Ecosystem Ecology: Terrestrial Ecosystems
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch. 20.2-20.3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
what is an ecosystem
the biotic community and its abiotic environment, functioning as a system
examples of ecosystems
lakes, forests, tundra, tropical rain forests
what is ecosystem ecology
the study of natural systems with emphasis on energy flow and nutrient cycling
common types of ecosystem-level questions focus on ___________ and _____________
energy flow and nutrient cycling
what is primary productivity
the rate at which autotrophs convert carbon dioxide (in the atmosphere or water) into organic compounds
what is gross primary productivity (GPP)
total rate of photosynthesis (energy assimilated) by autotrophs
what is net primary productivity (NPP)
rate of energy story as organic molecules after energy is expended for cellular respiration (R)
NPP=
GPP - R
many environmental factors influence productivity in
terrestrial ecosystems
many environmental factors including __________ influence productivity in terrestrial ecosystems
climate
warm + wet =
high npp
warm + wet = high NPP
plants can photosynthesize quickly and have enough water
warm + dry =
low NPP
warm + dry = low NPP
warm temperatures increase water demand, but lack of water limits growth
cold =
low NPP (regardless of water)
cold = low NPP (regardless of water)
low temperatures slow down photosynthesis and growth
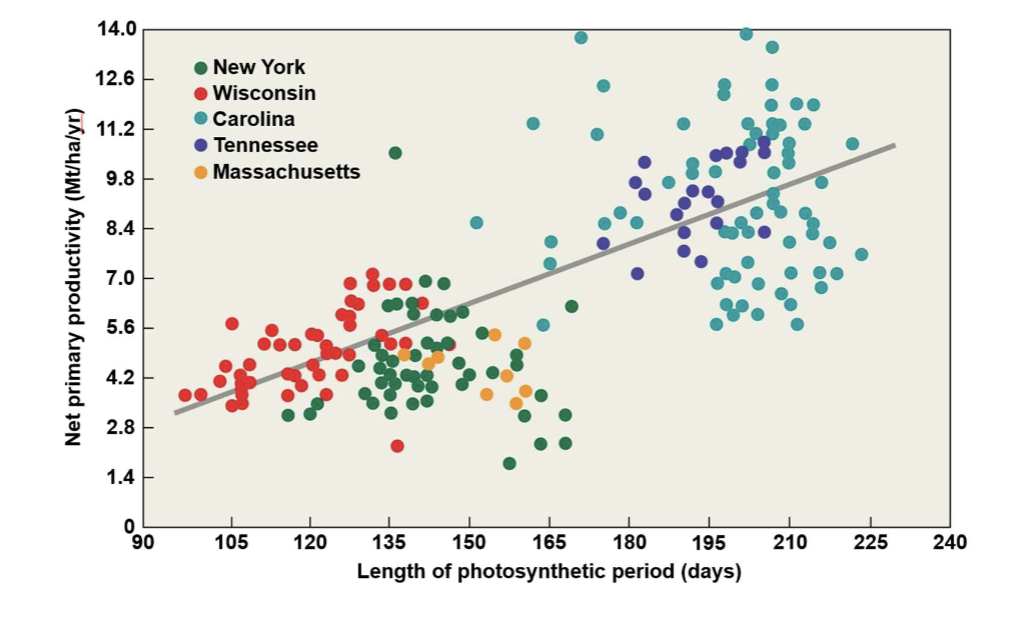
ecosystems with longer growing seasons have
higher plant productivity
why do ecosystems with longer growing seasons have higher plant productivity
plants have more time to photosynthesize and produce biomass
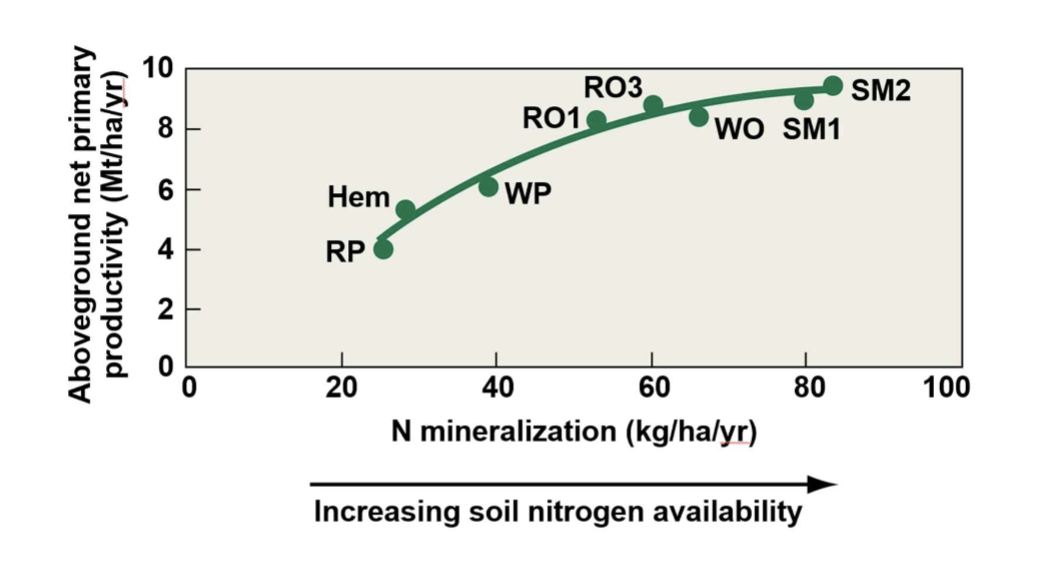
the availability of essential nutrients also affects ecosystem productivity
more available nutrient → higher NPP
nutrients come from the
atmosphere or form rocks
nutrients enter the ______ or _______ and are absorbed by ________
soil or water and are absorbed by plants
many nutrients are stored in the
bodies of living organisms
when organisms die, those nutrients return to the
soil as dead organic matter, feeding decomposers
what is nutrient cycling
the mineralization of organic nutrient by microbial decomposers. these minerals are then available for the autotrophs to take up and use to build new tissues.
key decomposers include
fungi, bacteria, mites, springtails, millipedes, and earthworms
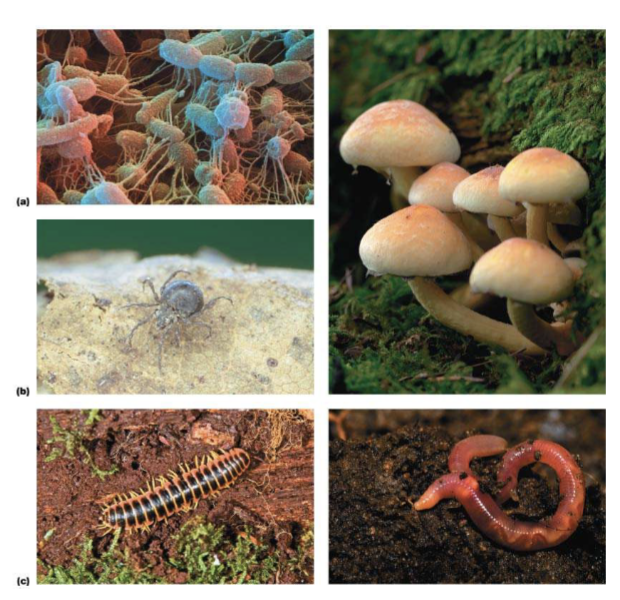

