2.1 T lymphocyte development
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
T cells recognize what in MHC?
peptide; MHC most diverse set of genes
ineracts w MHC + peptide
how are TCRs made?
randomly through V(D)J recombo
how do we end up w TCR that see target peptide in MHC?
what prevents our T cels from targeting self peptides
explain the difference between T and B cell receptor structure
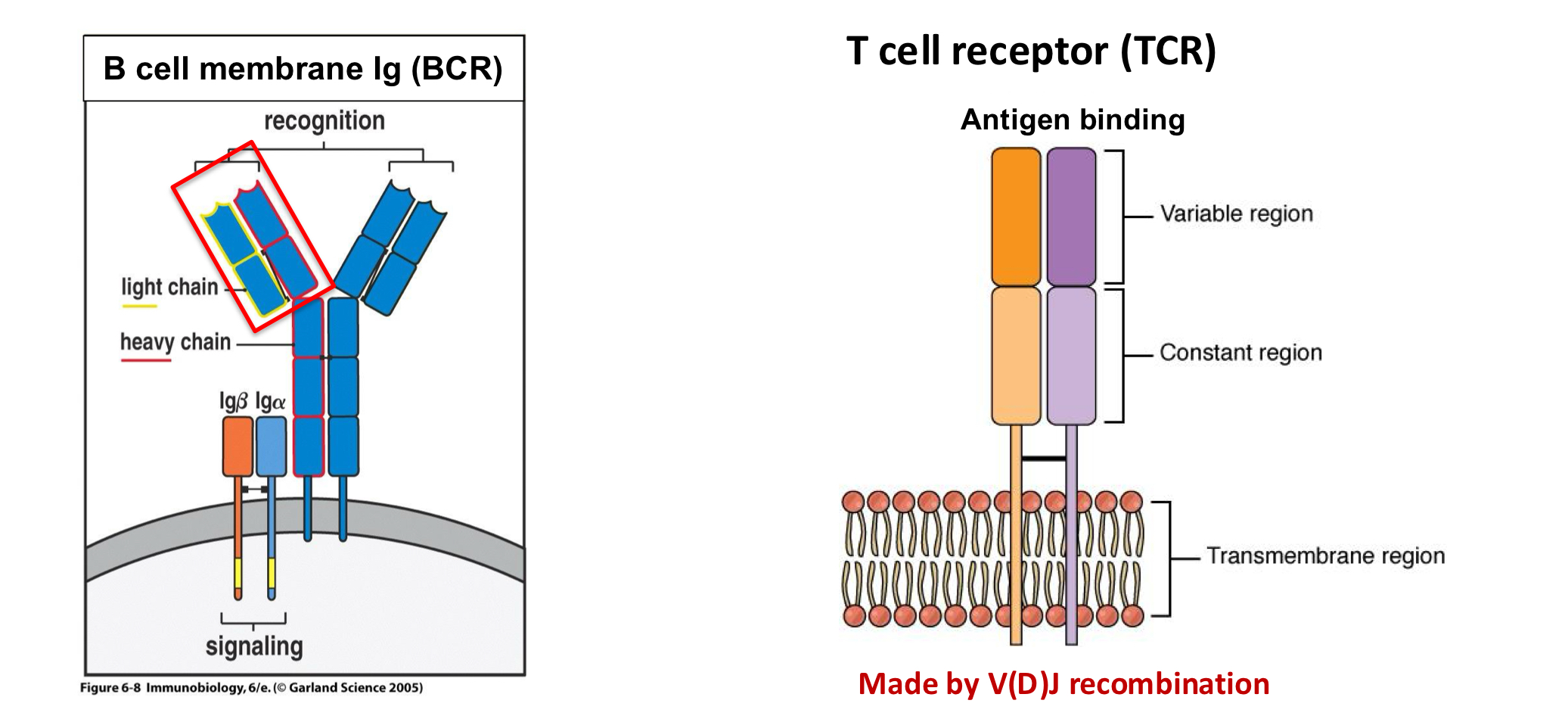
is there a soluble form of TCR?
no! so there is no CSR and SH
what are the two chains of the TCR?
alpha and beta
few have gamma and delta
what is always associated wth TCR?
