AS Product Design
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
generation and development of ideas (4 points)
Understand Problem, Discuss with client, Come up with idea, Test,
User Centred Design
The user, or target market, should be consulted
regularly throughout the design process – they
are an important part of it!
Effective design specifications
Measurable Criteria, sorted into needs and wants
Methods of communicating Design Ideas (5 points)
Sketches, Card Modelling, 2D and 3D CAD models, CAM rapid prototyping, Formal Design Drawings
Benefits of CAD (7 points)
Increases productivity, more complex designs can be achieved, designs can be edited/reused easily, Designs can be easily understood, CAD files can easily be shared, no physical space required, Links to CAM seamlessly
Benefits of CAM (5 points)
Faster and more accurate, continually produces identical outcomes, creates complex outcomes, cost efficient, reduces labour costs
Disadvantages of CAD/CAM (6 points)
Expensive Setup cost, Requires servicing, parts are often expensive, training required, manual workers still needed, production becomes reliant on CAM, errors cam cause delays
Softwood
Comes from coniferous trees, evergreen, faster growth, softer and lighter and cheaper
Examples of Softwood
Pine, Cedar, Spruce
Hardwoods,
Deciduous Trees, shed leaves, grow slower, more expensive, harder, heavier
Examples of Hard wood
Oak, Beech, Mahogany
Thermosetting Polymers examples (4 points)
ER, MF, PR, ABS
Thermoforming Polymers examples (3 points)
acrylic, polystyrene, hips
Ferrous Metals
contain iron, magnetic, corrode
Non-ferrous metals
no iron, dont corrode, not magnetic
Examples of ferrous metals
Steel, Cast Iron, wought iron
Examples of non ferrous metals
copper, lead, aluminium
Alloy
A mixture of metals to improve properties or aesthetics
Examples of Alloys
Bronze, Stainless Steel, Brass
Composite material
A mixture of materials to enhance properties or aesthetics
When a material is light but strong, what do we say?
It has a high strength to weight ratio
Metal Finishes - Galvanising
Plating a metal with zinc, improves durability, corrosion resistance and exterior appearance
Metal Finishes - Heat Treatment
Hardening, increases durability
Metal Finishes - Anodising
Aluminium is anodised to provide corrosion resistance
Natural Timbers Finishes (4 points)
Stains, Varnishes, Paints, Pressure Treatment (used in outdoor fences)
Why do we apply finishes to Natural Timbers
Mainly decretive, but also protects against moisture. Pressure Treatment is used in outdoor fences
Finishes for Manufactured Boards
MDF, plywood, hardboard and chipboard are all absorbent and need to be sealed before a finish can be applied. Veneers often provide a finishing layer to manufactured boards and timbers.
Properties of natural timbers
durability, strength, hardness, toughness, and elasticity. Natural timbers are not good conductors of heat and electricity, and are therefore good insulators.
Properties of Manufactured Boards
Good insulators of heat and electricity, and do not warp as much as natural timbers. Manufactured boards are strong.
Properties of Metals
good conductors of heat and electricity, high density malleable and ductile, can be increased when a heat treatment finishing process is applied to some metals.
Modern Materials - Carbon Fibre
High strength to weight ratio, can be shaped into complex forms, smooth finish, can be sprayed and laqured
Modern Materials - Kevlar
fibre-based material which is commonly spun into sheets of fabric and used to produce protective clothing and jet engine linings
Nanomaterials
Nanomaterials are between 1 and 100 nanometres,
Smart materials
change in reaction to external stimuli
Thermochromic Pigments
Changes colour based on temperature
Photochromic pigments
Darken when light is applied
Shape memory alloys
can be set to a specific shape, and after it dents, it will return to the original shape
Hydrochromic Paint
Changes colour when it comes in contact with water
Phosphorescent materials
absorbs daylight and stores it, so it glows in the dark
Moulding
process involving shaping a liquid or malleable raw material using a frame, mould, former or cavity.
Extrusion
used to create objects with a fixed cross-sectional shape. A hot or cold material can be pushed through a die to create complex shapes that are consistent in length.
Laminating
technique of manufacturing materials in multiple layers
Milling
Using rotary cutters to remove material from a work piece
Casting
Process where liquid is poured into a mould and it cools to solidify
Forming
is where mechanical deformation changes the shape of a material. The shape of the material is permanently deformed without adding or removing any material.
