Poultry Nutrition Pat 1
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Gallus domesticus
Domestic hen species, domesticated since 2000 B.C.

Jungle Fowl
Common ancestor of domestic chickens, found in Southeast Asia.
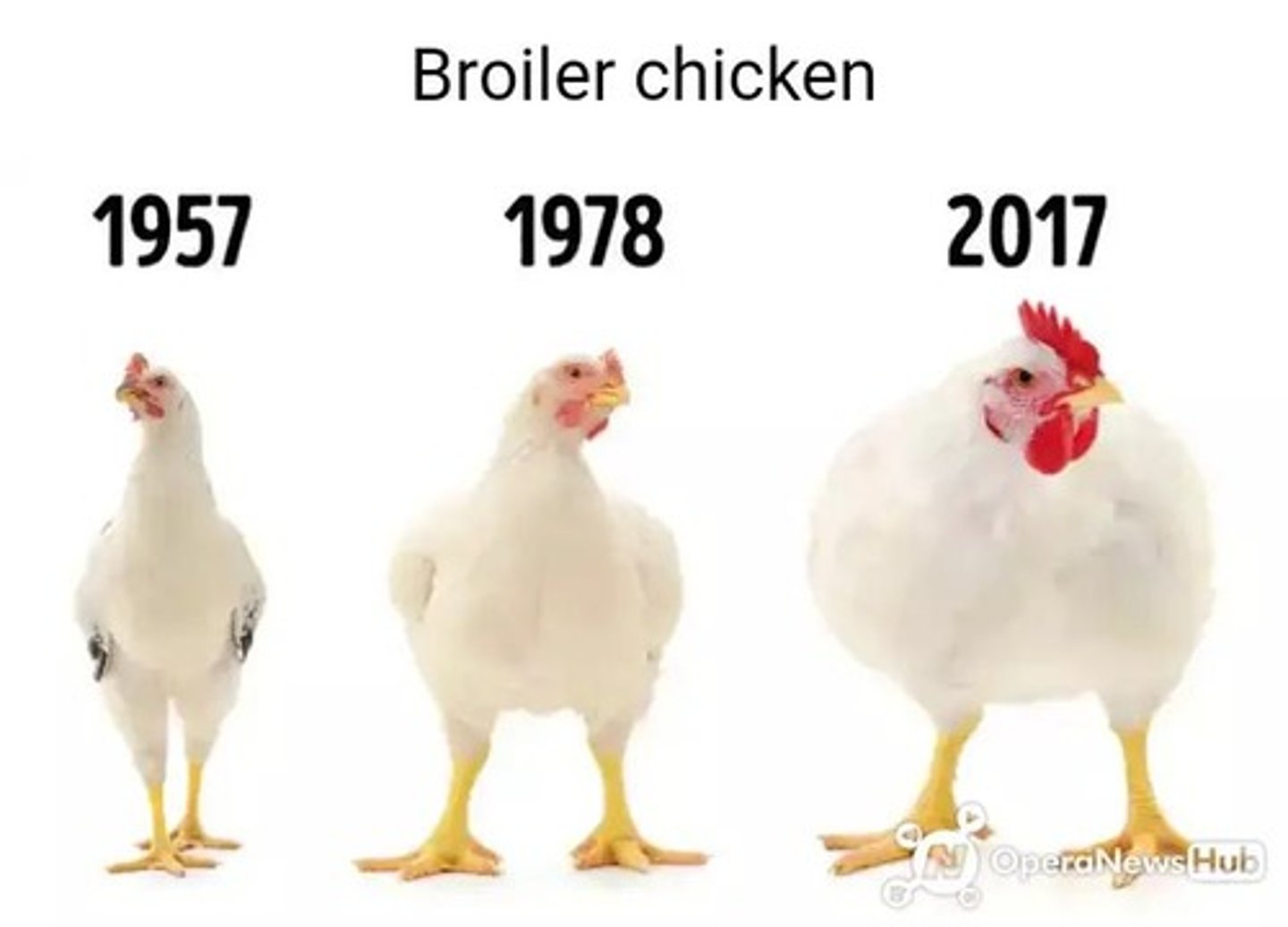
Broilers
Chickens raised specifically for meat production.