CD3; it transduces signals this way (vs CD19 and CD 20 for B cell)
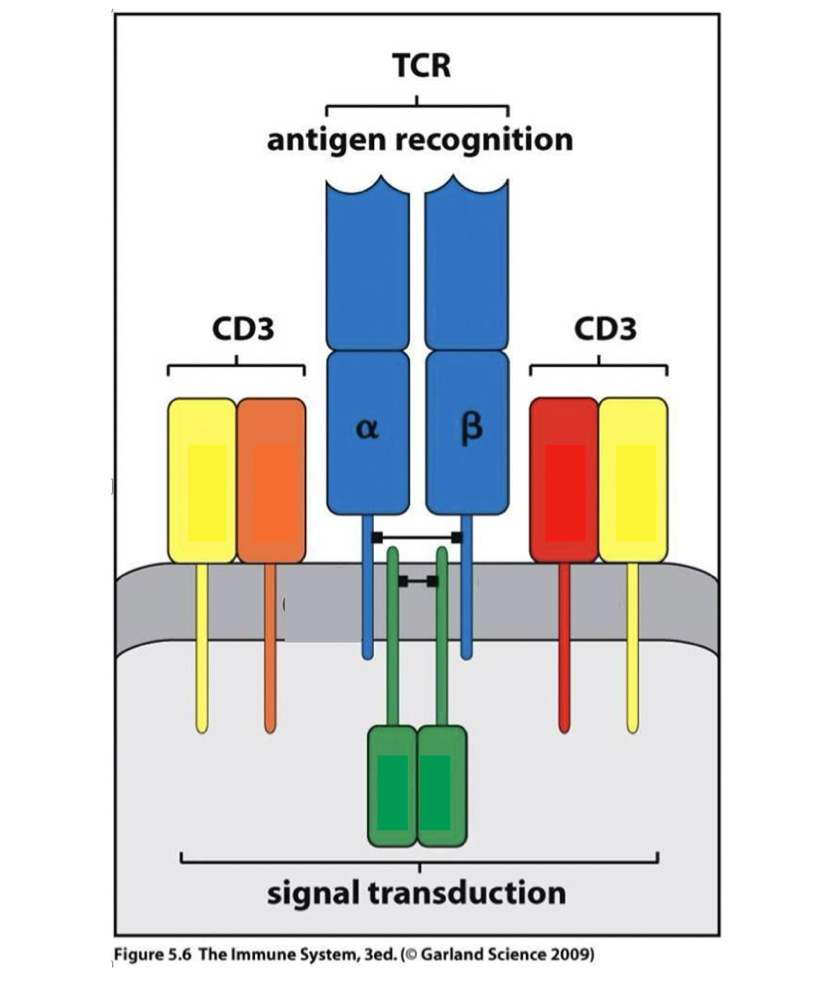
which cell receptor
recognizes antigen but does not have intracellular tails
CD3 makes it invariant
TCR
what antigen type do TCR recognize?
protein antigen, not soluble
how do pathogens and protein antigens get into host cell?
infection or ingestion by endocytosis or phagocytosis (know MHC class I vs class II, APC vs self peptides)
how many alleles possible?
12! (see 1.3)
THC restriction, interacts with only 1 allele w/in said sid
MHC restriction
mature αβ T cells recognize peptides of antigenic proteins that are bound to MHC as peptide–MHC (pMHC) complexes, but essentially nothing else
MHC Class I on expressed on
ALL nucleated cells (not RBCs and platelet)
MHC class II expressed on
APCs: DC, B cell, macrophages (phagocytic)
thymic non-lymphoid cells
