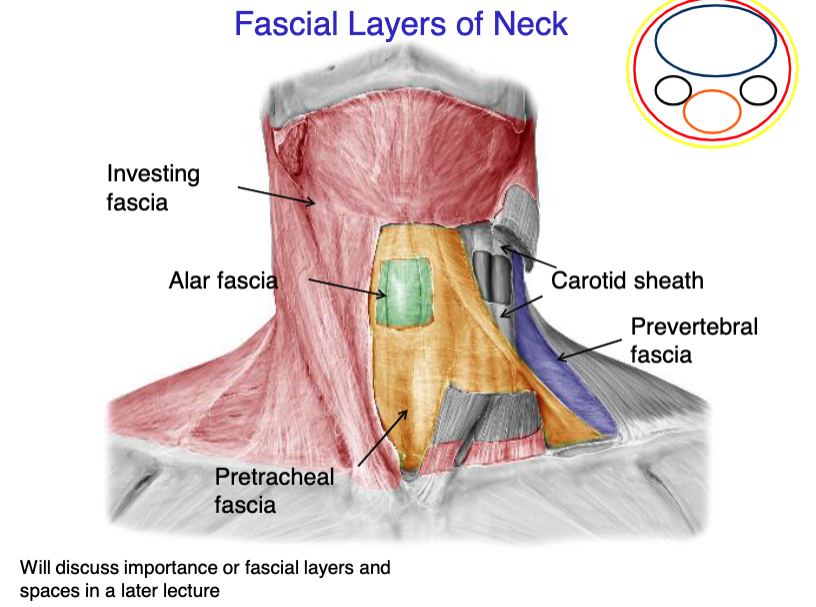
prevertebral fascia
this fascial layer of the neck encloses most of the muscles of the back (except trapezius), and the vertebrae
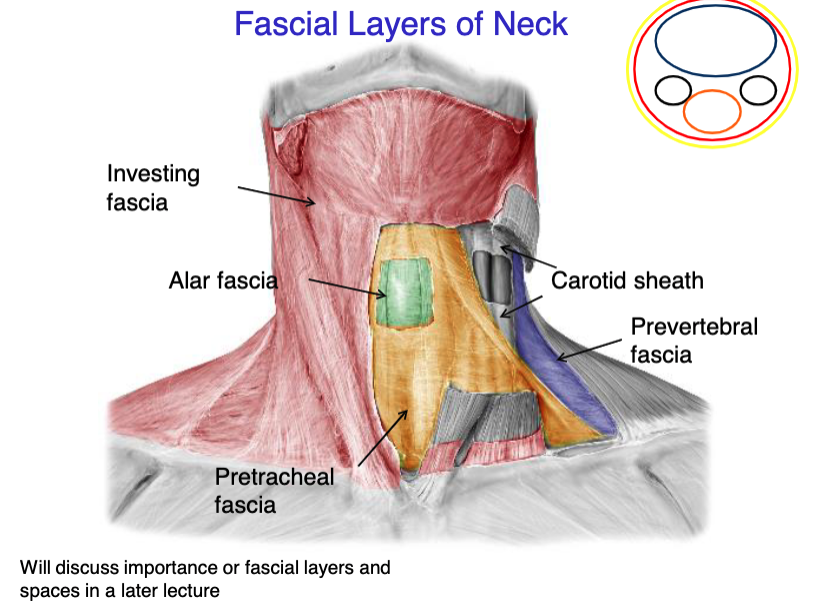
alar fascia
this fascial layer of the neck lays between the pretracheal and prevertebral fascia
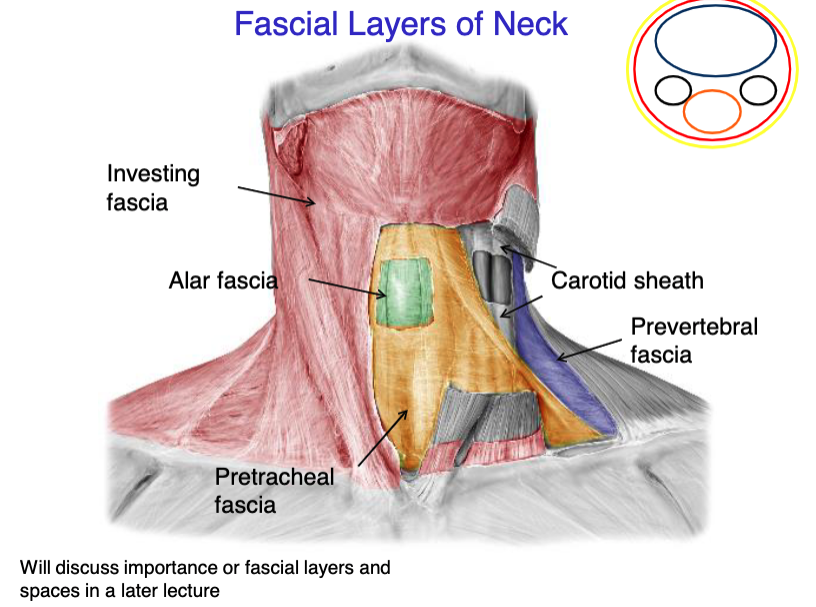
vagus nerve
internal jugular vein
common carotid artery
what 3 structures the the carotid sheath contain?
investing fascia
identify the fascial layer
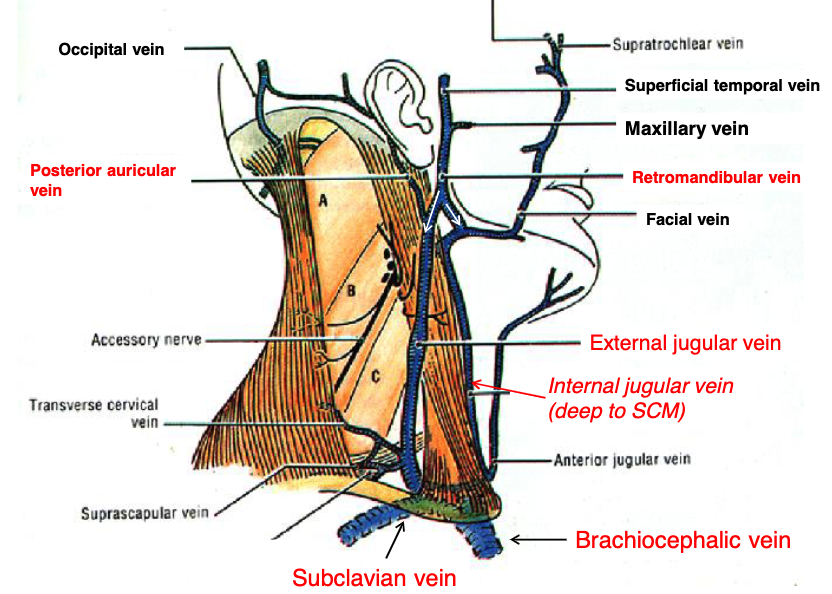
posterior auricular v.
retromandibular v.
what two veins join to form the external jugular vein?
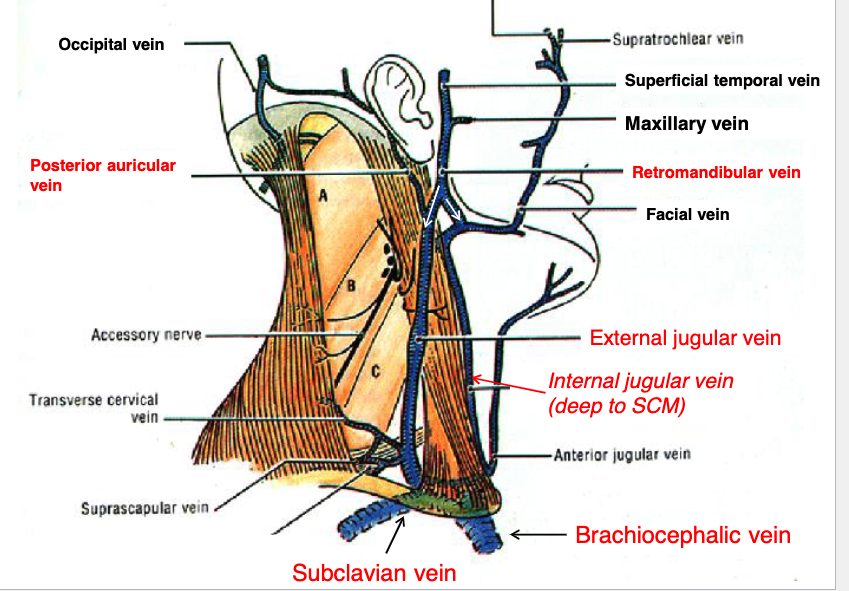
external jugular v.
the posterior auricular v. and retromandibular v. join to form the:
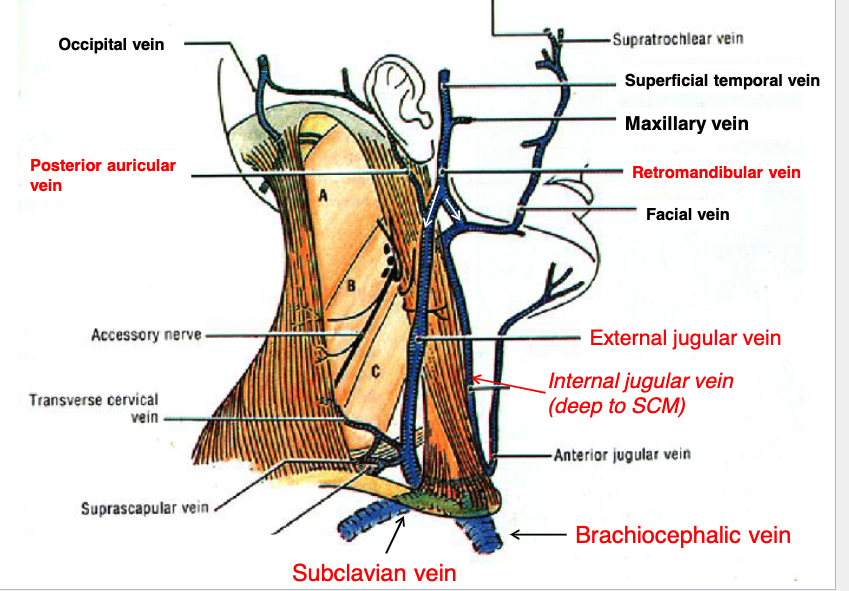
sublcavian v.
the internal and external jugular veins empty into what vein?