FCR
Feed Conversion Ratio; feed needed per weight gain.
56-day body weight
Weight of broilers at 56 days, measured in grams.
Egg production
Process of laying eggs, influenced by nutrition.
Nutritional needs
Essential dietary requirements for poultry health.
Greenhouse gas emissions
Environmental impact reduced by modern egg production.
Protein source
Eggs provide high-quality protein and essential nutrients.
Digestive system
Processes food for digestion and nutrient absorption.
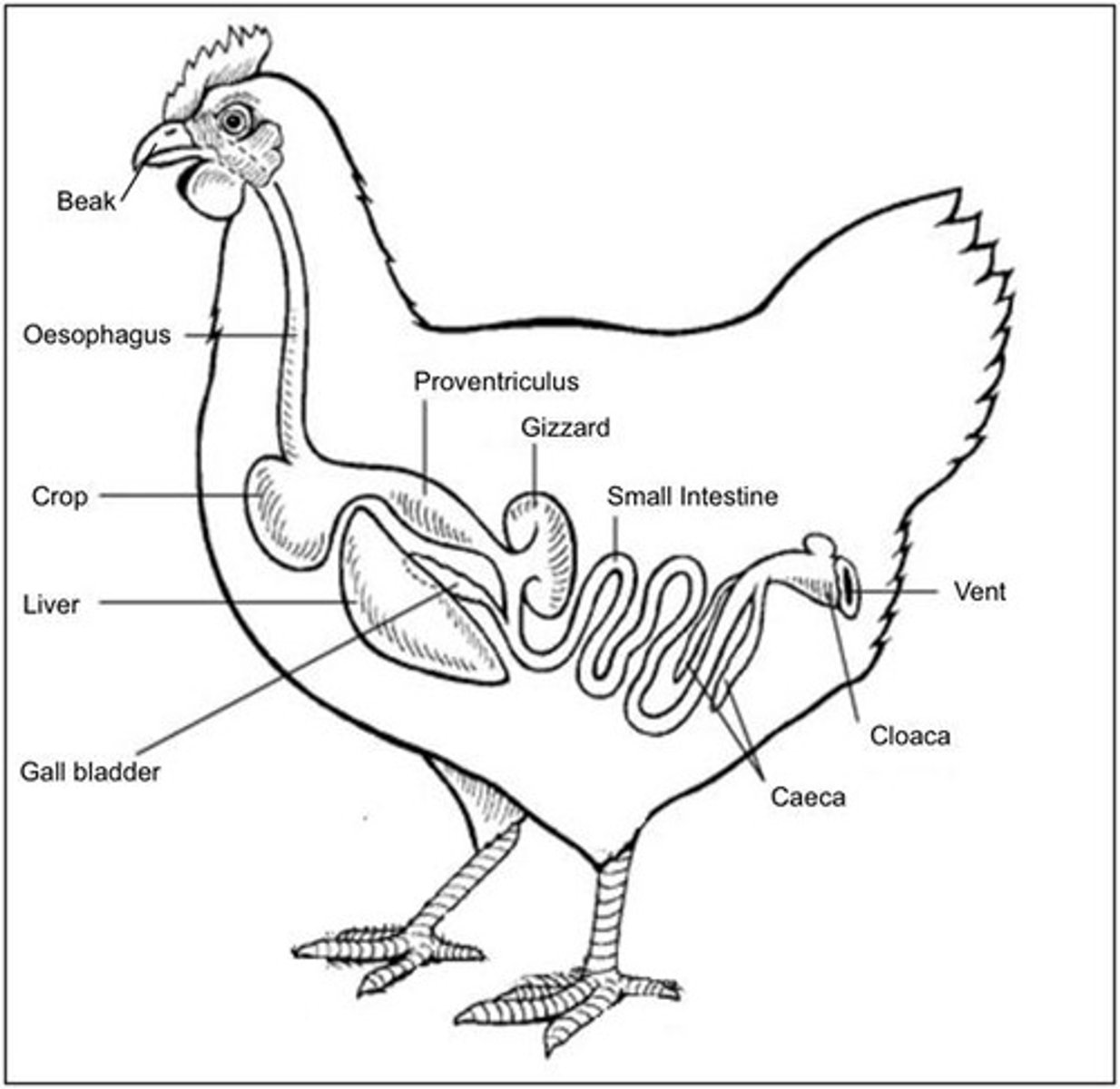
Digestion
Breakdown of complex compounds into absorbable units.
