phase equilibria
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
exothermic phase changes
condensing and freezing
explain equilibrium including pressure for boiling point
X (l) ⇌ X (g) - increasing T shifts this eqm to the right
at the boiling point, Tb, vapour pressure (partial pressure) is equal to the pressure of the surroundings. below this, some of the substance is still in the gas phase but eqm lies to the left.
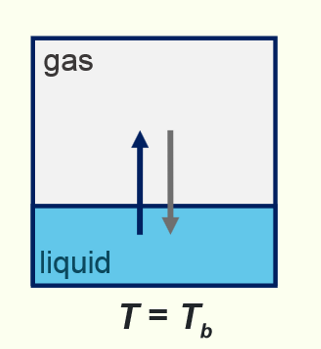
normal boiling point
pressure = 1 atmosphere
standard boiling point
pressure = 1 bar
define system and surroundings for entropy
system is where experiment is carried out, eg beaker, anything outside this is the surroundings and the universe if the system and surroundings combined
open system
matter and energy can be transferred
closed system
matter cannot be transferred but energy can
isolated system
neither energy nor matter can be transferred
adiabatic boundary
thermal energy cannot be exchanged between the system and surroundings
diathermal boundary
thermal energy can move freely between the system and surroundings
what is entropy and its symbol
entropy, S, is a measure of the distribution of energy
system and surroundings equation

change in entropy from solid → liquid → gas
increase in translational and rotational freedom
ΔS = +ve
can enthalpy and entropy be measured directly
entropy yes, enthalpy no
equation for entropy change of the system
do you multiply by the stoichiometry
yes

how can ΔSsurr be found
calculate from
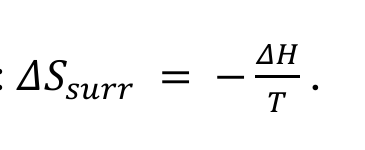
system and surroundings equation rearrangement without ΔSsurr
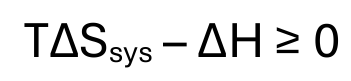
gibbs free energy equation
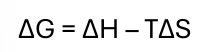
when is a process spontaneous
when ΔG < 0
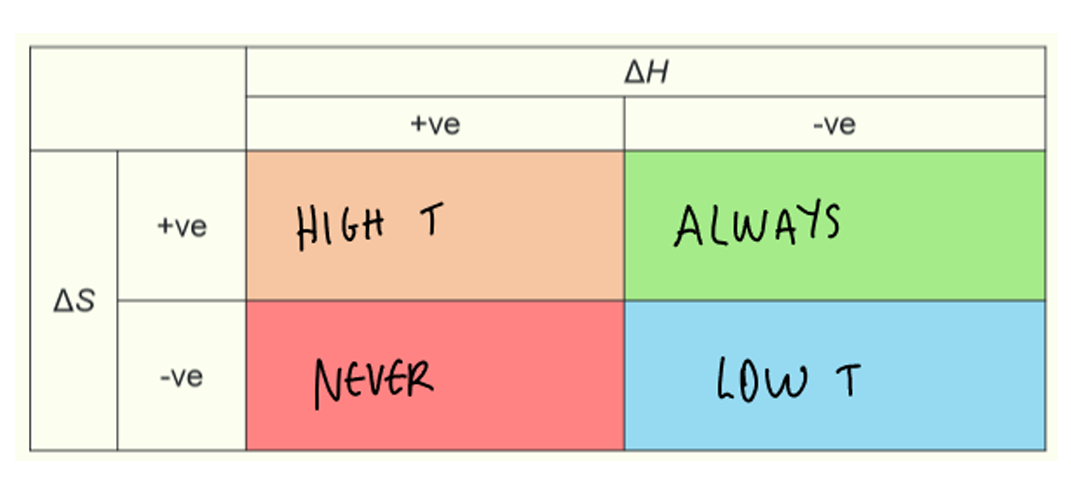
ΔG for solid, liquid and gas transitions
from solid to liquid to gas, ΔS and ΔH are both positive
at low T, ΔH > TΔS and ΔG is positive
at high T, ΔH < TΔS and ΔG is negative
table for positive and negative ΔH and ΔS
what is trouton’s rule
exceptions?
many substances have a similar entropy of vaporisation (ΔS⦵vap ≈ 85 JK-1mol-1)
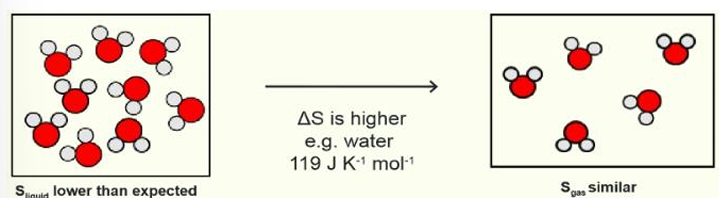
substances with strong H bonding
strong H bonding in the liquid phase
Sliquid is lower than expected and Sgas is similar to expected so ΔS is higher
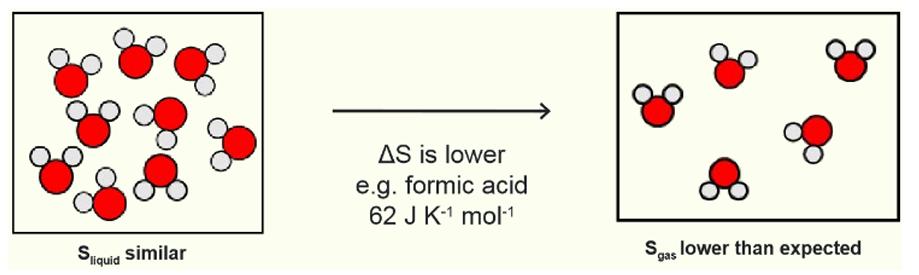
strong H bonding in the gas phase
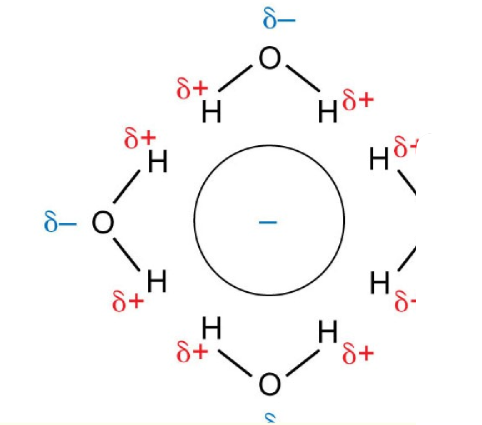
hydration of a cation
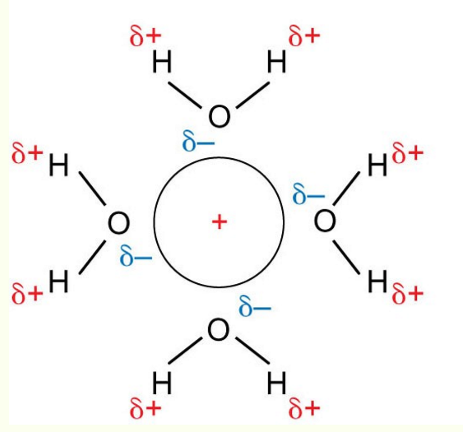
hydration of an anion