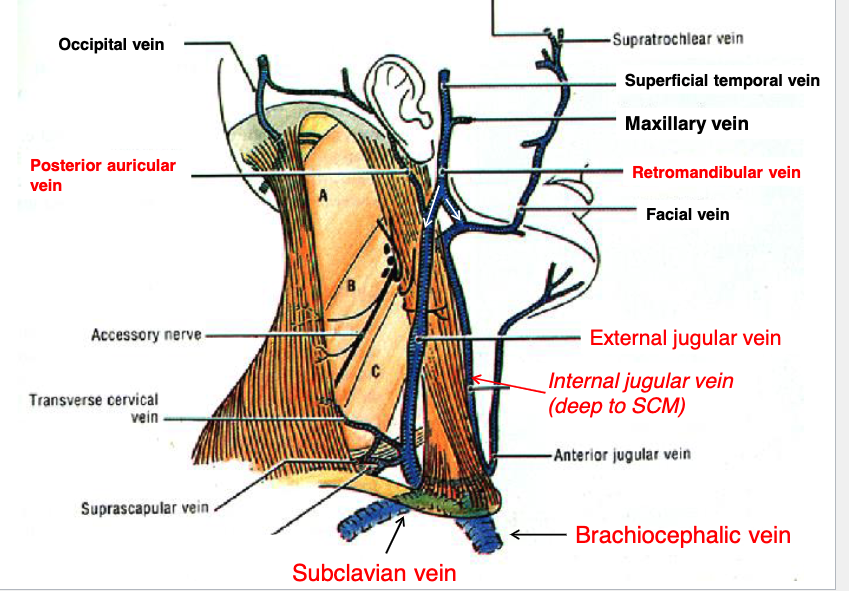
brachiocephalic v.
the subclavian vein drains into the:
sternocleidomastoid m.
what muscle runs in between the internal and external jugular veins?
external jugular v.
if a patient has a blockage of blood returning to the heart, clinically you may see distention of what structure?
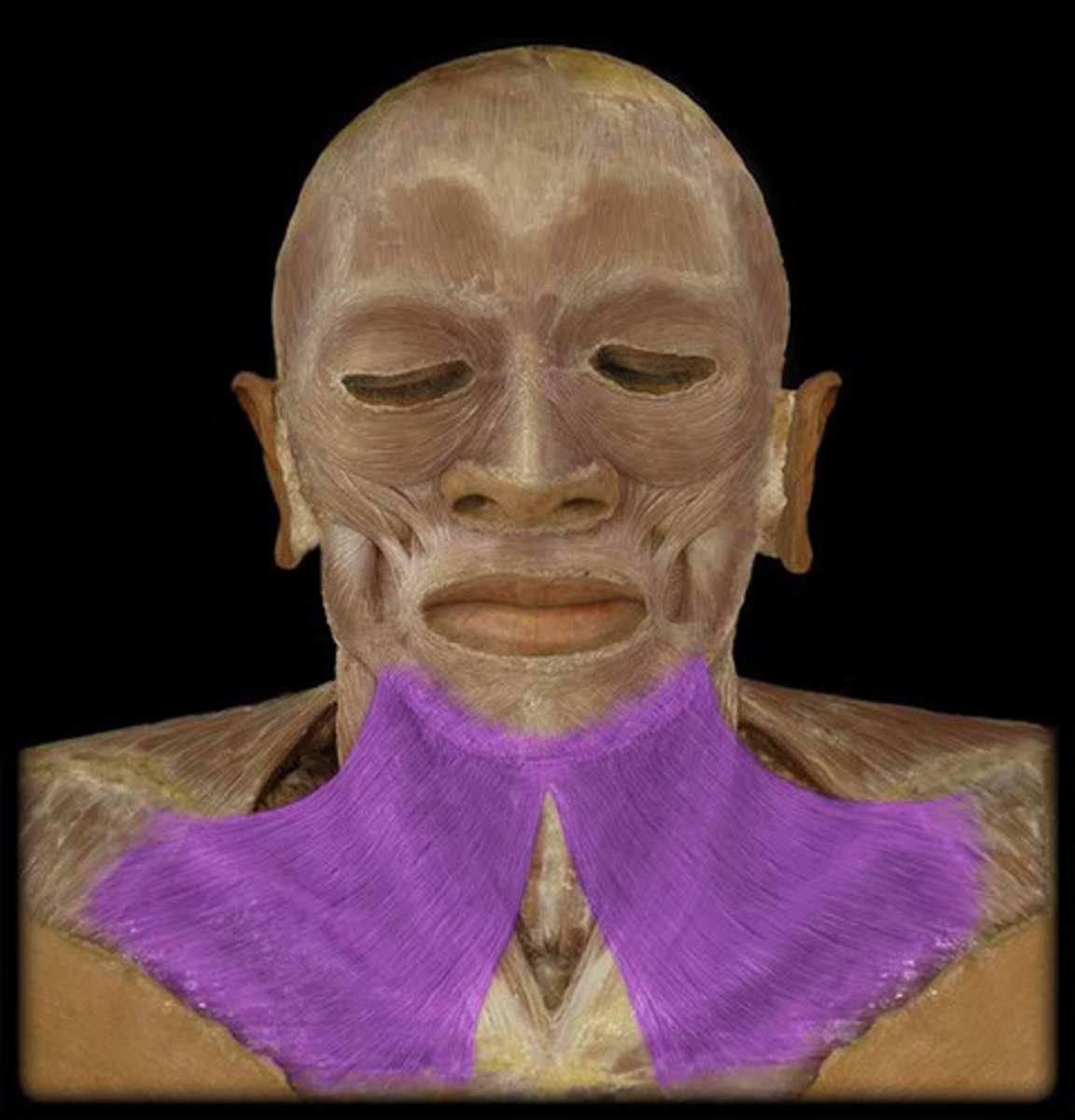
Depresses mandible, draws down the lower lip and the angle of mouth
Tenses skin in anterior neck
platysma m. action
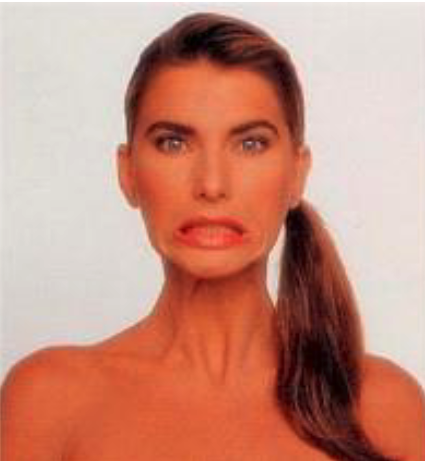

cervical branch of facial nerve (CN VII)
innervation for platysma m.
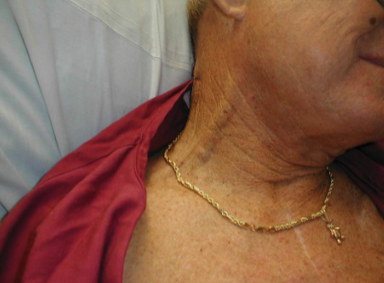
external jugular vein distention
diagnosis
platysma m.
identify the structure
spinal accessory nerve (XI)
innervation for the trapezius muscle:
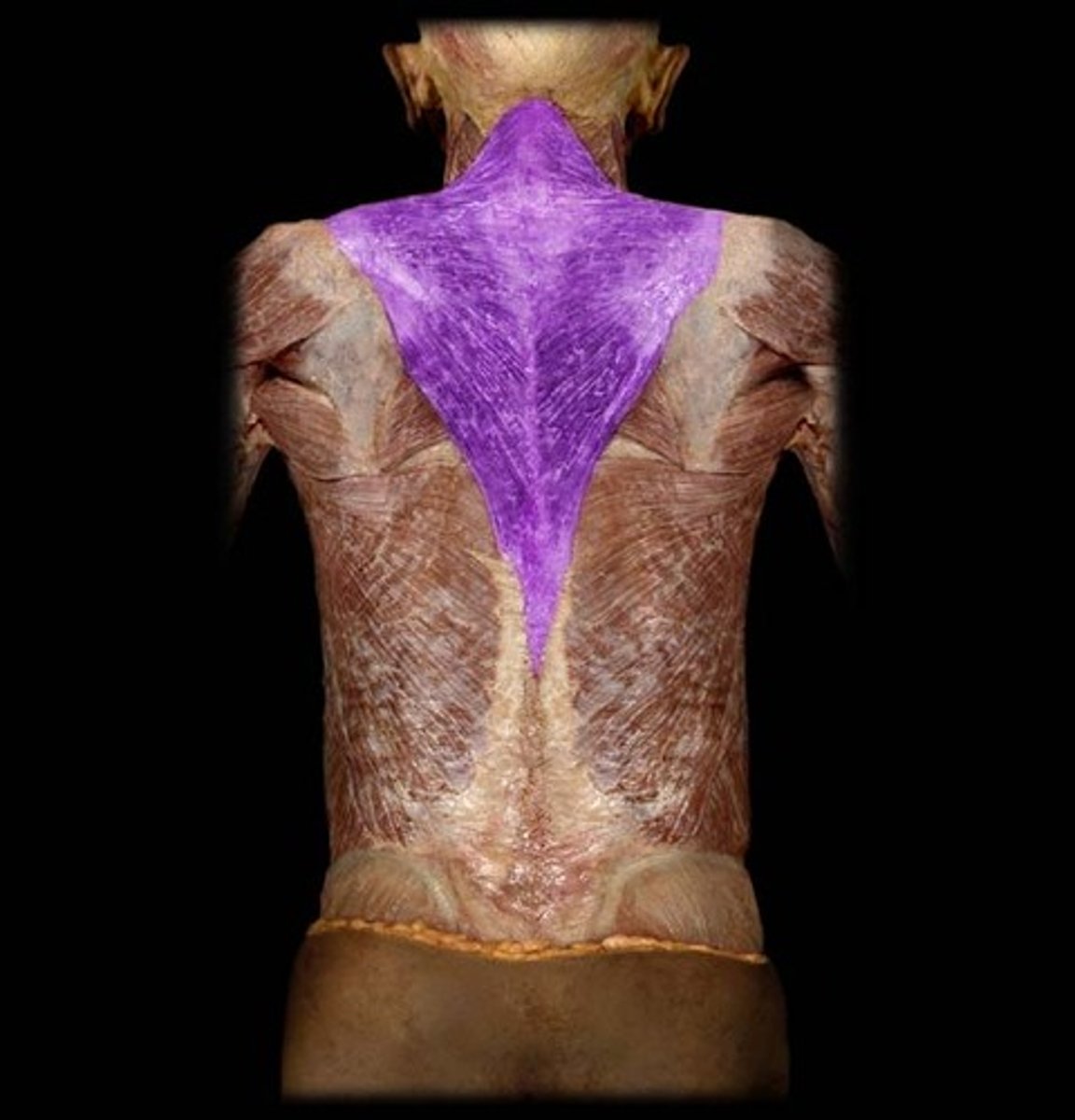
Superior part - elevates and upwardly rotates scapula
Middle part - retracts scapula
Inferior part - depresses and rotates scapula superiorly
trapezius m. action
trapezius m.