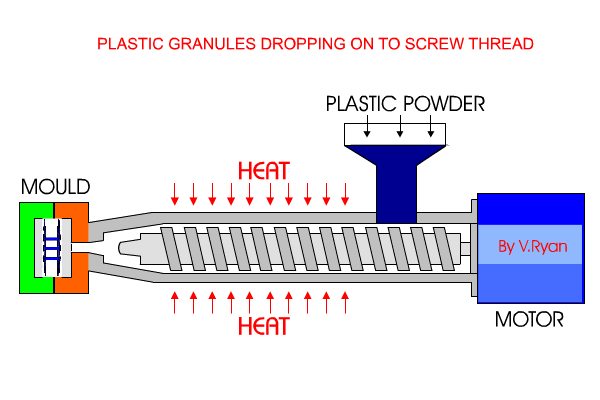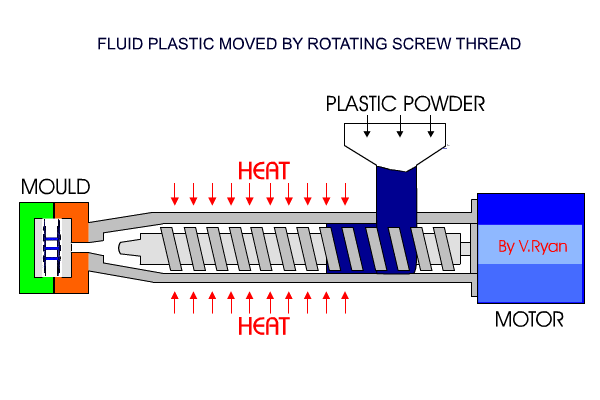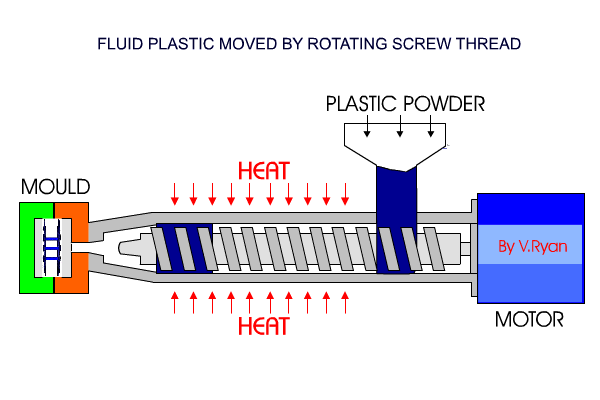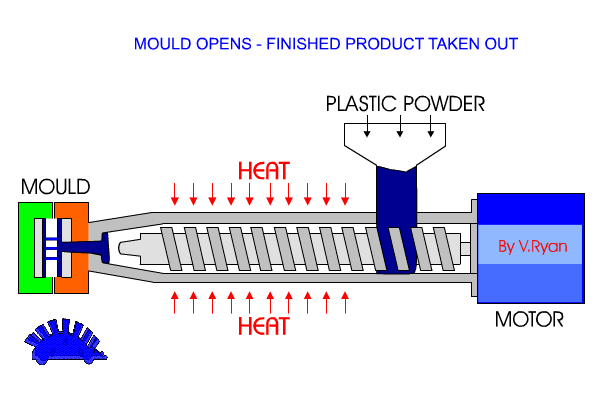
Injection Moulding
Granular form pellets are fed into a hopper, and gravity is fed into a heater where they become molten. The molten plastic is injected into the mould cavity under pressure, until the cavity is filled. This is then cooled and ejected or removed from the mould
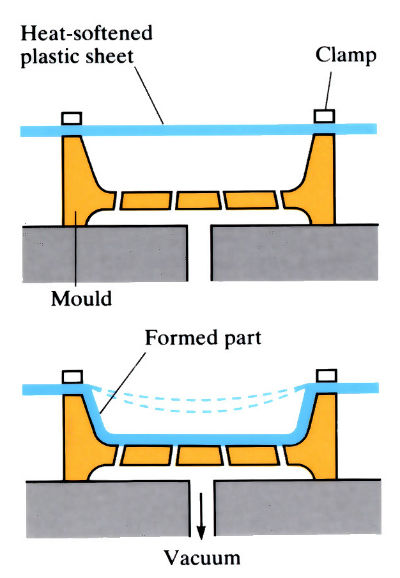
Vacuum Forming
A heater polymer tube is placed inside a cavity or mould and inflated to take the shape of the chamber, at the same time creating a hollow form with a thin wall.