CD4 positive T cells recognize the peptides
CD8 and CD4 are (BLANK) that (BLANK) binding and (BLANK) signaling
co-receptors
stabilize
enhance
*do not bind antigen but bind to constant part of MHC
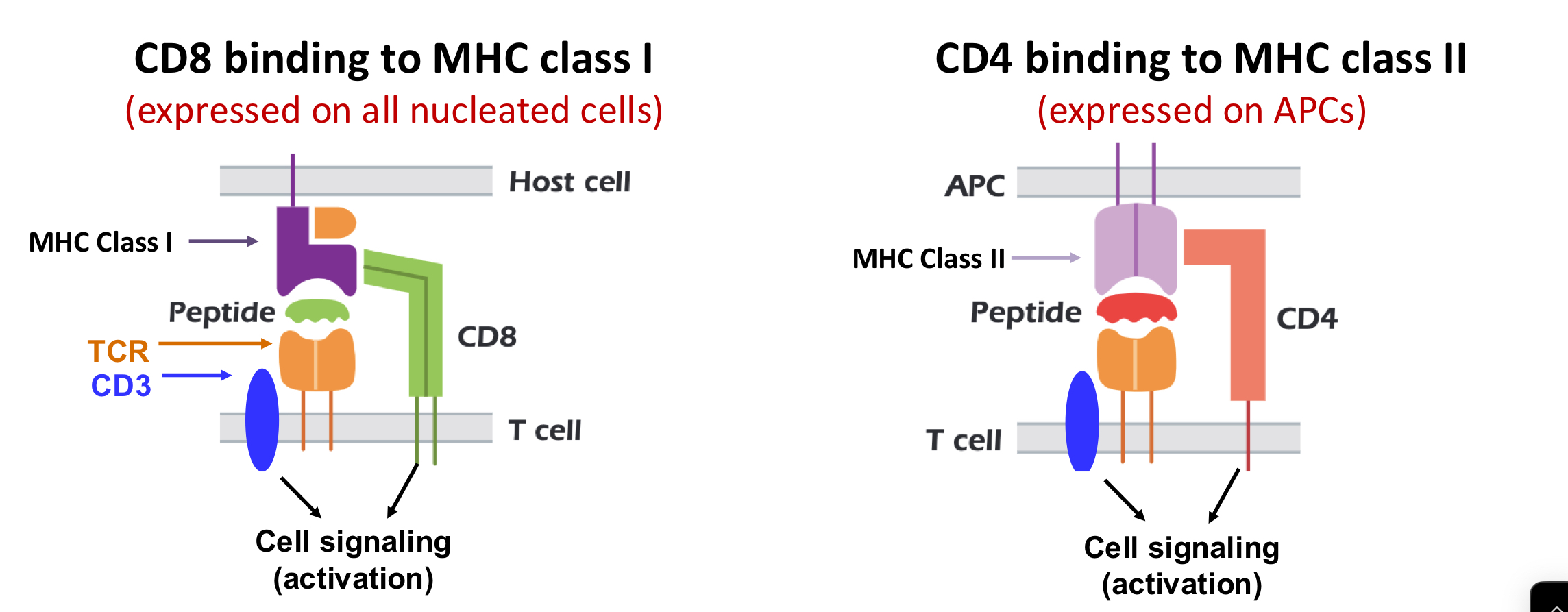
explain in short plain terms T cell, alpha beta, and co-receptor
TCR: V(D)J but no SH and CSR; CD3 signal transduction
chains, antigen recognition
co-receptor determines function
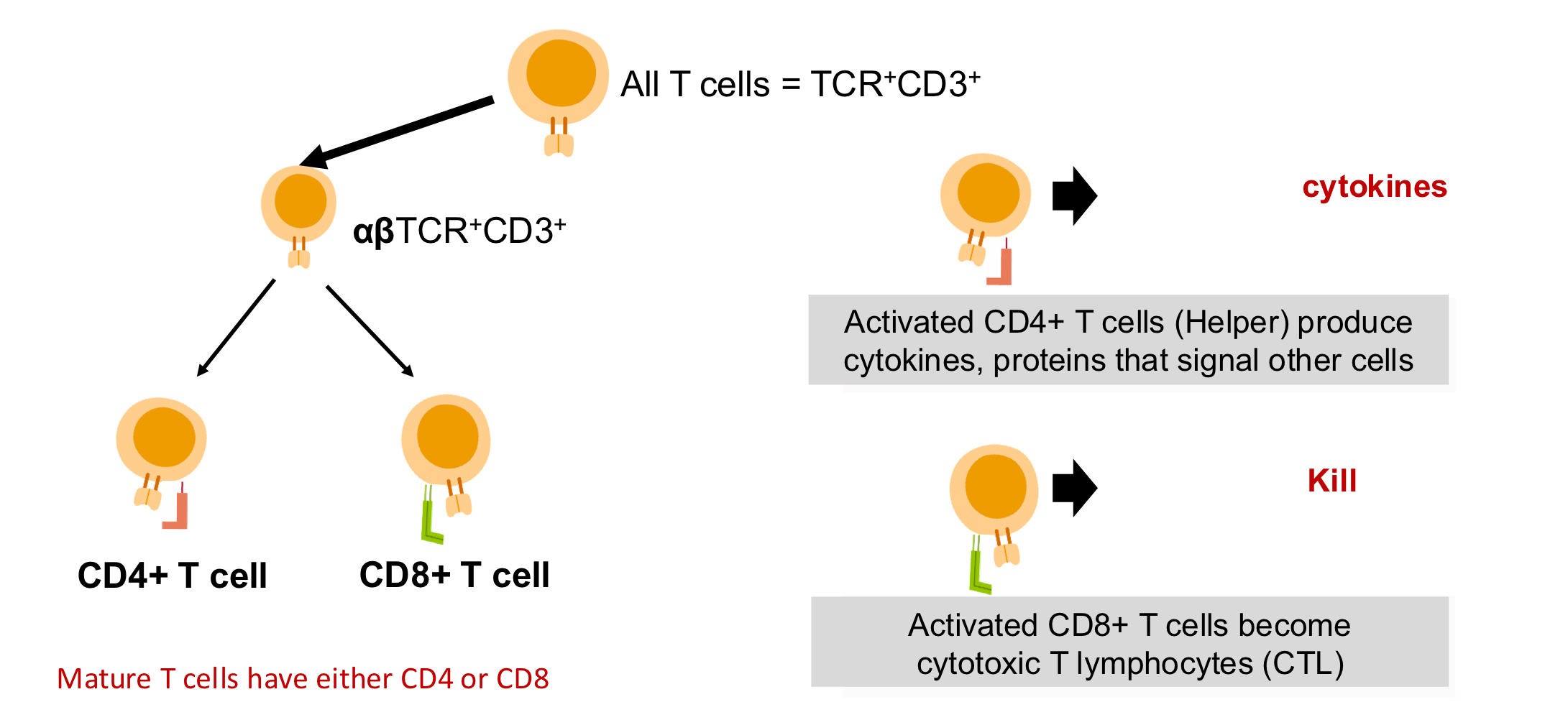
what are the 3 key molecules expressed by T cells?
TCR: alpha and beta chains for antigen recognition
CD3: signal transduction w TCR
co-receptors: CD4 and CD8 adhesion and enhanced signal transduction through TCR
what are the differences in chains btwn TCR and BCR?
TCR: two chains alpha and beta
BCR: four chains 2H and 2 L
what are the differences in antigen binding sites btwn TCR and BCR?