decomposition is influenced by
quality of litter/OM
soil/sediment properties (ex. pH)
climate (temperature/precipitation)
climate and nutrient availability don’t just affect how much plants grow
it also affects what kinds of plants can grow
what are biomes
biotic units that are classified by predominant plant types
there are how many major terrestrial biomes
8
characteristics of tropical rainforest biome
equatorial zone
warm
wet year-round
high NPP
dense vegetation
high biodiversity
nutrients are mostly stored in living plants, not soil
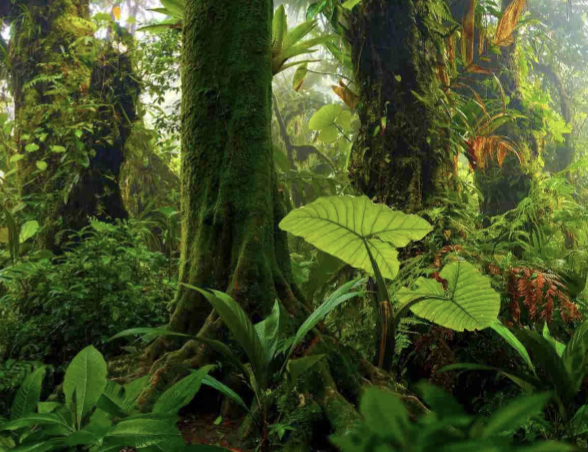

tropical rainforests cover less than ____% of earth’s surface
2
tropical rainforests are home to an estimated ___% of all terrestrial species
50

