PSY 250 Lecture 8 Light and the Eye Notes & Retina and Photoreceptors
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Our objective is to understand how the _______ “sees” the world around us
brain
_____________ is very important for vision
Light (protons)
Light is ______________ radiation
electromagnetic
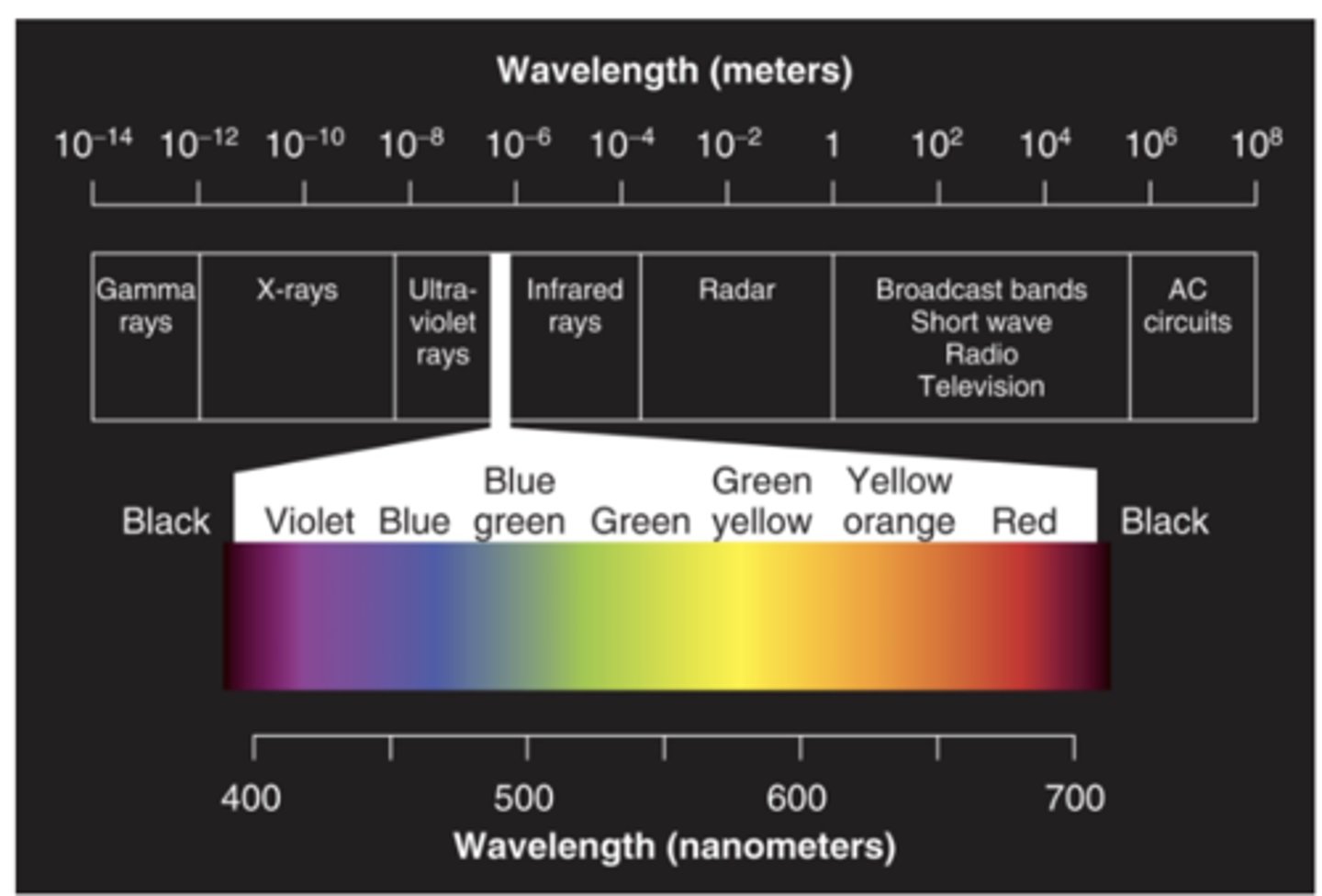
Human vision is limited: We can only see part of the electromagnetic spectrum (__________ of wavelength)
380-760
What is Visual Acuity?
The ability to distinguish between two nearby points in space (i.e., visual resolution)

What is Visual Sensitivity?
The ability to detect changes in the levels of light
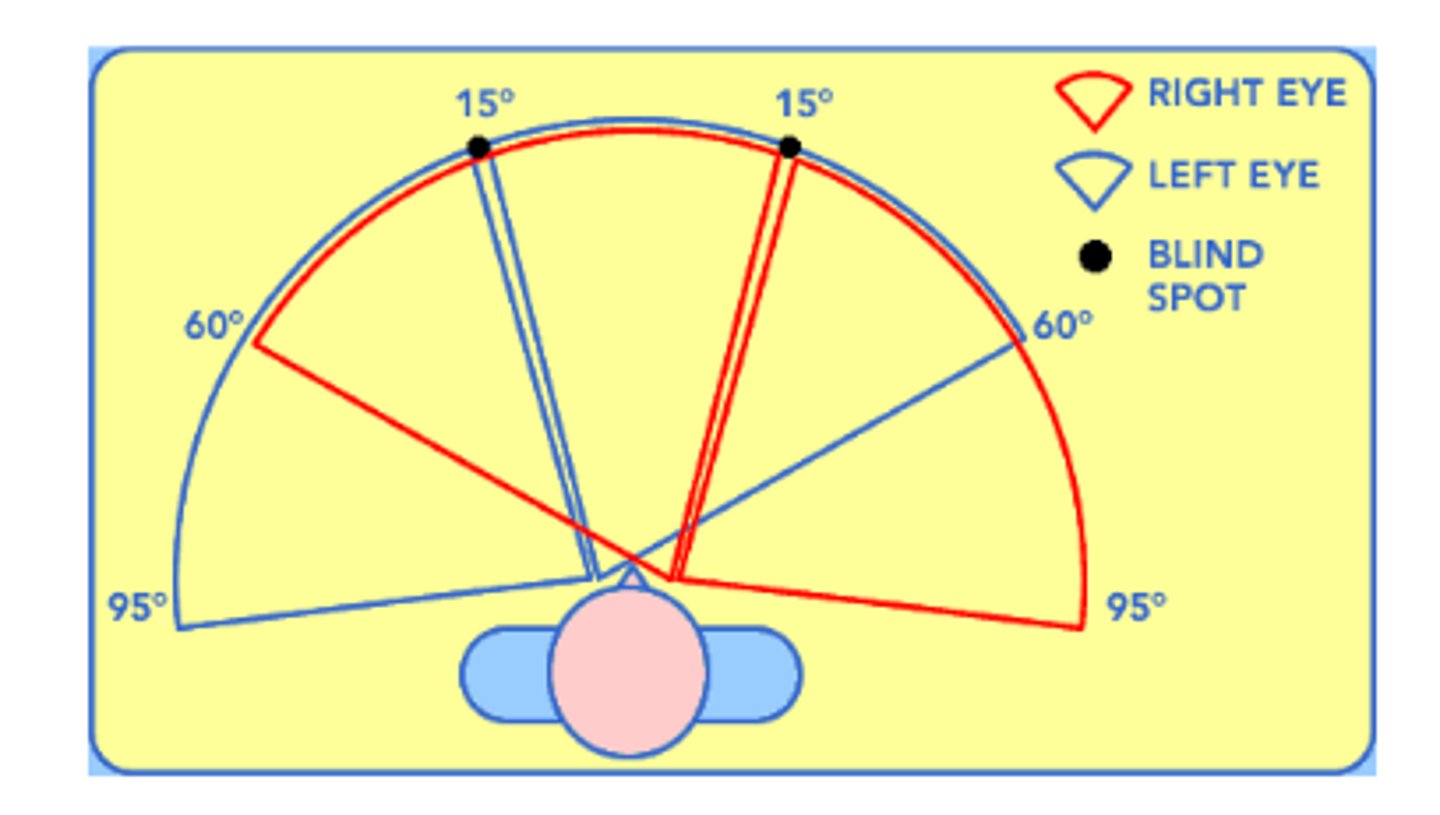
What is Visual Field?
