AP Psych Unit 3: Development and Learning
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
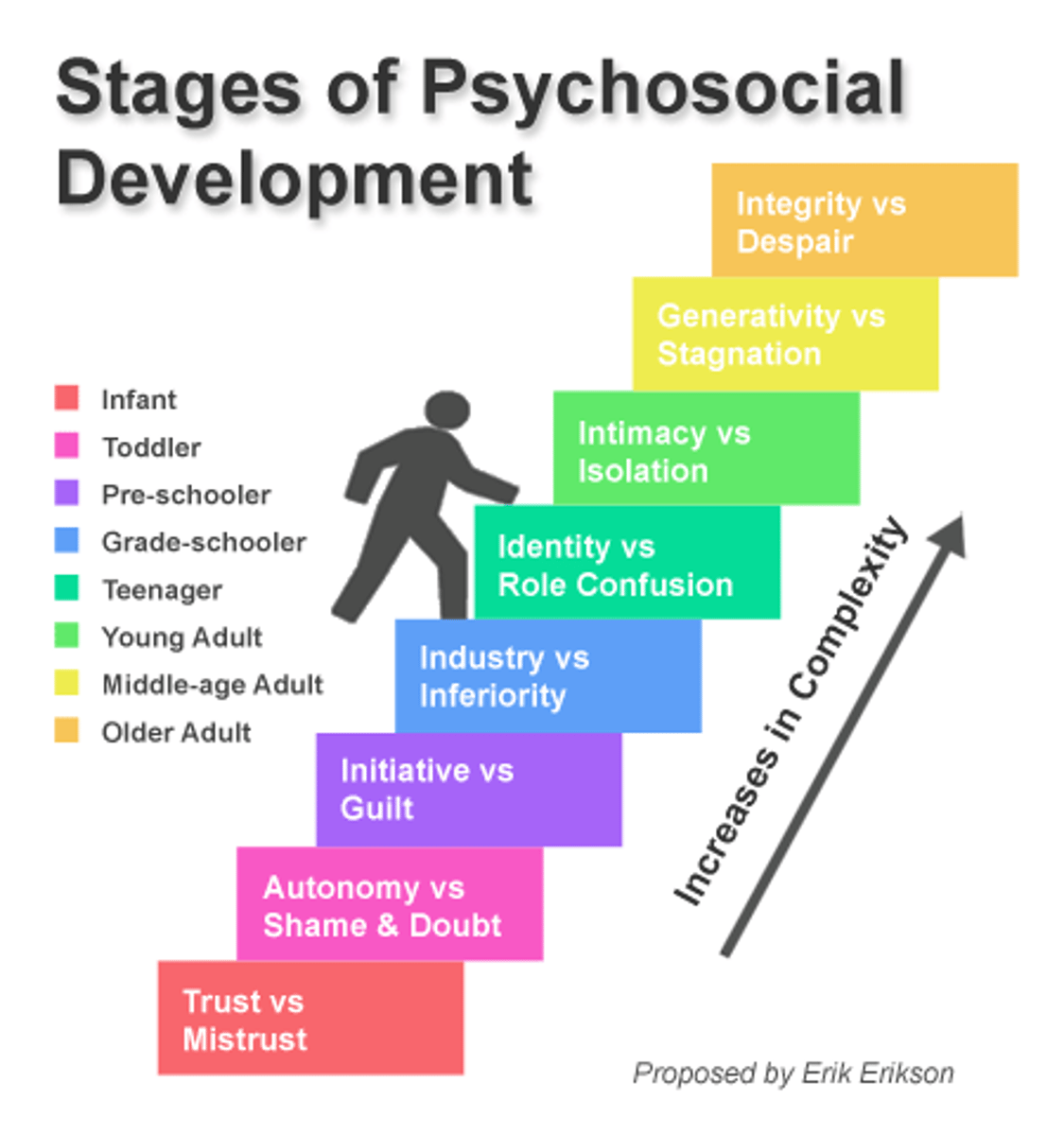
8 psychosocial stages of development
neo-Freudian, humanistic theory showing how people evolve through the life span. Each stage is marked by a psychological crisis that involves confronting "Who am I?"
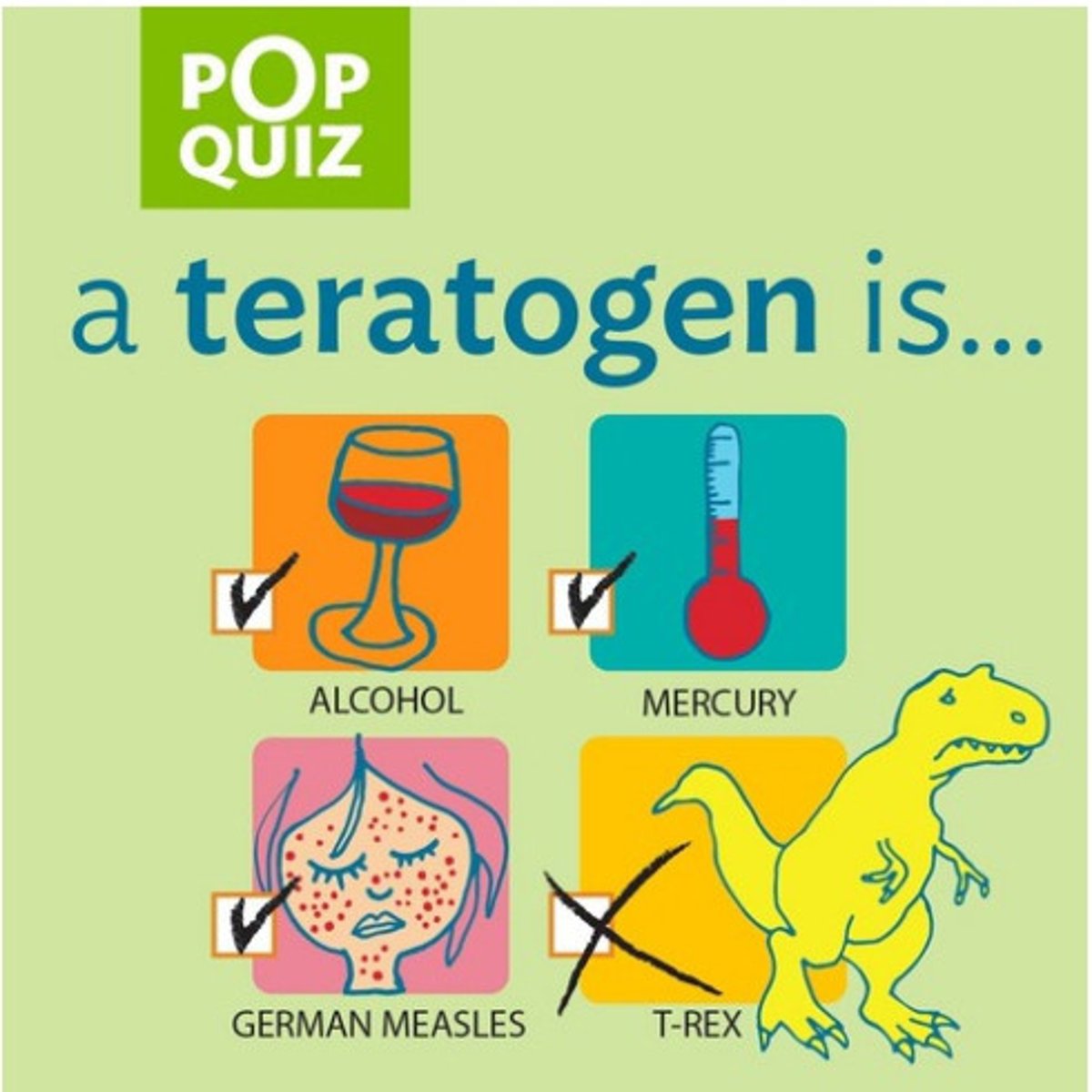
Teratogens
agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm
Assimilation
interpreting our new experiences in terms of our existing schemas

accommodation
adapting our current understandings (schemas) to incorporate new information

sensorimotor stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage (from birth to about 2 years of age) during which infants know the world mostly in terms of their senses and movement

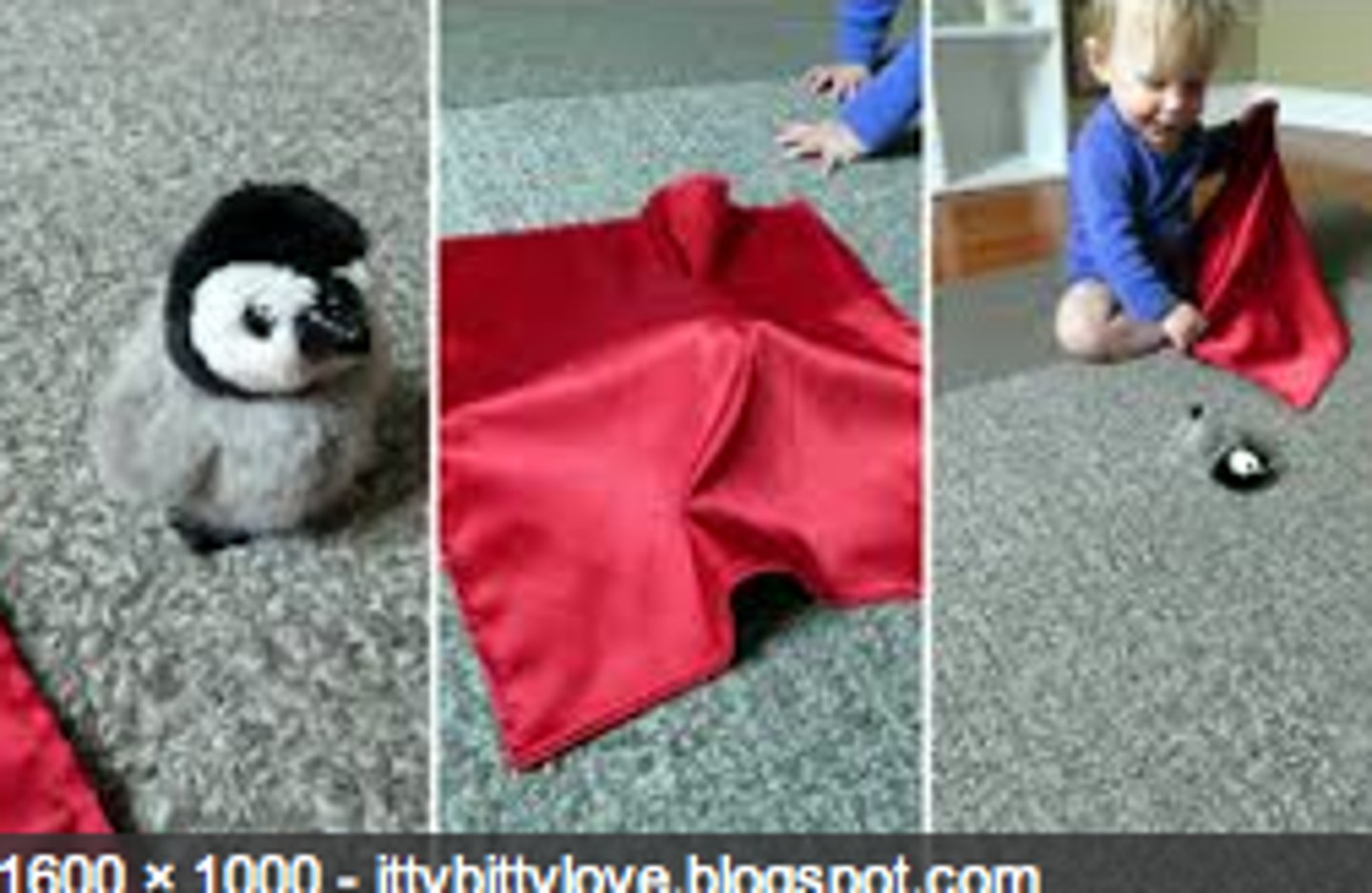
object permanence
the awareness that things continue to exist even when not perceived

