Government
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Governance
The act or process of governing or overseeing the control and direction of something
Reformed
Having been changed in such a way to be improved
Direct Democracy
All citizens participate directly in the political process by voting in every decision
Representative democracy
Citizens vote to elect representatives to act on their behalf and voice the view of the voters
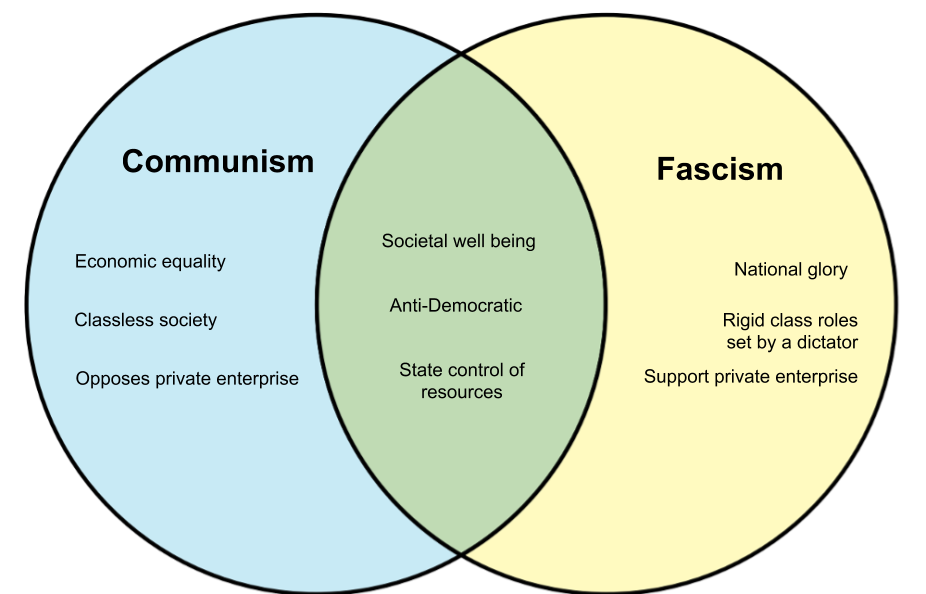
Communism
extreme left-wind ideology
calls for abolishment of private property, promotes collective ownership
Capitalism
An economic system in which trade and industry of the economy is owned and controlled by private individuals, to make profit
Socialism
principle means of product, distribution, and exchange are common ownership
supports government intervention and regulation in the economy
Facism
a nationalistic, top down system with rigid class roles that is ruled by an all powerful dictator
extreme right wing ideology
no freedom
Constitutional monarchy
a form of a monarch in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution.
Federal jobs
foreign policy
immigration
taxation and currency
criminal laws
transportation
national defence
employment insurance
the postal system.
Provincial jobs:
education
healthcare (the federal government pays a portion of the cost of healthcare and higher education)
provincial taxation
provincial police
the management of natural resources
roads and bridges
workers' compensation programs
housing
Municipal Jobs
libraries
local police
local school
fire departments
public transport
building permits
parks and recreation
garbage and recycling collection.
Executive Branch
make and apply government decisions
Legislative branch
debates, makes and amends laws
Judicial branch
interpreting laws and passing judgments
Prime Minister
head of federal government
Cabinet
committee of minsters that holds executive power
Question period
a time when the opposition members can question government action or raise issues of concern
Shadow Cabinet
leader of opposition and other opposition party leaders are allowed to ask first questions in the daily question period
Parliment
Canada’s legislature, the federal institution with the power to make laws, raise taxes, authorize government spending
The senate: upper chamber
composed of 105 senators
appointed by governor general on advice of PM
represent canada’s regions/provinces/territories
may serve until mandatory retirement at 75
House of commons: lower chamber
elected assembly of parliament
elected by Canadians to represent electoral districts (ridings)
336 seats in the house of commons
government
broader term
inside house of commons = usually refer to PM, cabinet, and other members of governing party
outside the house = the term also includes government departments
Majority government
party holds more than half the seats in the house of commons
minority government
more seats than any other party
not more than the others combined
coalition government
A type of minority government when two parties join together to temporarily form government. made up of both parties
Backbenchers
members of governing party who are not in the cabinet
party whip
some parties elect an MP of their party in charge of disciplining their members if they speak out against their party
public servants
employees of federal government who represent the link between citizens and the government. daily tasks of answering questions, gathering statistics and delivering mail
Deputy ministers
most senior public servants. play large role in advising ministers and even help in drafting new laws
Caucus
a type of meeting
provides a place/forum where members can debate amongst themselves privately
Bill
a proposed law that may or not be passed into an actual law
first reading
bill is introduced into house of commons
printed and distributed to all members
second reading
members of parliament debate the bill’s principle
comittee stage
smaller groups of MPs study the bill
hear from witnesses
amends may be proposed/developed
report stage
members of parliament in the house of commons suggest amendments
amendments debated by members before being approved
third reading
members debate whether the bill should be passed by the house of commons or not
final vote called
passed by house of commons
the senate (law)
senate reviews bill
serves as final check
royal assent
governor general gives final approval to the bill
bill = law
Compare and contrast fascism
Fundemental freedoms
Including those pertaining to conscience, religion, thought, expression, peaceful assembly, and association
Democratic rights
The right to vote and be eligible to serve for the House of Commons and the legislative assembly, and the right to elections at least every five years.
Mobility rights
To enter, remain in, or leave Canada, and to move into and earn a living in any province. This is subject to certain limitations in order to provide for “affirmative action” programs for the socially or economically disadvantaged.
Legal rights
Includes such things as the right to a fair and reasonably prompt public trial by an impartial court.
Equality rights
No discrimination on grounds of race, national, or ethnic origin, religion, sex, sexual orientation, age, or mental or physical disability
Official language rights
Makes English and French the official languages of Canada that must be represented in all government institutions.
Minority language education rights
Allows for French- or English-speaking minority groups to be educated in their own language.
Human rights
Rights to which all humans are entitled to
Based on morality
Not necessarily legally sanctioned in all countried
What event inspired the creation of the UN
Response to the injustices/human rights violations in the second world war
What are the four main purposes of the Un
To keep peace throught the wolf
To develop friendly relations among nations
To help nations work together to improve lives of people/conquer hunger, disease, literacy/encourage respect for each pther’s rights and freedoms
to be a center for harmonizing tthe nations to achieve these goals
Why is the UN significant
they acknowledge that all human beings have specific rights and freedoms.
It is also imporant because it aids in the fight against injustice and produces results.
UN limitations
The United Nations is not able to directly enforce any of it's decisions such as the Universal Declaration.
However, they are able to bring global attention to issues and offending countries.
What ways can the UN work to stop Human Rights injustices?
International attention: The UN is able to bring massive amounts of global attentions to issues.
Arbitration: A formal way to resolve disagreements.
Econmic sanctions: The withdrawl of trade and financial relations to foreign countries.