Pediatrics: Assistive Technology
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is assistive technology?
devices and services used to enhance abilities and participation of child with disabilities, while reducing limitations that may arise from impairments of body function and structures
What is included in assistive technology?
any item, piece of equipment, or product system whether acquired commercially off the shelf, modified or customized, that is used to increase, maintain, or improve the functional capabilities of a child with a disability
*medical devices that is surgically implanted or the replacement of such device is not included
What are assistive technology services?
-the evaluation of needs including a functional evaluation, in the child's customary environment;
-purchasing, leasing or otherwise providing for the acquisition of assistive technology devices;
-selecting, designing, fitting, customizing, adapting, applying, maintaining, repairing, or replacing of assistive technology devices;
-coordinating other therapies, interventions, or services with assistive technology devices, such as those associated with existing education and rehabilitation plans and programs;
-training or technical assistance for a child with disabilities, or where appropriate that child's family; and
-training or technical assistance for professionals (including individuals providing education and rehabilitation services), employers or others(s) who provide services to employ, or are otherwise, substantially involved in the major life functions of that child.
What is Individuals with Disabilities Education Act and Amendments of 2004 (IDEA)
-defines AT device and service
-no cost to family for AT identified as necessary in an IEP
-IEPs and IFSPs must consider AT needs
What is the Assistive Technology Act of 2004?