TCR: one
BCR: two
what are the differences in recognition of antigen types btwn TCR and BCR?
TCR: protein, peptides
BCR: protein, carbs, lipids
what are the differences in Ag bound/solubility btwn TCR and BCR?
TCR: Ag bound by MHC
BCR: Ag can be free/soluble
what are the differences in secretion btwn TCR and BCR?
TCR: not secreted
BCR: secreted as Ab by plasma cell
what are the differences in SHM btwn TCR and BCR?
TCR: no
BCR: yes
what are the differences in CSR btwn TCR and BCR?
TCR: not needed, CD3 invariant
BCR: IgG, IgA, IgE
what is primary lymphoid organ for T cell development?
thymus
explain DiGeorge Syndrome
little or no thymus
affects heart and parathyroid
characteristic facial features
no mature T cells and recurrent infections
no thymus = no mature T cells
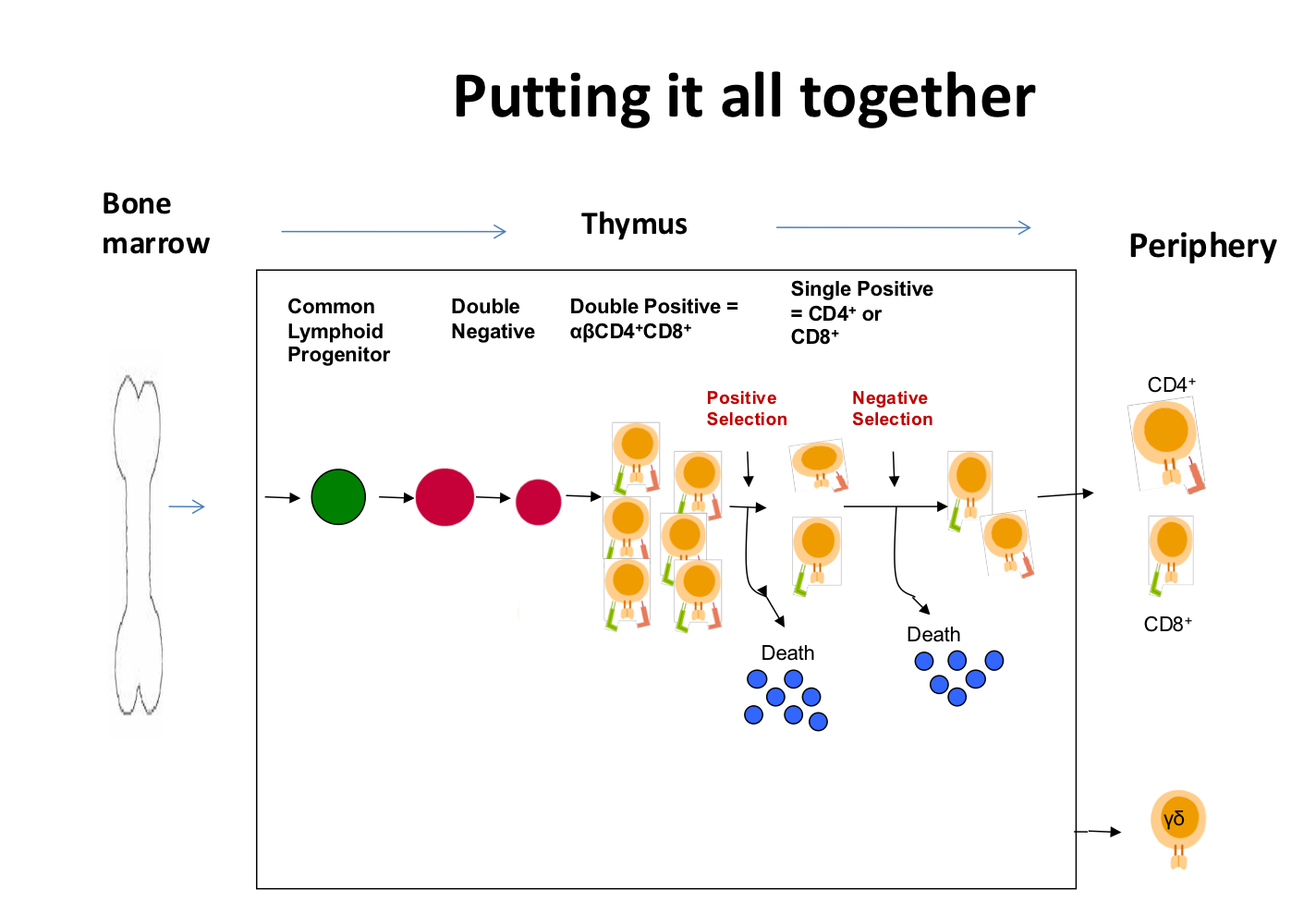
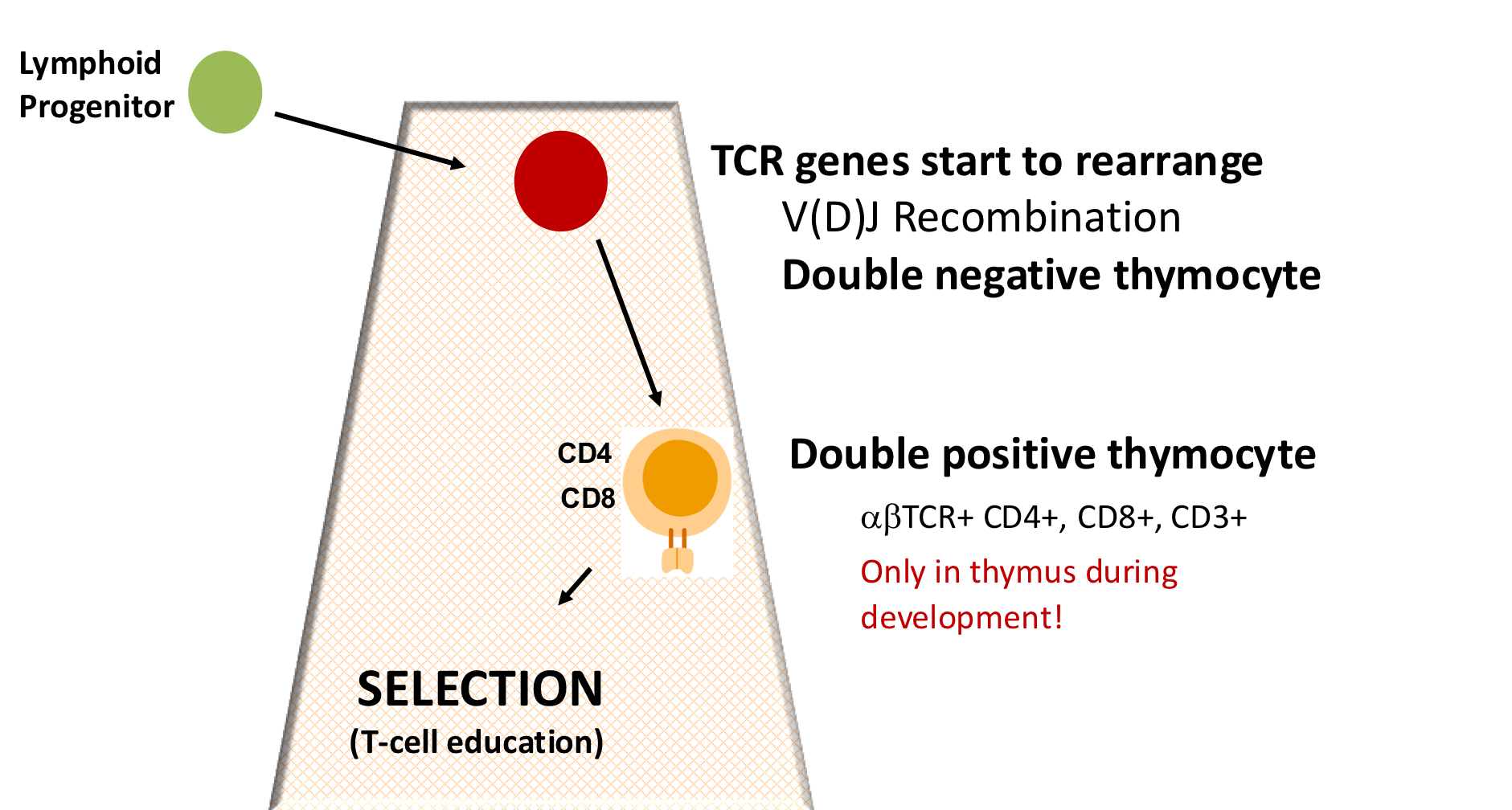
explain thymocyte to mature T cell
thymocyte migrate through thymus V(D)J recombo and eventually we get mature CD4 and CD8 positive T cells
what could lead to T cells dying?