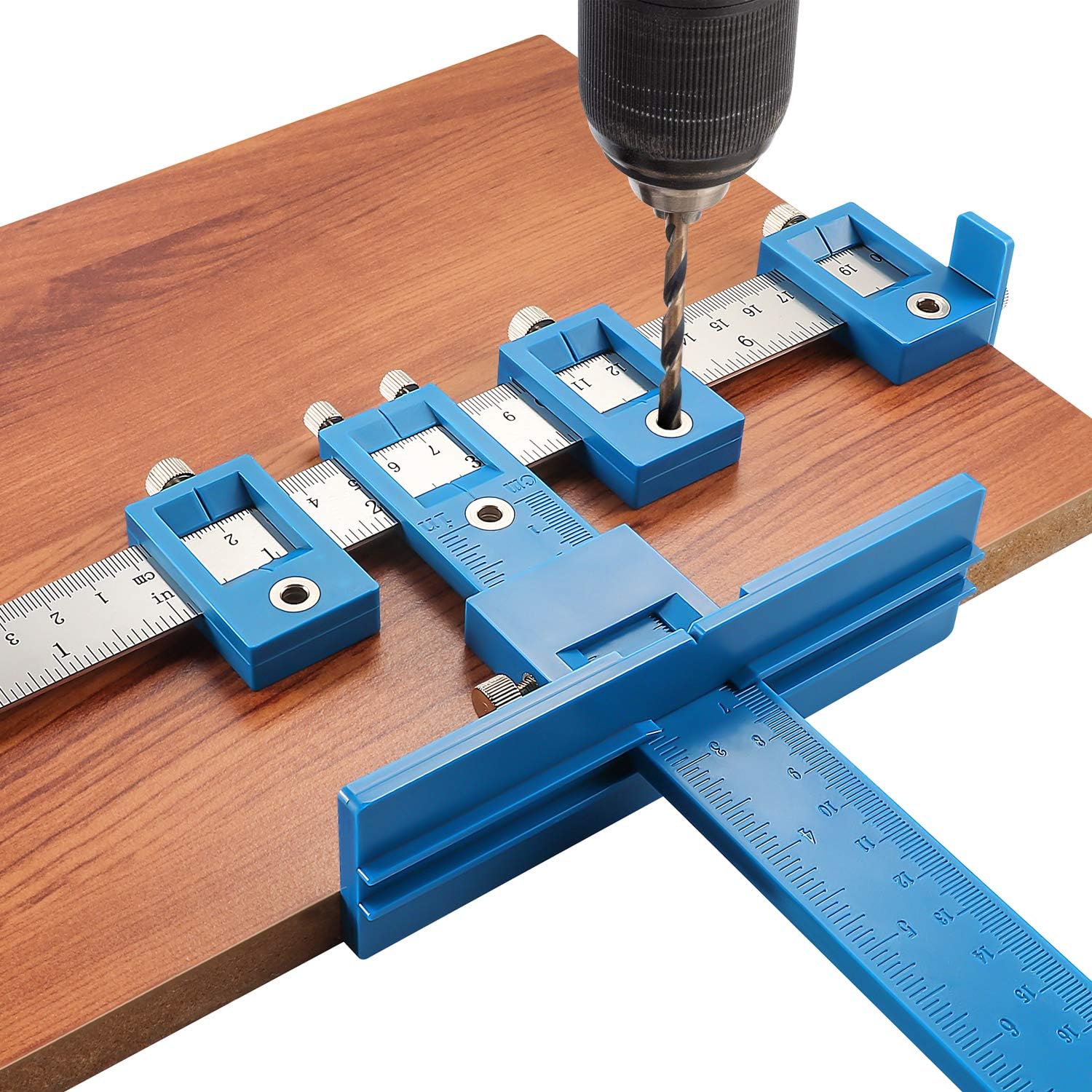
Jigs
A device used to guide a tool to a specific position on a workpiece
Fixture
Tool which holds the workpiece to a machine bed in a specific position

Stock Forms
materials machines into standard sizes or forms
5 Step risk assessment
IDERR - Identify, Decide, Evaluate, Record, Review