16 - Characteristics of Life, Metabolism, and Extremophiles
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Metabolism
The sum of catabolism and anabolism in an organism.
Catabolism
The breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy.
Anabolism
The synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring energy.
Fundamental requirements for life, as we know it
Necessary conditions for life: liquid water, organic compounds, and an energy source
what are the normal conditions necessary for life on Earth?
temperature of -40-+50ºC, pH of 4-8, pressure of 30-10000kPa, O₂, H₂O (liquid), and CO₂ (for autotrophs)
Extreme Environment
An environment with extreme conditions such as high or low temperatures, pH levels, or salinity.
Mt. Everest
A location with 1/3 of the oxygen concentration compared to sea level.
Atacama Desert
A desert in Chile with less than 1mm of rainfall per year.
Darkling Beetle Case Study
they live in the Atacama desert, which is incredibly dry. They have an ability to condense and absorb the water mist (i.e. morning dew) that forms on their backs, and then drink it!
Antarctic Ocean
The ocean surrounding Antarctica with water temperatures as low as -1.8°C, though it does not freeze because of the high salinity of the water
Ice Fish Case Study
live in Antarctic Ocean, which has super high oxygen levels; they are blue because they lack hemoglobin - instead of hemoglobin, they actively absorb oxygen through their skin
Extremophiles
need to live in extreme environments, does not just survive in them
Bacteria and Archaea
Single-celled microorganisms that can use almost anything as food due to their metabolic diversity and therefore have many more metabolic pathways
How does the metabolic flexibility of Archaeans and Bacteria allow them to expand into more extreme environments?
their diverse metabolic pathways means they are not limited to the same environmental constraints as eukaryotes; this allows them to use other compounds as electron donors/acceptors, and therefore to thrive in "extreme" environments that lack the typical compounds used for respiration
Acidophile
An organism that grows best at acidic (low) pH values.
Alkaliphile
An organism that grows best at high pH values.
Anaerobe
An organism that can grow in the absence of oxygen.
Endolith
An organism that lives inside rock or in the pores between mineral grains.
Halophile
An organism requiring high concentrations of salt for growth.
Methanogen
An organism that produces methane from the reaction of hydrogen and carbon dioxide, member of the Archaea.
Barophile
An organism that lives optimally at high hydrostatic pressure (>71000kPa).
Psychrophile
An organism with optimal growth at temperature 15 °C or lower.
Thermophile
An organism with optimal growth at temperature 40 °C or higher.
Hyperthermophile
An organism with optimal growth at temperature 80 °C or higher.
Xerophile
An organism capable of growth at very low water activity.
Yellowstone Hot Springs
Springs with high temperatures (>70°C) and H₂ oxidation, inhabited by various thermophiles.
Yellowstone and Aquificales Case Study: what are they?
fibrous strings that are chemolithoautotrophic thermophiles (chemical, rock associated, high temperature, make own food) that live in the Yellowstone Hot Springs whose metabolic pathway is H₂ oxidation
Yellowstone and Aquificales Case Study: what happens when there is a low sulphide compliation?
other extremophiles still live there, however species evenness is decrease and skewed toward the aquificales (since they metabolize hydrogen)
Yellowstone and Aquificales Case Study: what happens when there is a high sulphide compliation?
Thermodesulfobacteria flourish (eat sulphide), increasing species richness, however aquificales still flourish more relatively as the H₂ oxidation pathway releases more energy than the H₂S pathway
Lake Vostok
A lake in Antarctica with 1 million-year-old microbes found nowhere else in the world.
Lake Vostok and Microbe Case Study: what are they?
??????? I do not get this!
Deep Sea Hydrothermal Vents
Underwater geothermal springs that release hot, mineral-rich water, where methane and sulfur oxidation occur at temperatures as high as 120°C.
Sulphur oxidation
Process of converting sulfur and oxygen into sulfur trioxide
(S + 3/2O₂ → SO₃)
Methanogenesis
Process of producing methane using hydrogen and carbon dioxide
(4H₂ + CO₂ → CH₄ + 2H₂O)
metabolic ability
capability of an organism to perform chemical reactions and processes
Primitive symbiosis
Early form of symbiotic relationship between organisms
Hydrothermal Vents Case Study: Metabolic ability
Organisms living in these vents have metabolic abilities (sulphur oxidation and methanogenesis) as a result of primtive (endo)symbiosis between sulphate-reducing bacteria and methanotrophic archaea.