The extent of visual space seen by each eye
Visual field size for rodent and primate
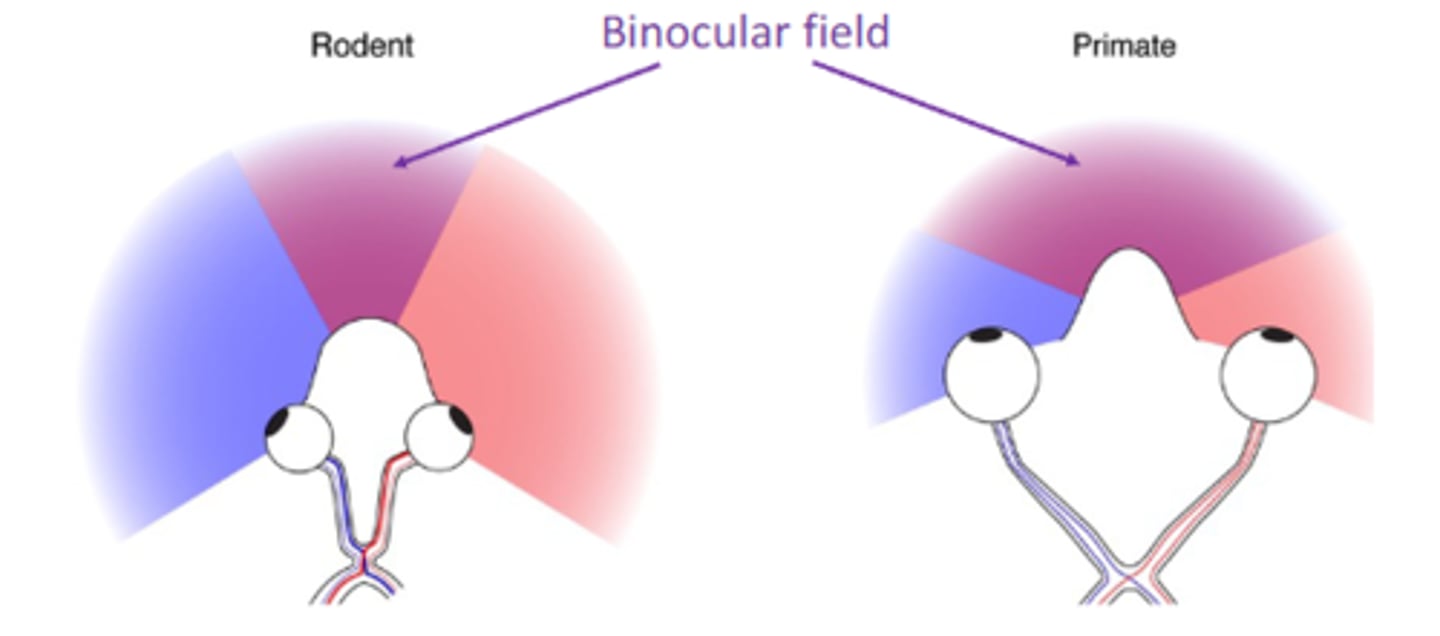
What is Binocular Disparity?
The difference in the position of the same image in the two eyes helps the brain create 3D/depth perception
What is Visual Transduction?