preoperational stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage (from about 2 to 6 or 7 years of age) during which a child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete logic
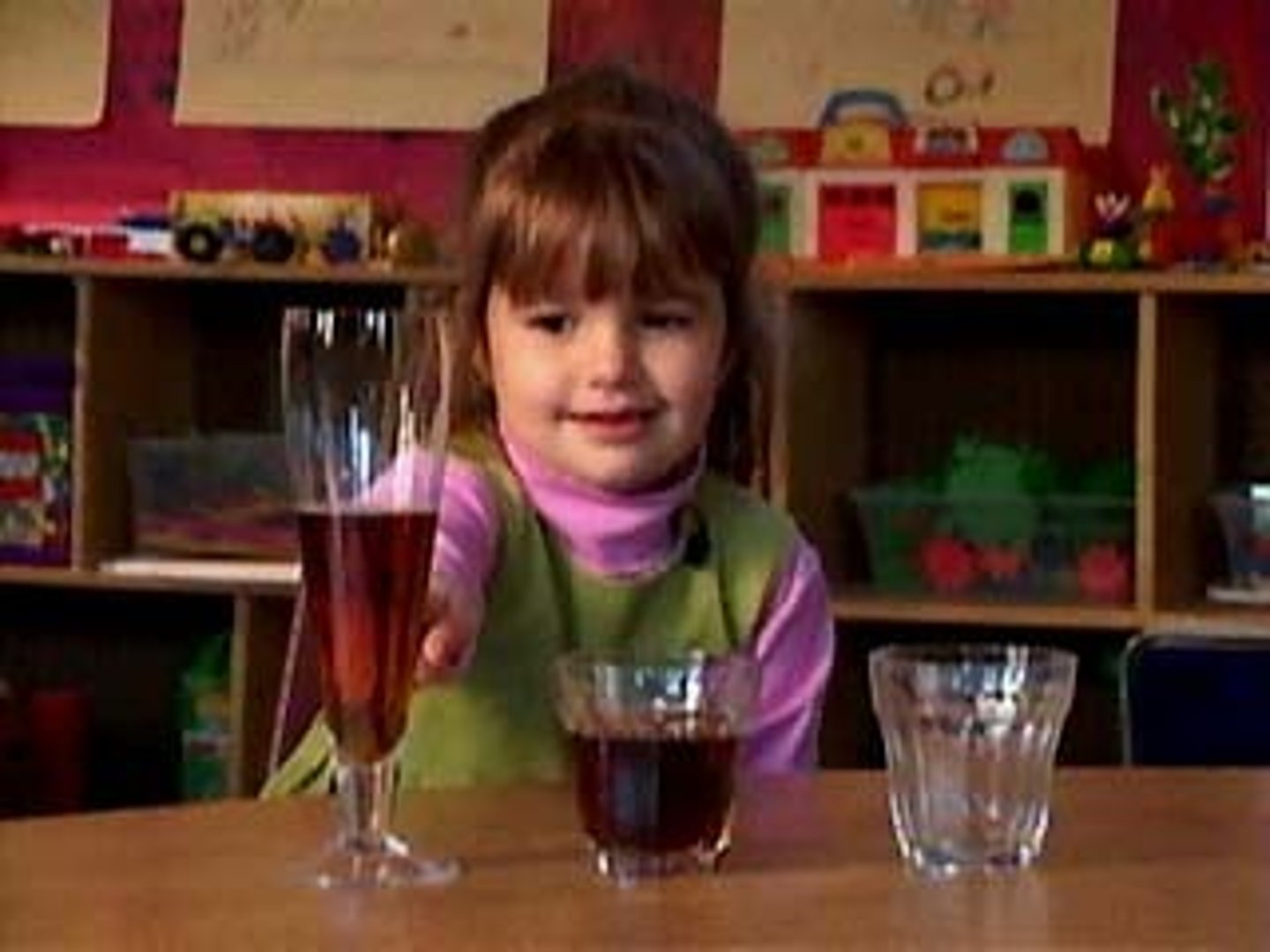

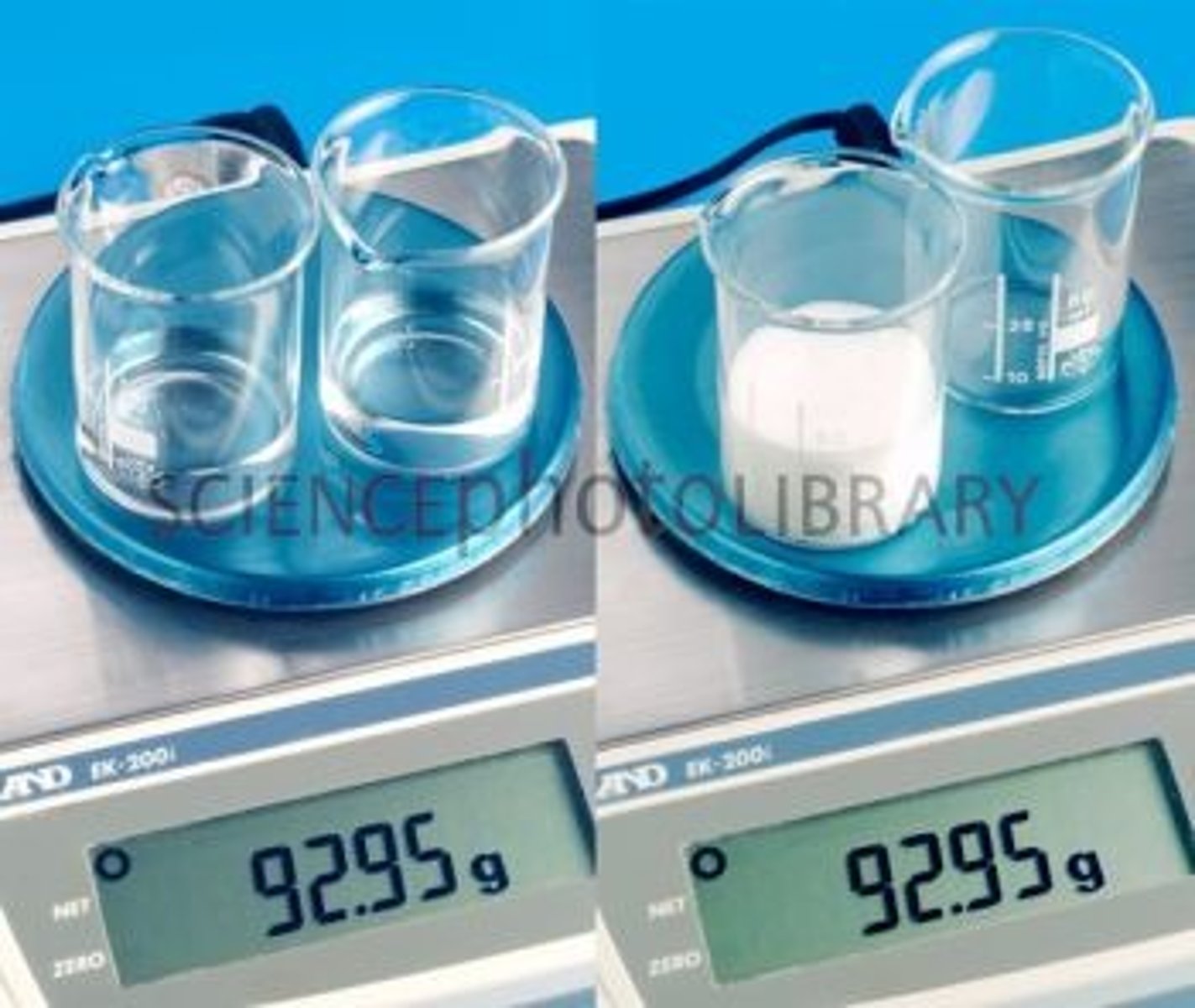
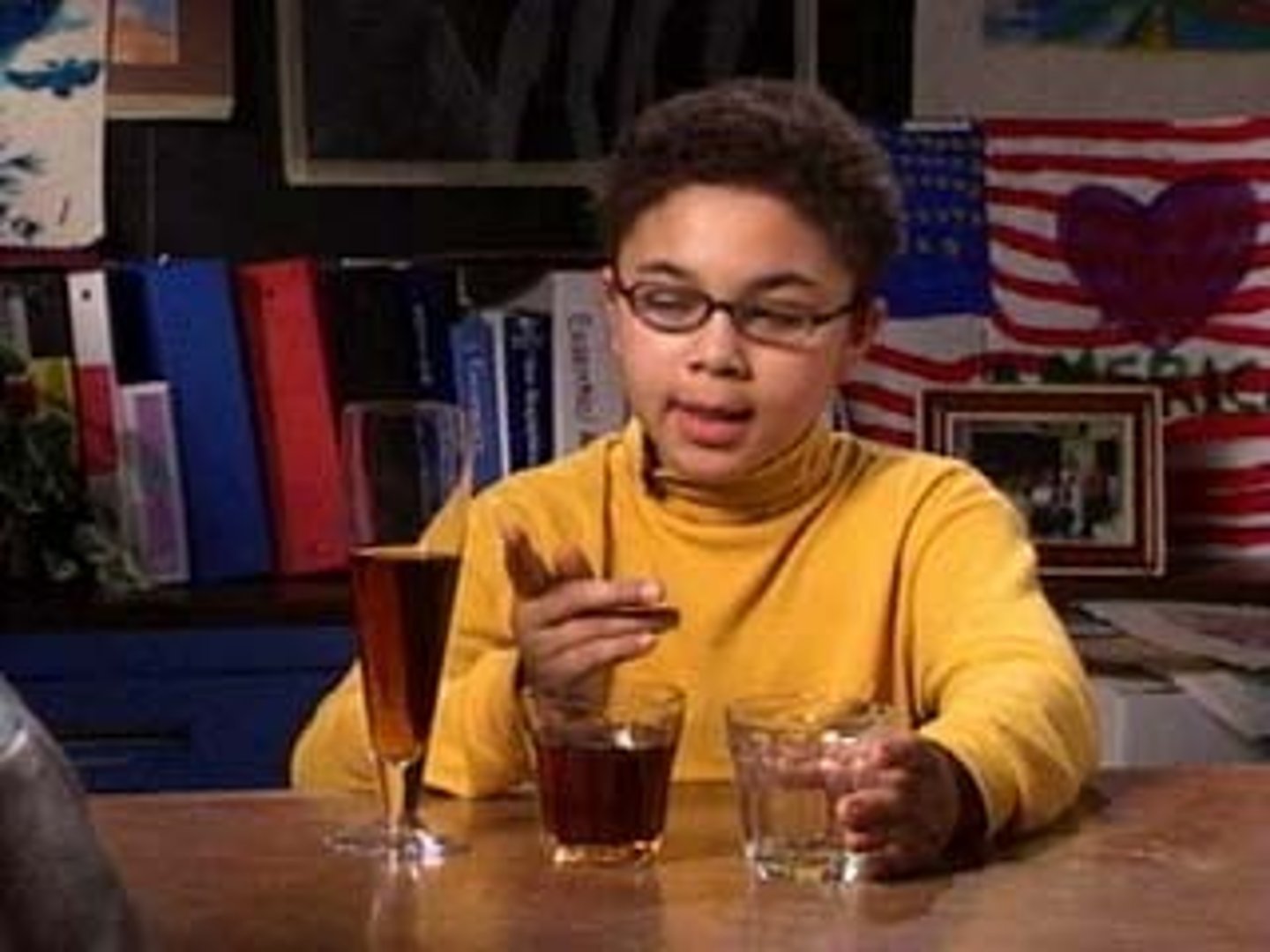
conservation
the principle that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects

