mcat evergrowing 🌱
1/594
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(FL & qbank reviews) im losing my mind :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
595 Terms
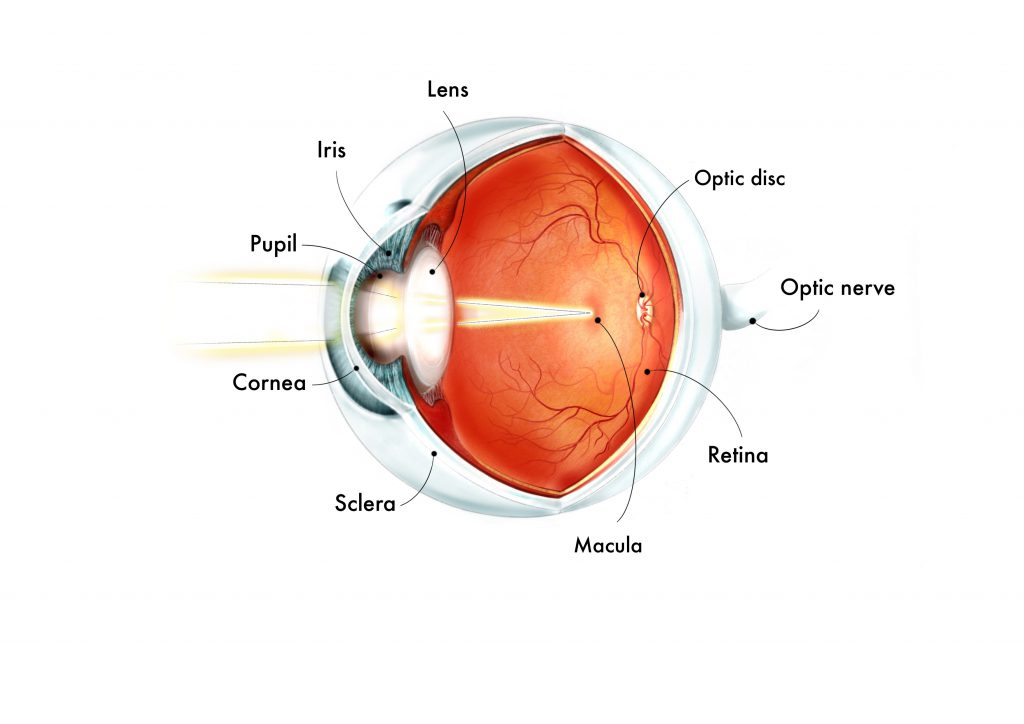
sclera
white, outer layer of the eye; responsible for protection and form
ex: Think of them as the security guard at the club who’s always wearing (white) sunglasses, even at night.
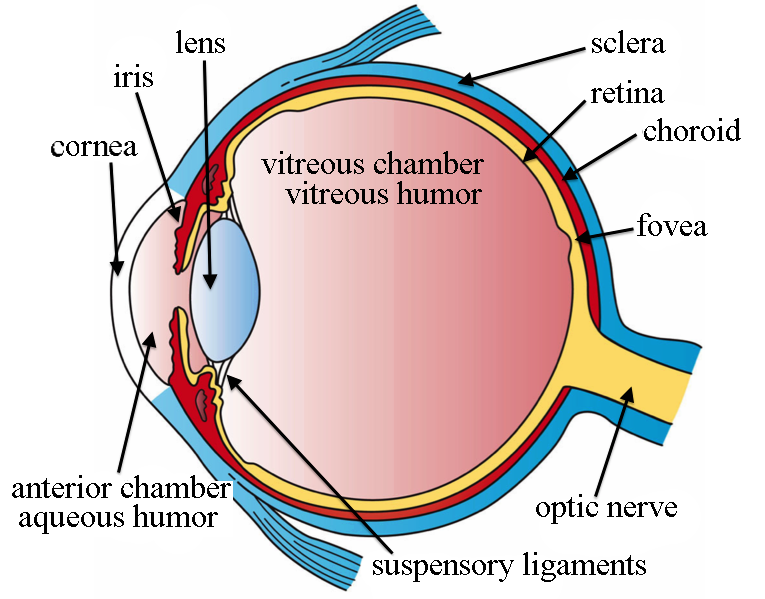
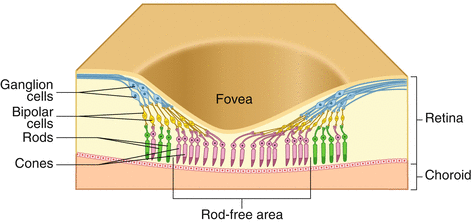
fovea
region in the center back of the eye; has a high density of cones
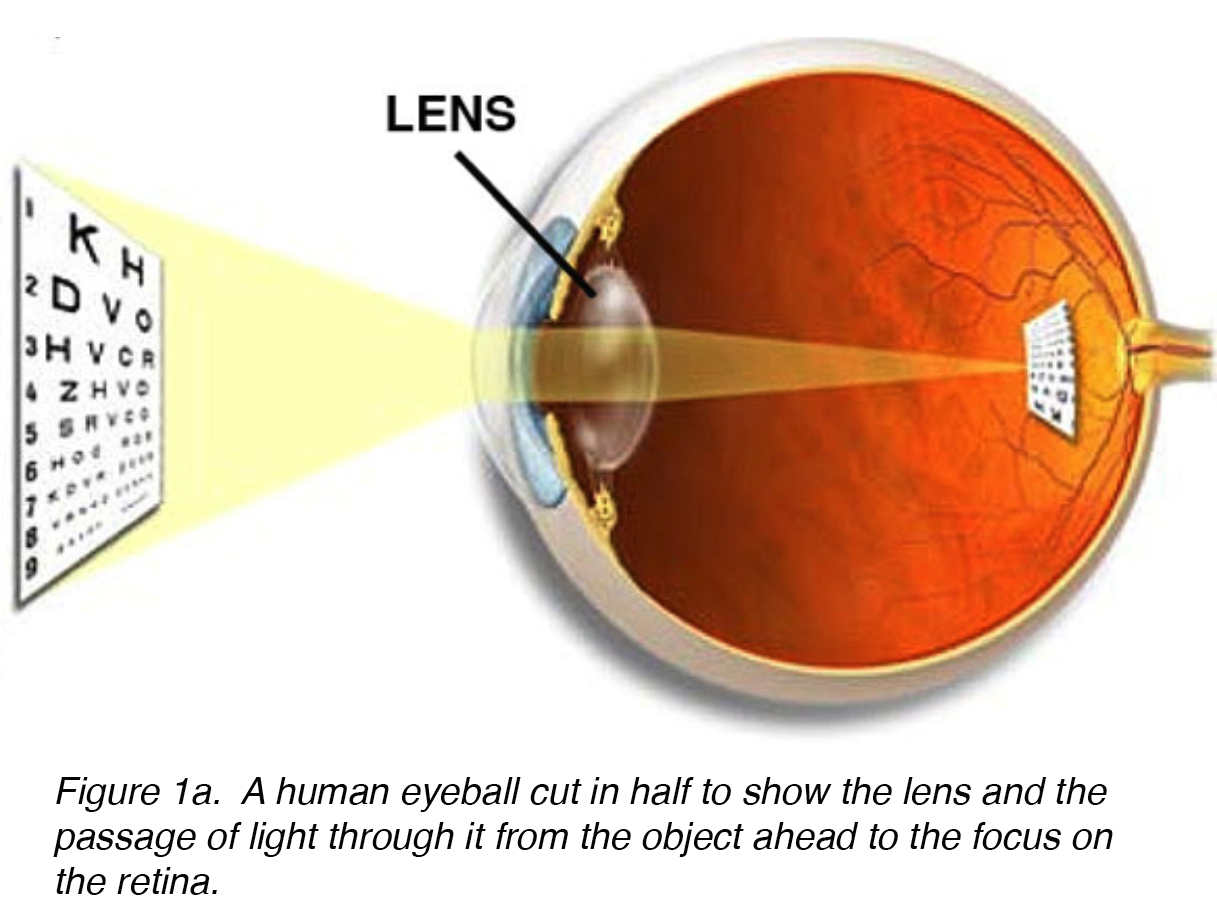
lens
transparent biconvex structure in the eye that (w/ the cornea) helps to refract light; responsible for focusing light onto retina (does not aid in perception of color)
optic disc
where the optic nerve connects to the retina; point of exit for ganglion cell axons leaving the eye; aka blind spot because it lacks photoreceptors (rods & cones) required to detect light
occipital cortex/lobe
lobe of the brain responsible for processing visual information; includes:
color
shape
movement
temporal cortex/lobe
controls hearing and other speech functions; aka responsible for perception of auditory information
somatosensory cortex
processes sensory information experienced throughout the body (touch, pain, and temperature)
motor cortex