no working receptor
does not work with MHC
explain early stages of T cell diff in thymus: rhomboid slide
double negative: no CD4 or CD8
double positive: CD4 and CD8 (only in T cell development in thymus, double pos in thymocyte in periphery? cancer)
selection: “T cell edu” test with MHC
bind class 1: CD8
bind class II: CD4
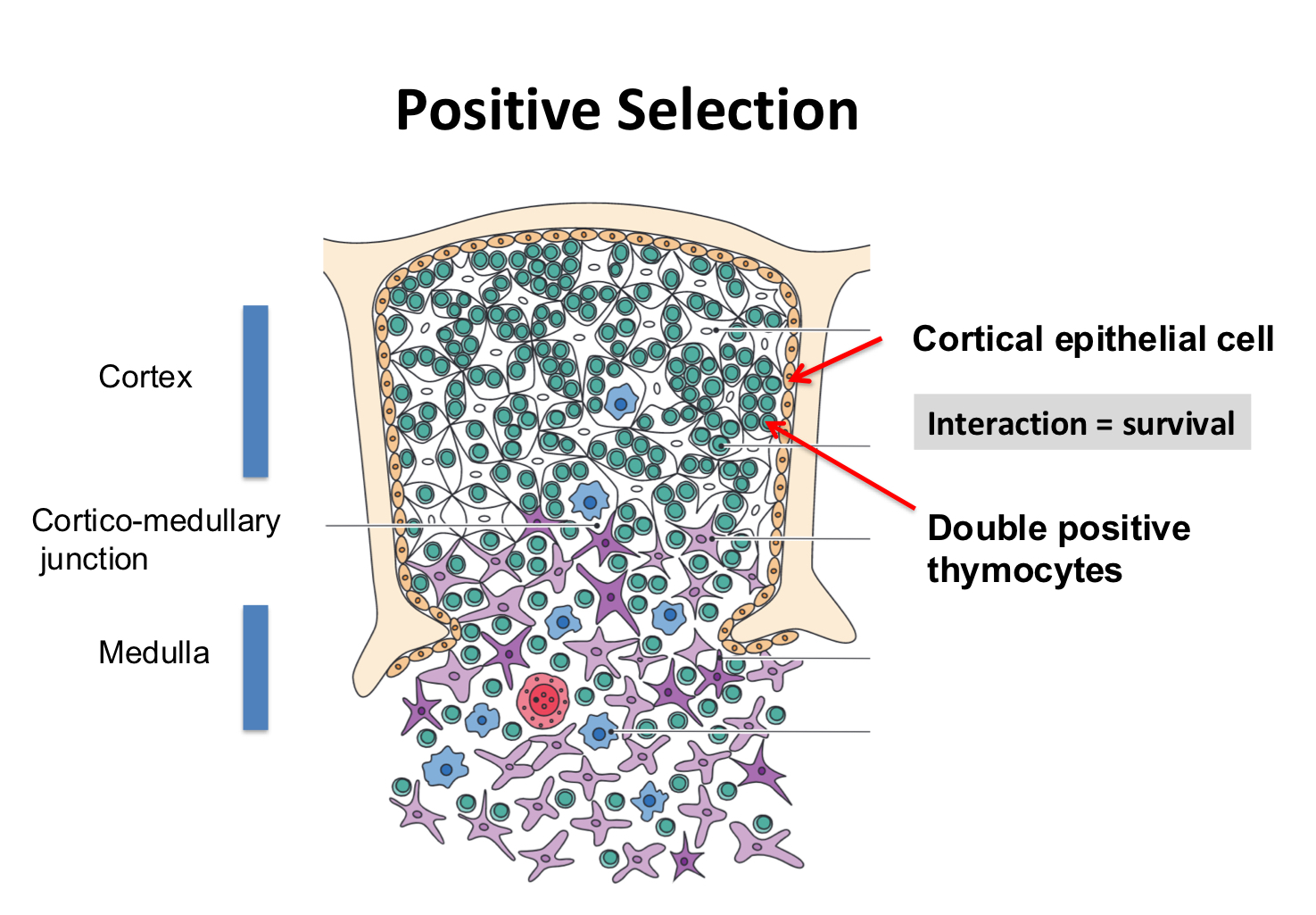
what do double positive thymocytes interact with?
cortical epithelial cells which have class I and II on surface
interaction = survival
detailed positive selection