Egocentrism
the preoperational child's difficulty taking another's point of view
theory of mind
an awareness that other people's behavior may be influenced by beliefs, desires, and emotions that differ from one's own
concrete operational stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (from about 6 or 7 to 11 years of age) during which children gain the mental operations that enable them to think logically

formal operational stage
in Piaget's theory, the late stage of cognitive development during which people begin to think logically about abstract concepts

Scaffolding
Adjusting the support offered during a teaching session to fit the child's current level of performance

stranger anxiety
the caution and wariness displayed by infants when encountering an unfamiliar person

authoritarian parenting
style of parenting in which parent is rigid and overly strict, showing little warmth to the child

permissive parenting
style of parenting in which parent makes few, if any demands on a child's behavior

authoritative parenting
parenting style characterized by emotional warmth, high standards for behavior, explanation and consistent enforcement of rules, and inclusion of children in decision making

secure attachment
a relationship in which an infant obtains both comfort and confidence from the presence of his or her caregiver

insecure attachment
Infants are wary of exploring the environment and resist or avoid the mother when she attempts to offer comfort or consolation

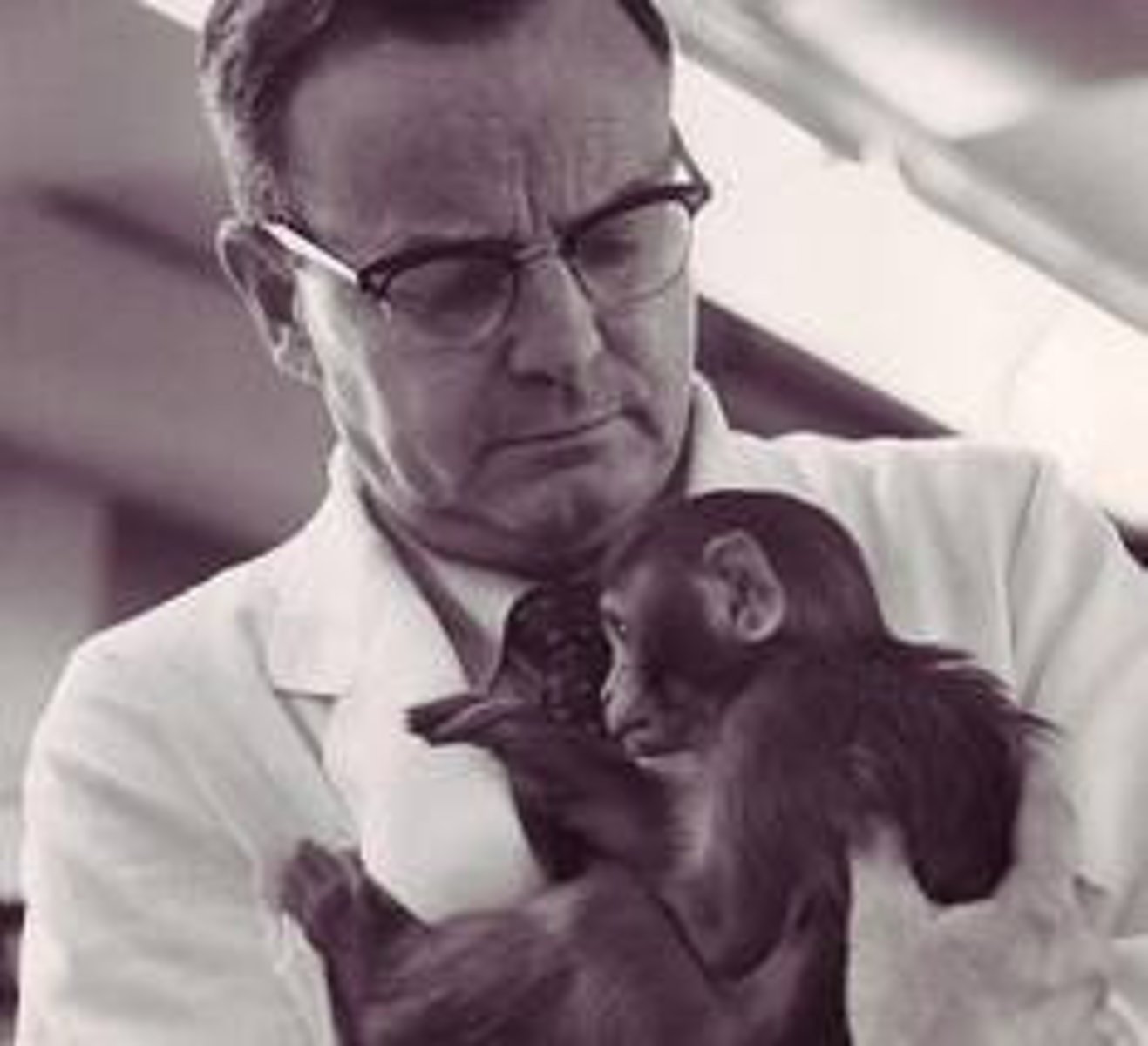
Harry Harlow Rhesus Monkey Studies
development, contact comfort, attachment; experimented with baby rhesus monkeys and presented them with cloth or wire "mothers;" showed that the monkeys became attached to the cloth mothers because of contact comfort

gender
the socially constructed roles and characteristics by which a culture defines male and female

social learning theory
we learn social behavior by observing and imitating and by being rewarded or punished

Gender Identity
the individual's sense of being male, female, genderqueer or non binary.
menopause
the time of natural cessation of menstruation; also refers to the biological changes a woman experiences as her ability to reproduce declines

learning
the process of acquiring new and relatively enduring information or behaviors

habituation
decreasing responsiveness with repeated stimulation. As infants gain familiarity with repeated exposure to a visual stimulus, their interest wanes and they look away sooner.

classical conditioning
a type of learning in which one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events
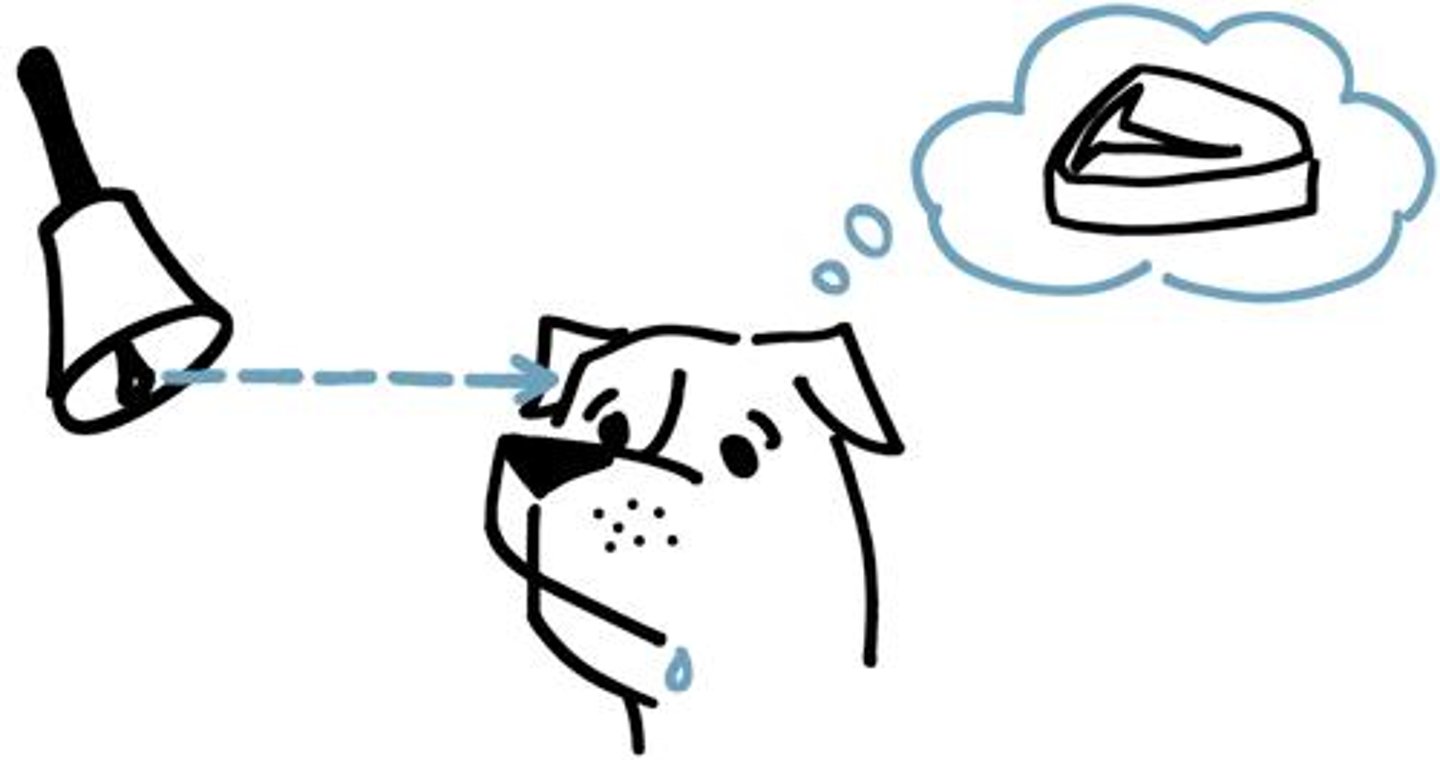
operant conditioning
a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher

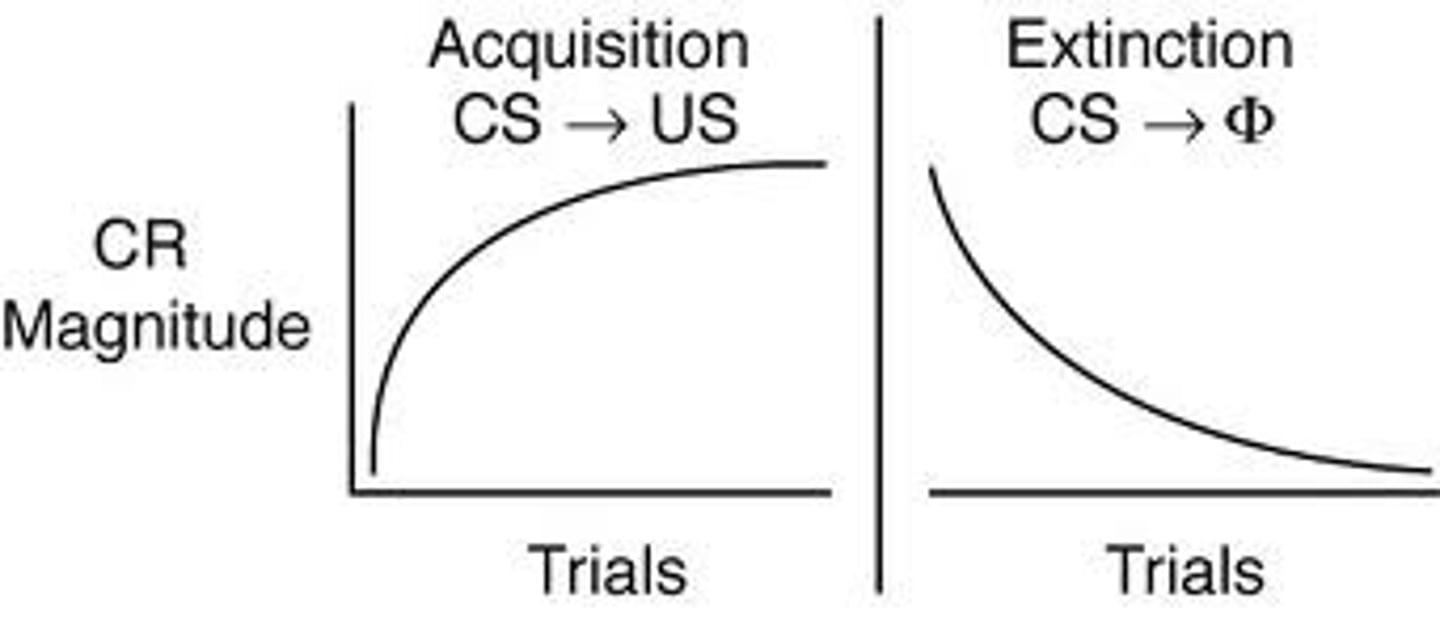
acquisition
In classical conditioning, the initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned response. In operant conditioning, the strengthening of a reinforced response.
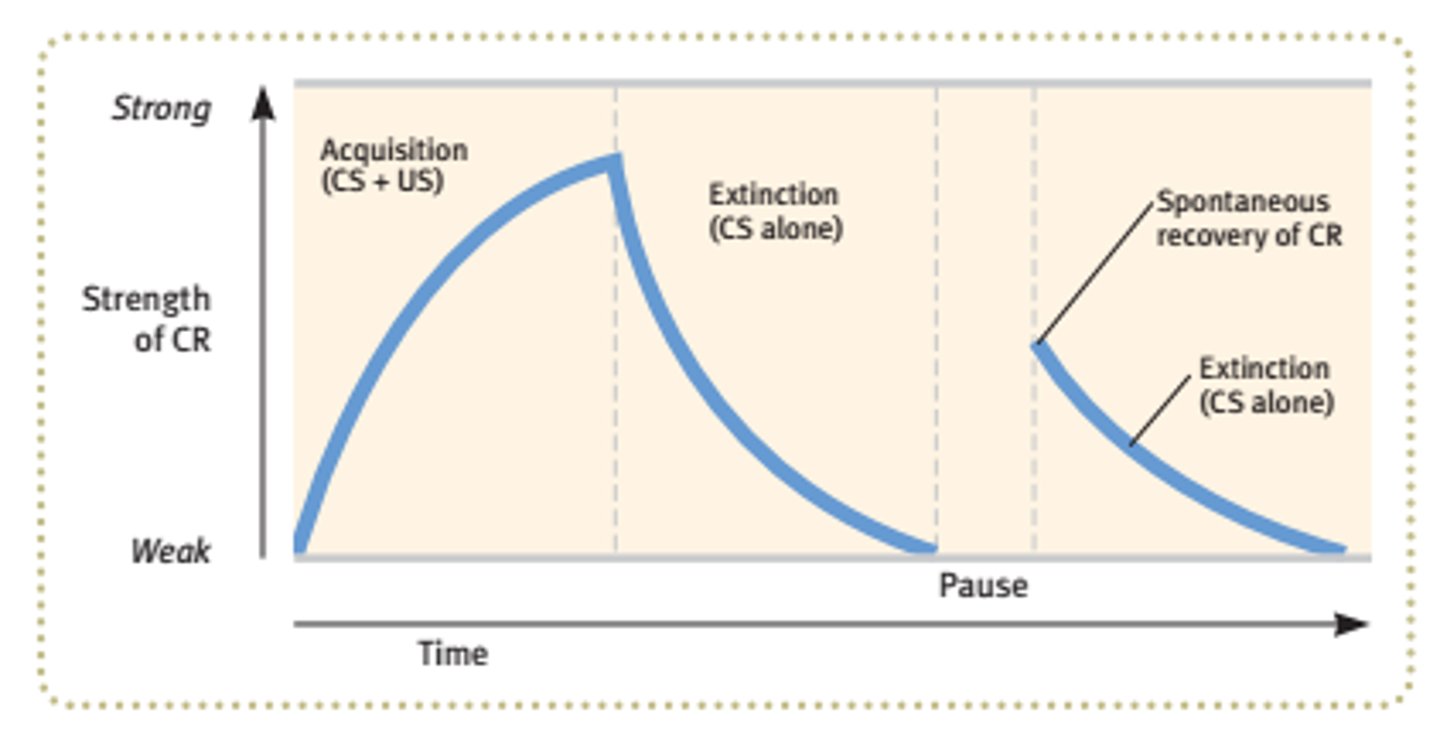
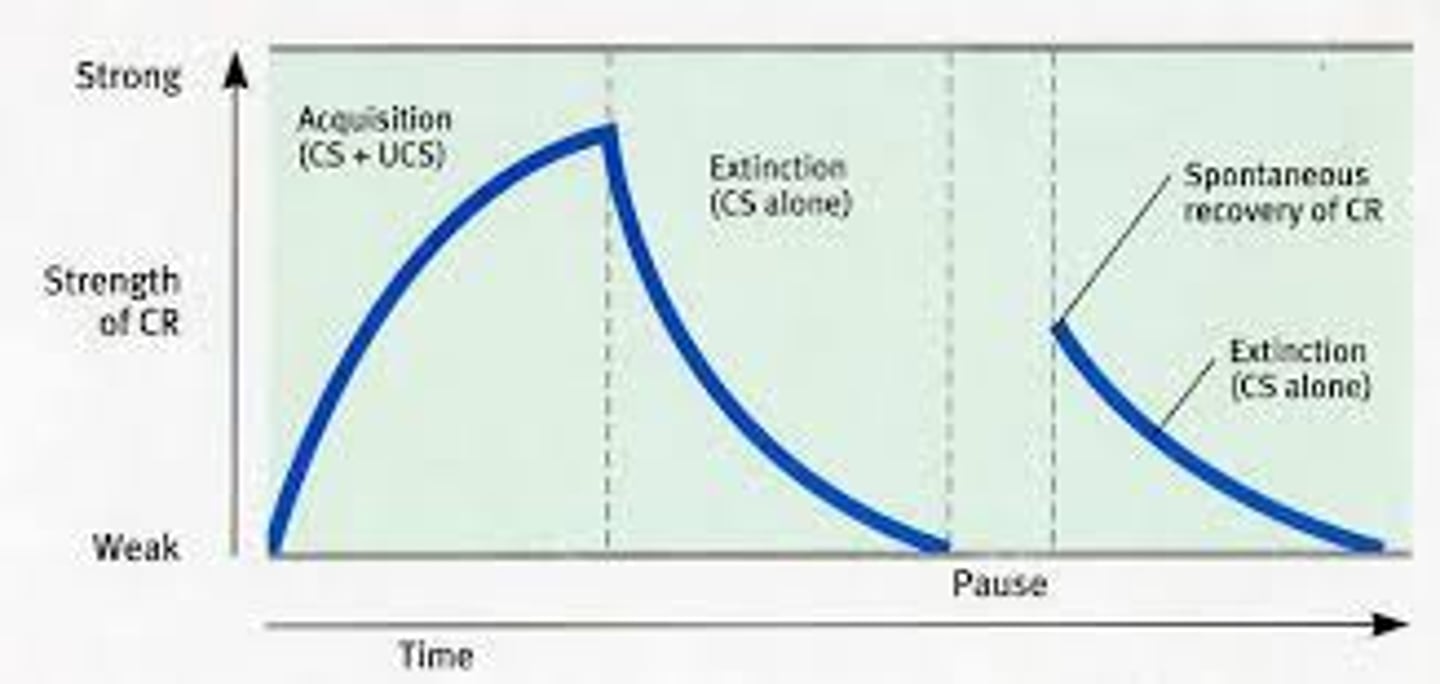
extinction
the diminishing of a conditioned response; occurs in classical conditioning when an unconditioned stimulus (US) does not follow a conditioned stimulus (CS); occurs in operant conditioning when a response is no longer reinforced.
spontaneous recovery
the reappearance, after a pause, of an extinguished conditioned response
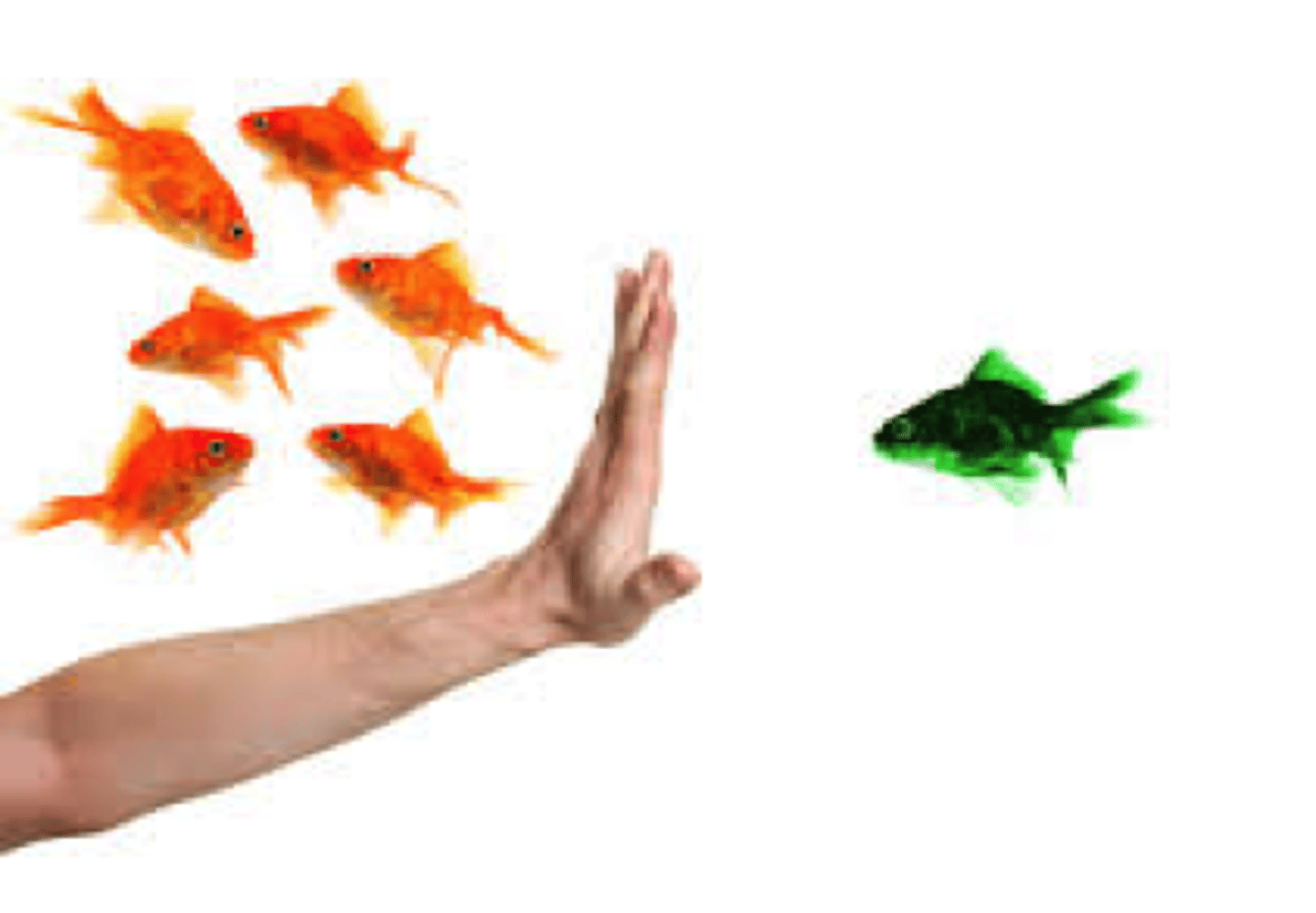
generalization
the tendency, once a response has been conditioned, for stimuli similar to the conditioned stimulus to elicit similar responses