The process that light is converted into neural signals
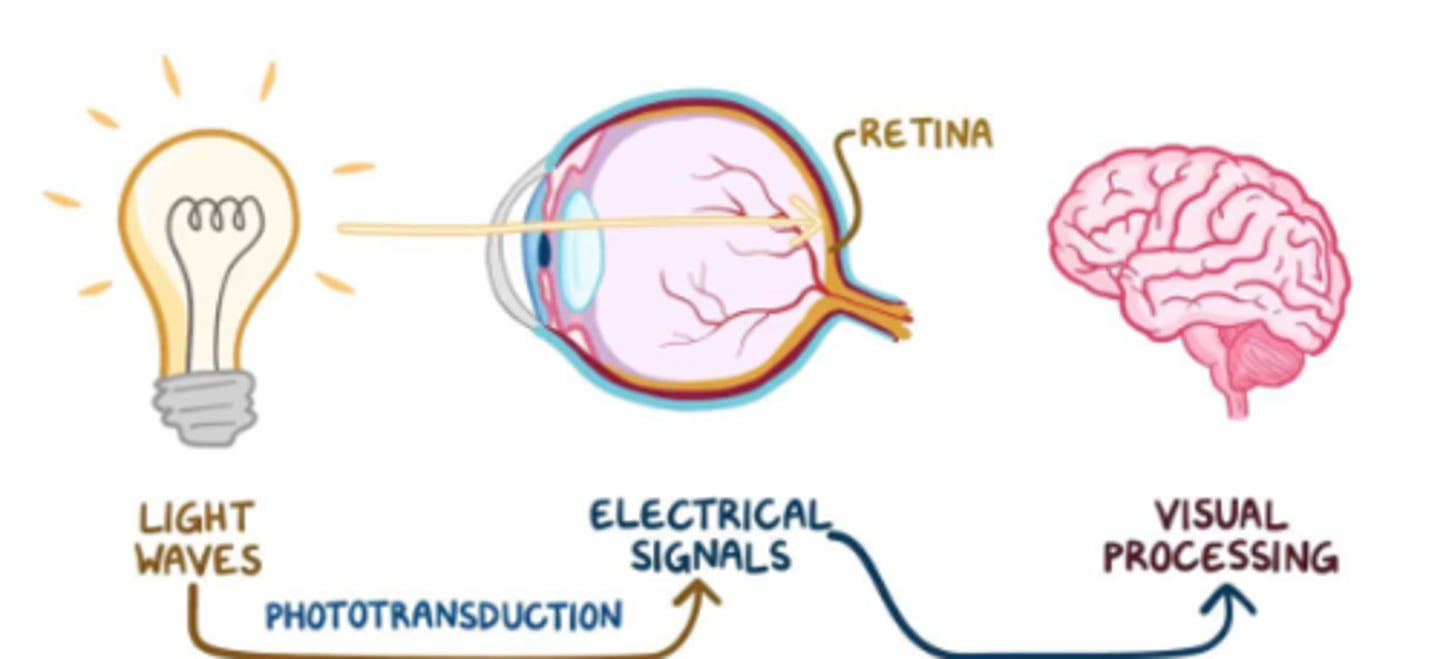
What covers the iris and the pupil, allowing light to enter?
Cornea
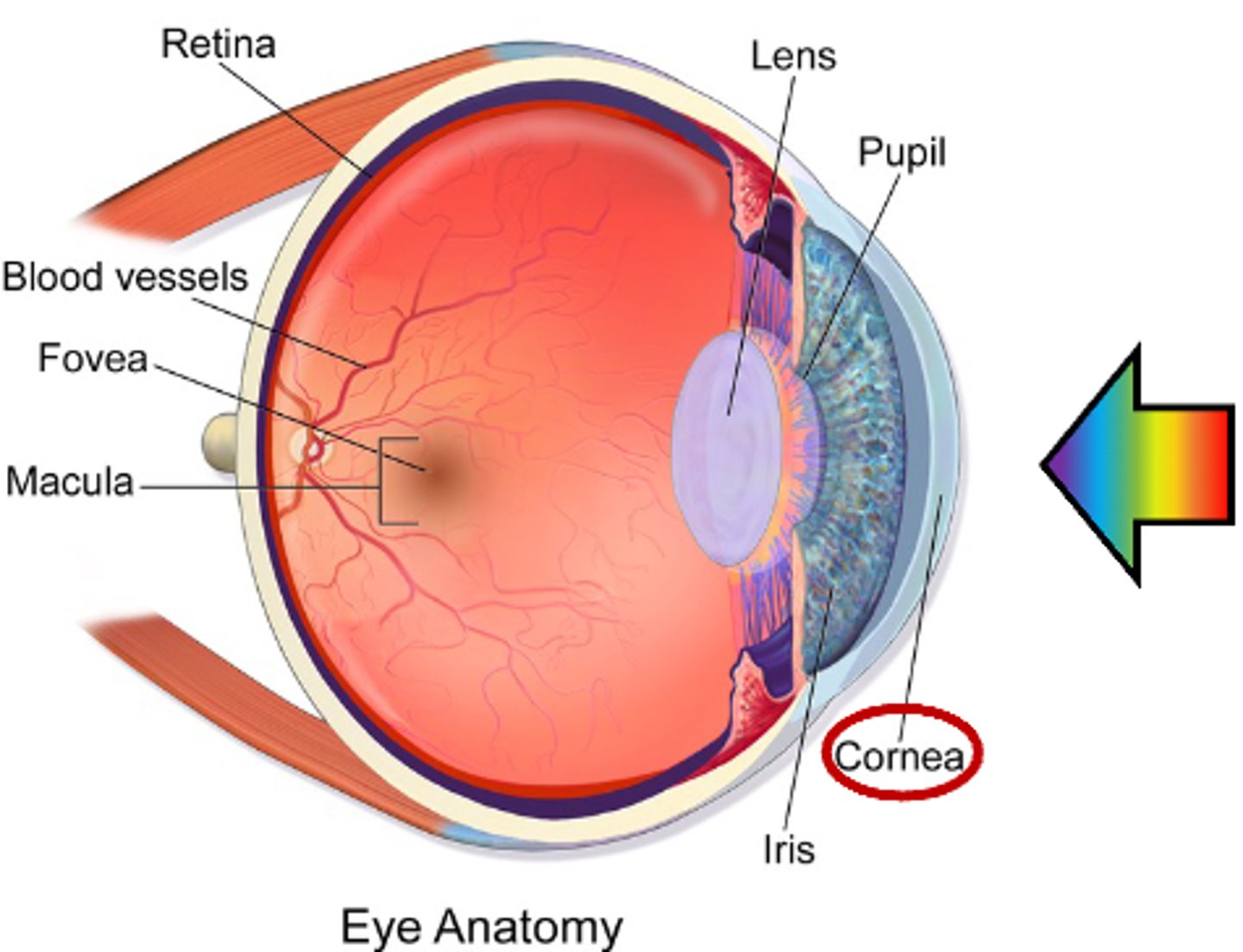
What regulates the amount of light entering the eye?