controls and executes voluntary movement
fixed ratio
providing the reinforcer after a consistent number of target behaviors; predictable and count-based
ex: for every 5 books you buy, B&N gives u a free sweet treat
variable ratio
providing the reinforcer after varying number of target responses (varies around a predetermined average)
ex: You're posting fire makeup looks on Insta, and randomly, one goes viral and you get a brand deal.
BEST FOR LONG-TERM BEHAVIOR (most resistant to extinction)
fixed interval
provides the reinforcer when the target behavior is performed for the first time after a consistent interval of time has elapsed
ex: Let’s say your crush only texts you every Saturday at 7 PM.
It doesn’t matter how many cute memes you send during the week — he ONLY responds if you text after 7 PM on Saturday.
variable interval
provides the reinforcer when the target behavior is performed for the first time after a varying interval of time has elapsed
ex: You're obsessed with a cozy little indie bookstore that sends surprise discount codes by email.
Sometimes they send it the next day, sometimes a week later, sometimes two days—you never know when it’s coming.
So what do you do?
You start checking your email randomly all day like:
“Is today the day I get 25% off and treat myself to another fantasy romance? 👀”
social status
one’s standing in the community and his/her position in social hierarchy
ex: regina george > cady heron; in other words, regina has high social status (power & influence to watch the world burn) whereas cady isn’t really popular initially
roles
a set of rules or norms that function as plans or blueprints to guide behavior within a particular society
ex: percy jackson = chosen one; brave leader of the group
social capital
includes the advantages conferred by one’s social network (aka access to professional opportunities and insider knowledge)
ex: Never Been Kissed
Josie Geller is the new girl undercover in high school.
At first, she’s low-key invisible — no social capital.
But as she starts to make friends, gain trust, and join the popular crowd, her ____ _____ grows.
Suddenly, she has connections that help her navigate the school’s social scene, score invites, and get inside info.
cultural capital
accumulation of knowledge, behaviors, and skills that a person can tap into to demonstrate one’s cultural competence and social status
ex: The Devil Wears Prada
Andy Sachs starts as a normal girl with little “fashion knowledge” or insider style.
Miranda Priestly and her crew? Total cultural capital bosses:
They know every fashion trend, designer, and industry secret.
Their style, vocabulary, and attitude give them serious social power in the fashion world.