tropical rainforests are the most _______ and ________ terrestrial ecosystems on our planet
diverse and productive
plant growth forms found in rain forests include
climbing vine, epiphytes, and strangler figs
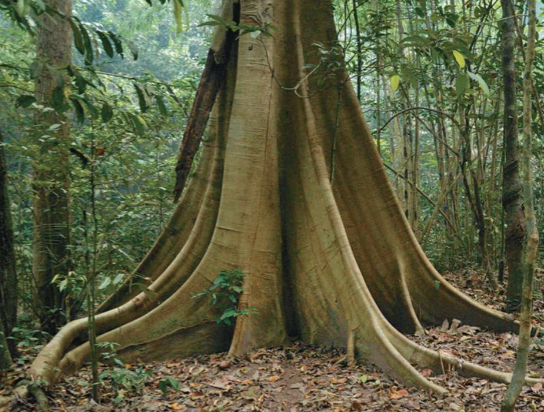
many trees grow buttresses
that function as prop roots in shallow soil that offers poor anchorage
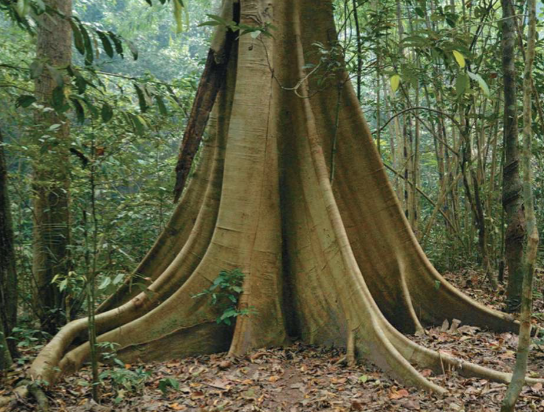

many trees grow buttresses that function as
prop roots in shallow soil that offers poor anchorage

characteristics of tropical savanna biome
warm
semiarid regions
seasonal rainfall (wet + dry season)
high NPP
drought resistant plants (shrubs and trees)
fire-maintained ecosystem
diversity of herbivores that graze on vegetation

tropical savana supports a large number of
insects, carnivores (lions and hyenas), and scavengers (vultures)

savannas have a two-layer _______ _______
vertical structure (grasses + trees/shrubs)
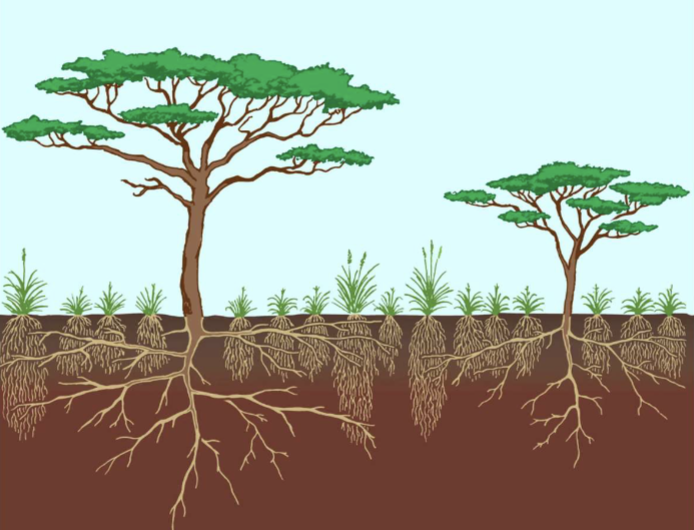

in savannas, trees create small ___________
microenvironments
what are microenvironments
“resource hotspots” that support biodiversity than the surrounding grassland
characteristics of tree microenvironments
soil is richer (more leaf litter and nutrients)
shaded ground is cooler
soil holds more moisture
characteristics of temperate deciduous forest biome
moderate temperature + rainfall
broadleaf deciduous trees dominate
rich soils and understory of shrubs, ferns, wildflowers
moderate NPP
seasonal changes affect plant growth and animal behavior
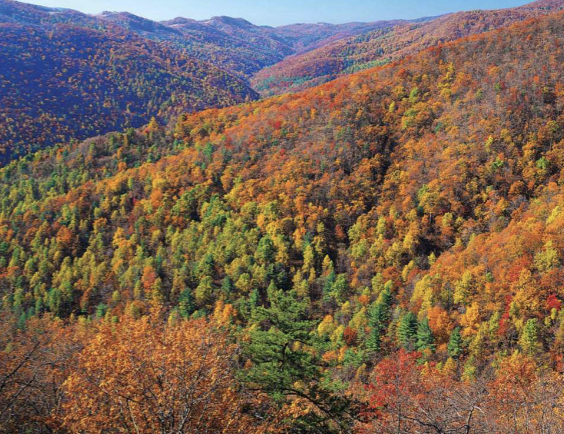

in deciduous forests, there are usually _______ vertical layers
four

a diversity of anima life is associated with
vertical stratification and plant growth forms
highest diversity in the forrest occurs
on and just below the ground layer
characteristics of temperate grassland biome
moderate temperature
low precipitation
often experience drought
low to moderate NPP
dominated by herbivores, insects, large grazers, burrowing animals

grasslands evolved under the __________ __________ of grazing
selective pressure

grasslands evolved under the selective pressure of
grazing

grazing stimulates primary production to a point,
moderate grazing can stimulate grass growth, but heavy grazing reduces productivity