Iris
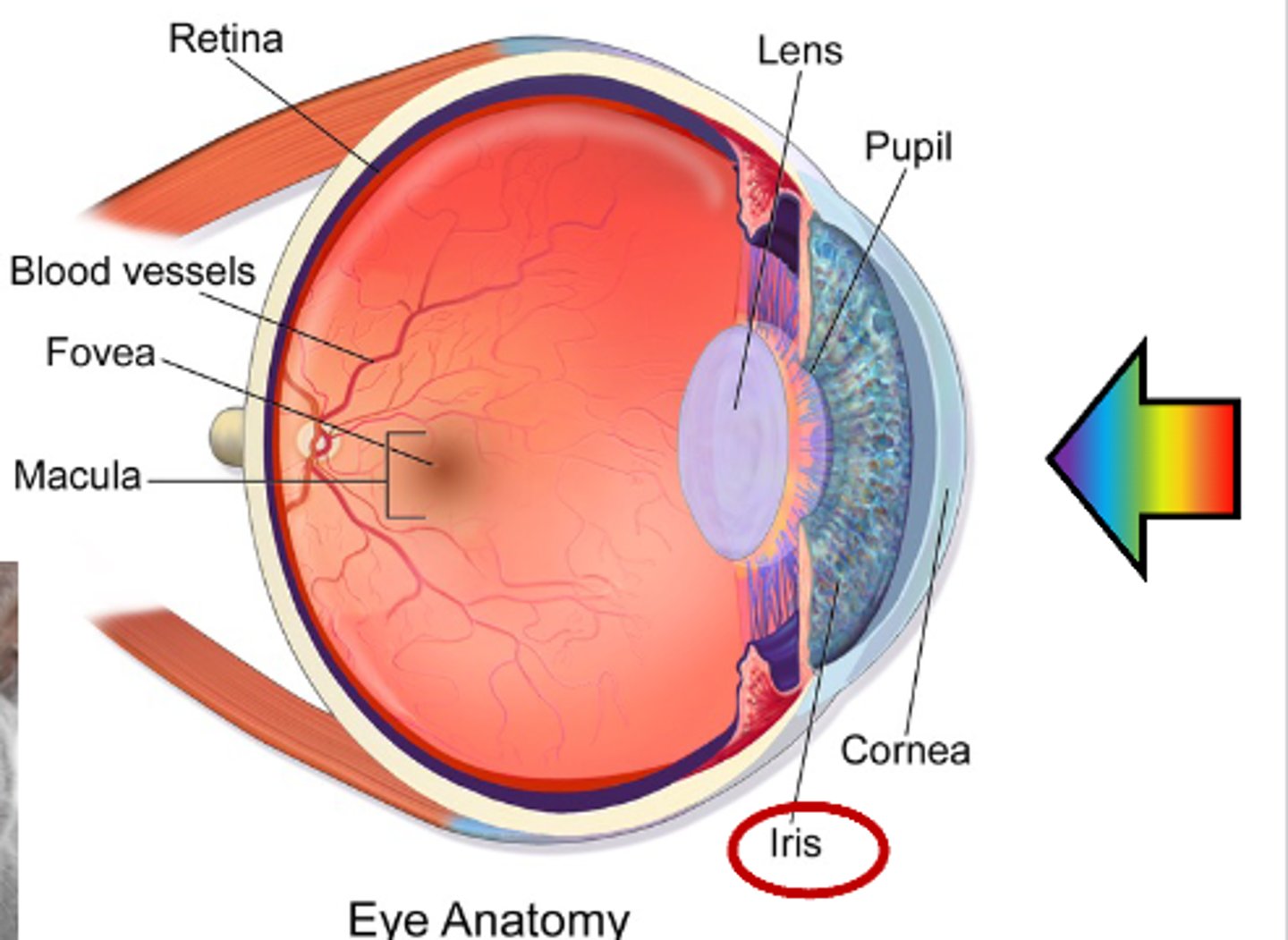
What is the area called where the light enters the eye?
Pupil
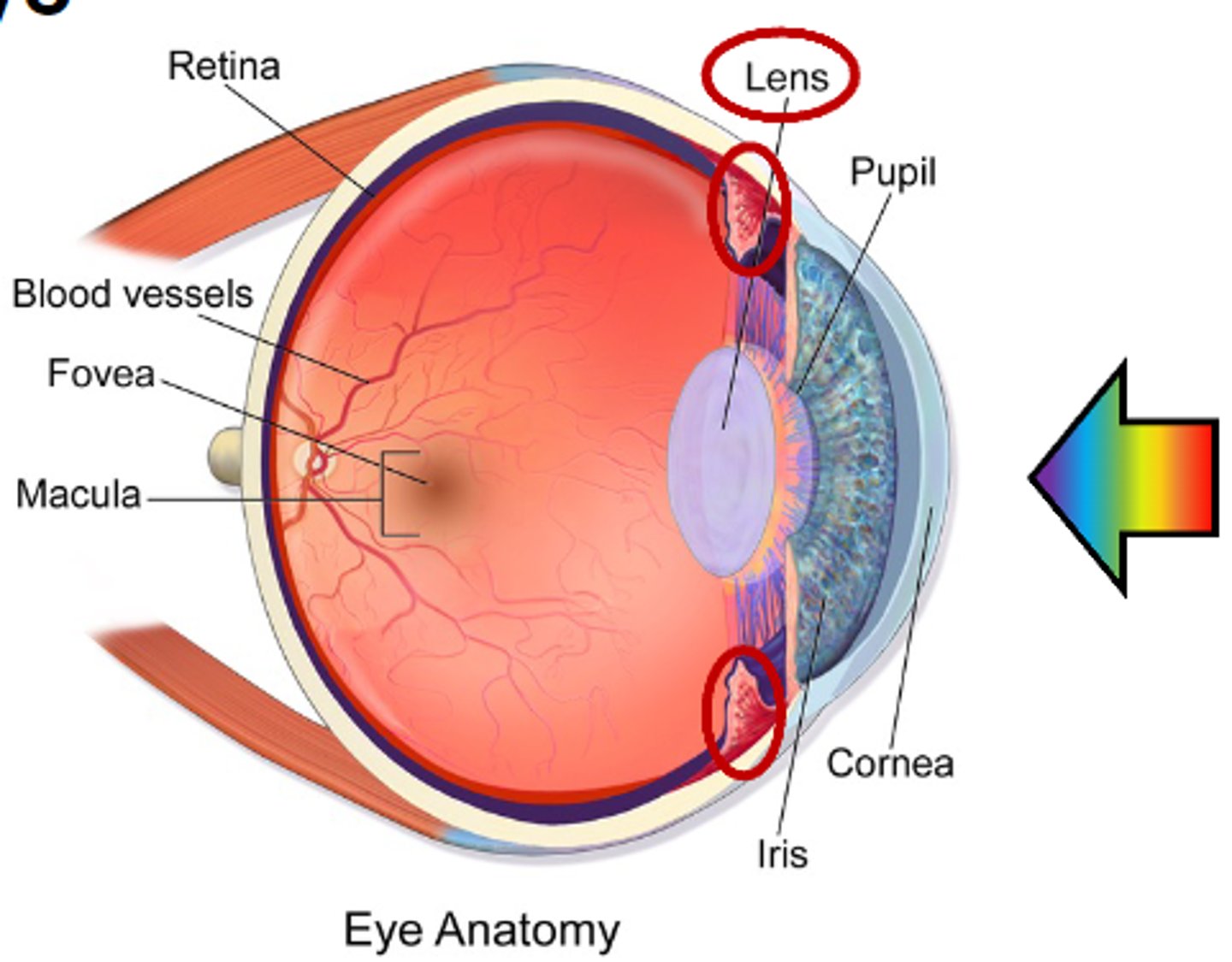
What is the area called where changes in shape and/or relative position to focus?