As Andy learns the ropes, she gains ____ _______ — and suddenly she fits in with the elite fashion crowd.
cultural values
include defined standards that serve as broad guidelines for social living
norms
rules and expectations by which a society guides the behavior of its members
material culture
relationship between artifacts and social relations
symbolic culture
ideas, beliefs, values, or norms that shape a society
conflict theory
sociological perspective that studies society by focusing on inequality between different groups and sees social life as a competition/focuses on distribution of resources and power between these groups
dependency ratio
the number of people who can’t work (economically dependent) compared to the number of people who can work (economically productive) and support them.
social gradient in health
difference in health outcomes by social status
life course perspective
views aging as changes in social, psychological, and biological processes w/ time
intersectionality
refers to how all individuals have multiple aspects of identity and different social backgrounds, therefore producing differential outcomes for an individual
linguistic relativity hypothesis
states that the structure of a language influences the way its speakers conceptualize the world
source-monitoring error
memory error in which the source of a memory is incorrectly attributed to some specific recollected experience
conversion disorder
involves having symptoms that cannot be supported by medical evaluation
schizophrenia
disorder of psychosis in which the person’s thoughts, perceptions, and behaviors are out of contact with reality
retrograde amnesia
inability to retrieve old memories; refers to memories that occur prior to a specific point in time
dissociative disorder
involve pathological separation form conscious awareness and range from mild to extreme; cannot recall important autobiographical information, usually related to a trauma or stressor
classical conditioning
involves learning in which the stimulus or experience occurs before the behavior, and then gets paired or associated with the behavior
operant conditioning
focuses on changes in an individual’s observable behaviors; new or continued behaviors are impacted by new or continued consequences → influence behavior as a result.
positive reinforcers add wanted/pleasant stimulus to increase or maintain frequency of behavior
latent learning
learning that takes place in the absence of reinforcement or punishment; not directly relevant to reward-seeking motivation
meritocracy
ideal system based on belief that social stratification is the result of personal effort/merit that determines social standing
ex: in Utopia, those who were in the acceptable class were awarded certain privileges based on their academic performance
socialization
process by which the new gen learns the knowledge, attitudes, and values that they will need as productive citizens
ex: the “flaw club” acted as an agent of socialization (in utopia) to take down Tamara’s rule
social identity
involves an individual’s self-concept derived from perceived membership in a social group
absolute poverty
measure of poverty based on a set standard that is consistent over time and between countries, referring to the ability of individuals or groups to meet their basic needs
marginal poverty
involves lacking stable employment & cannot achieve minimum standards of living
relative poverty
refers to social disadvantage by income or wealth as compared to social advantages linked to income or wealth in society (wealth vs median income)
structural poverty
related to lack of economic opportunities for individuals to leave poverty
socioeconomic gradient in health
wealthy people are found to live longer on ave than middle-class people; middle class people live longer than poor people
fundamental attribution error
tendency to over-value internal (personality-based) explanations and under-value external (situational) explanations for another person’s behavior
dissonance
when a person experiences conflict in the their cognitions; strongest when a discrepency has been noticed between one’s self-concept and one’s behavior
modeling
aka observational learning; occurs from watching, retaining and replicating a behavior observed from a model
schemas
Jean Piaget; interpretation and understanding of world → is a mental representation. as we encounter things in our environment, we develop additional schemas
ABCs of attitude
affective
behavioral
cognitive
affective
(part of ABCs of attitude) and deals with feelings
behavioral
(part of ABCs of attitude) and deals with the effect of the attitude on behavior
cognitive
(part of ABCs of attitude) and deals with beliefs, ideas, and knowledge
subconscious
occurs beyond conscious awareness and CANNOT be captured by a measure of explicit attitude
selection bias
occurs when the participants in the study differ from the general population; negatively impacts results of a study
social desirability
participants reporting answers that are more socially acceptable; done to make themselves look better
stereotype threat
experience of anxiety or concern in a situation where a person has the potential to confirm a negative stereotype about their social group
primary group
small social group whose members share close, personal, enduring relationships (i.e. family and close friends)
secondary groups
large groups whose relationships are impersonal and goal-oriented; temporary
in-group
social groups to which an individual feels he or she belongs
out-group
individual who doesn’t identify w/ particular group is considered ______.