DP cells with both CD4 and CD8 receptors
thymic epithelial cells with MHC Class I and II molecules
binds to said class? lineage commit
stop making unneeded co-receptor
CD4 class II CD8 Class I
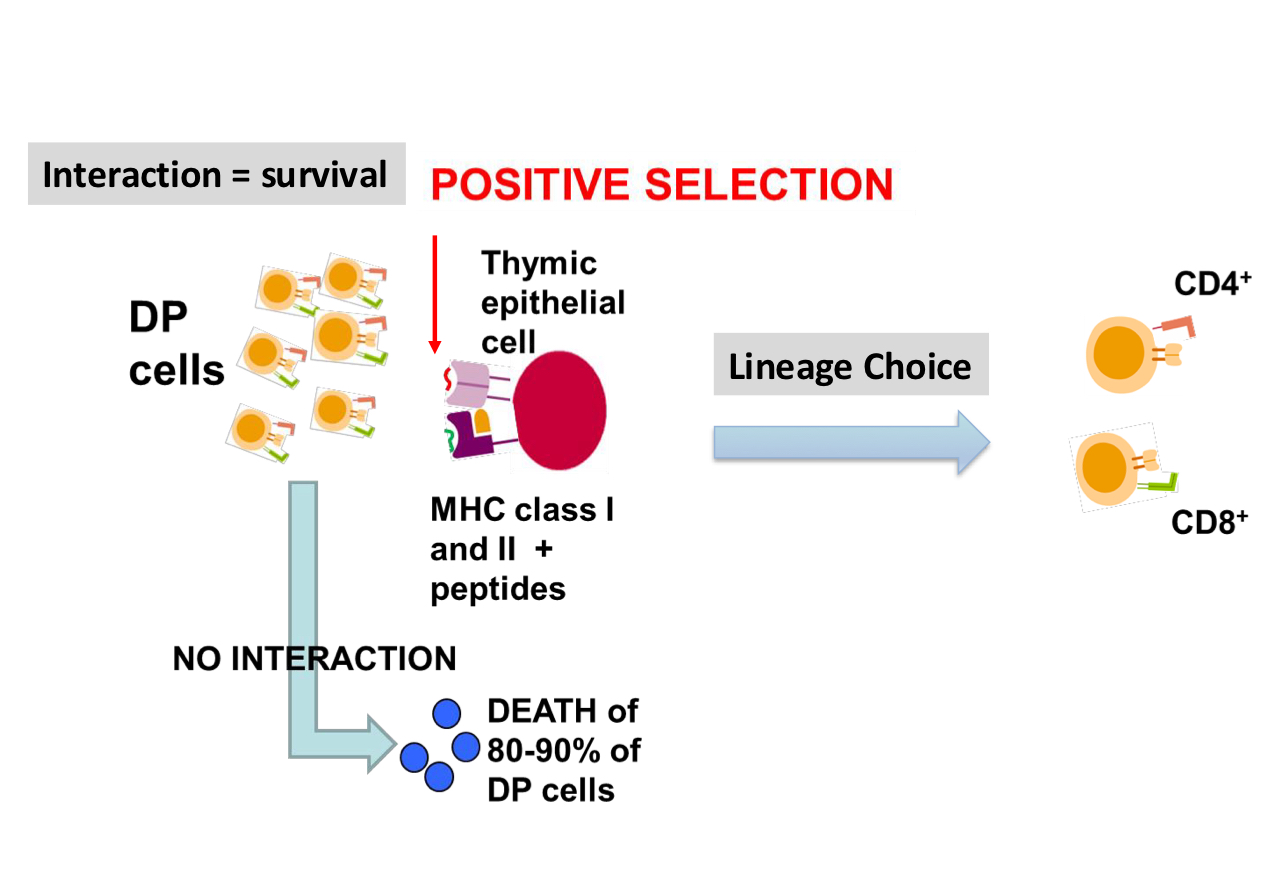
what would happen if there was a lack of positive selection?
double positive, recognize both = death, no T cells
what would the T cells look like of an animal with no MHC Class II?
no CD4
explain negative selection
for cells that recognize self, go to medulla, they are single positive and if they interact with self peptide with thymic dendritic cell they die
