INTRODUCTION TO CLIENT SERVER | CLIENT SERVER MODEL (MODULE)
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
client-server network
designed for end-users, called clients, to access resources such as files, songs, video collections, or some other service from a central computer called a server.
serve its clients
server's sole purpose
Client-server model or Client-server architecture
distributed application framework dividing tasks between servers and clients, which either reside in the same system or communicate through a computer network or the Internet.
client
relies on sending a request to another program in order to access a service made available by a server
server
runs one or more programs that share resources with and distribute work among clients
Client-server communication
communicates in a request–response messaging pattern and must adhere to a common communications protocol, which formally defines the rules, language, and dialog patterns to be used.
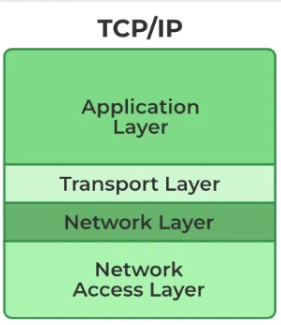
TCP/IP
Client-server communication typically adheres to the _________ protocol suite.
TCP protocol
maintains a connection until the client and server have completed the message exchange
TCP protocol
determines the best way to distribute application data into packets that networks can deliver
TCP protocol
transfers packets to and receives packets from the network
TCP protocol
manages flow control
TCP protocol
retransmission of dropped or garbled packets
IP
a connectionless protocol in which each packet traveling through the Internet is an independent unit of data unrelated to any other data units.
organized and prioritized in a scheduling system
Client requests are?
client-server approach
enables any general-purpose computer to expand its capabilities by utilizing the shared resources of other hosts.
email
the World Wide Web
network printing
Popular client-server applications
host
any computer connected to a network
host
a versatile, multifunction computer
User-host
Computer used by a client.
server-host
Computer devoted to serving.
clients and servers
____ and _____ are just programs that run on a host.
server
In the client-server model, a ______ is more likely to be devoted to the task of serving.
"Separating Data from Function in a Distributed File System",
An early use of the word client in a paper on 1978 by Xerox PARC computer scientists Howard Sturgis, James Mitchell, and Jay Israel.
1992
the word server had entered into general parlance
client–server model
does not dictate that server-hosts must have more resources than client-hosts
client–server model
It enables any general-purpose computer to extend its capabilities by using the shared resources of other hosts.
Centralized computing
specifically allocates a large amount of resources to a small number of computers
Centralized computing
More computation offloaded to central computers → simpler client-hosts.
Centralized computing
It relies heavily on network resources (servers and infrastructure) for computation and storage.
diskless node
loads even its operating system from the network
Computer terminal
Only input/output interface to the server.
fat client
a personal computer, has many resources, and does not rely on a server for essential functions.
microcomputers
As _______ decreased in price and increased in power from the 1980s to the late 1990s, many organizations transitioned computation from centralized servers, such as mainframes and minicomputers, to fat clients.
web applications
During the 2000s, _________ matured enough to rival application software developed for a specific microarchitecture.
cloud computing
This maturation, more affordable mass storage, and the advent of service-oriented architecture were among the factors that gave rise to the _________ trend of the 2010s.
client server computing
works with a system of request and response system where the client sends a request and the server responds with information.
common communication protocol
The client and server should follow a ________ so they can easily interact with each other.
application layer
All the communication protocols are available at the _____________
limited number of client requests
A server can only accommodate a ______ at a time.
system based to priority
Client server computing uses a ________ to respond to the requests.
Denial of Service attacks
can disrupt a server’s ability to respond to real client requests by flooding it with false requests.
web server
It returns the web pages to the clients that requested them.
CHARACTERISTICS OF CLIENT COMPUTING
The client server computing works with a system of request and response. The client sends a request to the server and the server responds with the desired information.
CHARACTERISTICS OF CLIENT COMPUTING
The client and server should follow a common communication protocol so they can easily interact with each other. All the communication protocols are available at the application layer.
CHARACTERISTICS OF CLIENT COMPUTING
A server can only accommodate a limited number of client requests at a time. So, it uses a system based to priority to respond to the requests.