Absorption
Nutrient passage into bloodstream from digestive cells.
Laying hens
Chickens raised for egg production.
Nutrient needs
Varied dietary requirements across poultry life stages.
Growth rates
Speed of weight gain affecting nutritional requirements.
Commercial poultry
Poultry raised for profit in the industry.
Cost-effective
Affordable source of nutrition for various age groups.
Nutritional composition
Unique blend of nutrients in poultry meat and eggs.
Water usage
32% less water needed for egg production since 1960.
Feed efficiency
Reduction in feed needed for egg production over time.
Social pecking order
Hierarchy within flocks, originating from Jungle Fowl.
Jejunum
Main site for digestion and absorption in poultry.
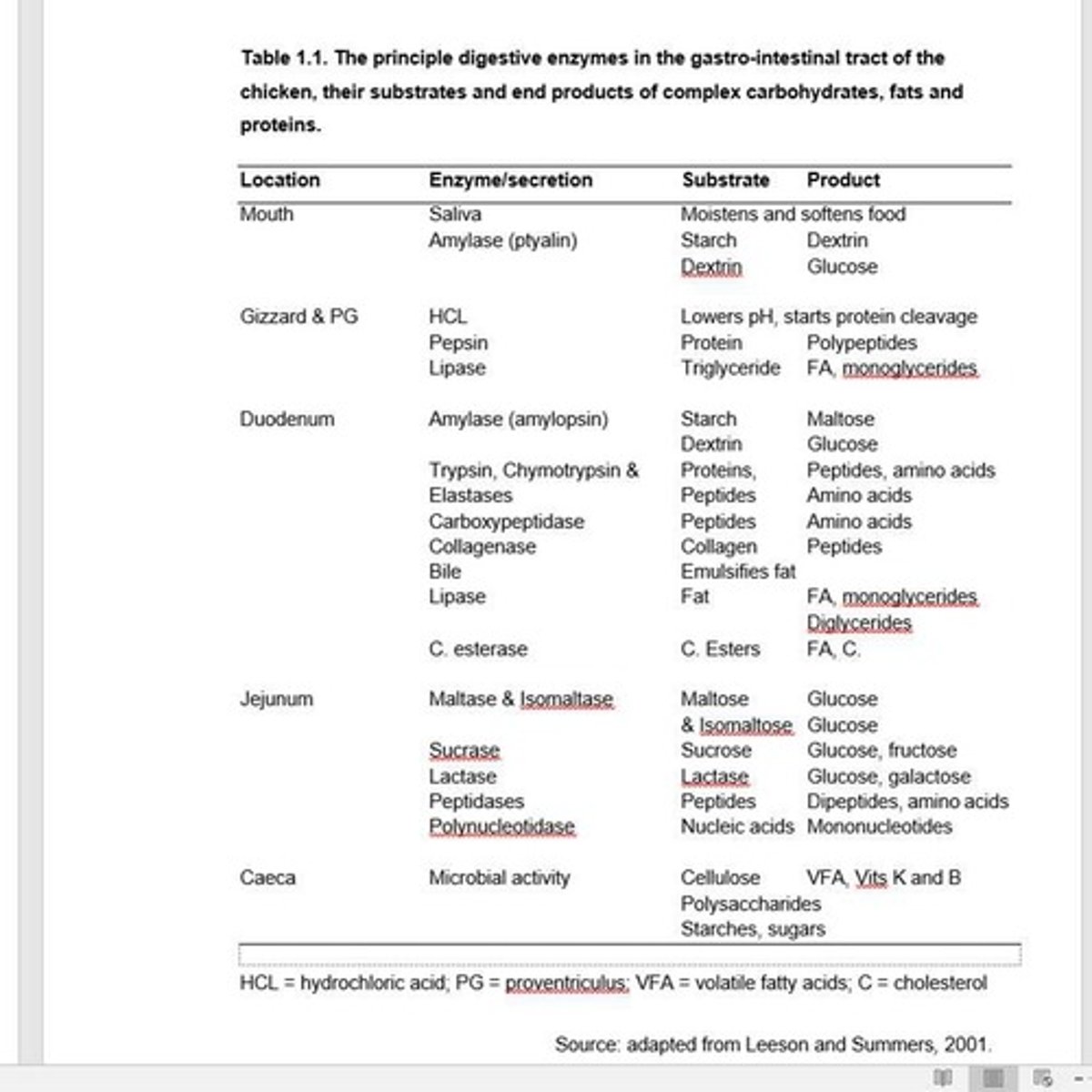
SCFA
Short-chain fatty acids from carbohydrate fermentation.