front-stage
encompasses behavior a player performs in front of an audience
backstage self
employed when players are together, but no audience is present
impression management
process of consciously making behavioral choices in order to create a specific impression in the minds of others
ex: “dont be weird, lissa”
dispositional
focus on stable, internal traits such as personality
situational explanations of behaviors
emphasize environmental factors which surround the individual
habituation
diminishing of a physiological or emotional response to a frequently repeated stimulus
tolerance
decreased effectiveness of the substance after prolonged use
withdrawal
involves the effects of either reducing or quitting the use of a substance; can be physiological or behavioral
craving
powerful desire to ingest a substance
stimulants
increase the activity of the nervous system; used medically to boost endurance and counteract fatigue (ex. caffeine); individuals use and chase the feeling of facilitating the activity of neurotransmitters
hallucinogens
alter sensory input to the brain, therefore can alter perception of reality; relatively low risk of dependence
alcohol
depressant/sedative on CNS; person can become physically dependent
sedatives
slow down brain activity; relaxing feeling = addictive and cause dependence (also impacts CNS)
stratification
involves a system by which a society ranks categories of people in a hierarchy (socioeconomic, morals, etc)
racialization
process where a majority group in society ascribes a behavior or characteristic to a minority group that they do not identify with themselves
gentrification
occurs when members of the middle and upper classes enter and renovate city areas that have been historically less affluent while poor urban underclass is forced by resulting price pressures to leave those neighborhoods (= displacement)
dopamine
neurotransmitter involved in reward and pleasure, motivation, focus & learning, and movement
euphoria
intense feeling of pleasure, happiness, or excitement = dopamine high
confounding variable
variable that can influence the results but is not considered
social loafing
people are more productive alone than in a group; individuals are less critical and less creative in groups
groupthink
members of group prioritize agreement over critical thinking when coming to a decision
concrete operational stage
Piaget; 7-11 years → concrete thought and logical reasoning
sensorimotor stage
Piaget; 0-2 years → involves coordinate of senses w/ motor responses and lacking object perminence
preoperational stage
Piaget; 2-7 years → children start to talk and use symbolic thinking
formal operational
Piaget; 12+ → acquiring abstract reasoning skills
thalamus
functions to relay motor and sensory signals to the cerebral cortex
cerebellum
located underneath the backside of the cerebrum (occipital lobe) and governs balance and fine motor movements; functions to maintain coordination throughout the body
amygdala
seat of emotions; located in medial temporal lobe
medulla oblongata
responsible for autonomic functions
trust vs mistrust
Erikson; birth to 12 months
competence vs inferiority
Erikson; 6-12 yrs
autonomy vs shame & doubt
Erikson; 1-3 yrs
initiative vs guilt
Erikson; 3-6 yrs
oral stage
0-1 yrs; mouth is pleasure center for development → freud believed this is why infants are born w/ sucking reflex
fixation: smoking, gum-chewing, nail-biting, overeating
anal stage
1-3 yr; bowel/bladder control
fixation:
anal-retentive: super neat, stubborn, perfectionist
anal-expulsive: messy, disorganized, rebellious
phallic stage
3-6; genitals (esp w/ gender identity and power dynamics)
Oedipus/Electra complex: unconscious desires and conflicts related to parents
oedipus: boy’s attraction to mother
electra: girl’s attraction to father (developed by Carl Jung)
fixations: vain, jealous, or struggle with identity & authority
latency stage
6-12 yrs; nothing sexual, goal is to develop social skills, friendships, hobbies, etc
fixations: n/a → problems could mean being social awk or emotionally distant
genital stage
12+; focus on genitals and forming mature romantic relationships & balancing life
fixation: intimacy issues (if older stages weren’t resolved)
self-serving bias
tendency of individuals to make internal attributions when their actions have a positive outcome but external attributions when their actions has a negative outcome (ie. situational variables)
confirmation bias
a person tends to look for information that supports their idea or approach instead of looking at new information that may contract their approach or ideas
hindsight bias
belief that the event just experienced was predictable
response bias
involves responding inaccurately or falsely to self-report questions