Client and Family Education
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is teacher-centered teaching
An instructional approach where the teacher is the primary authority, focusing on direct instruction, lecturing, and controlling the learning process.
What is Learner-centered teaching
An instructional approach that emphasizes the student's active role in the learning process, where they engage in hands-on activities, collaborative projects, and discussions to take ownership of their learning.
Key characteristics of Teacher-centered teaching
Characteristics include structured lessons, teacher-led discussions, a focus on tests and assessments, and limited student choice.
Key characteristics of Learner-centered teaching
Characteristics include flexibility in learning, student engagement in content creation, emphasis on critical thinking, and adaptability to diverse learning styles.
What are the benefits of Teacher-centered teaching
Benefits include efficient information delivery, clear expectations, and direct guidance from the teacher.
What are the benefits of Learner-centered teaching
Benefits include increased student motivation, enhanced understanding through exploration, and the development of critical thinking skills.
Behaviorist framework
The idea that all behaviors are learned through interaction with the environment. This learning theory states that behaviors are learned from the environment, and says
Social cognitive theory
Mastery experiences
Vicarious experiences (i.e., social modeling)
Social persuasion
States of emotions and physiology
Emphasizes the dynamic interaction between people (personal factors), their behavior, and their environments
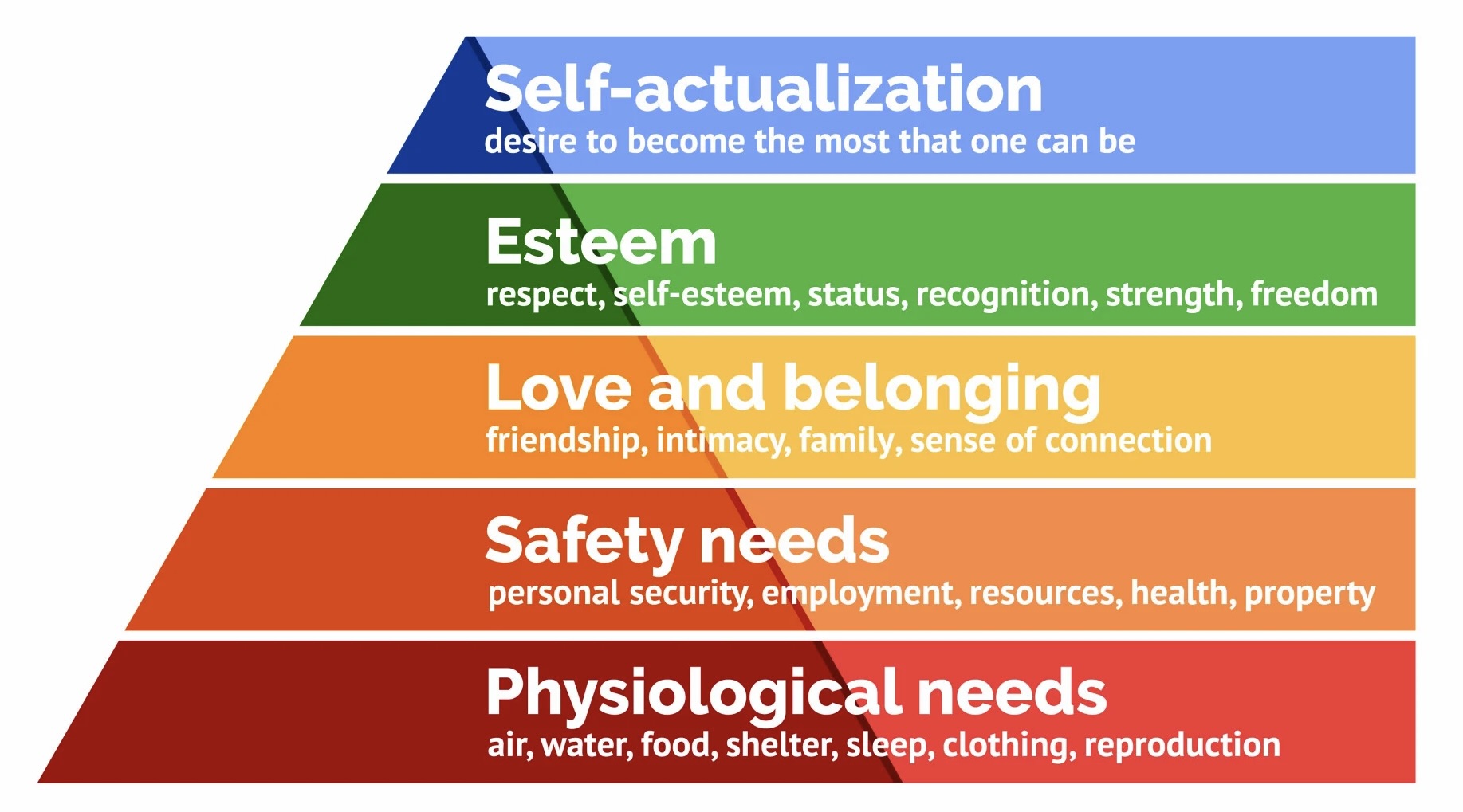
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
Physiological (food and clothing)
Safety (job security)
Love and belonging needs (friendship)
Esteem
Self-actualization.