- Ciliary muscles connects to the lens
Lens
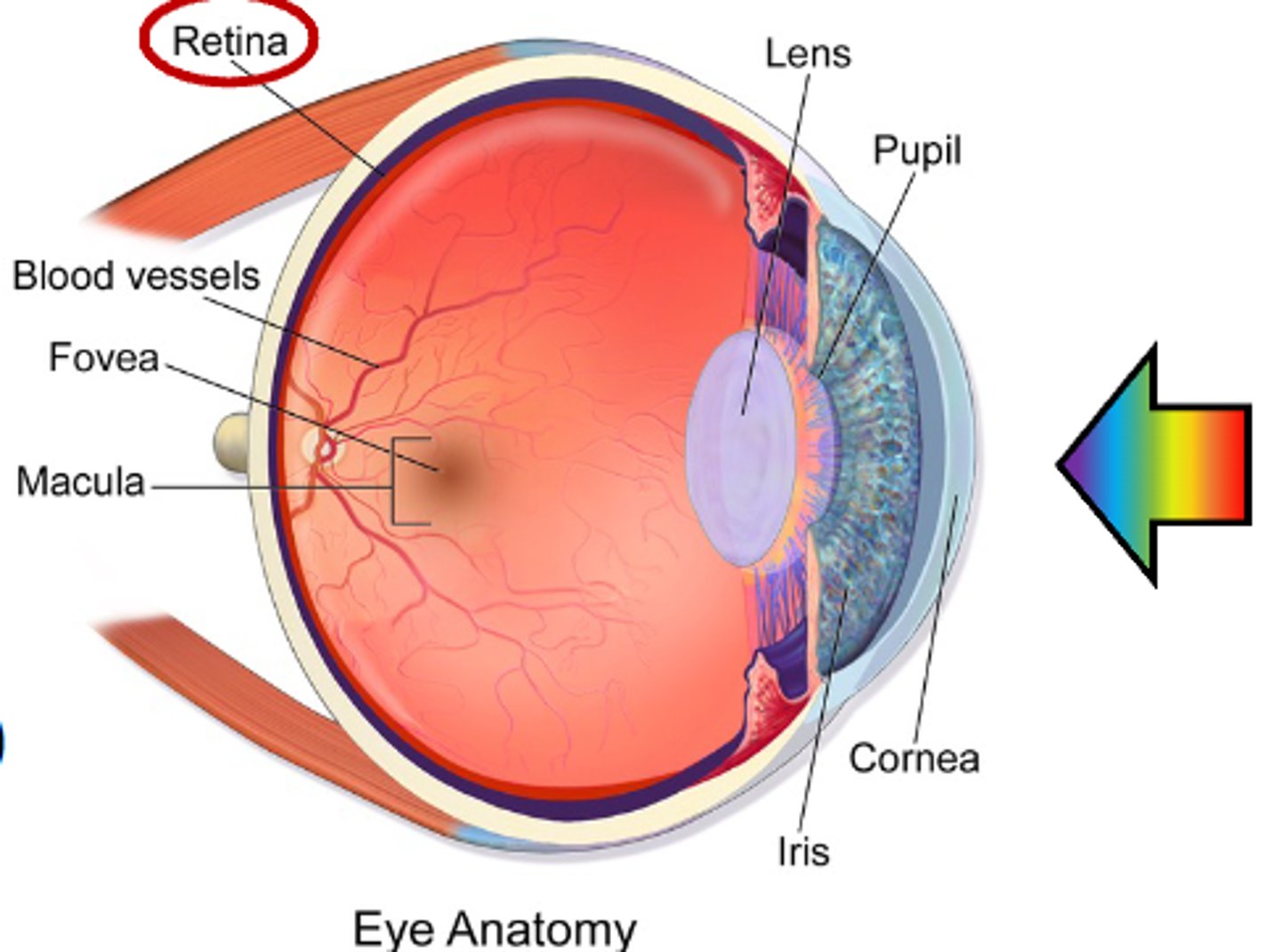
What is the area called where the layer of cells where light rays are converted into neural signals (by photoreceptors)?
Retina
What is the area called that is the center of retina, high concentration of photoreceptors: central vision?
