Ant Seg L2: Eyelids Anatomy
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
what is the thinnest skin in the body?
eyelid
what are the LAYERS of the EYELID SKIN
1. Epidermis
2. Dermis
3. Areolar Connective Tissue
4. Subcutaneous Tissue
5. Fat pad (Only in Orbital portion)
what are the LAYERS of the EPIDERMIS?
1. Keratinized superficial layer
2. Granular layer
3. Basal germinal layer
what two muscles are in the pretarsal portion of the palpebral muscle?
Horner Muscle → Deep palpebral fibers that wrap around the lacrimal canaliculi • Function: Moves tears
Riolan Muscle→ at lid margin around both sides of each meibomian gland openings • Function: Maintains lid globe congruity, express meibum
What is the Gray Line?
Anatomical landmark →Divides lid into anterior and posterior
Riolan Muscle
_____________ form a sleeve around SPL and changes it's direction to superoinferior
Ligaments
• Superior transverse ligament (Whitenall's) • Intermuscular transverse ligament
______________: (fan-like tendonous expansion of the SPL) • Pierces the orbital septum and attaches to superior tarsal plate • Attachment to skin & orbicularis = upper eyelid crease
Levator Aponeurosis
______________: Posterior inferior extension of SPL • Smooth muscles with sympathetic autonomic innervation
Tarsal Muscle of Muller
Retractor of the upper eyelids located within the orbit extending into upper eyelid
Superior Palpebral Levator Muscle
what is the function of the Capsulopalpebral fascia (lower lid aponeurosis)?
• Extension of the inferior rectus muscle sheath and inferior suspensory ligaments • Retractor of lower eyelids
What is the function of the Inferior tarsal muscle?
• Extension of inferior rectus muscle sheath inserting into lower palpebral conjunctiva and lower tarsal plate • Smooth muscle with sympathetic autonomic innervation
____________ Dense connective tissue of upper and lower eyelid that serves as a barrier and separates the anterior and posterior extent of the orbit.
Orbital Septum
the orbital septum is Continuous with _____________ of the orbital bones (orbital rim)
periorbita and periosteum
What are Zeis Glands?
Sebaceous glands • Coats lash follicles with sebum
What are Moll Glands?
• Sweat (apocrine) glands
What are Meibomian Glands?
Sebaceous glands • Embedded in tarsal plate • Secretes meibum which forms the lipid layer of tear film
What are the Accessory Lacrimal Glands?
1. Wolfring Glands • @ orbital border of tarsal plate
2. Krause Glands • @ conjunctival fornix
Secretion contribute to aqueous layer of tear film
what is the Lymphatic Drainage of the eyelid?
Lateral Conjunctiva: Preauricular Lymph Node
Medial Conjunctiva: Submandibular Lymph Node
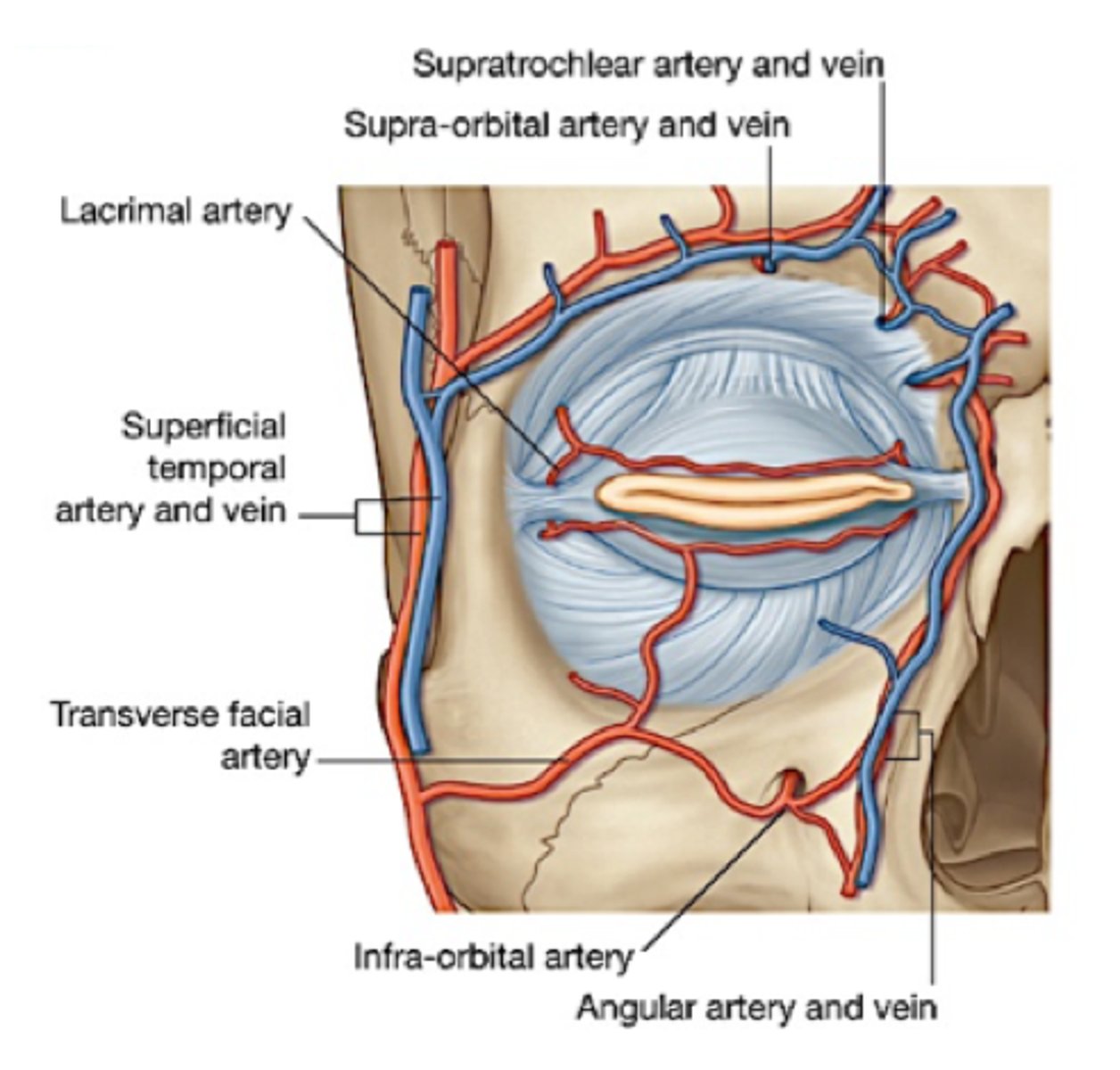
what is the blood supply of the eyelid
Internal Carotid Artery (ICA): deep eyelid tissue
External Carotid Artery (ECA): superficial eyelid skin
what is the motor Innervation of the eyelid?
CN 7 → Zygomatic branch → Orbicularis Function: Eyelid closure
CN 3 → Superior Palpebral Levator & Inferior Rectus Function: Eyelid retraction (open)
Sympathetic nervous system→ Muller muscle, inferior tarsal muscle Function: small eyelid retraction
what is the sensory innervation of the eyelid?
CN 5
V1: Ophthalmic
V2: Maxillary Upper eyelid Lower eyelid sensation sensation
Spontaneous Blinking
15/Min Contraction of Palpebral portion of Orbicularis (-) stimulus
Reflex Blinking
Contraction of Palpebral portion of Orbicularis (+) sensory stimulus Auditory, Touch, Dazzle, Menace
Forced Blinking
Contraction of Palpebral portion + Orbital portion of Orbicularis Winking, Voluntary blink