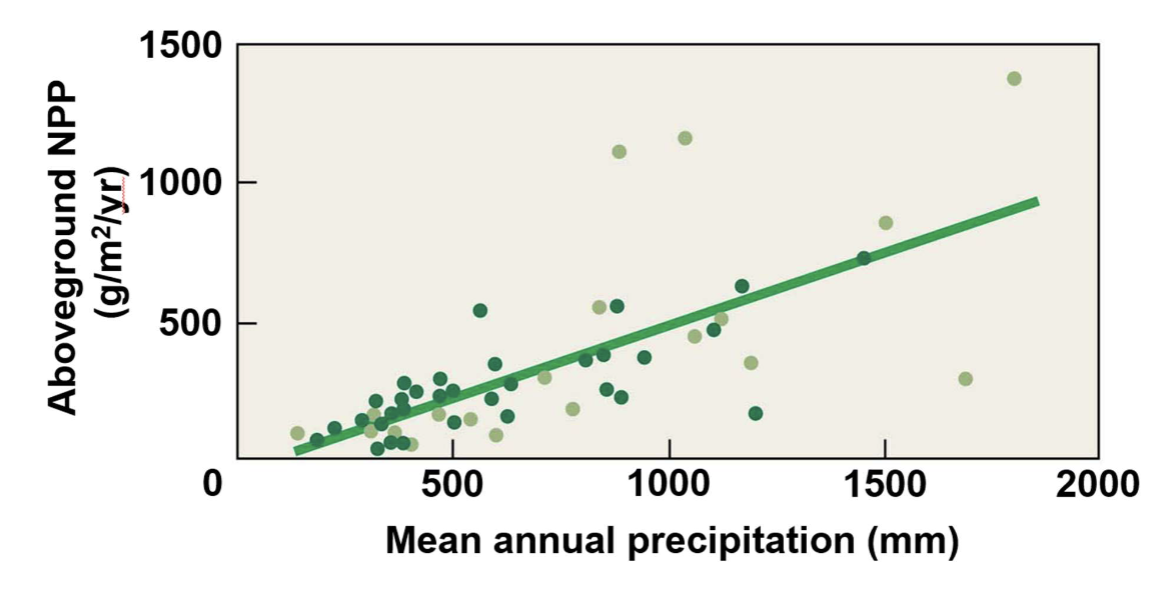
temperate grassland productivity is related to
annual precipitation
there are ______ strata in a grassland
3
what are the three strata in a grassland
herbaceous plants
ground cover
belowground root layer
can make up more than half of the plant biomass and extends deep into the soil
characteristics of shrubland biome
hot, dry summers
cool, wet winters
shrubs and dwarf trees dominate
soils are deficient in nutrients
plants are adapted for fire and low nutrients
moderate NPP

sclerophyllous plants are characteristic of _______ _____
shrubland biomes

what are sclerophyllous plants
thick, tough, and leathery leaves with a waxy coating that helps reduce water loss

shrublands are home to ______-_______ mammals, birds, and reptiles that use shrubs for food and shelter
drought-tolerant
shrublands are home to drought-tolerant mammals, birds, and reptiles that use shrubs for
food and shelter
characteristics of desert biomes
low precipitation
hot (sahara)
cold (gobi)
high evaporation rates
dry conditions
plants/animals adapt to very arid climate
low NPP

hot deserts range from those lacking vegetation to ones with
some combination of herbs, dwarf shrubs, and succulents
in hot deserts, animals avoid heat and ______ ________
conserve water
cold deserts range from vegetation dominated by
sagebrush, shadscale, woody shrubs, and grasses adapted to cold, dry conditions
cold deserts range from vegetation dominated by sagebrush, shadscale, woody shrubs, and grasses adapted to
cold, dry conditions
animals in cold deserts conserve ____ and survive long dormant seasons
heat
characteristics of boreal forest (taiga) biome
cold long winters
around 6-10 weeks warm enough to photosynthesize
dominated by evergreen conifers
needles prevent water loss
conical shape sheds snow
primarily occupies formerly glaciated land
low NPP
herbivores found in the boreal forest
caribou, moose, snowshoe hare, red squirrels, and procupine

predators found in the boreal forest
wolf, lynx, pine martin, and owls
as temperatures decreases and growing seasons shorten toward the Arctic,
trees become fewer, shorter, and more widely spaced
characteristics of the tundra biome
very cold
very low precipitation
dominated by
small shrubs
grasses
herbs
mosses
lichens
low animal diversity
dominant vertebrates are herbivores
very low NPP

in the tundra, only species that can withstand ______________ can survive
constant soil disturbance
arctic plants propagate almost entirely by
vegetative means