CHARACTERISTICS OF CLIENT COMPUTING
Denial of Service attacks hinders server’s ability to respond to authentic client requests by inundating it with false requests.
CHARACTERISTICS OF CLIENT COMPUTING
An example of a client server computing system is a web server. It returns the web pages to the clients that requested them.
Client-server architecture
a computing model in which the server hosts, delivers and manages most of the resources and services to be consumed by the client.
Client-server architecture
This type of architecture has one or more client computers connected to a central server over a network or internet connection.
Client-server architecture
also known as a networking computing model or client-server network because all the requests and services are delivered over a network.
Client-server architecture
It’s considered a form of distributed computing system because the components are doing their work independently of one another.
CHARACTERISTICS OF CLIENT SERVER ARCHITECTURE
Client and server machines need different amount of hardware and software resources.
CHARACTERISTICS OF CLIENT SERVER ARCHITECTURE
Client and server machines may belong to different vendors.
CHARACTERISTICS OF CLIENT SERVER ARCHITECTURE
Horizontal scalability (increase of the client machines) and vertical scalability (migration to a more powerful server or to a multi-server solution)
Horizontal scalability
increase of the client machines
vertical scalability
migration to a more powerful server or to a multi-server solution
CHARACTERISTICS OF CLIENT SERVER ARCHITECTURE
A client or server application interacts directly with a transport layer protocol to establish communication and to send or receive information.
CHARACTERISTICS OF CLIENT SERVER ARCHITECTURE
The transport protocol then uses lower layer protocols to send or receive individual messages. Thus, a computer needs a complete stack of protocols to run either a client or a server.
CHARACTERISTICS OF CLIENT SERVER ARCHITECTURE
A single server-class computer can offer multiple services at the same time; a separate server program is needed for each service
client–server model
describes how a server provides resources and services to one or more clients.
server
have a one-to-many relationship with clients, meaning a single server can provide resources to multiple clients at one time.
web servers
mail servers
file servers
Examples of servers
server
can either accept or reject the connection
server
If the connection is accepted, the _______ establishes and maintains a connection with the client over a specific protocol.
distributed computing
used to spread clients across multiple servers for smooth performance.
client
a computer (Host) i.e. capable of receiving information or using a particular service from the service providers (Servers)
server
a remote computer which provides information (data) or access to particular services.
Advantages of Client-Server Network
Client-Server Network has centralized control. i.e., centralized user accounts, security, and access to simplify network administration.
Advantages of Client-Server Network
It does not slow down with heavy use.
Advantages of Client-Server Network
The size of the network can be expanded to any size.
Advantages of Client-Server Network
Proper Management: All the files are stored in the same place. In this way, the management of files becomes easy. Also, it becomes easier to find files.
Advantages of Client-Server Network
As all the data is stored on the server it's easy to make a back-up of it.
Advantages of Client-Server Network
Reduces Data Replication- Data stored on the servers instead of each client, so it reduces the amount of data replication for the application.
Disadvantages of Client-Server Network
A specialist network operating system is needed.
Disadvantages of Client-Server Network
Server failure leads to the whole network failure.
Disadvantages of Client-Server Network
It is very expensive to install and manage as dedicated hardware (Server) and special software is required.
Disadvantages of Client-Server Network
Professional IT people are required to maintain the servers and other technical details of the network.
Authentication
It is required (email + password) before the server allows access or sends data.
Servers have traffic limits
too many clients can overload a single server
Centralized control
centralized user accounts, security, and access for easier administration
Scalable
network size can be expanded to any size
Proper file management
all files stored in one place, easier to manage and find
Easy backup
all data stored on the server makes backup simple
Reduces data replication
data stored on servers instead of each client
Client: Gmail, Outlook
Server: Gmail/Yahoo Mail Servers
send/receive email messages
Client: Chrome, Firefox
Servers: Apache, Nginx
Web Browsing
Access and display websites
Client: PC, Mobile App
Server: Google Drive, Dropbox Servers
Cloud Storage
Upload/download and sync files
The TCP/IP model and its layers