federal funding for states to train and deliver AT
What is the Americans with Disabilities Amendments Act of 2008 (ADA)?
AT may be reasonable accommodations for employment or public access
Categories of AT for the educational environment
-positioning
-mobility
-augmentative communication
-access
-computer based instruction
-environmental control
-ADLs
-recreation/leisure/play
-vision technology
-assistive listening
Low tech AT examples
-built up handles for utensils
-visual schedules
-fidgets
-binder clip for turning pages
-slant board
-velcro
Mid tech AT examples
-audio book
-gait trainer
-wheelchair
-adapted seating
-adapted switch
-calculator
-word prediction software
High tech AT examples
-computer or tablet
-speech Text
-augmentative and
-alternative Communication (AAC)
-power wheelchair
Who is apart of the AT team?
-Audiologist
-Counselor
-Early Intervention Specialist
-Instructional Assistant
-Nurse
-Occupational therapist
-Physical Therapist
-Physician
-Rehabilitation Engineer
-Social Worker
-Special Education Teacher
-Speech Language Pathologist
-Teacher of the Hearing Impaired
-Teacher of Visually Impaired
-Technology Coordinator
-Vocational Counselor
Process for providing AT
•Gather background information
•Gather objective Data for Decision-Making
•Assistive Technology Evaluation
•Feature Match with Child's Abilities
•Trial
•Recommendations
•Training and Implementation
Positioning definition
alignment of body parts in relation to one another and the environment
Positioning benefits
-normalize or decrease abnormal neurological influence on the body
-increase range of motion, maintain neutral skeletal alignment and control, and prevent skeletal deformities and muscle contractures
-manage pressure and prevent or decrease the potential for decubitus ulcers
-upgrade stability to increase function