Macula
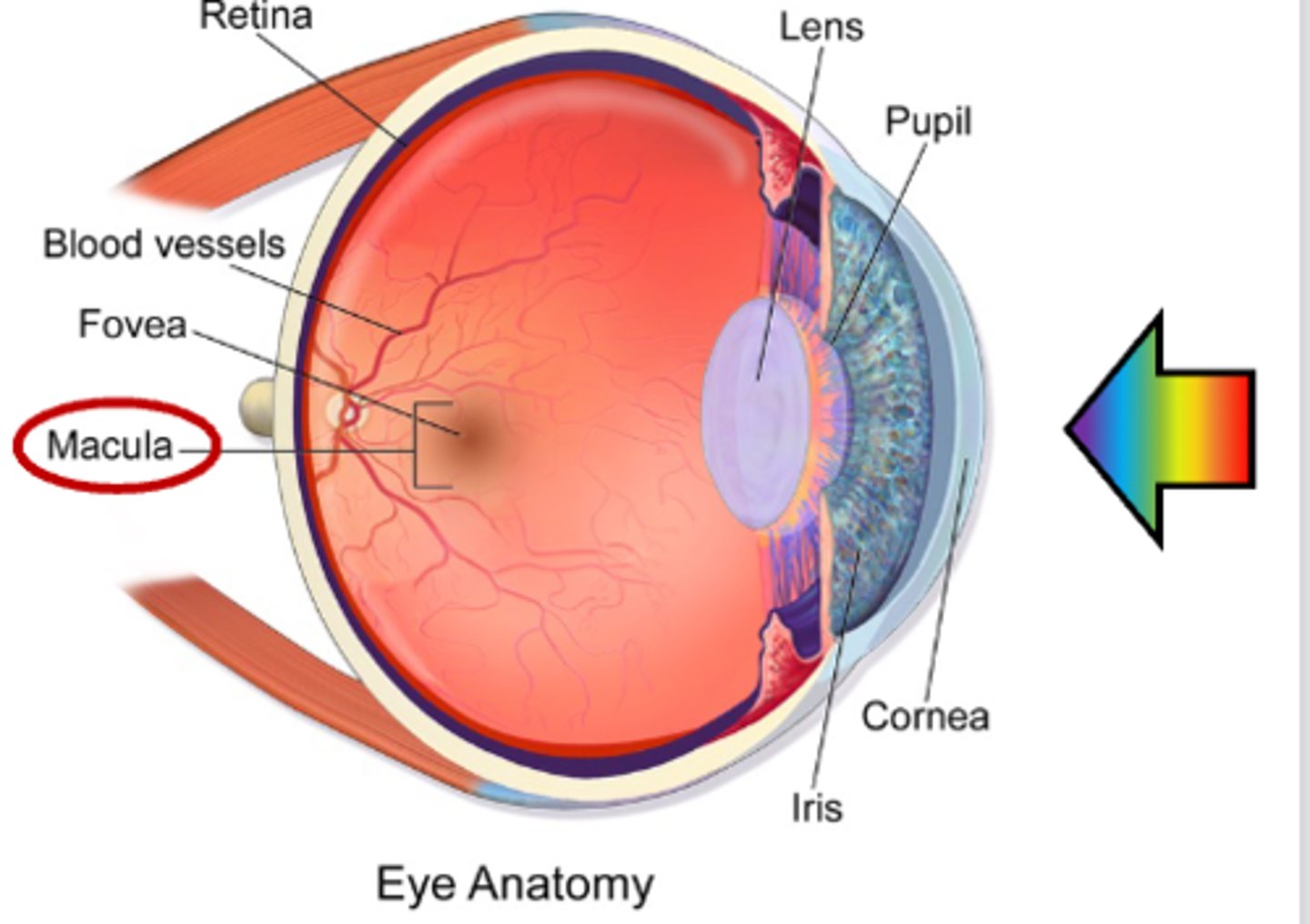
What is this?
• Leading cause of blindness in people > 60
• Risk factors: age, smoking, family history, hypertension
Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
What is the area called at the center of macula: area where visual acuity is the highest?
Fovea
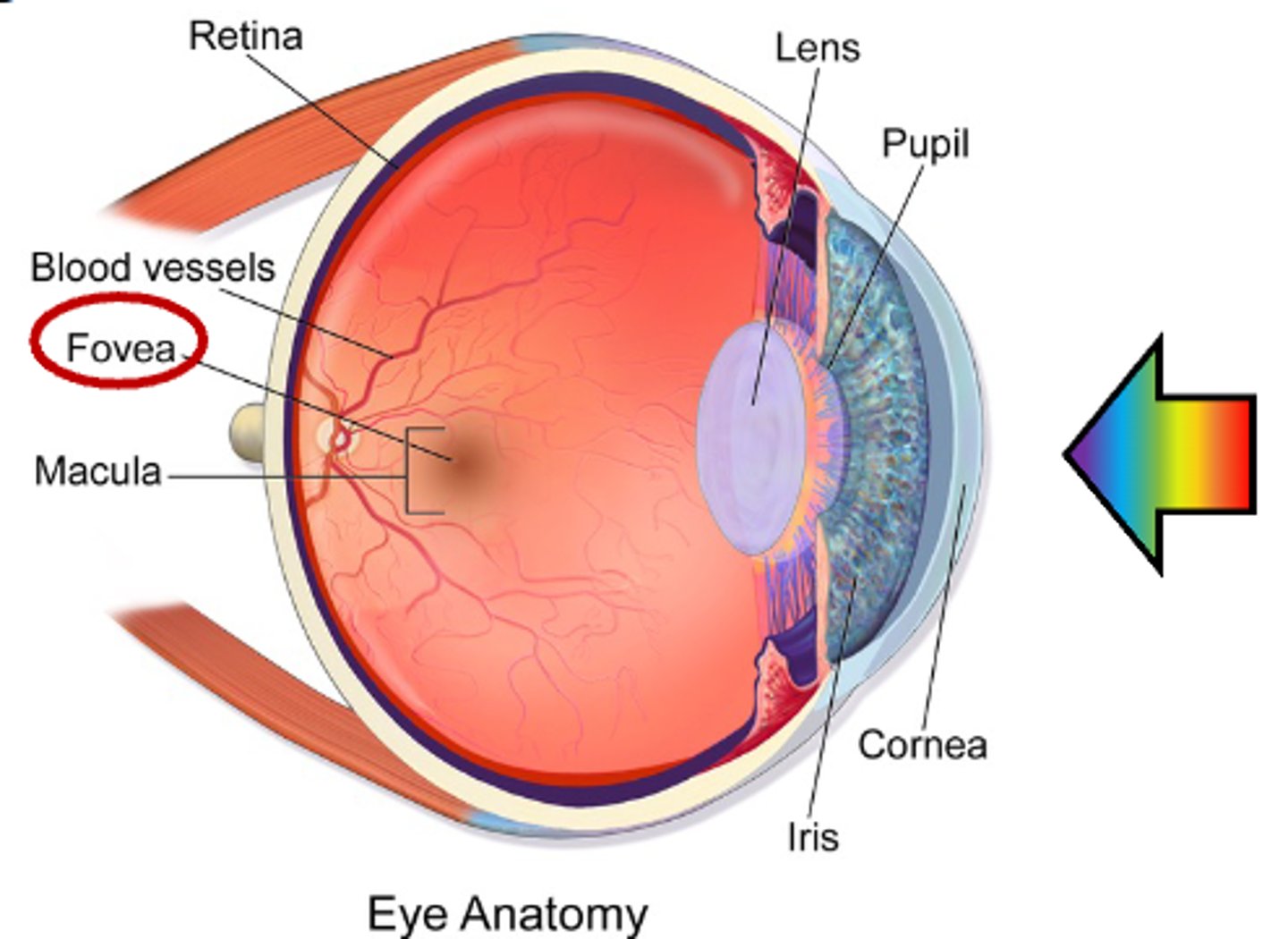
Cellular structure of the retina