discrimination
in classical conditioning, the learned ability to distinguish between a conditioned stimulus and stimuli that do not signal an unconditioned stimulus
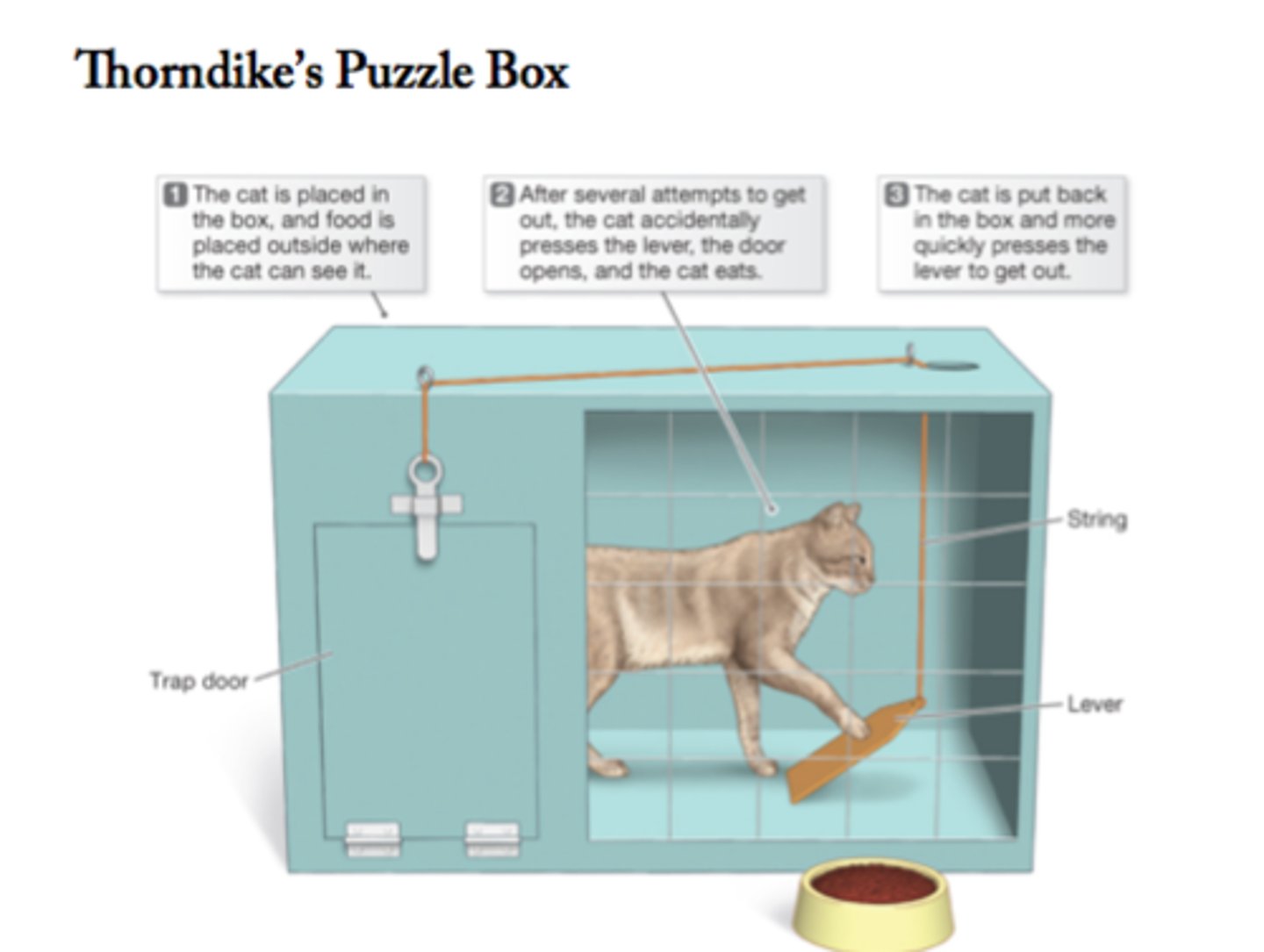
law of effect
Thorndike's principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and that behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely
shaping
an operant conditioning procedure in which reinforcers guide behavior toward closer and closer approximations of the desired behavior
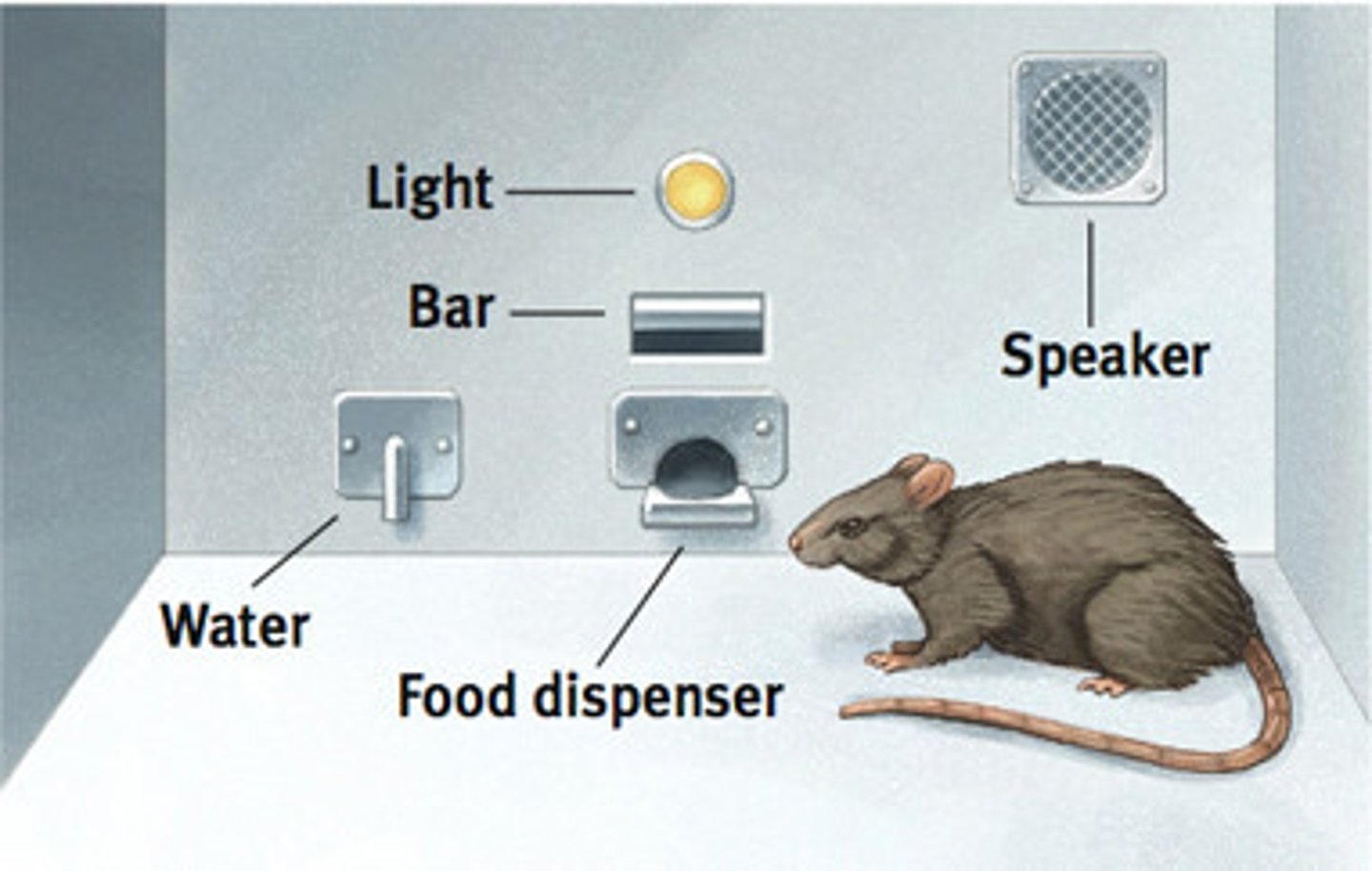
positive reinforcement
the reinforcement of a response by the addition or experiencing of a pleasurable stimulus