identify the structure
Both muscles acting together extend head at atlanto-occipital joint, and flex cervical part of vertebral column
Contraction of one muscle moves the face to the opposite side
sternocleidomastoid m. action
sternocleidomastoid m.
identify the structure
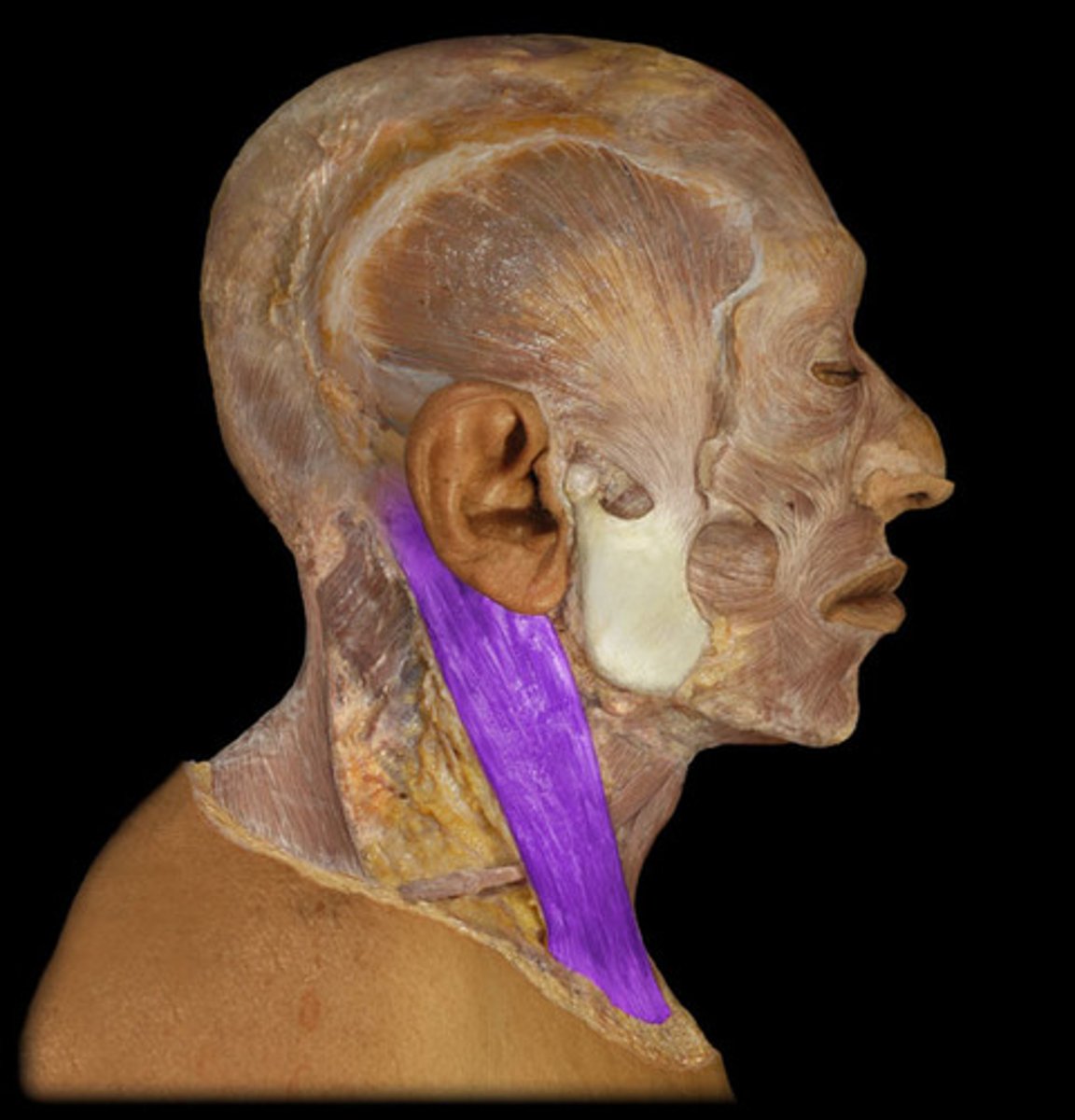
motor: spinal accessory n.
innervation for the sternocleidomastoid muscle:
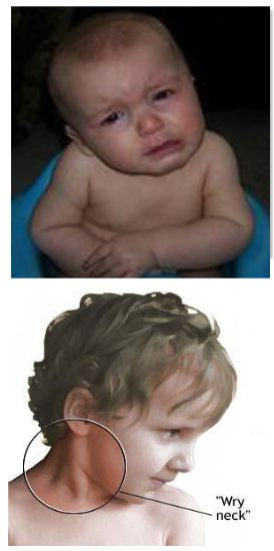
sternocleidomastoid m. (one side becomes shorter than opposite side)
Torticollis or 'twisted neck" or “wry neck” is a result of injury of what muscle?
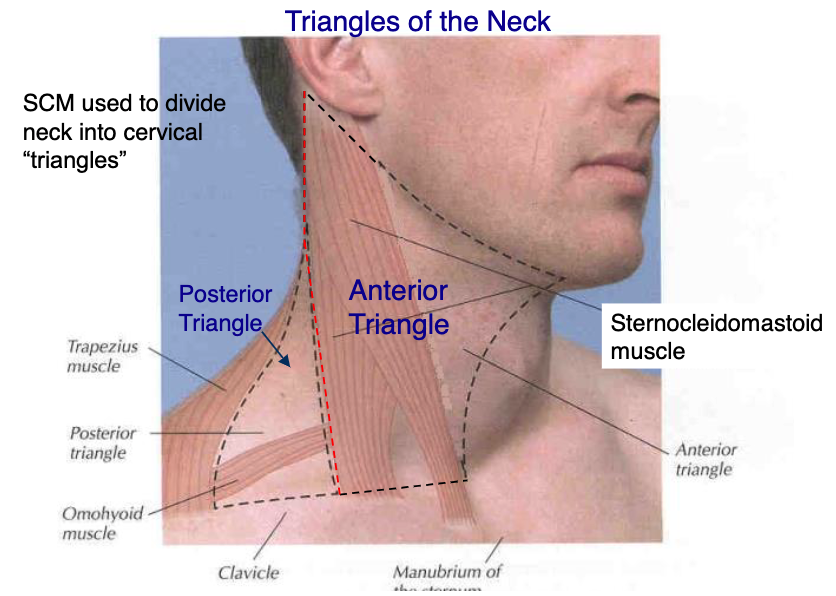
posterior border of sternocleidomastoid
what structure makes the anterior boarder of the posterior triangle?
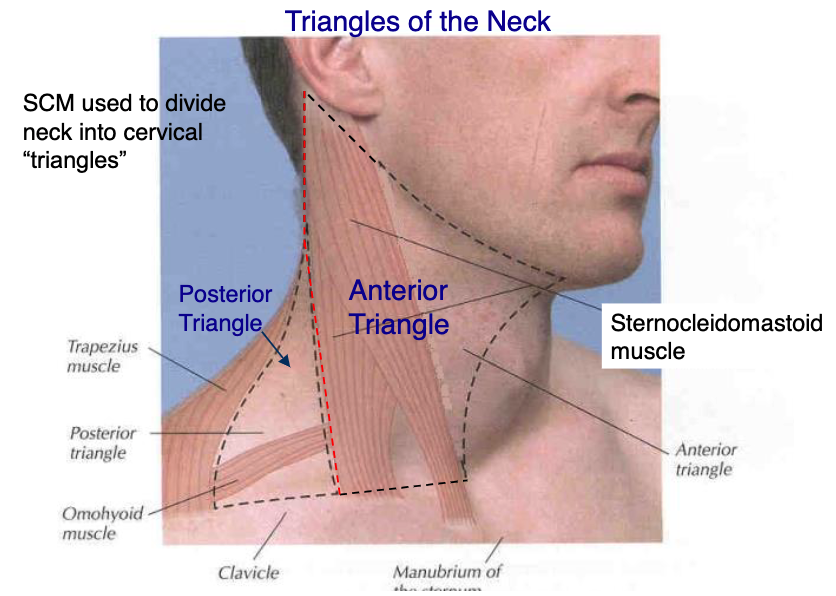
anterior boarder of trapezius
what structure makes the posterior boarder of the posterior triangle?
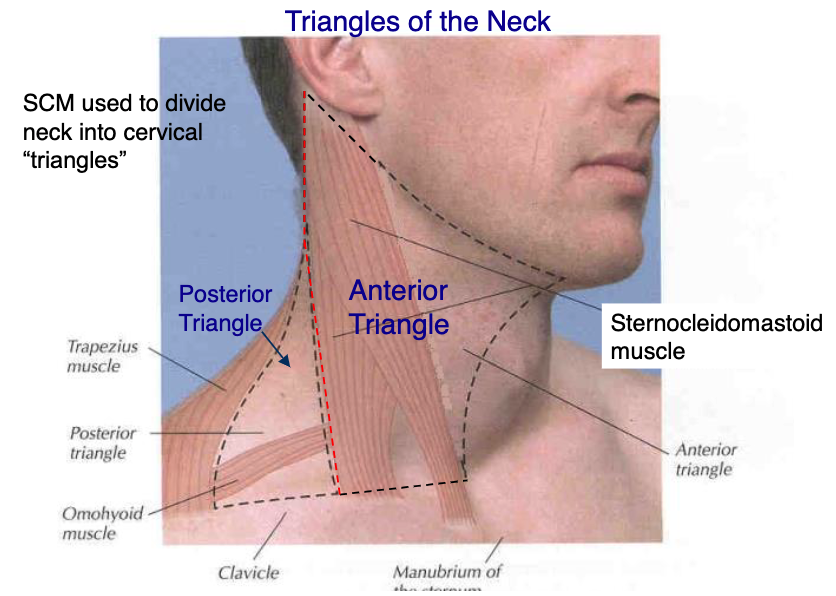
clavicle
what structure makes the inferior boarder of the posterior triangle?
investing fascia
what fascial layer makes the roof of the posterior triangle?
prevertebral fascia
what fascial layer makes the floor of the posterior triangle?