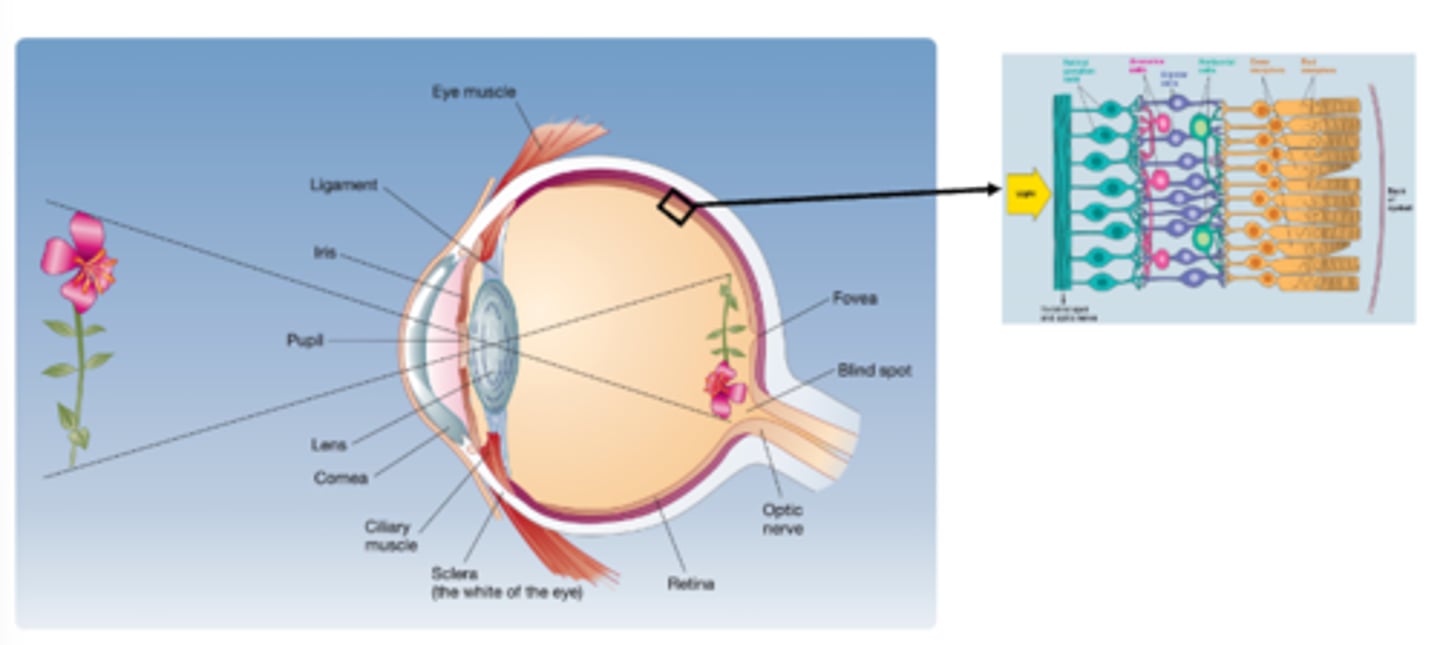
What are the layers of cells (from inside to outside)?
- Photoreceptors
- Horizontal cells
- Bipolar cells
- Amacrine cells
- Retinal ganglion cells
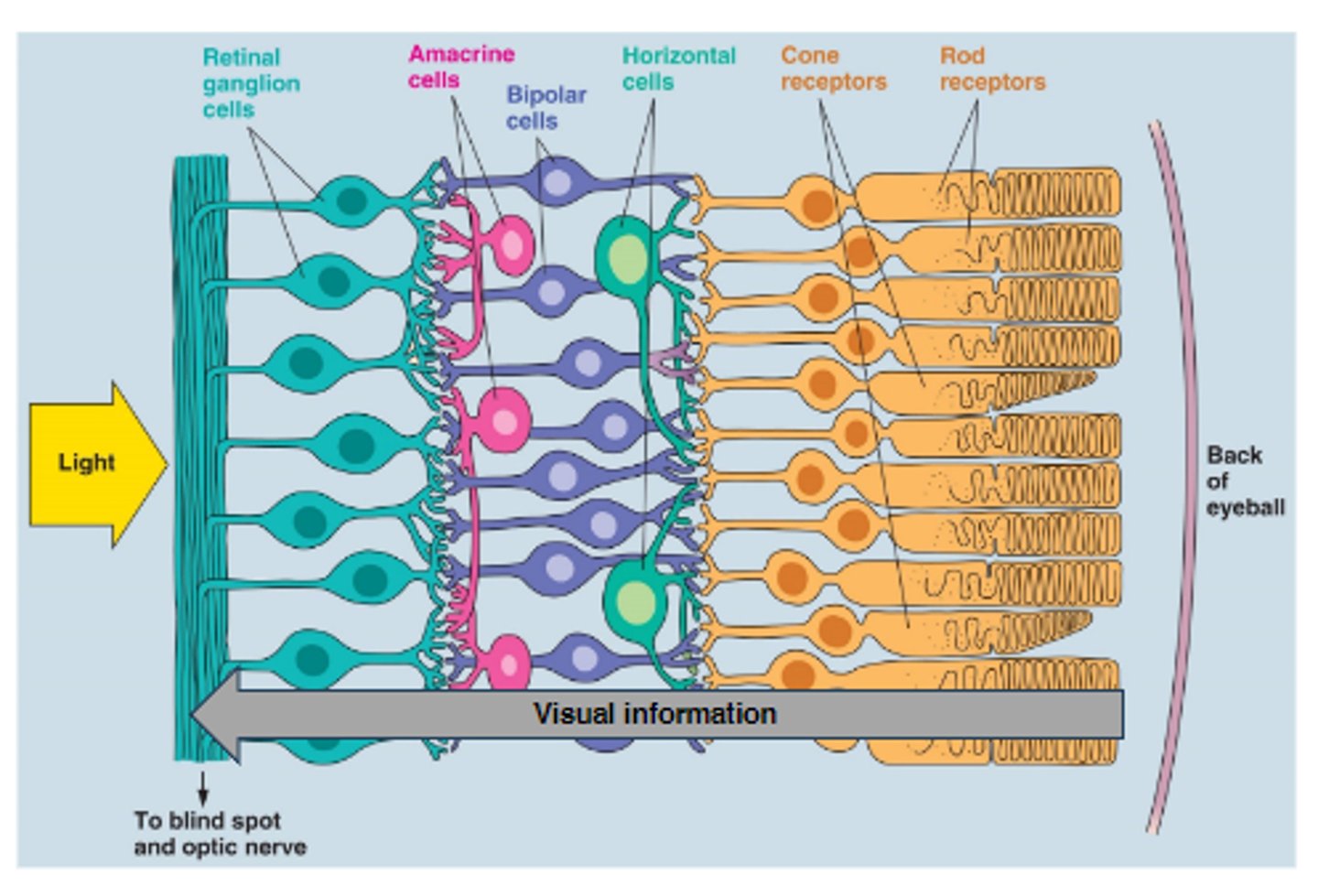
_____________________ respond to light. Convert light waves into a neural signal
Photoreceptors
Rods and cones have different "spectral sensitivity": .....