Butyric Acid
Preferred energy source for intestinal cells.
Volatile Fatty Acids
Includes acetic, valeric, propionic, butyric acids.
Poultry Feeding Standards
Nutrient requirements for different poultry types.
Nutrient Composition
Varies by genetics, age, and sex of birds.
Metabolizable Energy
Key factor in poultry dietary formulation.
Crude Protein
Essential for tissue synthesis and growth.
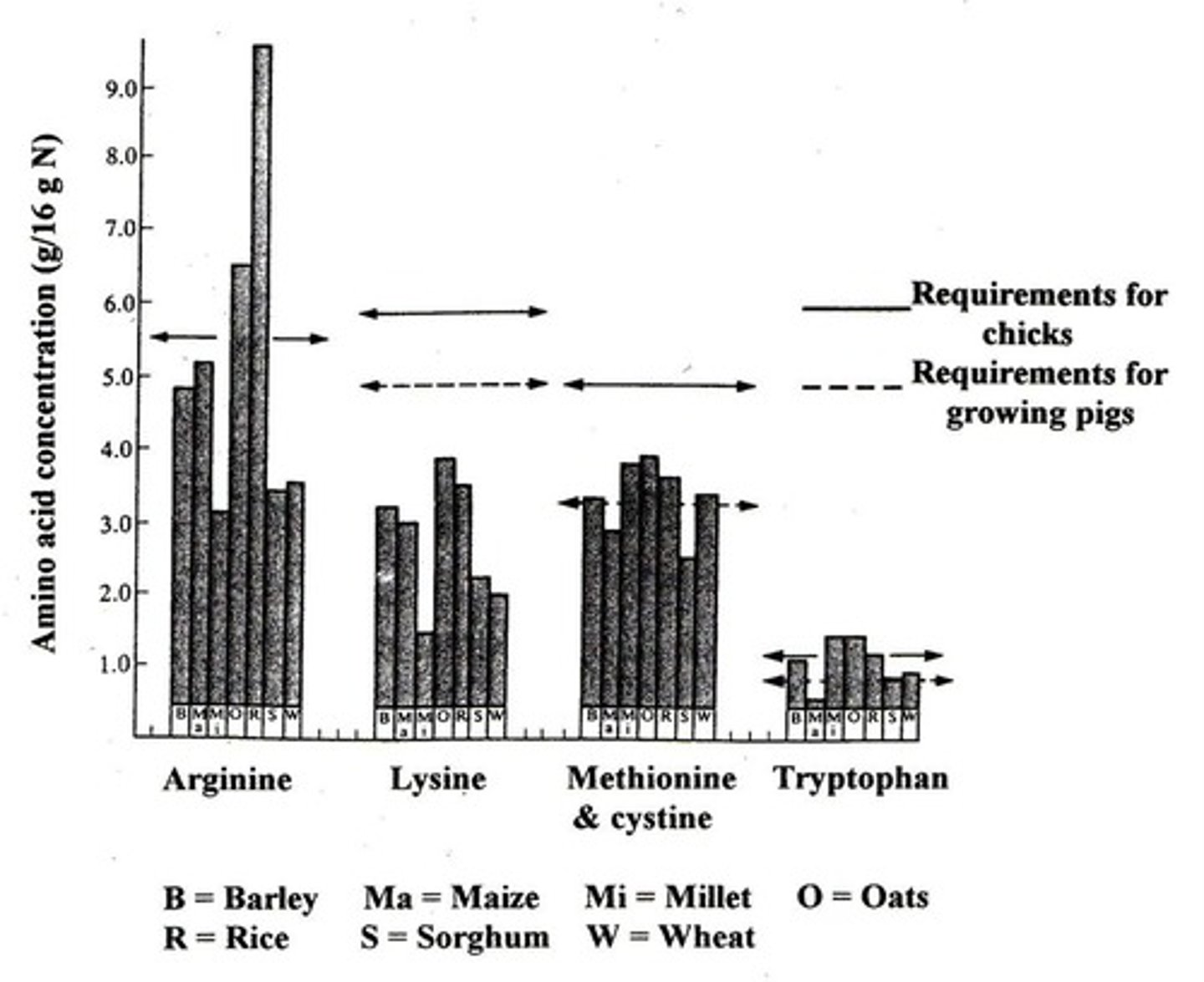
Lysine
A crucial amino acid in poultry diets.