-promote increased tolerance (comfort) of desired position
-enhance function of autonomic nervous system
-decrease fatigue
-facilitate components of normal movement
-facilitate maximum function with minimal pathology
Positioning: recumbent positions in
supine, prone, sidelying
Positioning: recumbent equipment
wedge, bolster, mat, sidelyer
Positioning: recumbent negatives
limit peer interaction and participation
Positioning: upright positions in
sitting or standing
Positioning: upright positions provides
-allows for participation and interaction
-weight-bearing options for children who do not stand independently
Positioning: upright equipment
wheelchair, adaptive seating, stander
Seating systems: sling
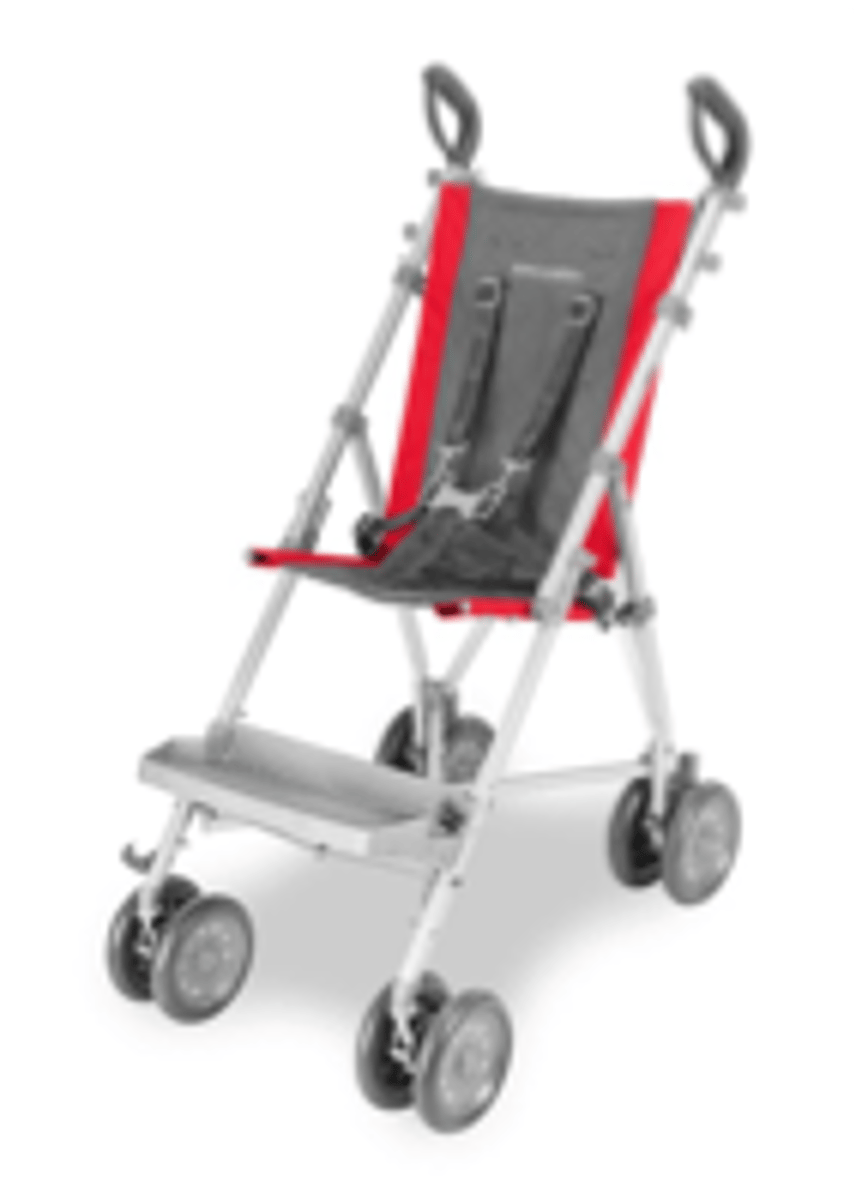

Seating systems: planar
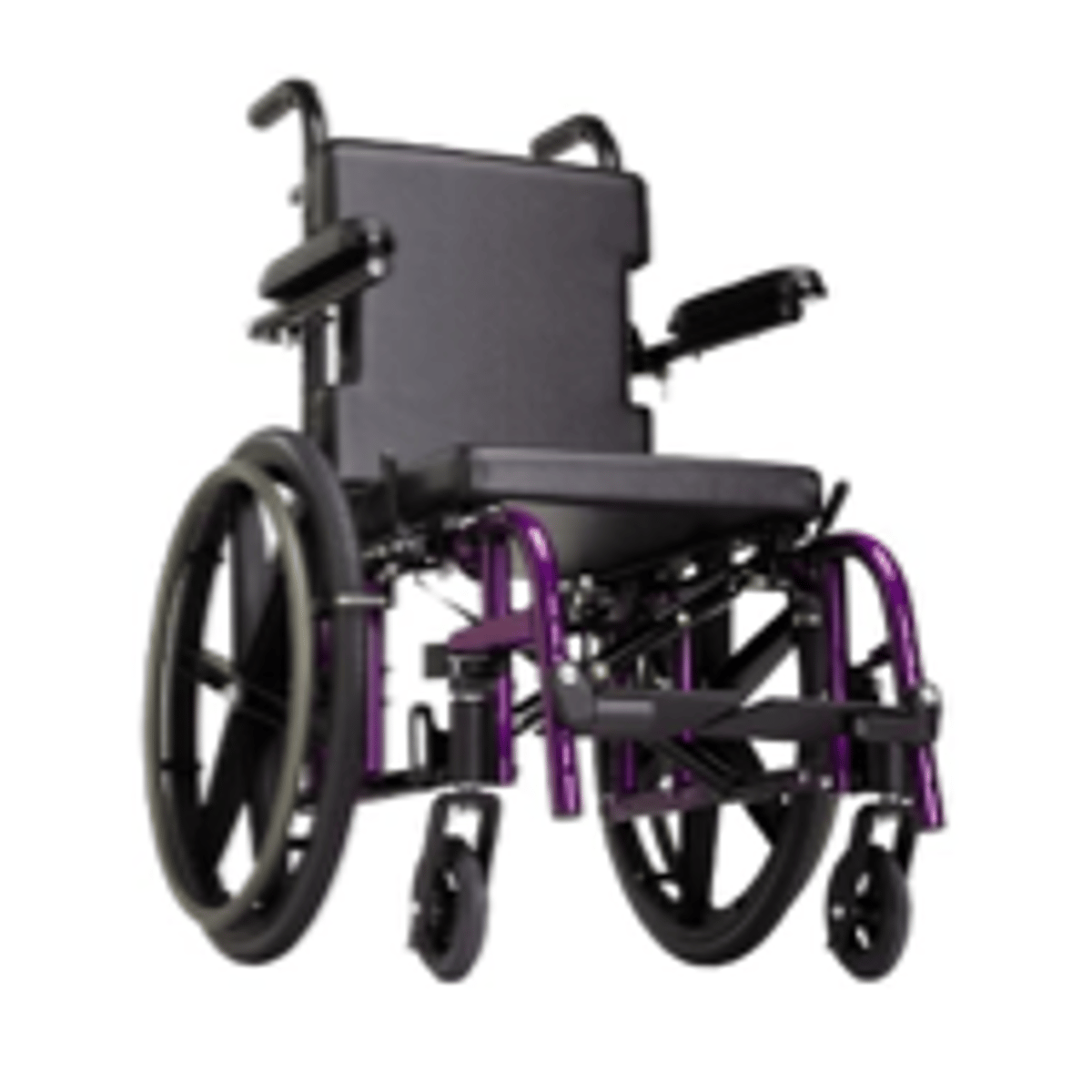

Seating systems: contoured
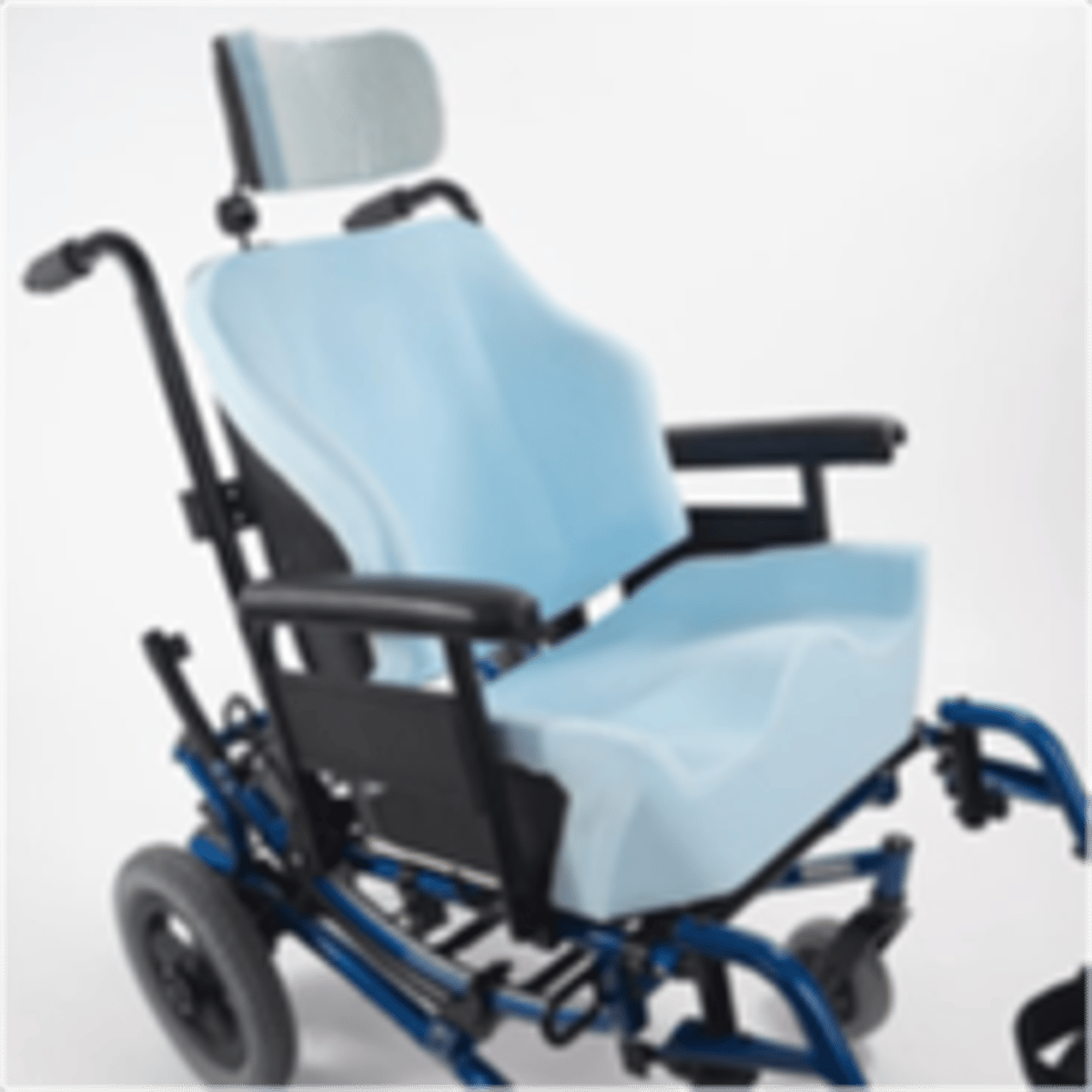

Seating systems: custom contoured