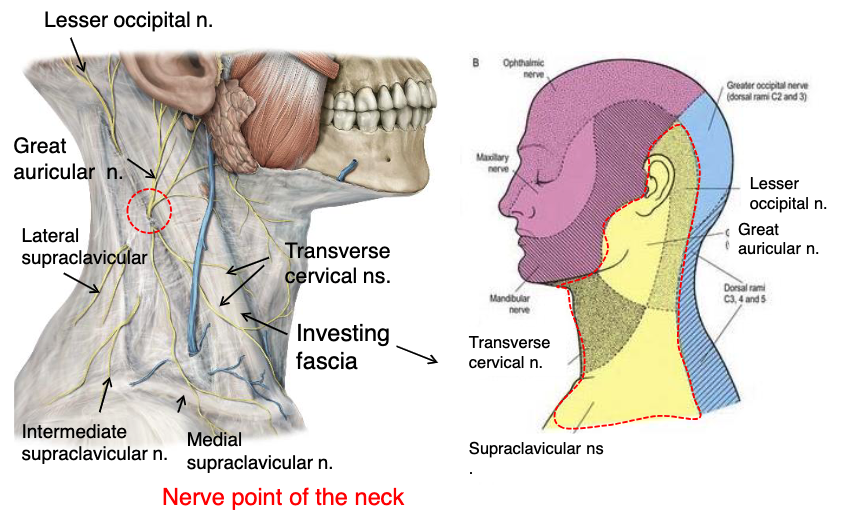
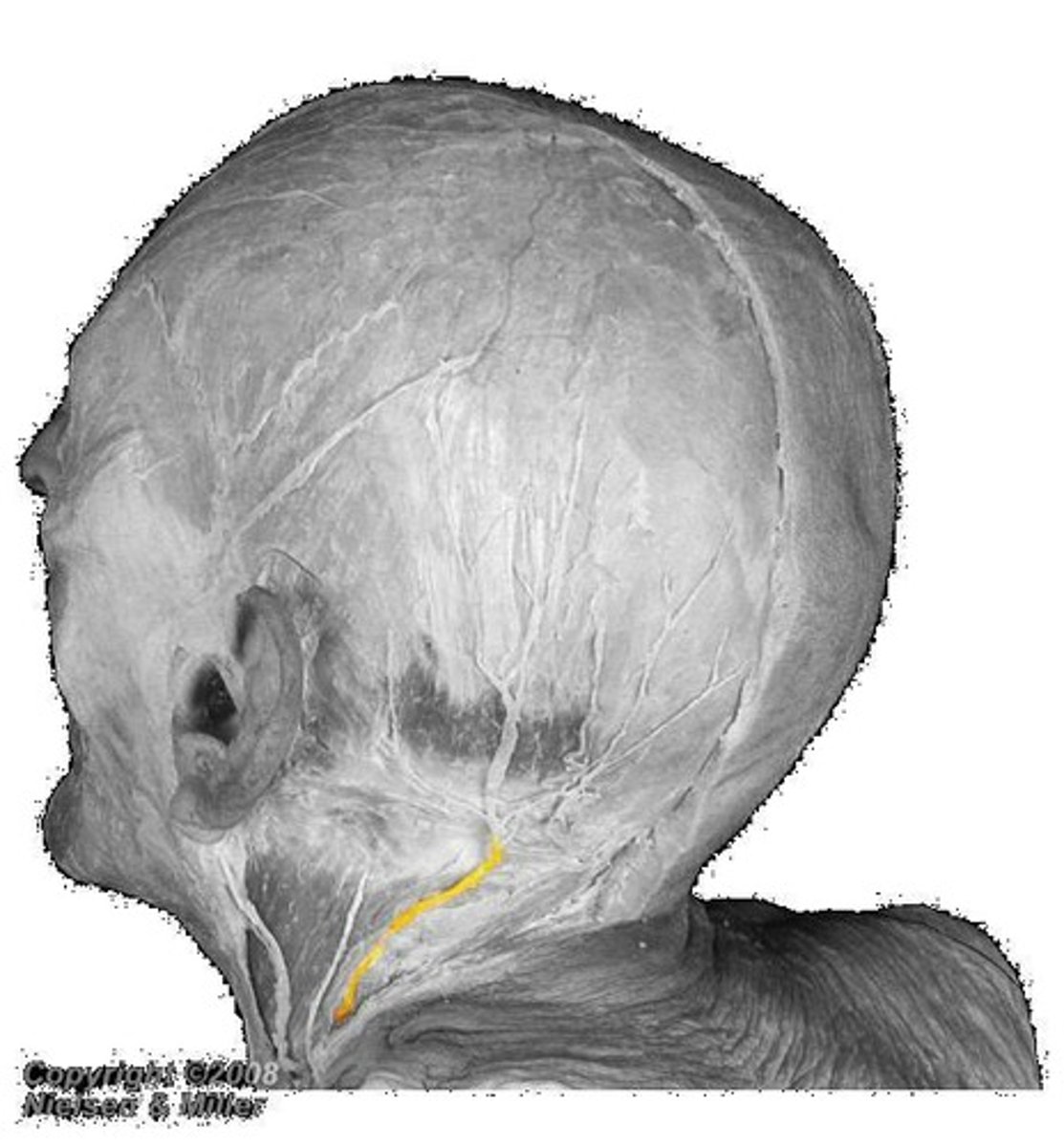
lesser occipital n.
what innervates the cutaneous surface behind the ear?
lesser occipital n.
identify the structure
great auricular n.
identify the structure
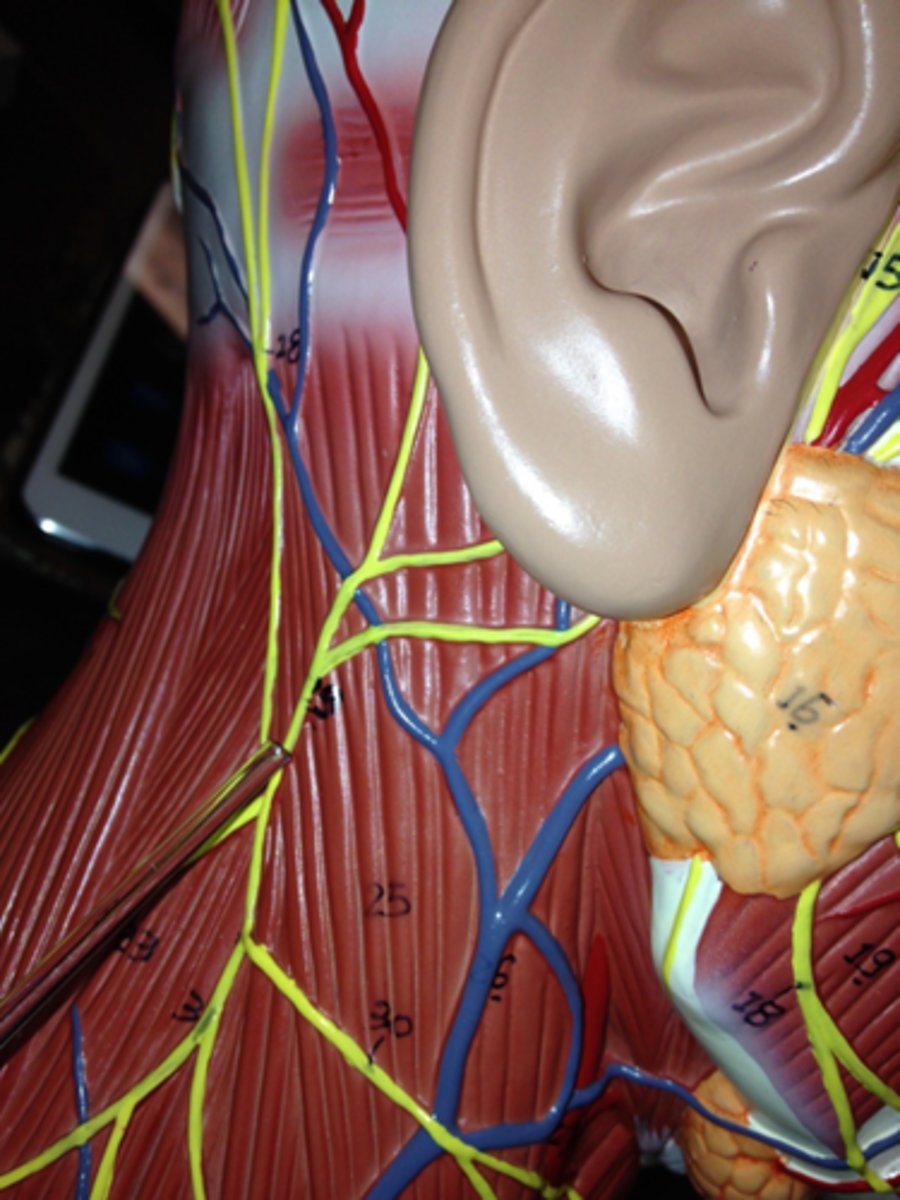
transverse cervical n.
identify the structure
supraclavicular n.