negative reinforcement
increasing the strength of a given response by removing or preventing a painful stimulus when the response occurs

primary reinforcer
an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need

secondary reinforcer
any reinforcer that becomes reinforcing after being paired with a primary reinforcer, such as praise, tokens, or gold stars

positive punishment
an new event that tends to decrease the behavior that it follows
continuous reinforcement
reinforcing the desired response every time it occurs

partial reinforcement
reinforcing a response only part of the time; results in slower acquisition of a response but much greater resistance to extinction than does continuous reinforcement
Taste Aversion(Garcia effect)
when nausea and a food are paired, the food will be averted in the future

instinctive drift
tendency for animals to return to innate behaviors following repeated reinforcement

cognitive map
a mental representation of the layout of one's environment
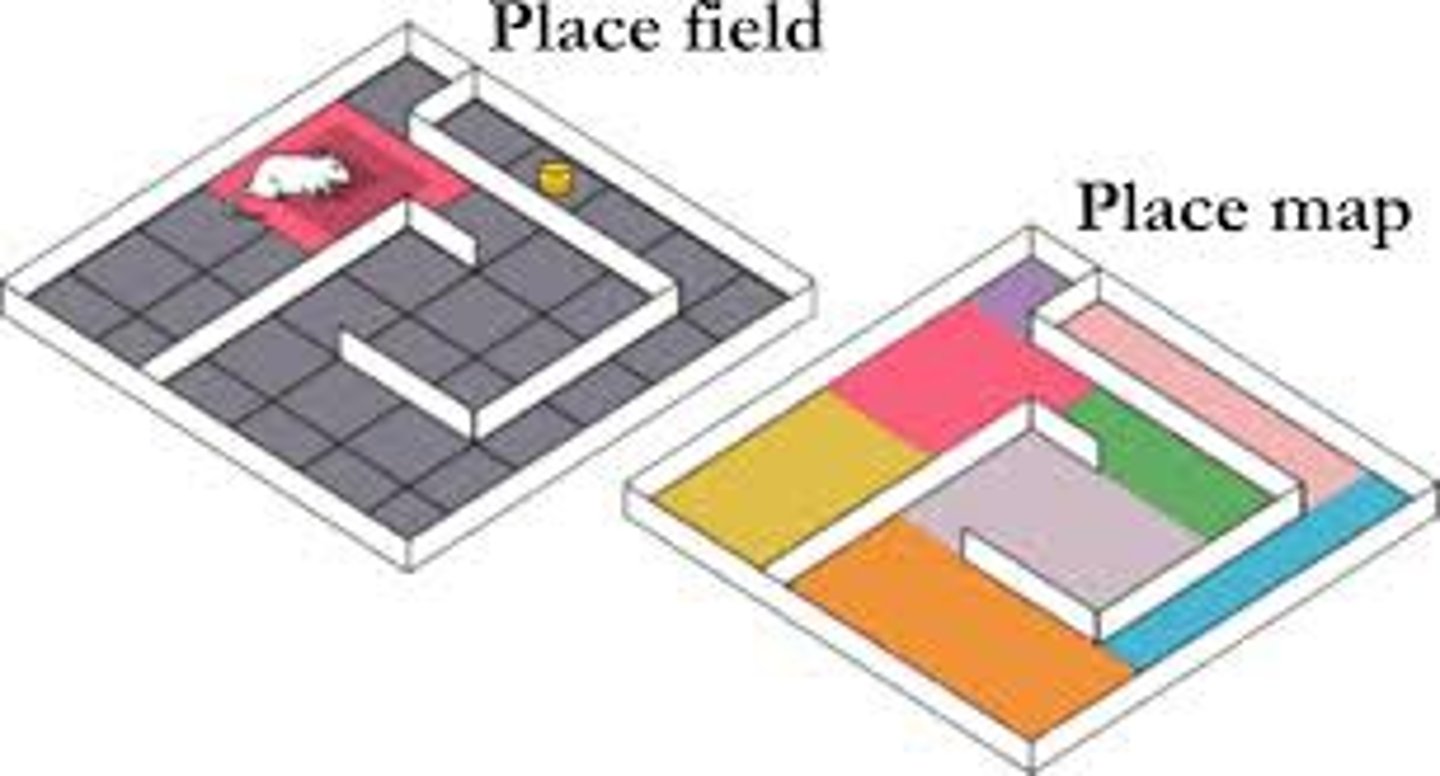
latent learning
learning that occurs but is not apparent until there is an incentive to demonstrate it

intrinsic motivation
a desire to perform a behavior effectively for its own sake

extrinsic motivation
a desire to perform a behavior to receive promised rewards or avoid threatened punishment

learned helplessness
the hopelessness and passive resignation an animal or human learns when unable to avoid repeated aversive events

Cross sectional study
a study in which people of different ages are compared with one another

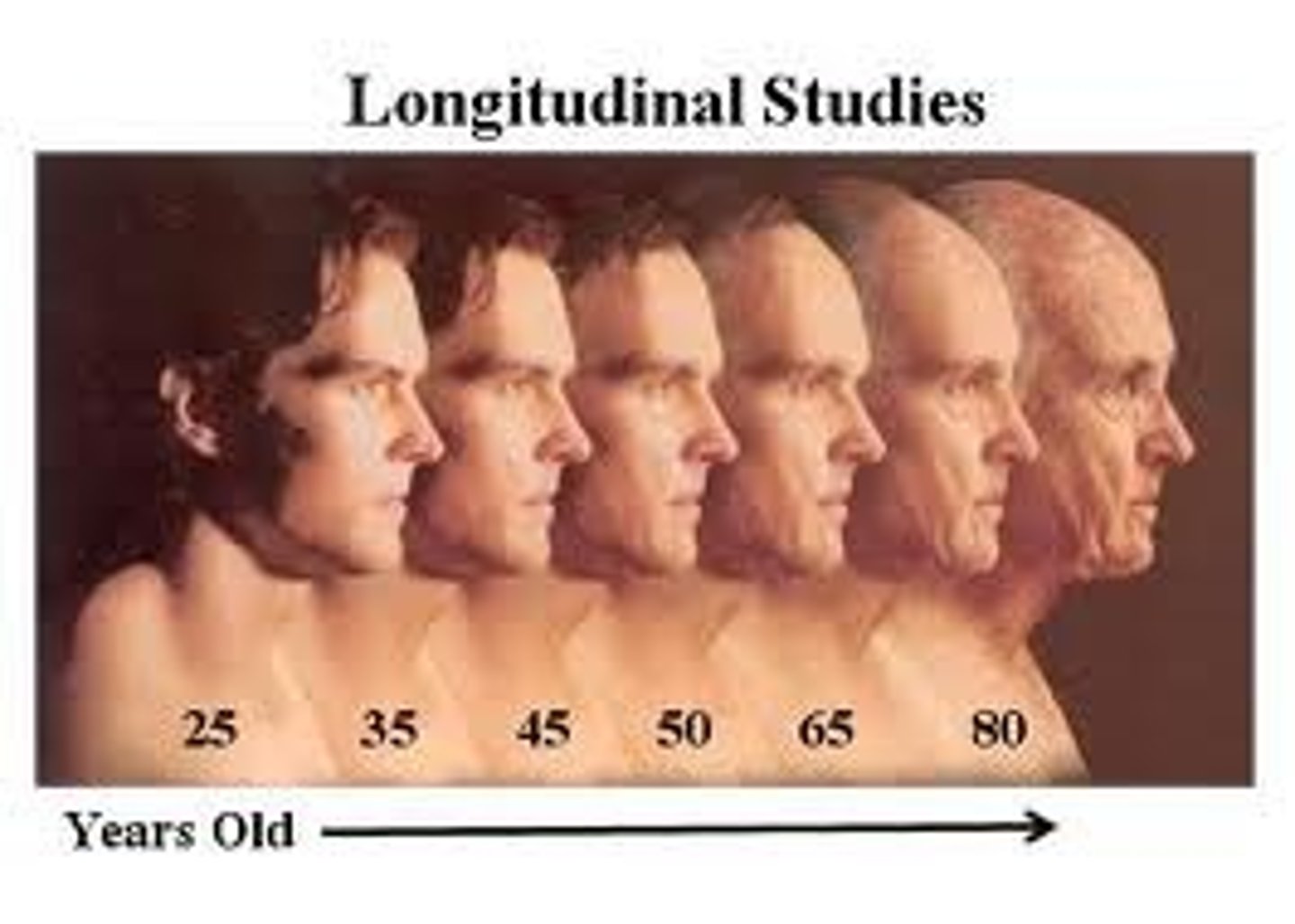
longitudinal study
research in which the same people are restudied and retested over a long period
Stability vs. change
Do our early personality traits persist through life, or do we become different persons as we age?

