Unit 7: Stoichiometry
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
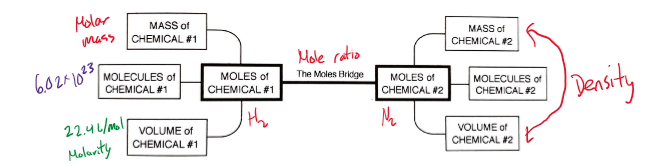
Mole ratio
To determine this ratio, you need to look at the coefficients in front of each chemical species in a reaction.
These coefficients can represent moles or molecules.
Stoichiometric calculation
Determine the balanced chemical equation.
Convert the amount you are given into moles.
Convert from moles of the known to moles of the unknown based on the coefficients in the balanced chemical reaction → mole ratio.
Convert from moles of the unknown to the units required.
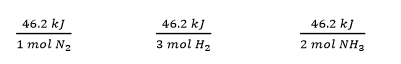
Enthalpy (ΔH) and moles
If an equation containing a heat term of ΔH is shown, coefficients always stand for moles.
N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3 + 46.2 kJ (exothermic!)
1 mole of N2 is used up → 46.2 kJ of heat is released.
3 moles of H2 are used up → 46.2 kJ of heat is released.
2 moles of NH3 are used up → 46.2 kJ of heat is released.
Limiting and Excess Reagents
Limiting reagent: Starting material that gets used up in a reaction.
Excess reagent: Starting material that is not used up in a reaction.
→ Use the limiting reagent to determine the yield.
Finding limiting reagent method:
Calculate the amount of product formed by each reactant.
The reactant that produces the lowest yield is the limiting reactant.
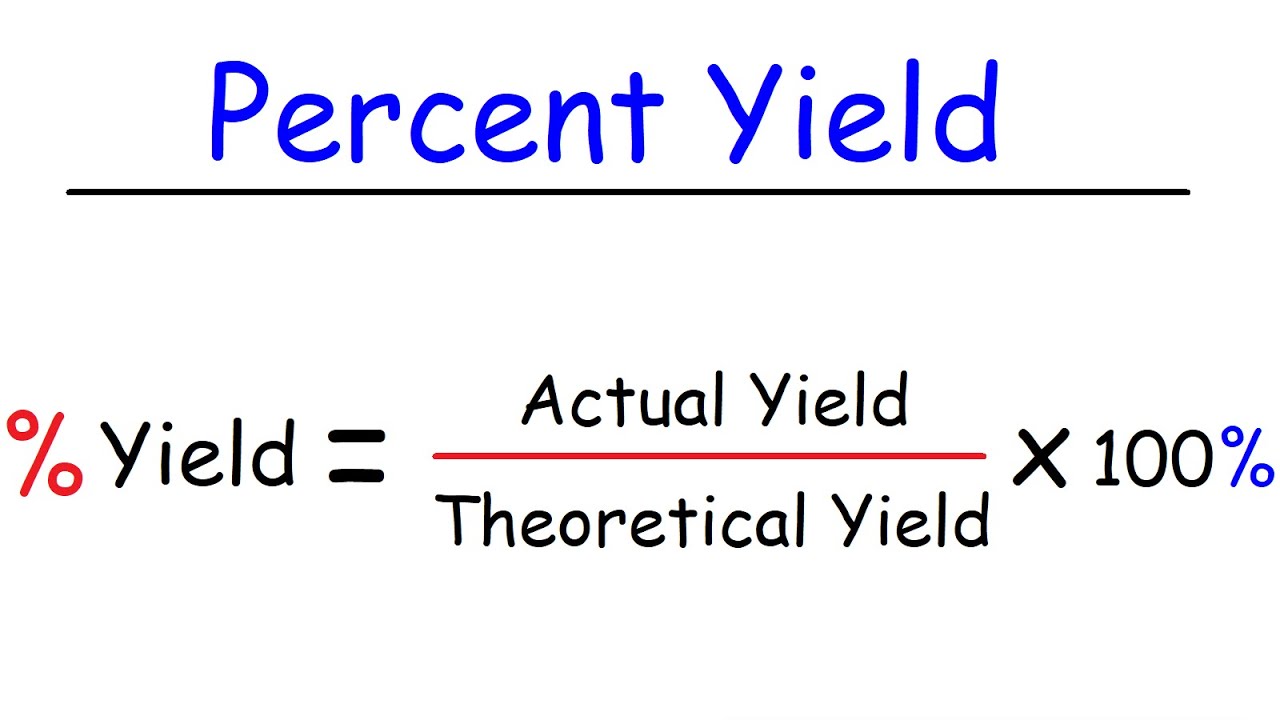
Percent yield
Actual yield: Result from the experiment.
Theoretical yield: Result from stoichiometry.
TUMS tablet
Reasons to take TUMS:
Treat heartburn
Treat indigestion
Treat upset stomach caused by too much stomach acid (HCl)
How TUMS works:
Reducing the amount of acid in the stomach.
→ Neutralizes the heartburn-causing acid in our esophagus and stomach on contact → fast relief.Acid found the stomach: HCl
Active ingredient in TUMS tablet: CaCO3