identify the structure
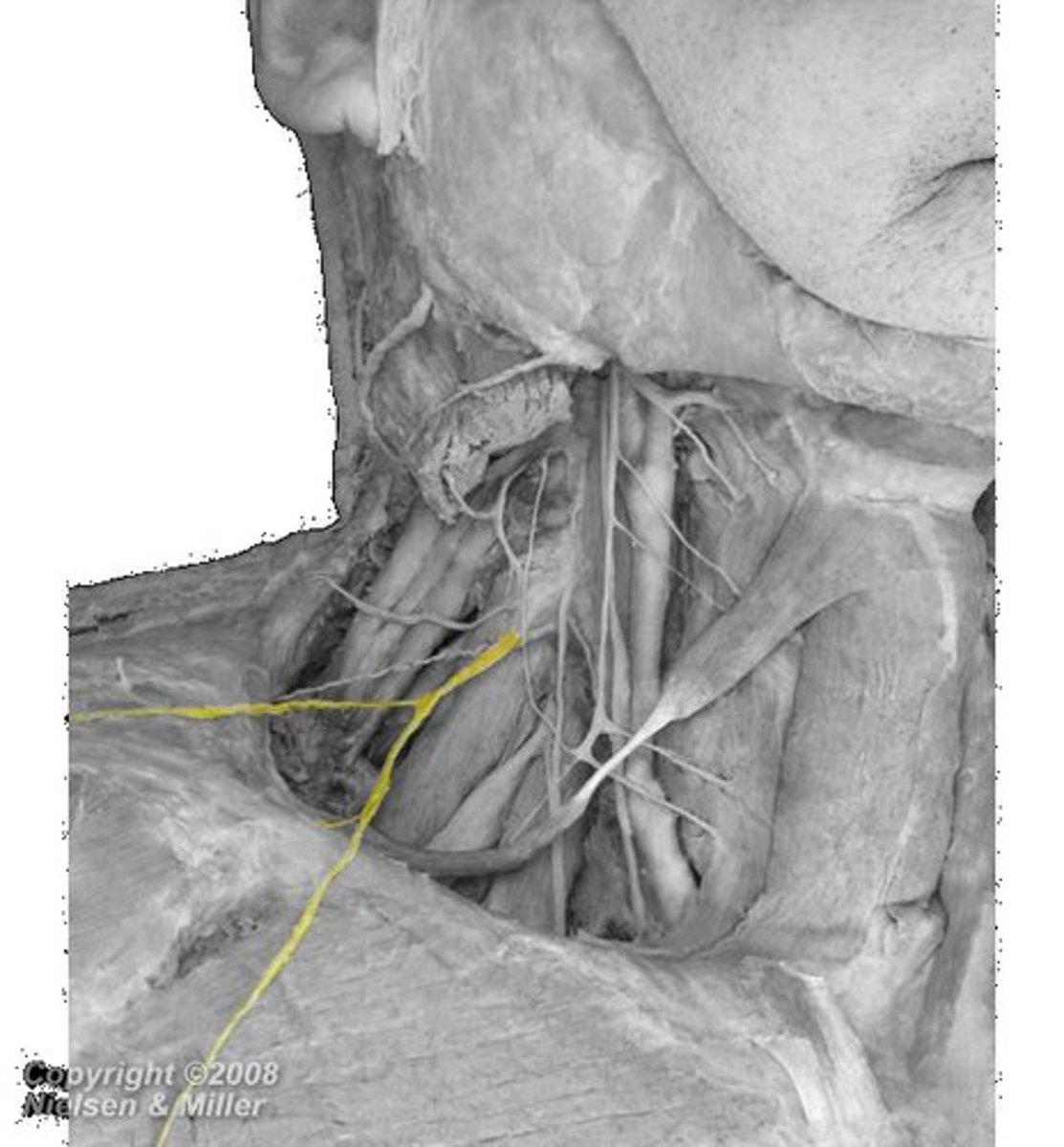
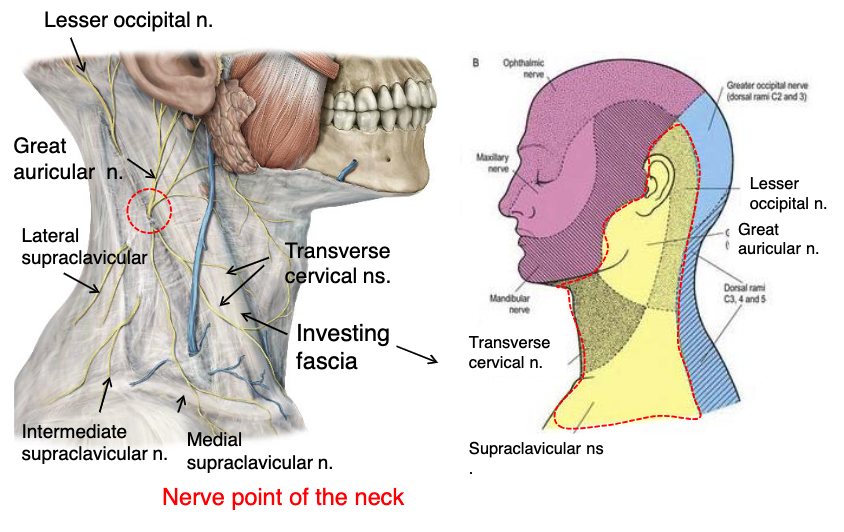
great auricular n.
what innervates the cutaneous surface covering the ear down to the mandible?
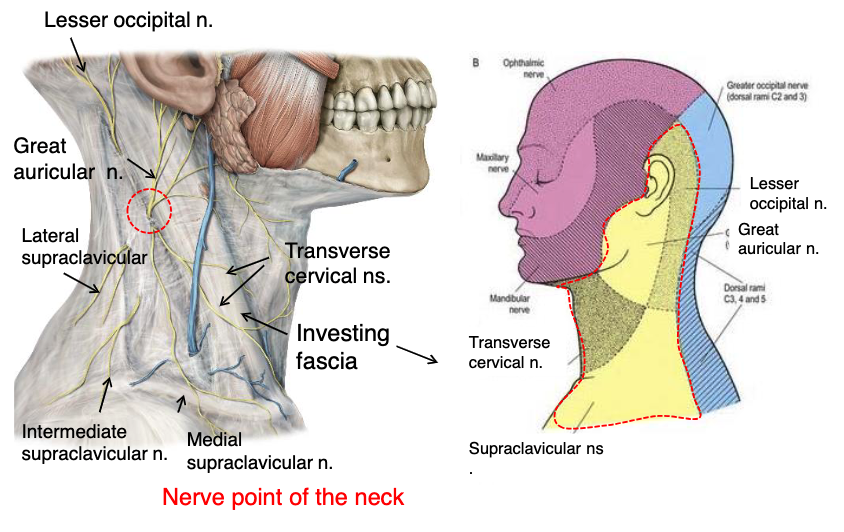
transverse cervical n.
what innervates the cutaneous surface covering the anterior triangle of the neck?
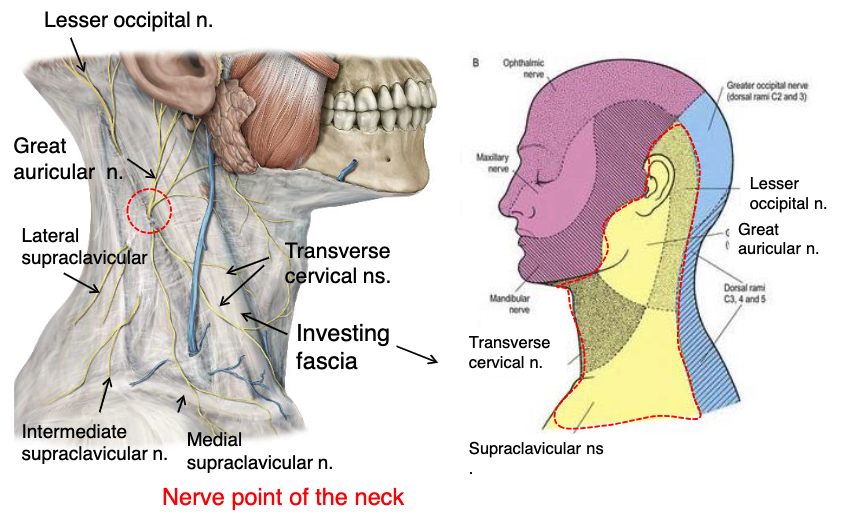
posterior border of sternocleidomastoid
where is the location of the nerve point of cervical plexus that emerges from the posterior triangle?
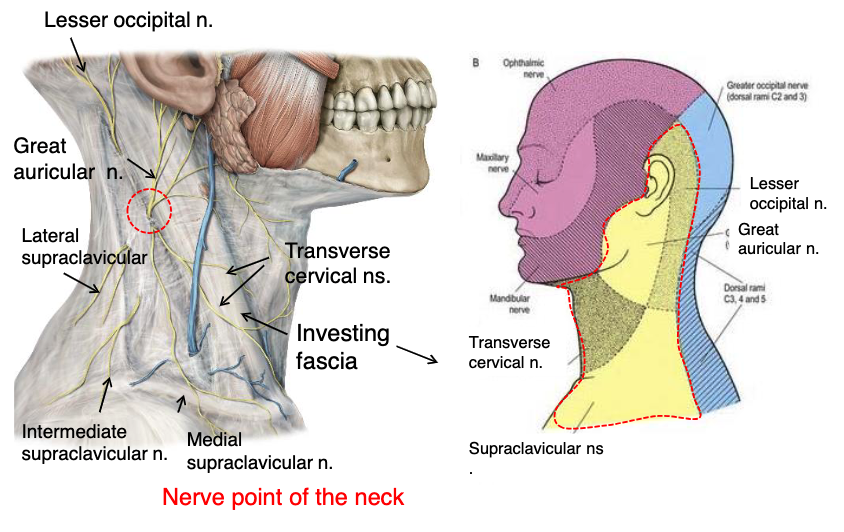
lesser occipital n.
great auricular n.
transverse cervical n.
supraclavicular n.
name the 4 nerves that emerge from the nerve point of the cervical plexus that emerges from of the posterior triangle:
posterior triangle
the nerve point of the cervical plexus is located in what triangle of the neck?
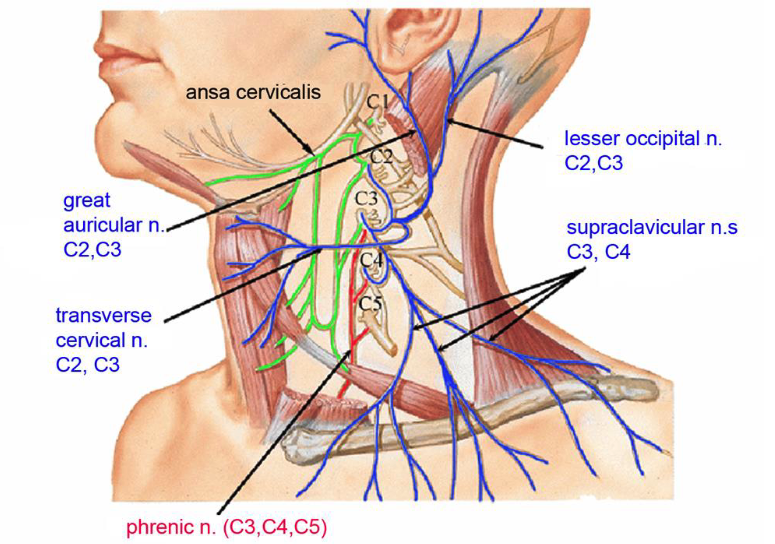
C1-C4
which spinal nerves make up the cervical plexus?
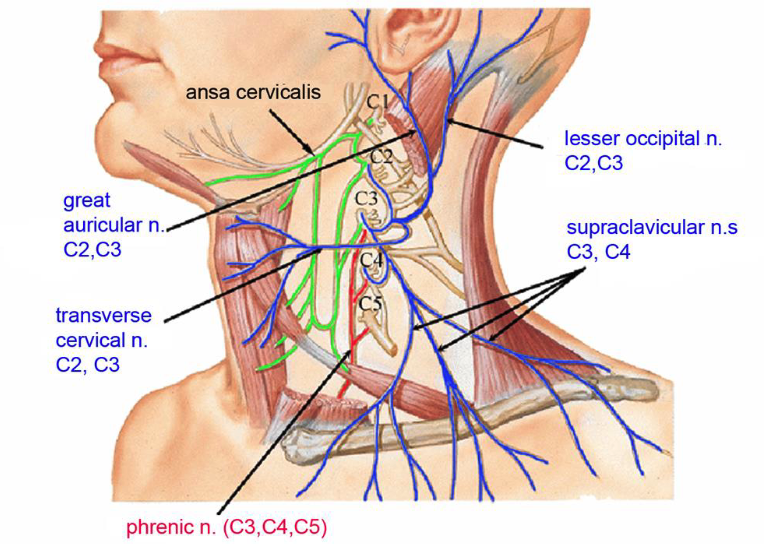
C2,C3
which spinal nerves originate the lesser occipital nerve?