A pyramid of the needs that motivate people
Constructionist learning theory
Learners construct knowledge rather than just passively take in information. As people experience the world and reflect upon those experiences, they build their own representations and incorporate new information into their pre-existing knowledge.
Learning considerations for children
Typically are in the process of developing cognitive skills and often learn best through hands-on, experiential activities. They may benefit from structured environments that provide direct instruction and guidance. Their learning can be highly influenced by play and social interaction.
Learning considerations for young adults
Usually possess more developed cognitive abilities and can engage in more abstract thinking. They often prefer collaborative and practical learning experiences that allow them to relate new information to their existing knowledge and real-life situations. Motivation may be linked to career and personal development.
Learning considerations for older adults
Often draw upon a wealth of life experiences that can enrich their learning. They may prefer self-directed and problem-based learning approaches, valuing relevance and applicability of content to their current lives. However, they might also face challenges such as cognitive decline or technology use that can affect their learning processes.
Health Literacy
The capacity to obtain and understand basic health information and services to make appropriate health decisions
Three levels of health literacy
Basic or functional literacy
Communicative literacy
Critical literacy
Elements of evidence-based practice
Best available evidence
HCP’s clinical expertise
Client’s values and preferences
Best available evidence
The strongest and most relevant information derived from systematic research that informs clinical practice and decision-making.
HCP’s clinical expertise
The knowledge, skills, and experiences that healthcare professionals (HCPs) acquire through their training and practice. This expertise is crucial in assessing patient needs, determining effective interventions, and making informed clinical decisions.
Client’s values and preferences
The individual beliefs, priorities, and choices that a client holds regarding their health, treatment options, and overall well-being. These factors are essential in ensuring that healthcare interventions align with what is most important to the client.
How to check the quality and reliably of health websites
Credibility
Content
Usability
External links
Interactive services
Telehealth
using technology to provide medical care for clients from a distance
Benefits of incorporating technology in client education
Enhance accessibility to information, facilitate remote consultations through telehealth, improve engagement with interactive content, provide personalized learning experiences, and enable continuous learning and support outside of traditional settings.
Advantages of social media use in medicine
Enhanced communication with patients, increased public awareness about health issues, the ability to share health information rapidly, engagement with broader audiences, and the potential for building supportive online communities.
Limitations of social media use in medicine
Potential for misinformation, privacy concerns regarding patient data, challenges in maintaining professional boundaries, risk of oversimplifying complex medical issues, and the potential to distract from direct patient care.
Influences on Teaching and Learning
Family structure and function
Culture
Gender and learning styles
Readiness to learn, self-efficacy, and readiness to change
Developmental stage
System factors that influence the teaching and learning process
Goals, associated interventions, and outcomes need to be:
Planned
Implemented
Evaluated
Assess, diagnose, plan, implement, and evaluate care for patients, integrating both clinical knowledge and patient advocacy in their practice.
Development of the teaching plan
Teaching strategies
Learning curve
Evaluation
Example of a teaching plan
Education is essential to provide clients and families with knowledge, skills, and confidence to deal with chronic illness. Research findings guide:
Assessment
Teaching plan development
Ultimate educational outcomes