Methionine
Important amino acid for poultry health.
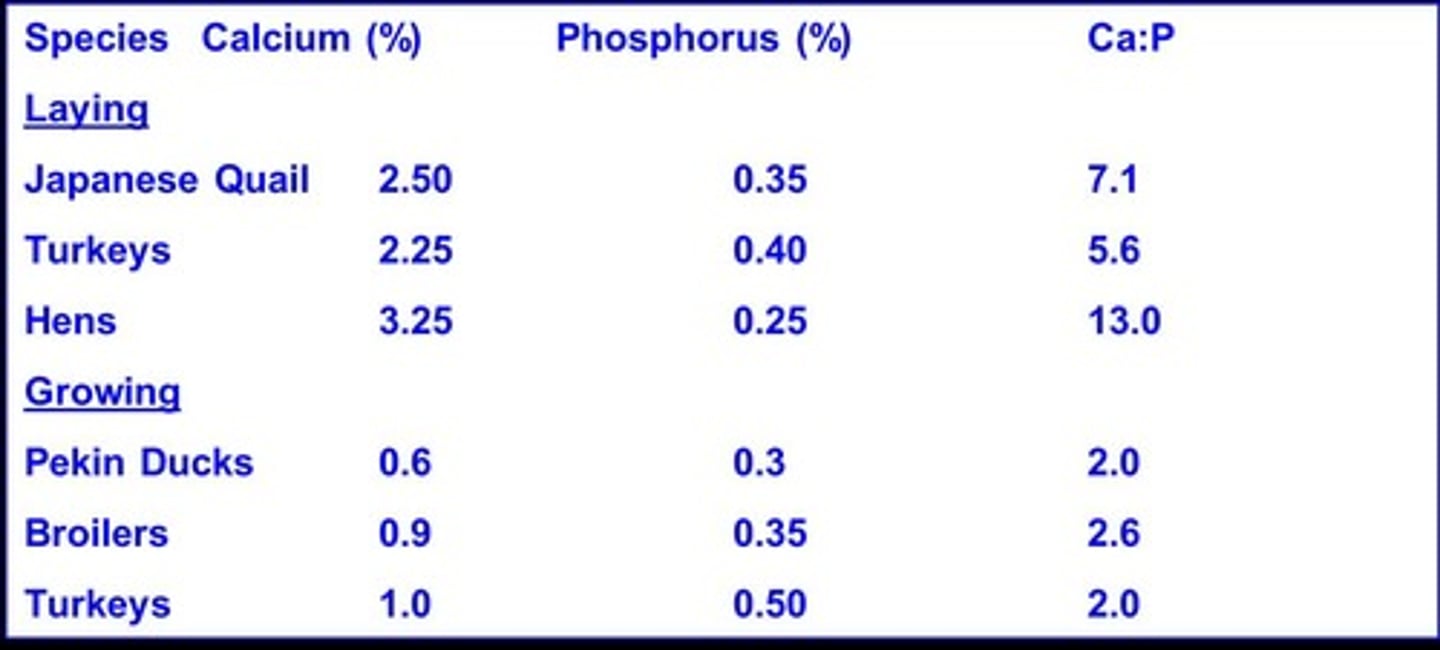
Calcium Requirements
Different for laying versus growing birds.
Cereal Grains
Major carbohydrate source in poultry diets.
Animal By-Products
Used in poultry feed formulations.
Vitamin Requirements
Organic compounds needed for growth and health.
Mineral Requirements
Inorganic nutrients essential for bodily processes.