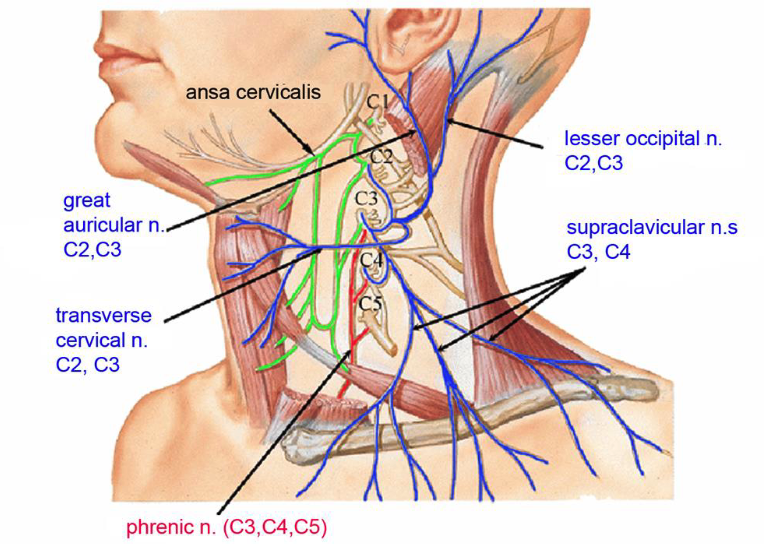
C2,C3
which spinal nerves originate the great auricular nerve?
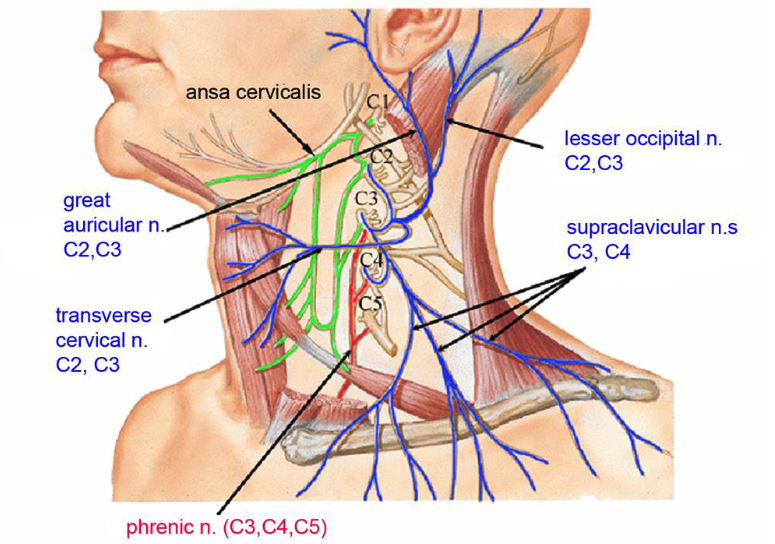
C2,C3
which spinal nerves originate the transverse cervical nerve?
C3,C4
which spinal nerves originate the supraclavicular nerve?
C3,C4,C5
which spinal nerves originate the phrenic nerve?
foramen magnum
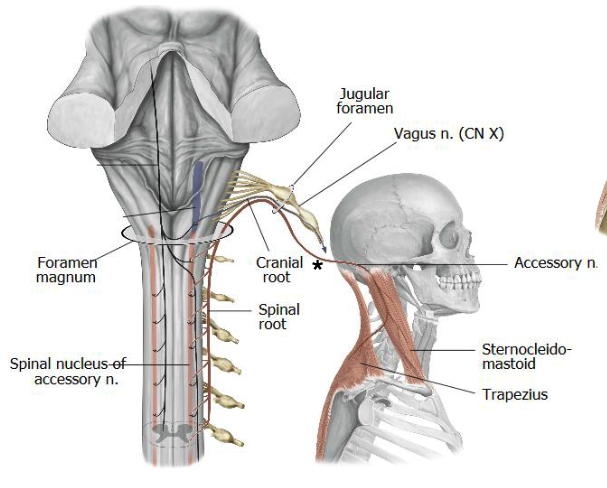
the spinal accessory nerves enters the skull via:
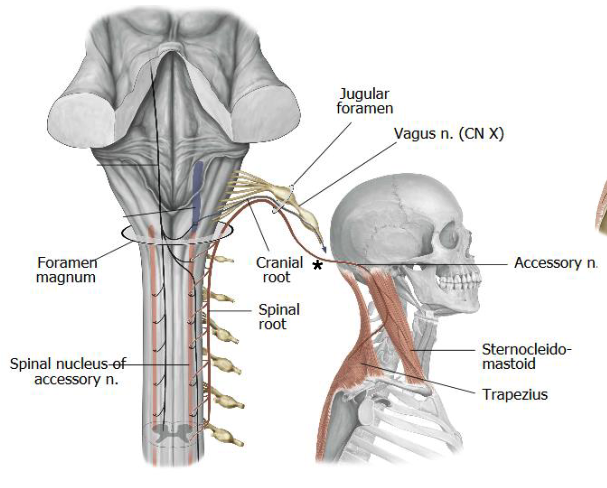
jugular foramen
the spinal accessory nerves exits the skull via:
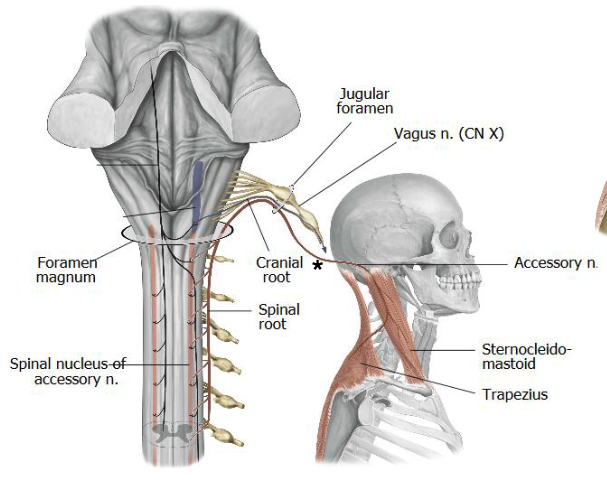
posterior triangle
from emerging from the jugular foramen, what must the spinal accessory nerve cross in order to innervate the trapezius muscle?
SCM and trapezius
what two muscles does the spinal accessory nerve innervate?
ventral
the cervical plexus originates from the _______ primary rami
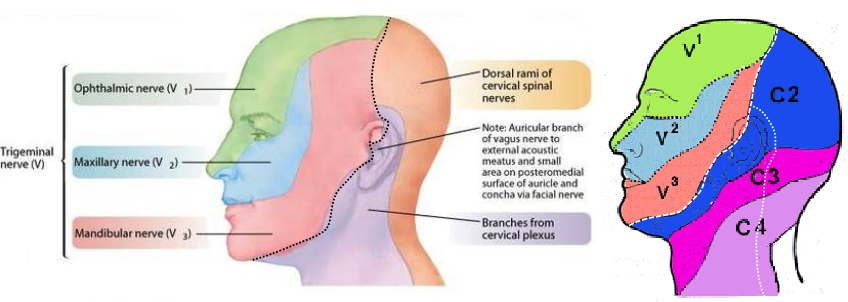
C1
which cranial nerve does not have an existing dermatome?
cervical plexus
what nerve network supplies the cutaneous surface neck, lower jaw and ear?
dorsal rami of cervical spinal nerves
what nerve network supplies the cutaneous surface posterior portion of the scalp and neck?
ventral rami of cervical spinal nerves C1-6
scalene muscles supplied by
trigeminal Nerve (CN V)
what nerve supplies the cutaneous surface of the anterior head and face?
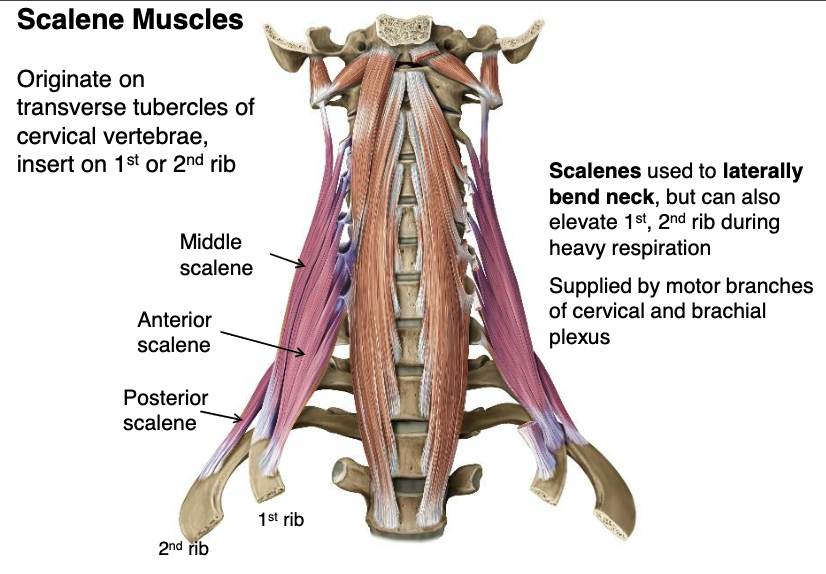
scalene mm.
what muscles originate from the transverse processes of cervical vertebrae used to laterally bend neck, but can also elevate 1st, 2nd rib during heavy respiration?
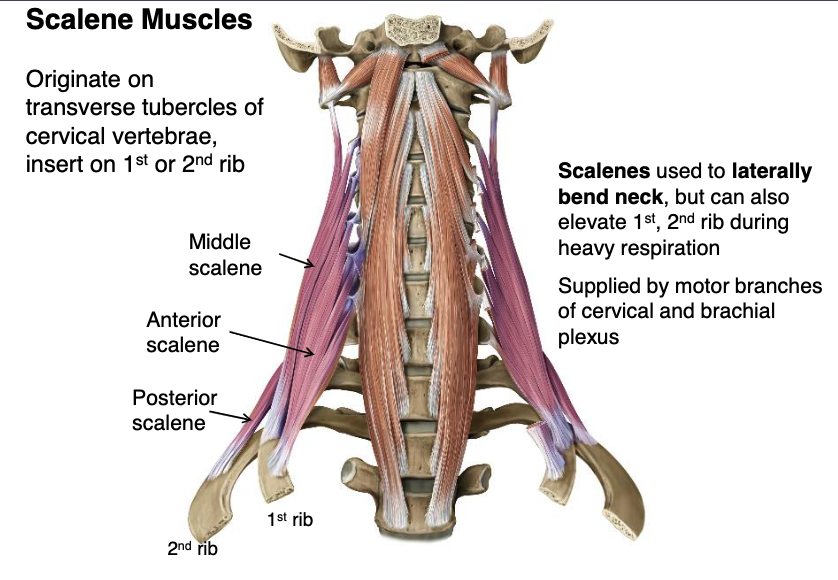
anterior and middle scalene mm.
which scalene muscles insert onto the 1st rib?
posterior scalene m.
which scalene muscles insert onto the 2nd rib?