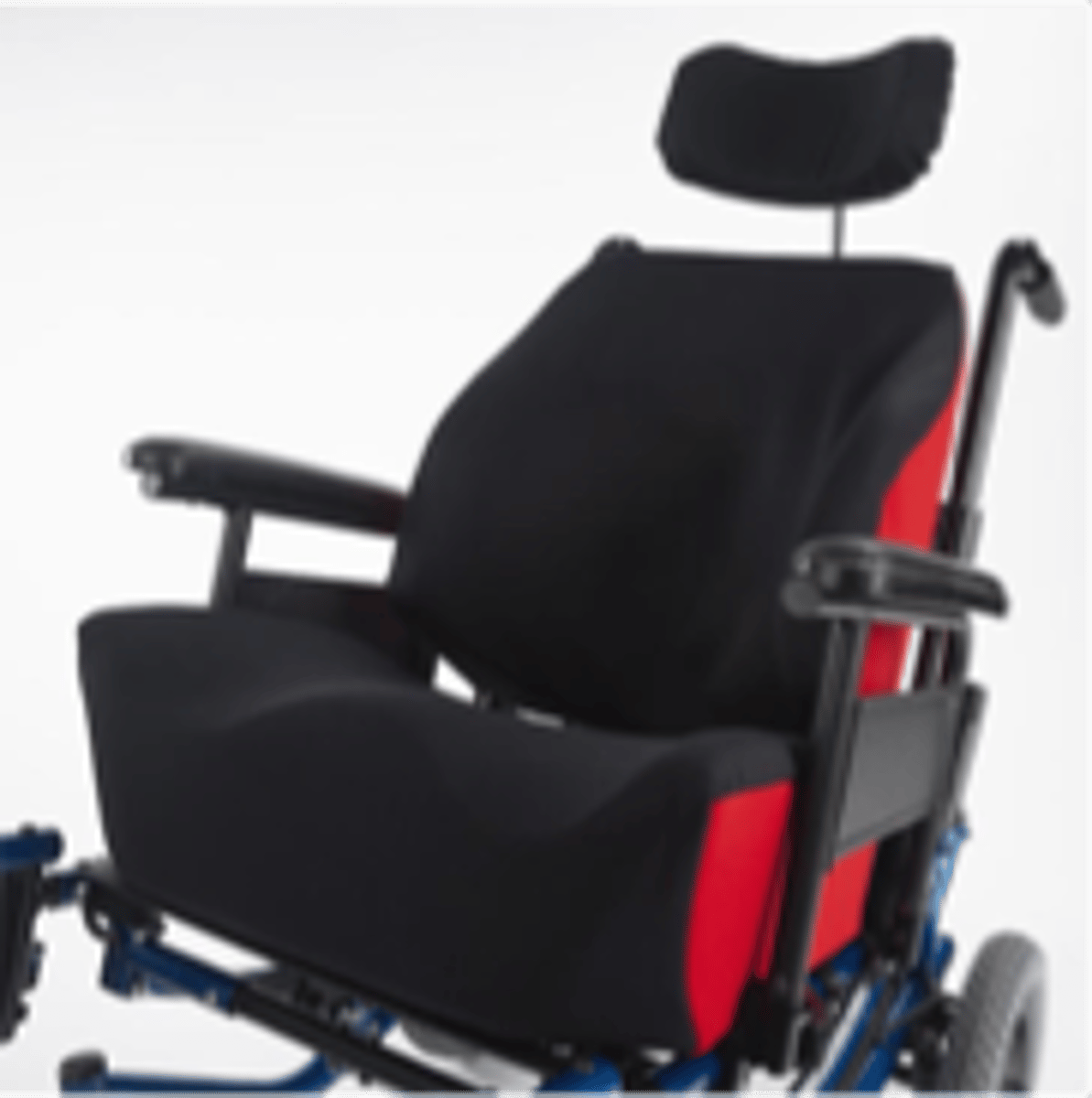

Seating systems: sidelyer
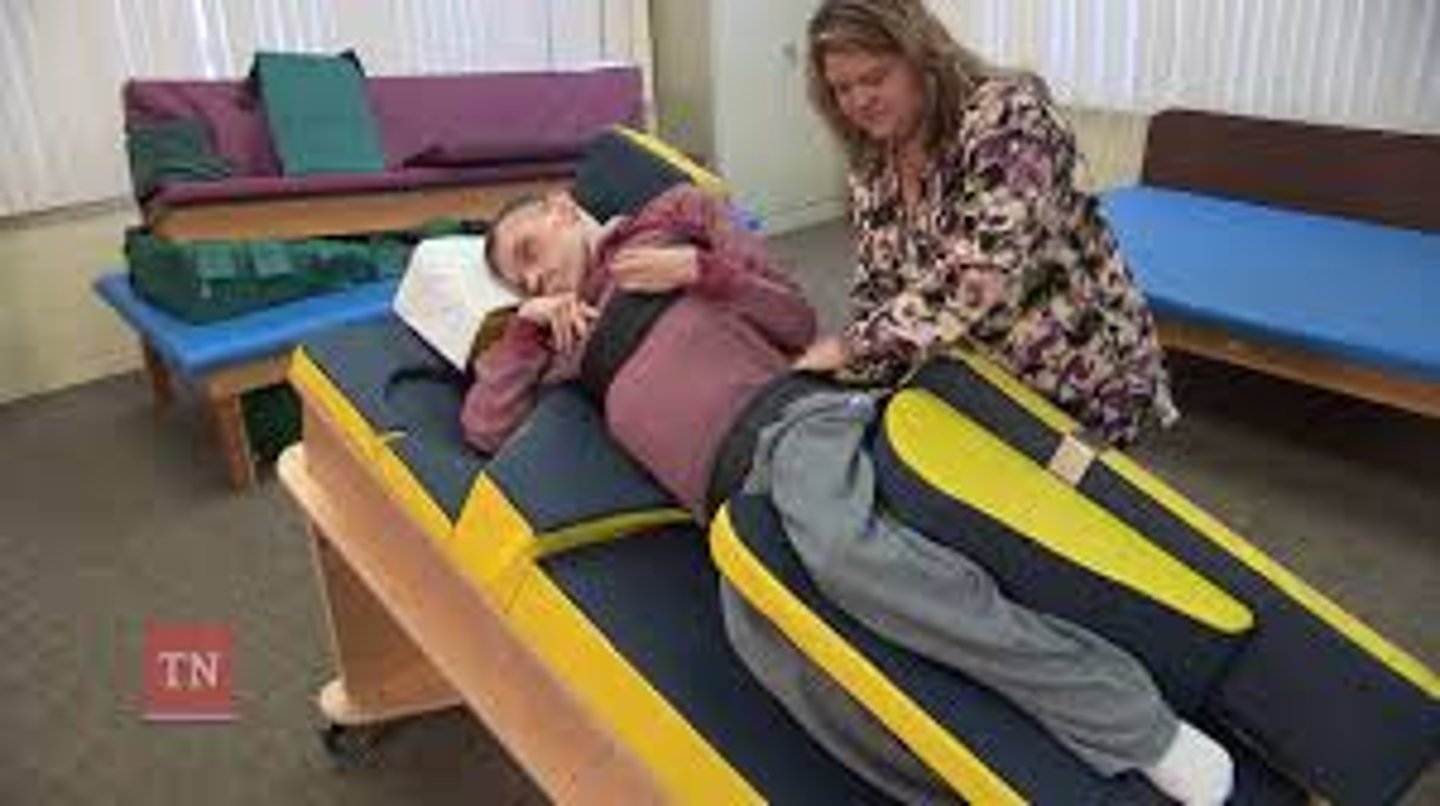
When are standing systems recommended to start?
~9months
How often should standing systems be used
5 days/week in peds
Standing systems use is the equivalent of ___ METS
1.5; light activity
Benefits of standing systems
-bone mineral density (60-90 min/day)
-decrease hypertonicity/spasticity (30-45 min/day)
-improve range of motion (45-60 min/day)
-hip health is 15-30° hip abd per side (60-120 min/day)
-bowel and bladder function
-psychological improvement
-pressure relief
-head control
AAC unaided
-gestures
-sign language
-facial expressions
-signals
AAC aided
-communication board
-simple voice output device
-leveled or layered device
-dynamic display device
AAC direct selection
-finger
-head pointer
-mouth stick
-eye gaze
AAC indirect selection
switch interface with scan techniques