Water
Vital for all physiological functions in poultry.
Genetics
Affects nutrient absorption and feed efficiency.
Age
Influences nutrient needs based on maturity.
Sex Differences
Minimal nutrient requirement differences before maturity.
Poultry Diet Composition
Mix of grains, meals, fats, vitamins, minerals.
Feed Cost
Accounts for approximately 70% of production costs.
Hindgut Fermentation
Provides up to 30% energy in pigs, 8% in poultry.
Dietary Formulation
Process to meet all nutrient requirements for growth.
Nutrient Requirements
Varies significantly post sexual maturity.
Reproductive State
Egg production and sexual activity affect nutrient needs.
Ambient Temperature
Cold increases energy needs; heat decreases them.
Housing System
Type influences bird activity and energy requirements.
Health Status
Diseased birds may need increased vitamin intake.
Production Aims
Nutrient composition varies by weight or egg goals.
Cereal and Grains
Main energy sources include maize, rice, and wheat.
Cakes or Oil Meal
Protein sources include soybean and sunflower meals.
Oils and Fats
Vegetable oils preferred over animal fats in diets.
Feed of Animal Origin
Includes meat, fish, and bone meals; restrictions apply.
By-products
Include rice bran, wheat bran, and rice polish.
Minerals and Vitamins
Enriched with calcium, phosphorus, and trace minerals.
Feed Additives
Includes antibiotics, probiotics, and antioxidants.
Exogenous Phytase
Incorporated in over 90% of poultry diets.
Amino Acids
Essential for protein synthesis; limiting in grains.
Phosphorus (P)
Essential mineral; inadequate supply reduces performance.
Phytate
Organic form of phosphorus; reduces bioavailability.
Phytic Acid
Complex form of phosphorus, not digestible by poultry.
Divalent Cations
Phytate chelates these, affecting nutrient absorption.
Bioavailability
Degree to which nutrients can be absorbed.
Anticoccidial Supplements
Used to prevent coccidiosis in poultry.
Feed Flavours
Enhance palatability of poultry feed.
Phytase
Enzyme hydrolyzing phosphate bonds in phytates.
Inorganic Phosphorus (P)
Supplement used to prevent phytate pollution.
E.C. 3.1.3.8
Enzyme classification for phytase activity.
E.C. 3.1.3.26
Enzyme classification for another phosphohydrolase.
Dietary Energy Sources
Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins provide energy.
Energy Utilization
Used for activity, heat, or stored as fat.
Excess Energy Storage
Unused energy stored as body fat.
Feed Cost Percentage
Feed accounts for 70% of production costs.
Bioavailable Energy Cost
Bioavailable energy is 70% of feed cost.
Farm Gate Cost
Bioavailable energy is 40% of product cost.
Production Efficiency
Reducing energy costs increases production efficiency.
Feed Intake Relationship
Intake correlates with dietary energy needs.
Lysine Deficiency Compensation
Chicks increase intake to offset lysine shortage.
Calcium Demand in Hens
Increased for eggshell formation in laying hens.