thymus transcribe proteins that would be produced in tissues all over the body; good filter!
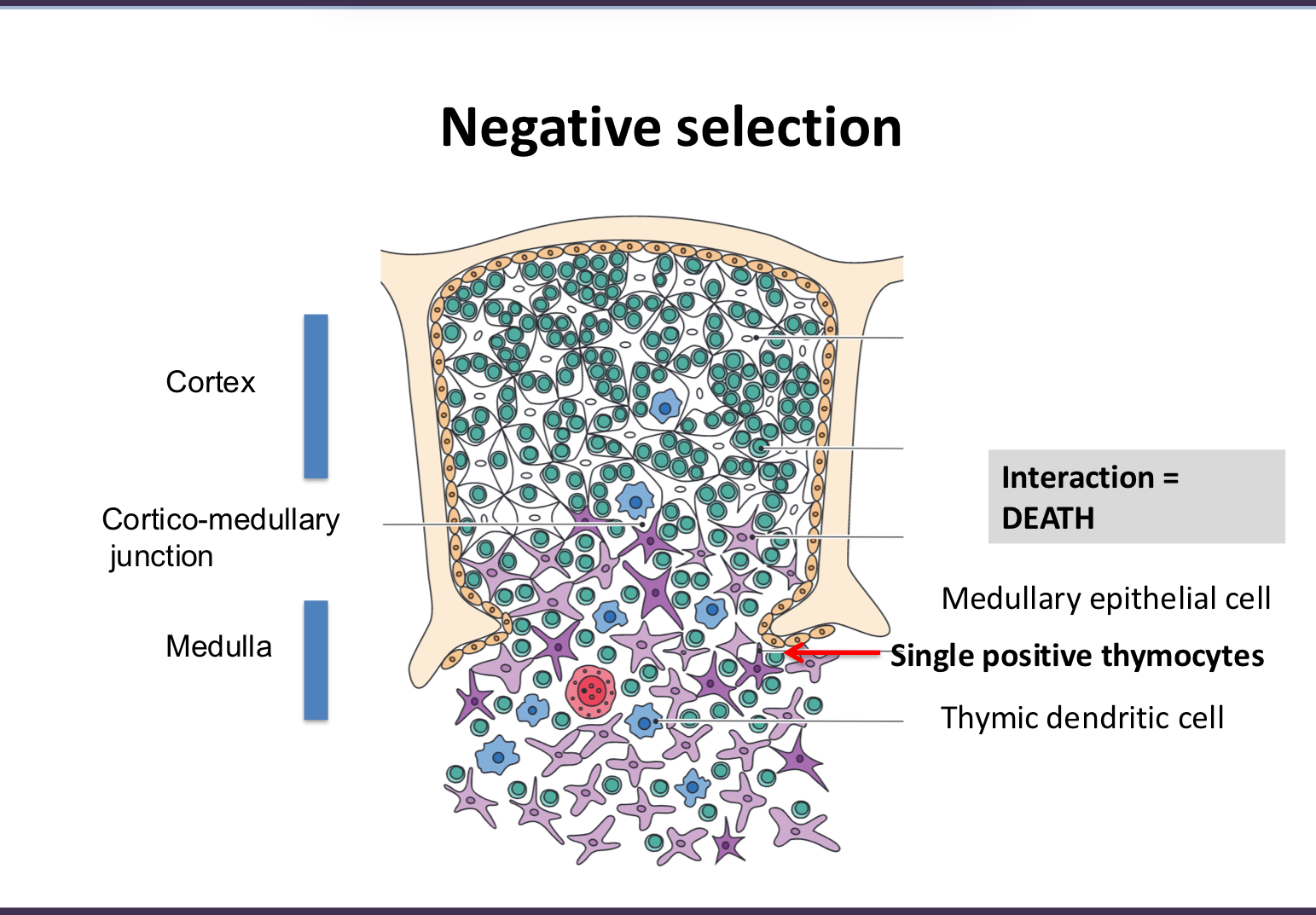
simple negative selection
interaction = death
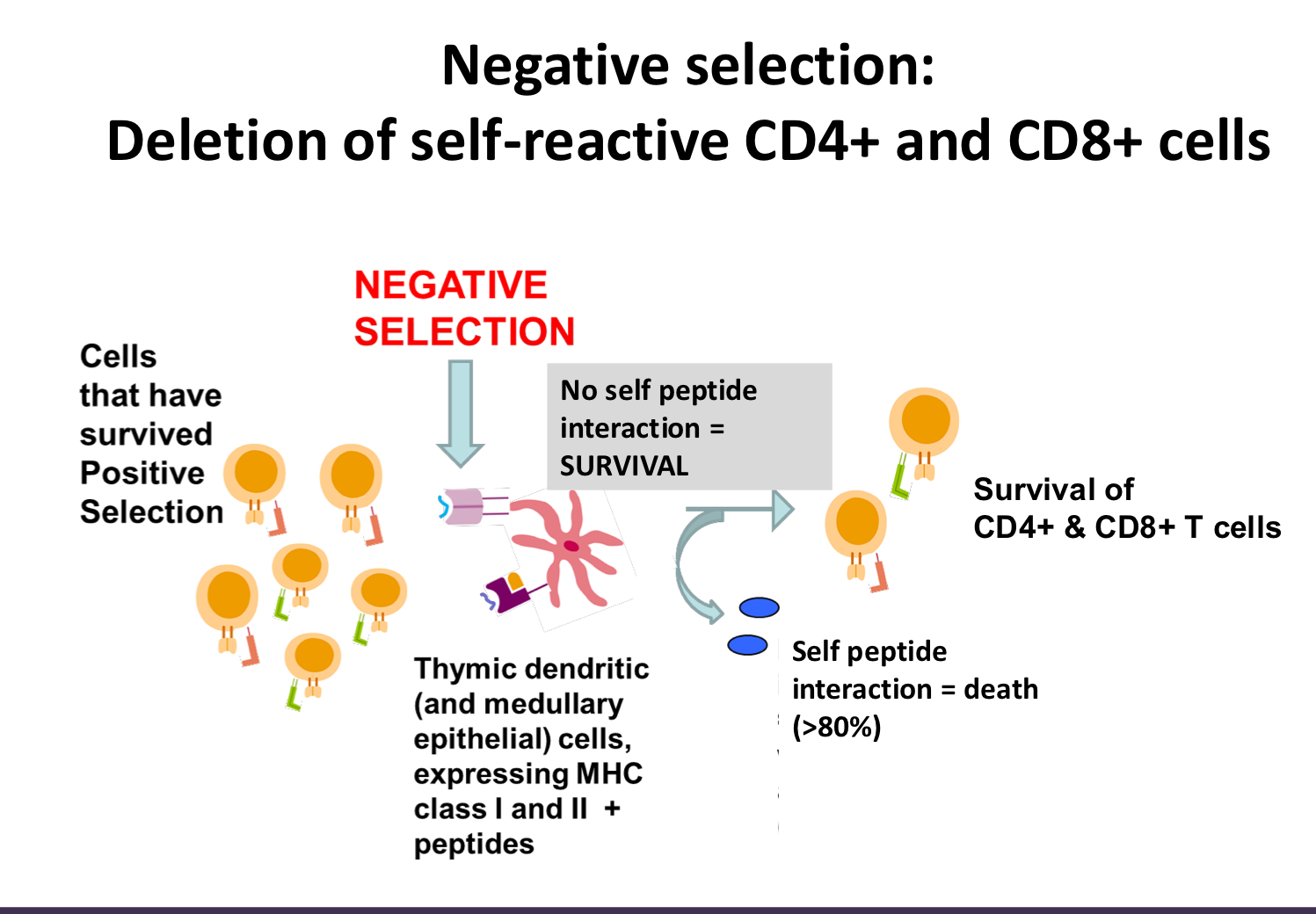
what would happen if there was a defect in negative selection?
self reactive T cells; autoimmune
main summary of T cell differentiation:
naive T cells from thymus
respond to foreign antigen bound in host MHC (HLA)
evert T cell works with one HLA!
do not respond to self aka tolerant to self