rods and cones are sensitive to certain wavelengths of light
______________
• Predominant in bright lighting
• High acuity: provide both color and detail
• Greater concentration in the fovea
• Color vision
Cones (photopic vision)
What is Fovea?
Area of the retina with fewer ganglion cells; allows for high acuity vision
__________
• Predominant in dim lighting
• High sensitivity to black/white, but lack acuity
• Greater concentration outside the fovea
Rods and cones differ in their _______________ _______
convergence ratio
What is High Convergence in Rods?
More sensitive to light, but less precise
What is Low Convergence in Cones?
Allows for high acuity vision
Transduction by photoreceptors converts light into a ....
neural signal
Transduction by photoreceptors: In the Dark -
Na^+ channels are partially open by the binding of...
- Releasing glutamate
cGMP (depolarized)
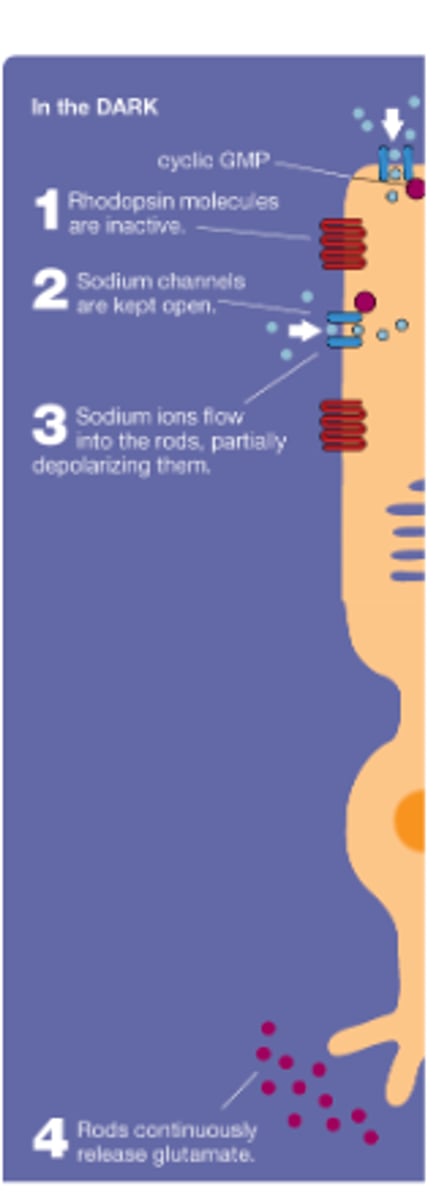
What is Rhodopsin?
A G-protein-linked receptor in rods that responds to light rather than to neurotransmitters
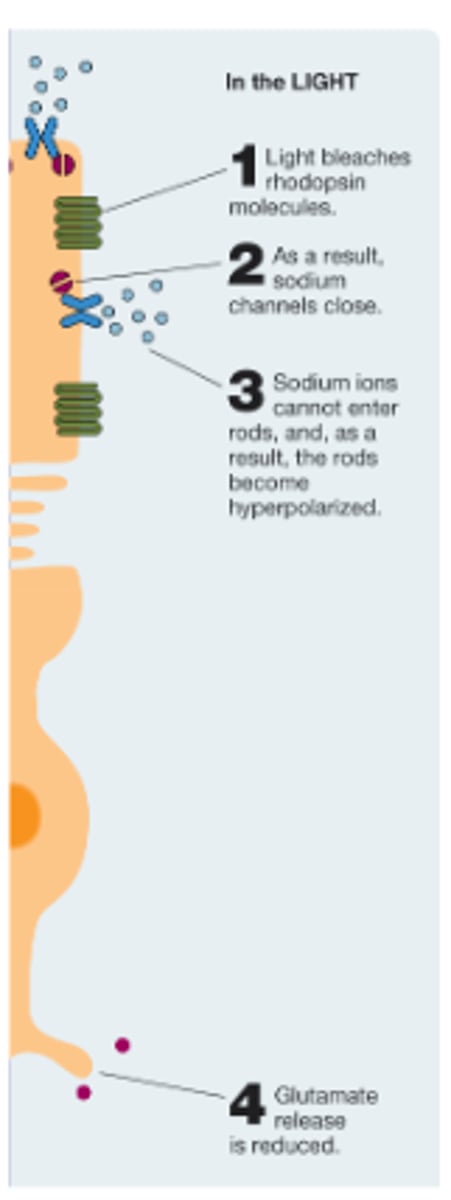
Transduction by photoreceptors: When Light Strikes -
• Na+ channels close with cGMP reduced
• Rods _____________
• Decrease in glutamate release
• Photoreceptors have inhibitory synapses onto bipolar cells
• Reduced release of glutamate on bipolar cell = activation
hyperpolarize
What are the two problems with the configuration of the retina?
1. Incoming light is distorted by other cell layers before reaching the photoreceptors
2. There is a blind spot in our visual field
Corresponds to where the optic nerve passes in the retina:
no photoreceptors
_______________________
• put object of interest on fovea
• Voluntary, involuntary
Eye movements (saccades)
What is Temporal Integration?
Our perception is the sum of the input received during the last few fixations