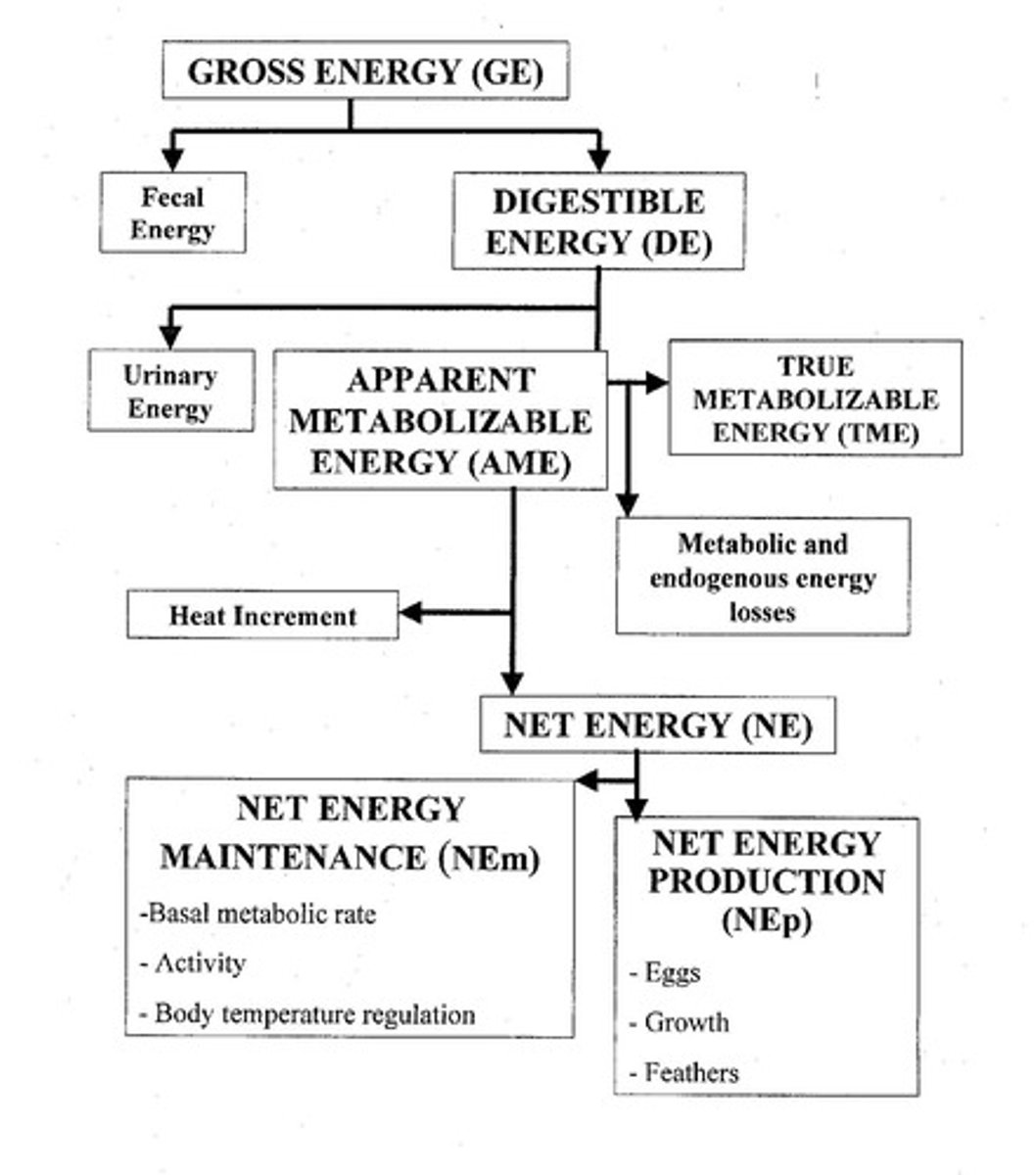
AME
Apparent Metabolizable Energy, measured in MJ/kg.
Gross Energy (GE)
Heat from complete oxidation of food.
Calorimetry
Measures heat produced in kilocalories or joules.

Kilocalorie Definition
Heat to raise 1000g water by 1°C.
Calorie to Kilocalorie
1 calorie equals 1/1000 kilocalories.
Joule Conversion
1 kilocalorie equals 4.184 kilojoules.
Gross Energy Concentration
Fat, protein, and carbs have specific GE values.
Digestible Energy (DE)
Energy absorbed post-digestion in poultry.
Gastrointestinal Digestion
Physical and chemical processes in nutrient absorption.
Cereal Gross Energy
Common cereals have about 18.5 MJ/kg DM.
Undigested Nutrients
Small nutrients voided in excreta.
Digestible Energy (DE)
Energy available after digestion, measured in MJ/kg.
Metabolizable Energy (ME)
Energy available after urine and feces losses.
Apparent Metabolizable Energy (AME)
Difference between digestible energy and urine energy.
ME Correction for Nitrogen
Adjusts ME based on nitrogen retention in birds.
Net Energy (NE)
Energy available for maintenance and production.
Net Energy for Maintenance (NEm)
Energy required to maintain body functions.
Net Energy for Production (NEp)
Energy used for growth and reproduction.
Gross Energy (GE)
Total energy content of feed before losses.
Energy Losses in Urine
Energy lost as nitrogenous wastes in urine.