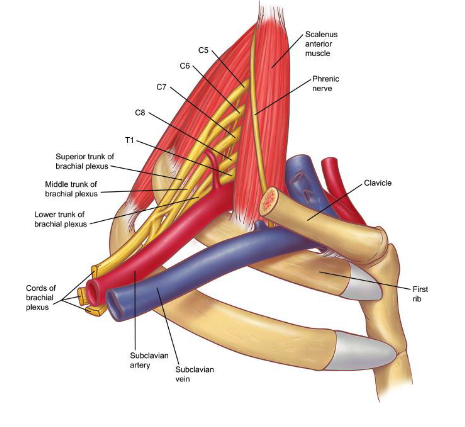
brachial plexus
subclavian a.
what two structures will be compressed in Scalene Compression Syndrome?
subclavian v.
which of the following structures is NOT affected by Scalene Compression Syndrome?
-sublcavian artery
-subclavian vein
-brachial plexus
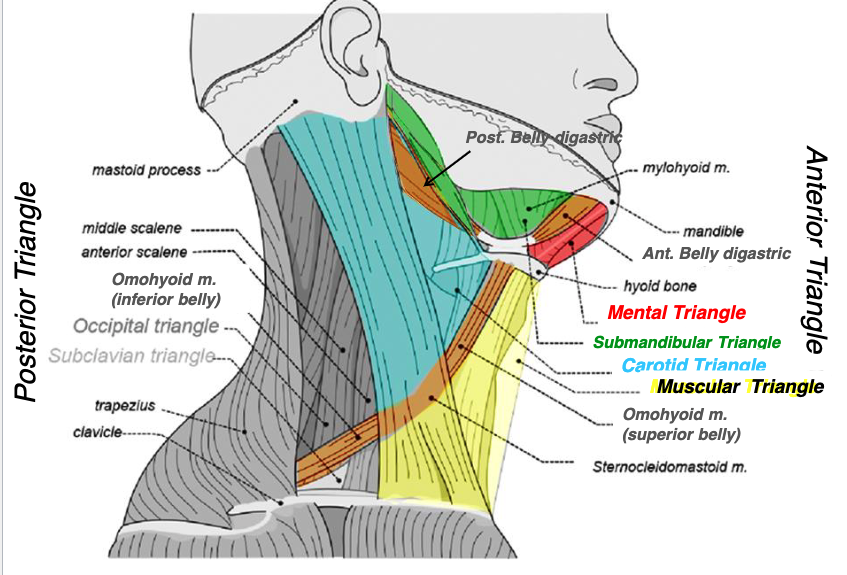
anterior belly of digastric m.
posterior belly of digastric m.
mandible
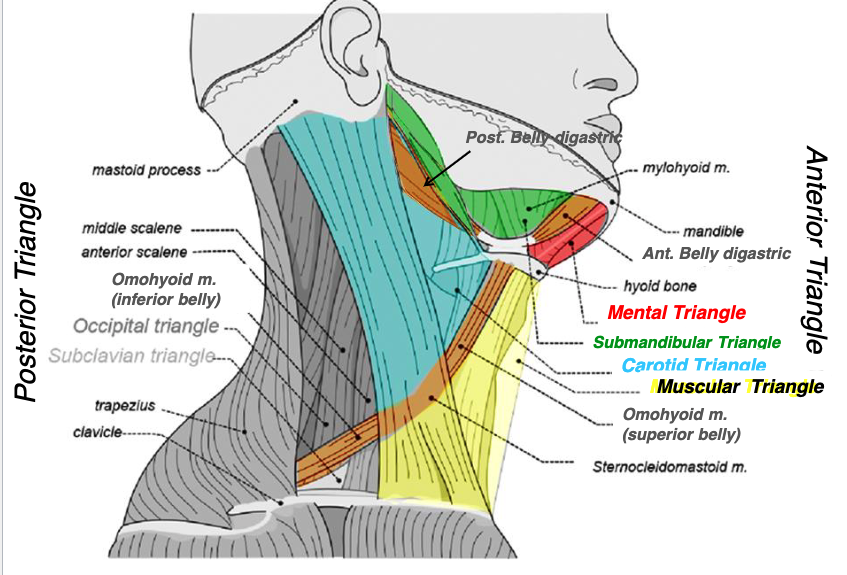
what structures form the submandibular triangle?
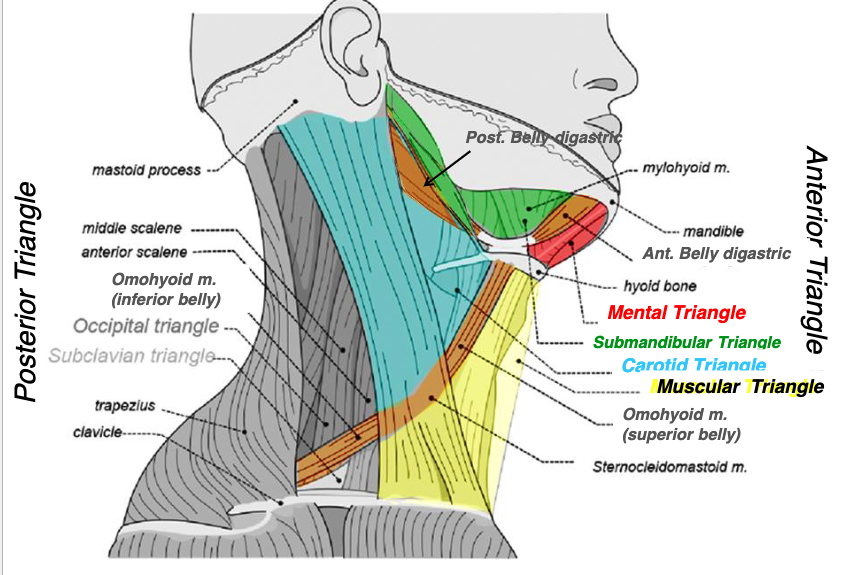
submandibular triangle
name the triangle formed by the following structures:
-anterior belly of digastric muscle
-posterior belly of digastric muscle
-mandible
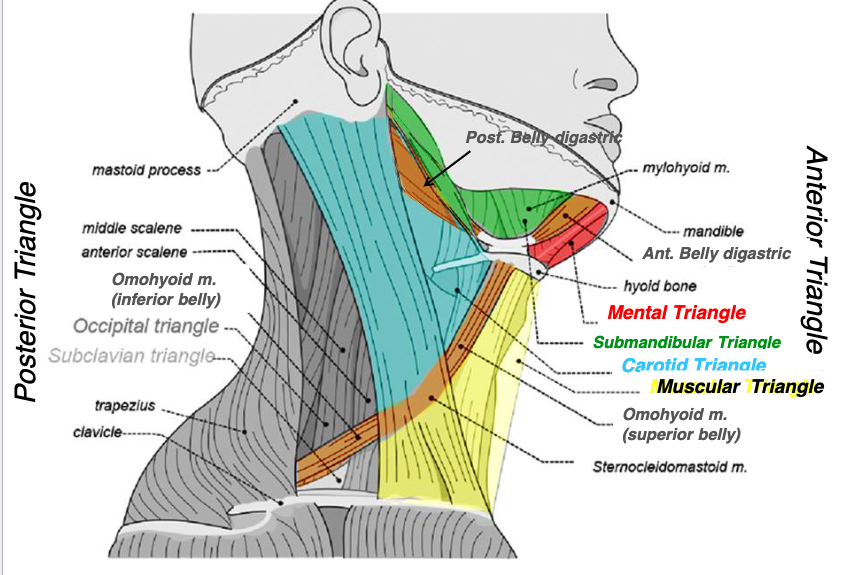
left and right anterior belly of digastric mm.
hyoid bone
what structures form the mental triangle?
mental triangle
name the triangle formed by the following structures:
-left and right anterior belly of digastric muscles
-hyoid bone
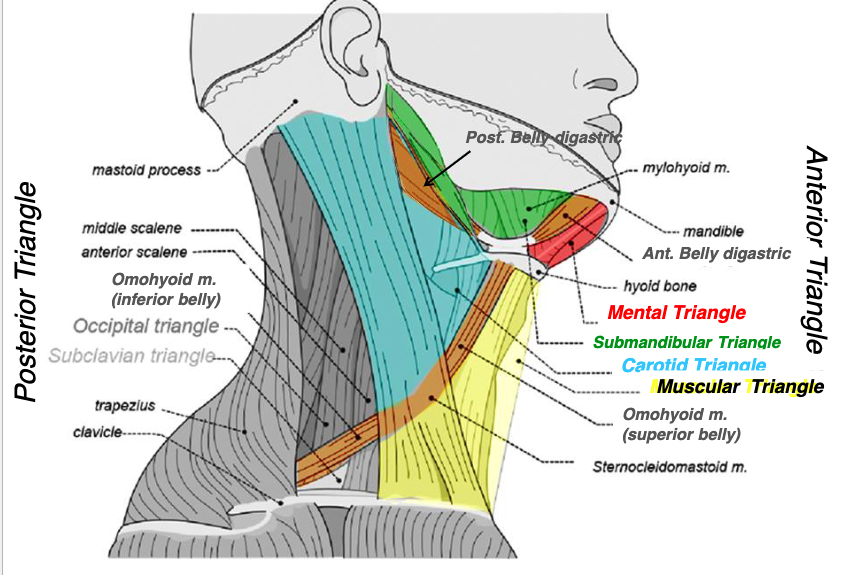
posterior margin of SCM
superior belly of omohyoid muscle
posterior belly of digastric
what structures form the carotid triangle?