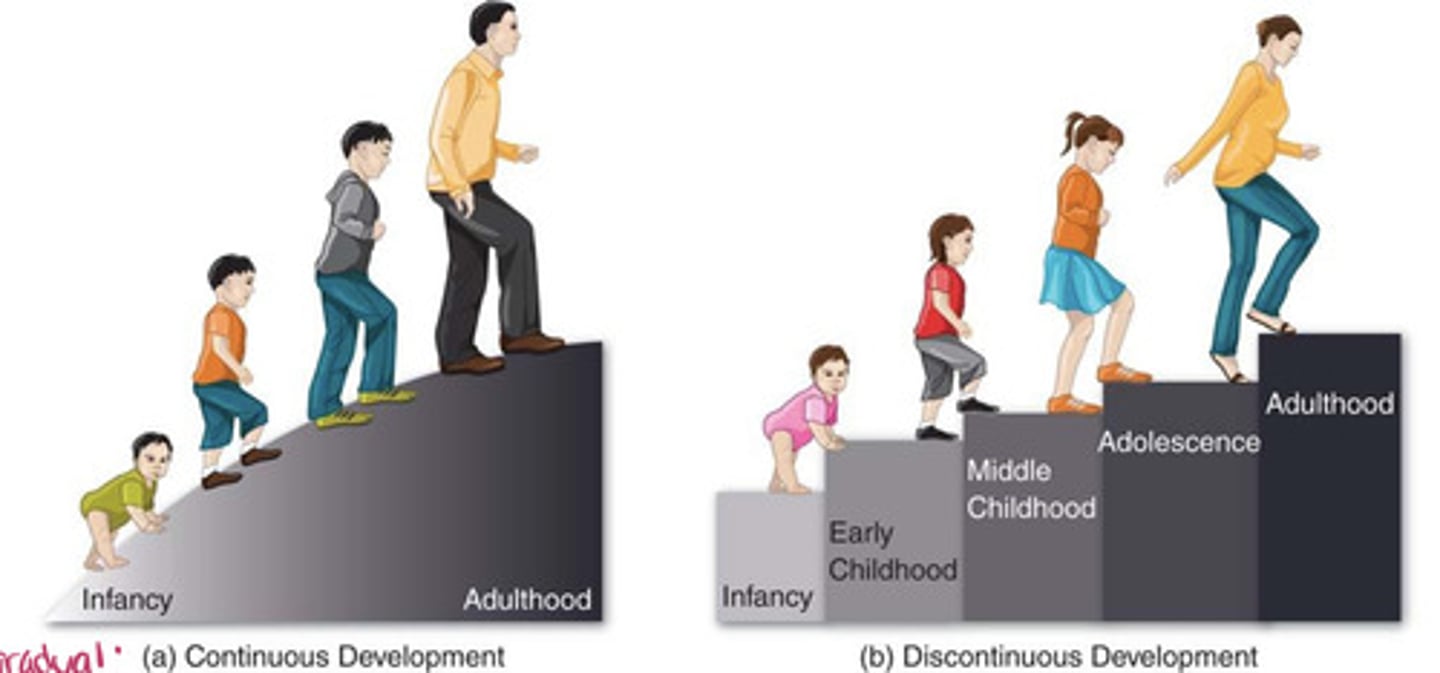
Continuous vs. discontinuous
Theory on whether development is gradual or whether children develop in bursts
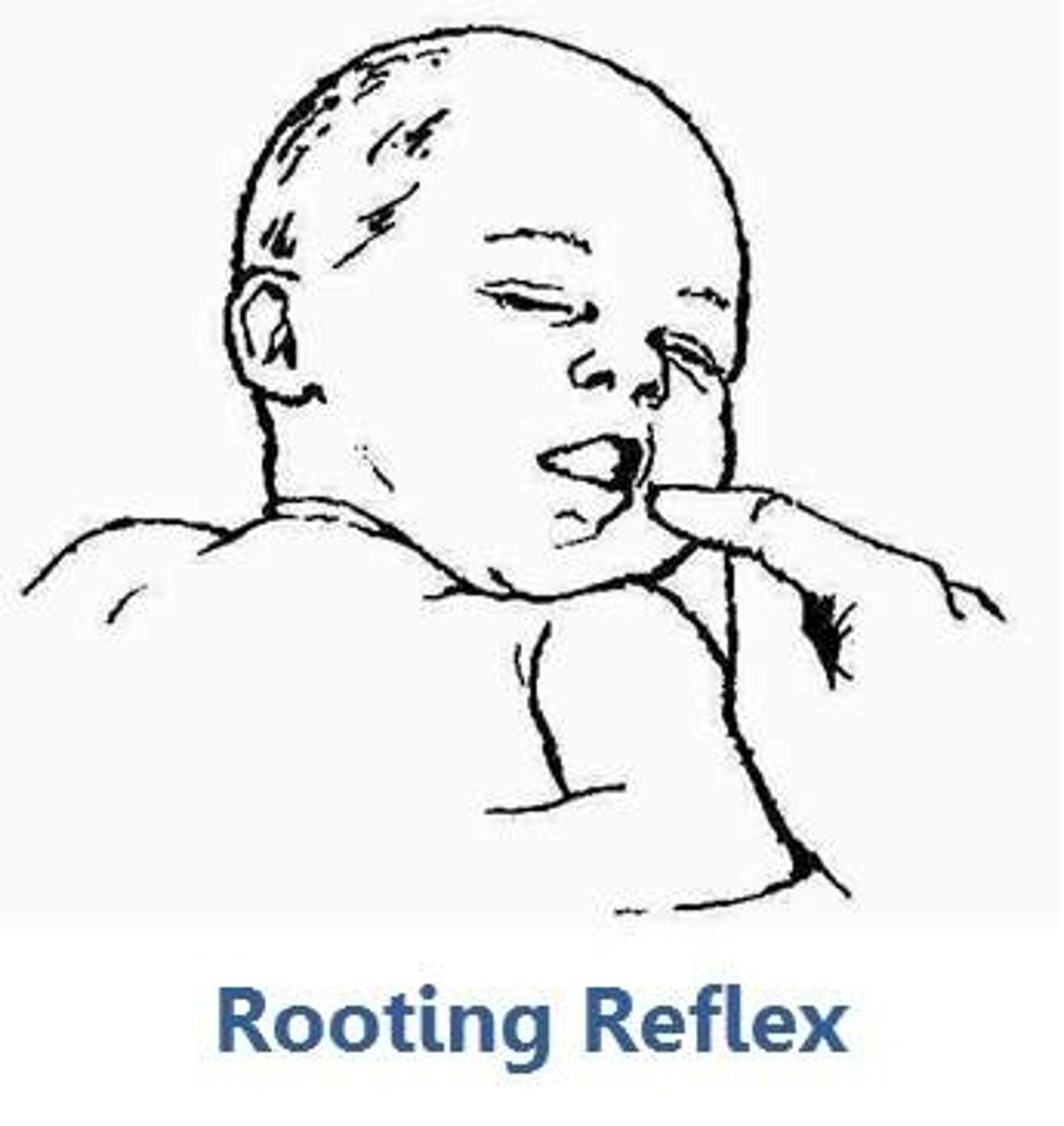
reflex rooting
an infant will turn its mouth toward a nipple (or anything else) that touches its cheek.
Critical period (sensitive period)
- a point in early development that can have a significant influence on physiological or behavioral functioning in later life