Hydrothermal Symbionts
organisms that form symbiotic relationships in hydrothermal environments where the end products of each organism's oxidation feeds the other (like plant-animal relationships)
Denitrification
Process of converting nitrates into nitrogen gas
Mono Lake
Alkaline and hypersaline lake in California, with pH 10 and salinity 105ppt, three times higher than the ocean.
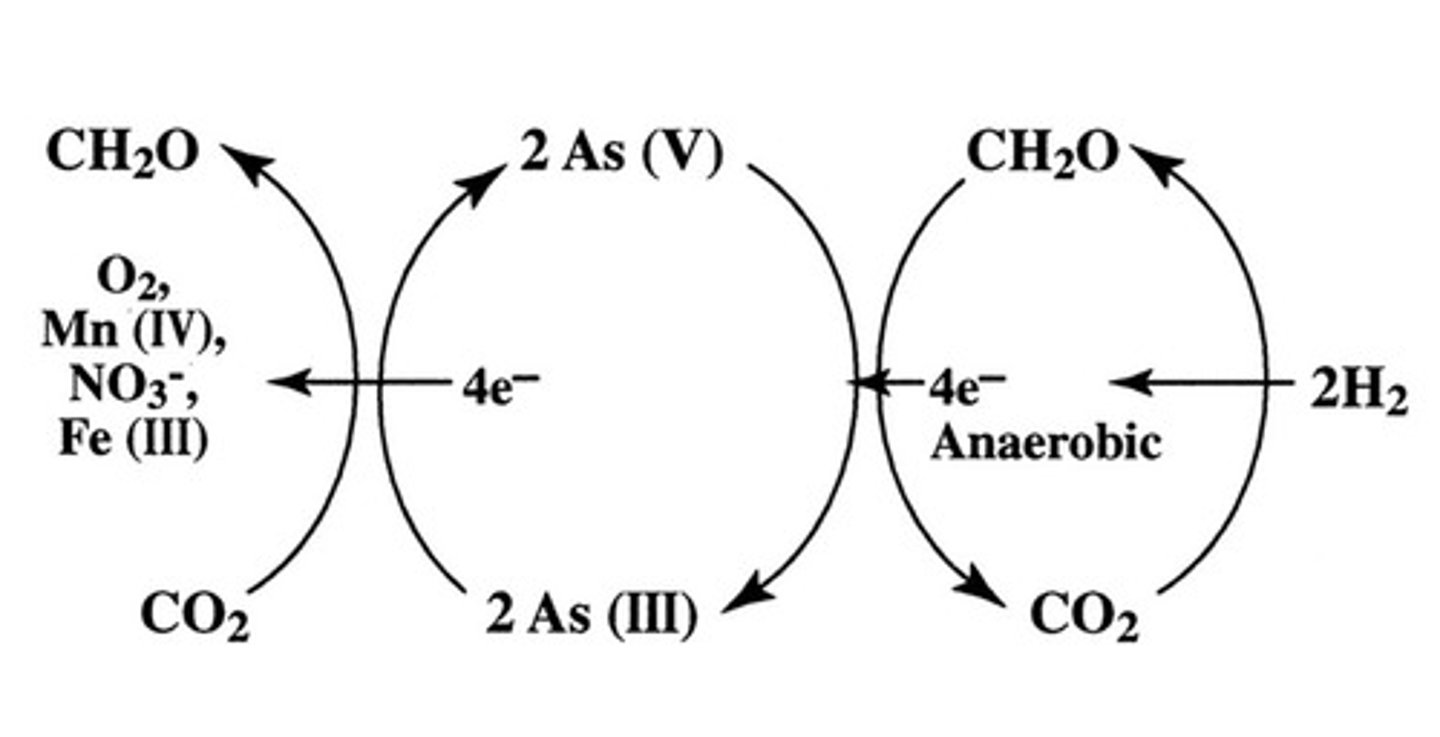
Photosynthetic Arsenic metabolism
Metabolic process in which organisms use arsenic (and formaldehyde!) for photosynthesis
Microbial life
Life forms that are microscopic in size
Niches
Specific habitats or ecological roles that organisms occupy
Heat vents
Openings in the Earth's surface that release hot water and gases
Chemical evolution
Process of chemical changes over time that lead to the origin of life