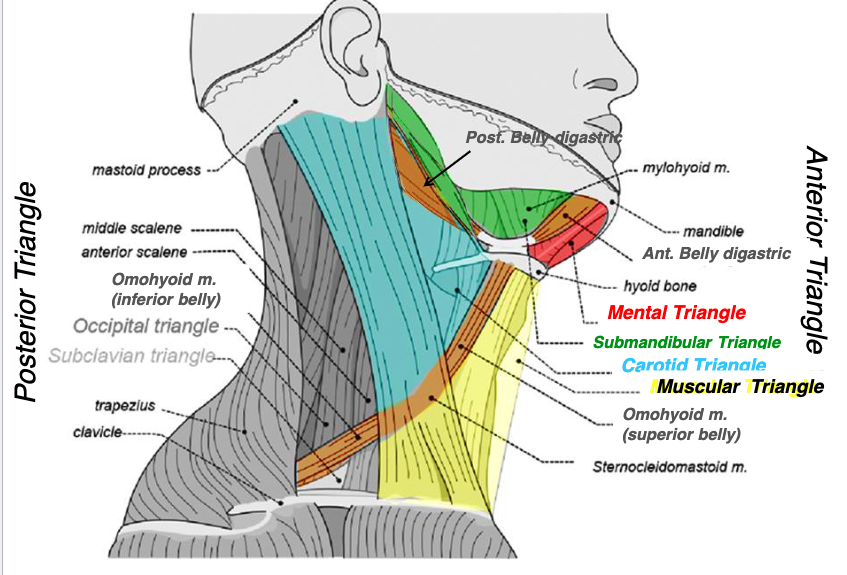
carotid triangle
name the triangle formed by the following structures:
-posterior margin of SCM
-superior belly of omohyoid muscle
-posterior belly of digastric
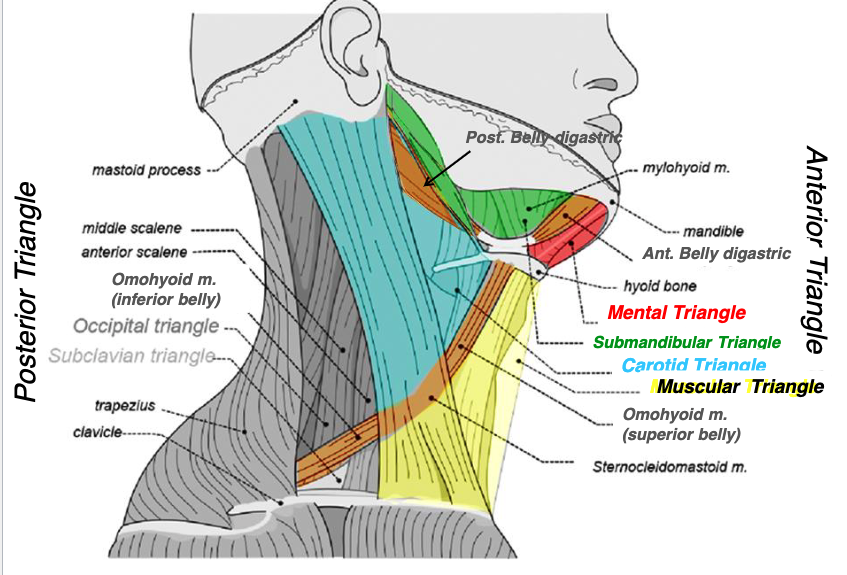
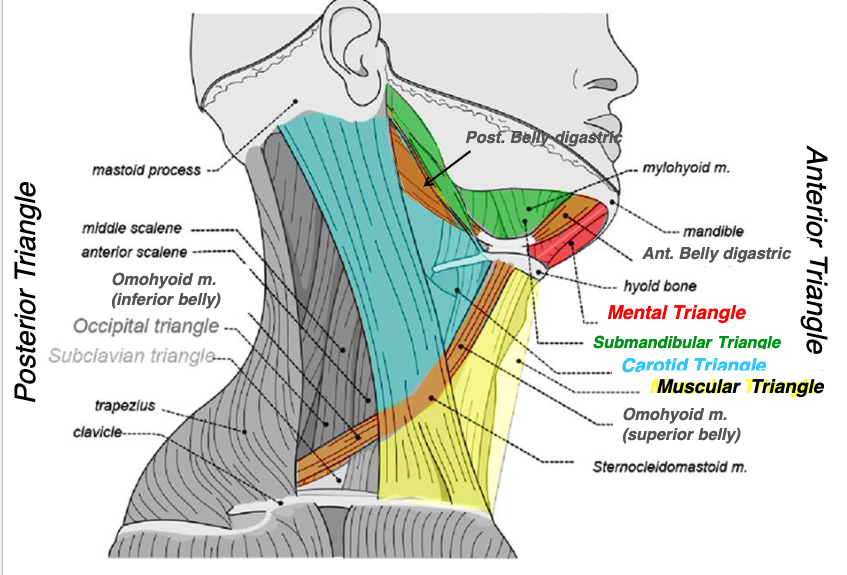
midline
superior belly of omohyoid
SCM
what structures form the muscular triangle?
muscular triangle
name the triangle formed by the following structures:
-midline
-superior belly of omohyoid
-SCM
platysma m.
what is the muscle of facial expression?
cervical branch of facial n.
innervation for the platysma muscle:
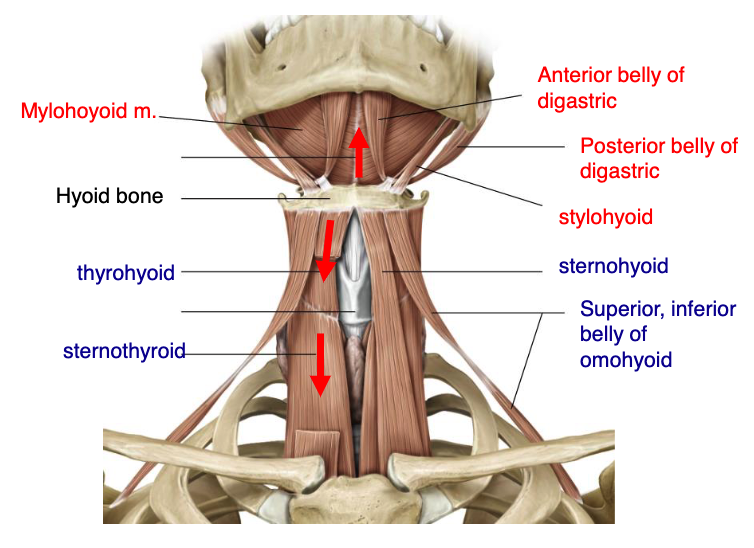
mylohyoid
anterior belly digastric
posterior belly digastric
stylohyoid
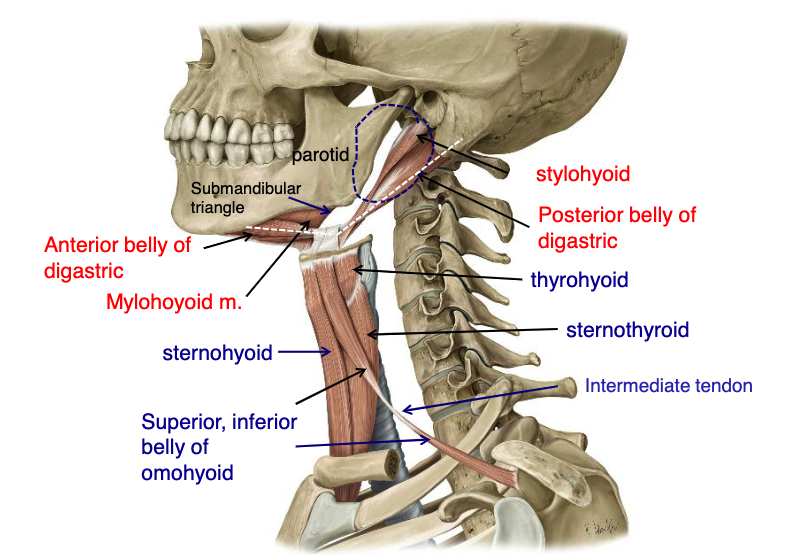
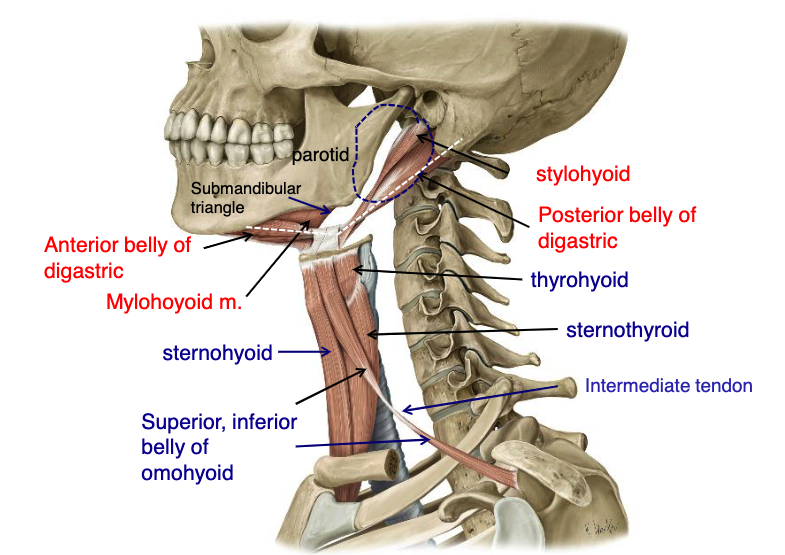
name the 4 suprahyoid muscles:
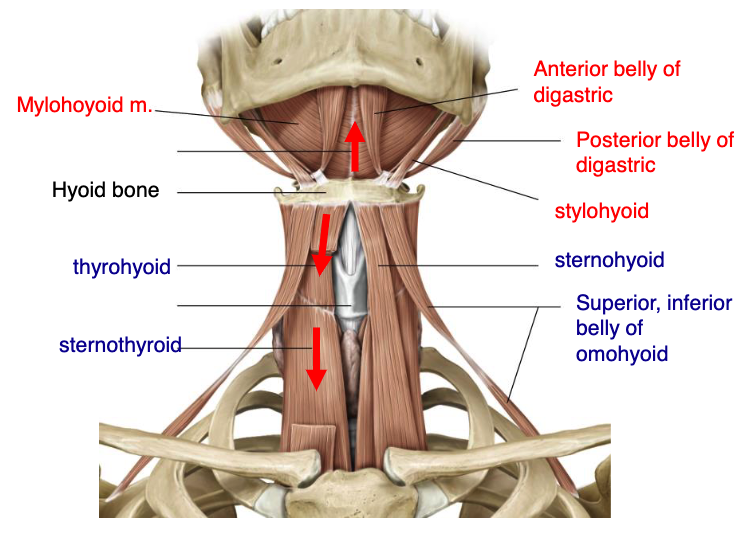
thyrohyoid
sternothyroid
sternohyoid
superior & inferior belly of omohyoid
name the 5 infrahyoid muscles:
posterior belly of digastric m.
what suprahyoid muscle attaches to the mastoid process?
stylohyoid m.
what suprahyoid muscle attaches to the styloid process?
anterior belly of digastric m.
what suprahyoid muscle attaches to the mandibular protuberance?
ansa cervicalis
what nerve plexus innervates the infrahyoid muscles