Cognitive Exam 4 Creativity
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
analogical problem solving
attempting to solve a problem using the solution to a similar problem
***we just did this
***mindset: I have a problem→ I can help you, something similar happened to me
• the Russian marriage solution can be used to solve the mutilated checkerboard problem
analogical transfer
experience solving one problem is transferred to another problem
Target problem: the problem we are trying to solve (CHECKBOARD PROBLEM)
Source problem: another problem that is similar to and may illustrate a way to solve the target problem (RUSSIAN MARRIAGE)
Analogical transfer example
🎯 Target Problem: Radiation Problem
A doctor needs to destroy a tumor with radiation.
A strong beam would harm healthy tissue.
A weak beam won’t destroy the tumor.
Solution (hard to find): Use multiple weak rays from different angles to converge on the tumor.
📖 Source Problem: Fortress Story
A general wants to attack a fortress.
Roads are mined to explode if too many troops travel down one road.
Solution: Send small groups down many roads to converge at the fortress.
analogical paradox
it can be difficult to apply analogies in the laboratory, but we routinely use analogies in real-world settings
expert and expertise
someone knowledgeable or skilled in a particular
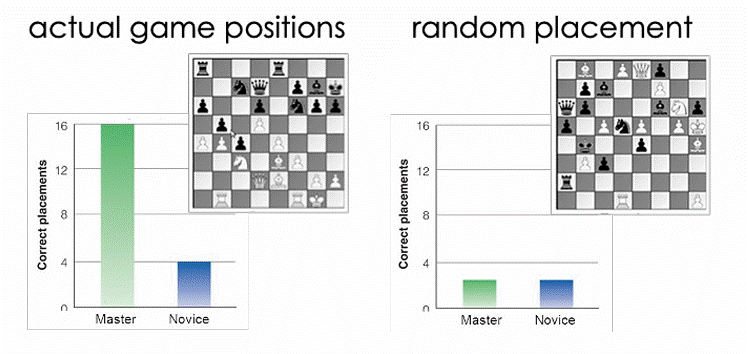
• experts solve problems in their field more quickly and more often than beginners
• experts possess more knowledge about their field (however the same level of knowledge for outside field like normal ppl) LOOK AT PHOTO
• experts organize their knowledge differently than novices
Creativity
the use of imagination or original ideas
divergent thinking
thinking that is open-ended and involves a large number of potential “solutions”
ex: how could you use this paper clip?
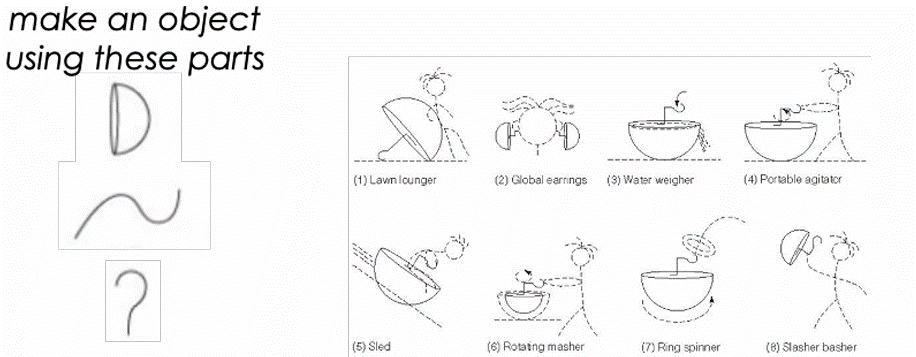
creative cognition
technique to train people to think creatively
ex: make an object using these parts
• creative problem solving is a process
Stage I – Problem Generation
Problem Finding – Identify that a problem exists or an opportunity is present.
Fact Finding – Gather relevant data and background info.
Stage II – Problem Formulation
Problem Definition – Frame the problem clearly.
Idea Finding – Generate possible solutions (brainstorming, divergent thinking).
Stage III – Problem Solving
Evaluation and Selection – Analyze and choose the best solution(s).
Planning – Map out how the solution will be implemented.
Stage IV – Solution Implementation
Selling Idea – Communicate and advocate for the solution.
Taking Action – Put the plan into effect.
daydreaming, solitude, mindfulness
• daydreaming: purposeful mind wandering
• solitude: avoiding distractions; giving the mind space and time to make new connections and find meaning
• mindfulness: pay attention to what is happening in our mind and in the environment