17-Population Genetics
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?
The state of a population in which the frequencies of alleles and genotypes remain constant from generation to generation, provided that only Mendelian segregation and recombination of alleles are at work.
What does it mean if a population is in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?
It means the population is not changing from genereation to generation. This means the population is not evolving.
What are the assumptions that must be met for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?
1. No mutations
2. No natural selection
3. The population is large
4. No migration is occurring
5. Random mating is occurring
What can occur if the assumptions of Hardy-Weinberg are not met?
Evolution. The population can change from generation to generation.
What can cause a population to evolve?
1. Mutations
2. Natural Selection
3. Genetic Drift
4. Gene Flow
5. Nonrandom mating
What is a mutation?
It is a change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA.
What is occurring if certain individuals are surviving and reproducing at a faster rate due to a heritable trait compared to individuals that lack the trait?
Natural Selection
What is the cause of change called, if a population changes because of a chance event?
Genetic Drift
What is it called if the size of a population is dramatically reduced by a chance event, like a natural disaster?
Bottleneck Effect
What is it called if a small group of individuals moves to a new location and establishes a population in the new location?
Founder Effect
Is genetic drift more significant for smaller or larger populations?
Smaller
If a population changes because of individuals migrating into the population, then what was the cause of change?
Gene flow
What is it called if there is a basis for mating partners in a population?
Nonrandom mating
What are the Hardy-Weinberg equations?
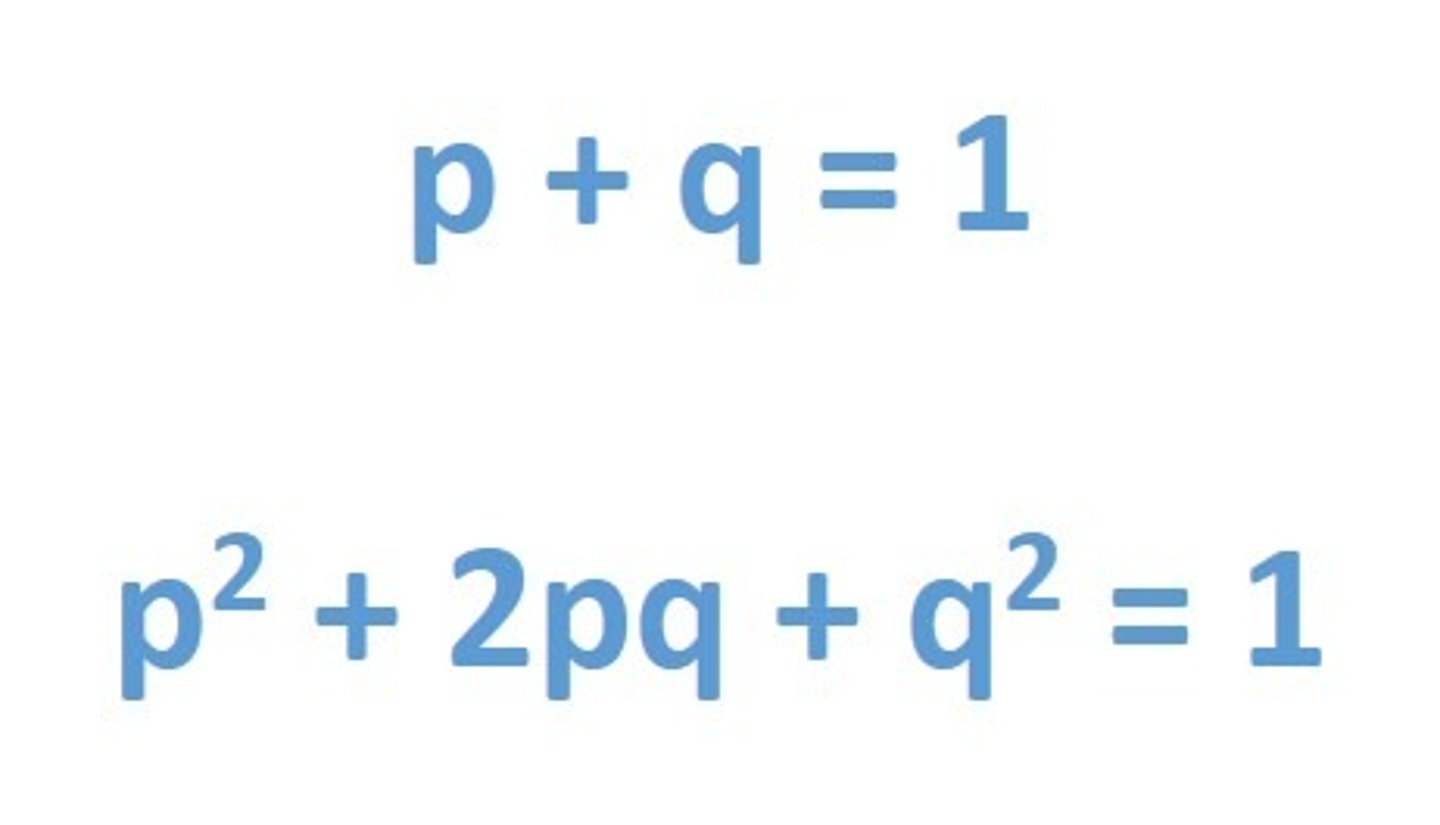
In the Hardy-Weinberg equations, what does p represent?
p represents the frequency of the dominant allele.
In the Hardy-Weinberg equations, what does q represent?
q represents the frequency of the recessive allele.
In the Hardy-Weinberg equations, what does p^2 (p squared) represent?
p^2 represents the frequency of homozygous dominant individuals.
In the Hardy-Weinberg equations, what does q^2 (q squared) represent?
q^2 represents the frequency of homozygous recessive individuals.
In the Hardy-Weinberg equations, what does 2pq represent?
2pq represents the frequency of heterozygous individuals.
What are the uses of the Hardy-Weinberg equations?
1. The equations can be used to see if a population is evolving.
2. They can be used to estimate the number of individuals who carry a disease causing allele.