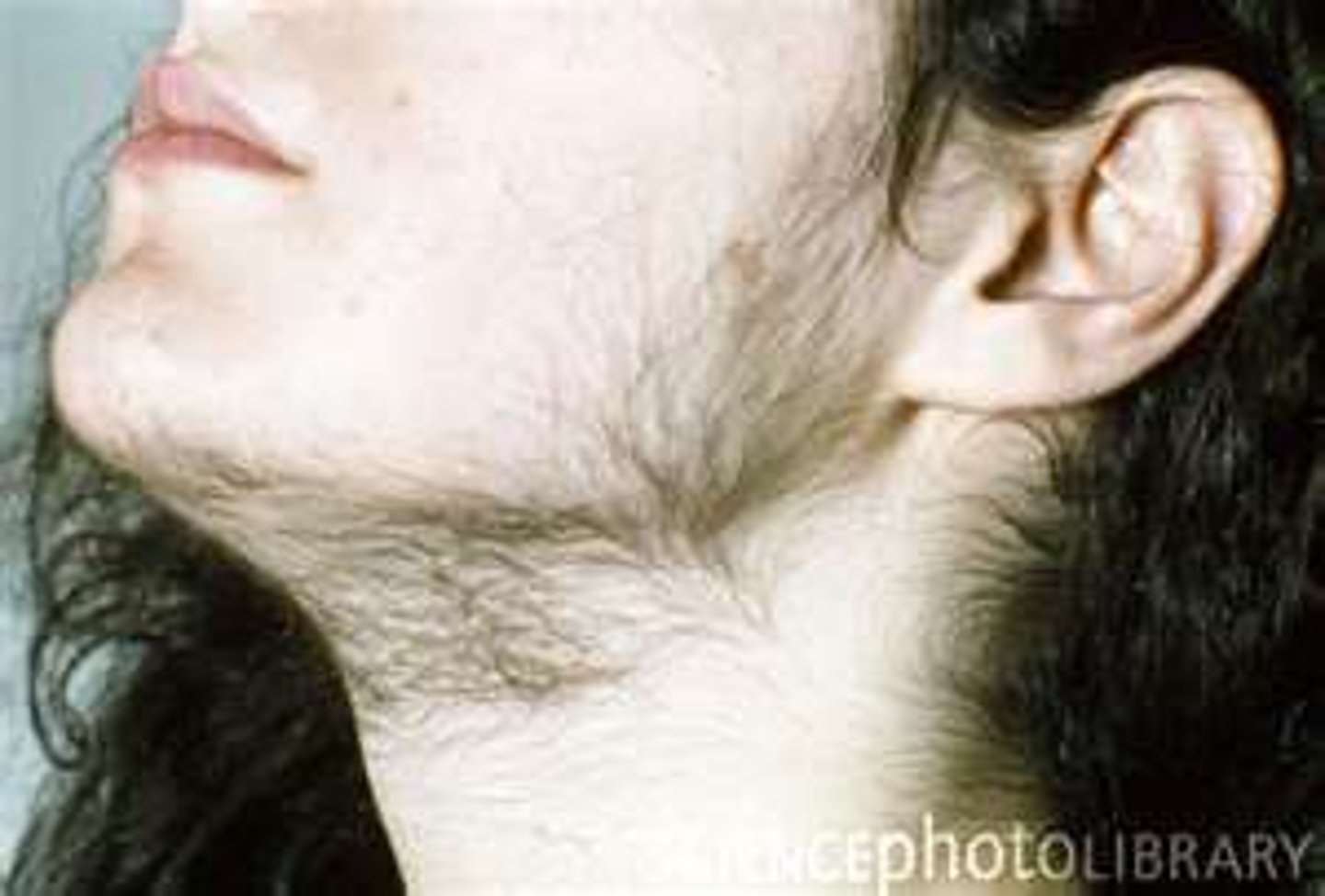
Secondary Sex characteristics
nonreproductive sexual characteristics, such as female breasts and hips, male voice quality, and body hair
Primary sex characteristics
the body structures (ovaries, testes, and external genitalia) that make sexual reproduction possible
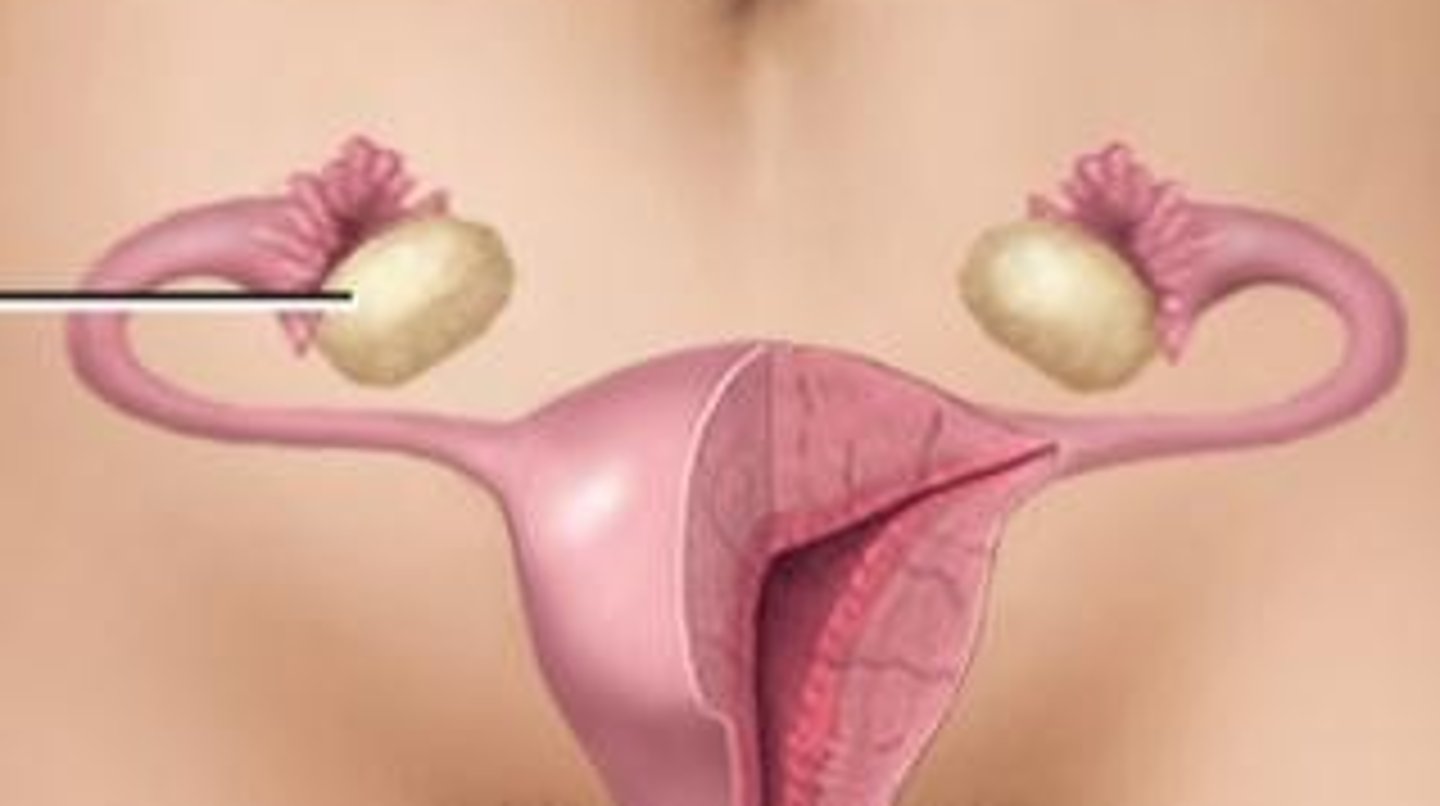
Menarche
the first occurrence of menstruation

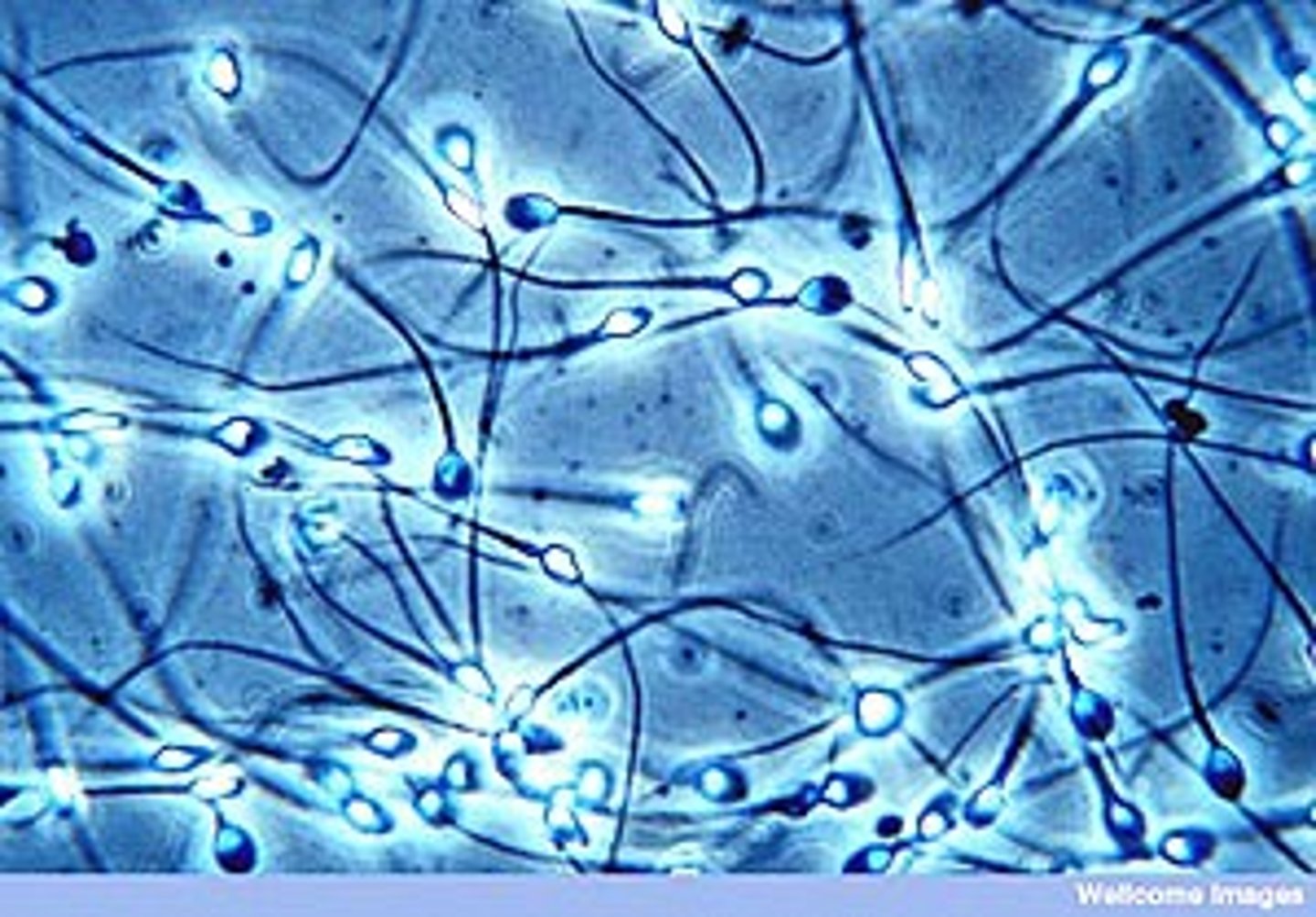
spermarche
first occurrence of ejaculation
puberty
the period of sexual maturation, during which a person becomes capable of reproducing
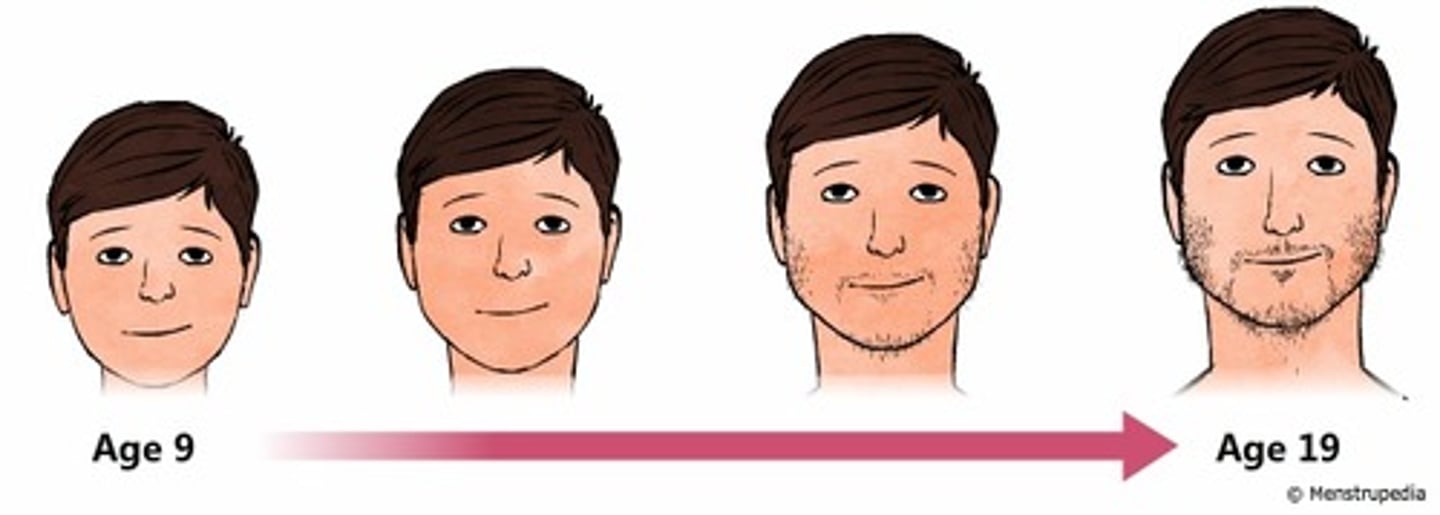
Adolescent growth spurt
The period of accelerated growth during puberty, involving rapid increases in height and weight.

Reversibility
the capacity to think through a series of steps and then mentally reverse direction, returning to the starting point

Animism
Belief that objects, such as plants and stones, or natural events, like thunderstorms and earthquakes, have a discrete spirit and conscious life.

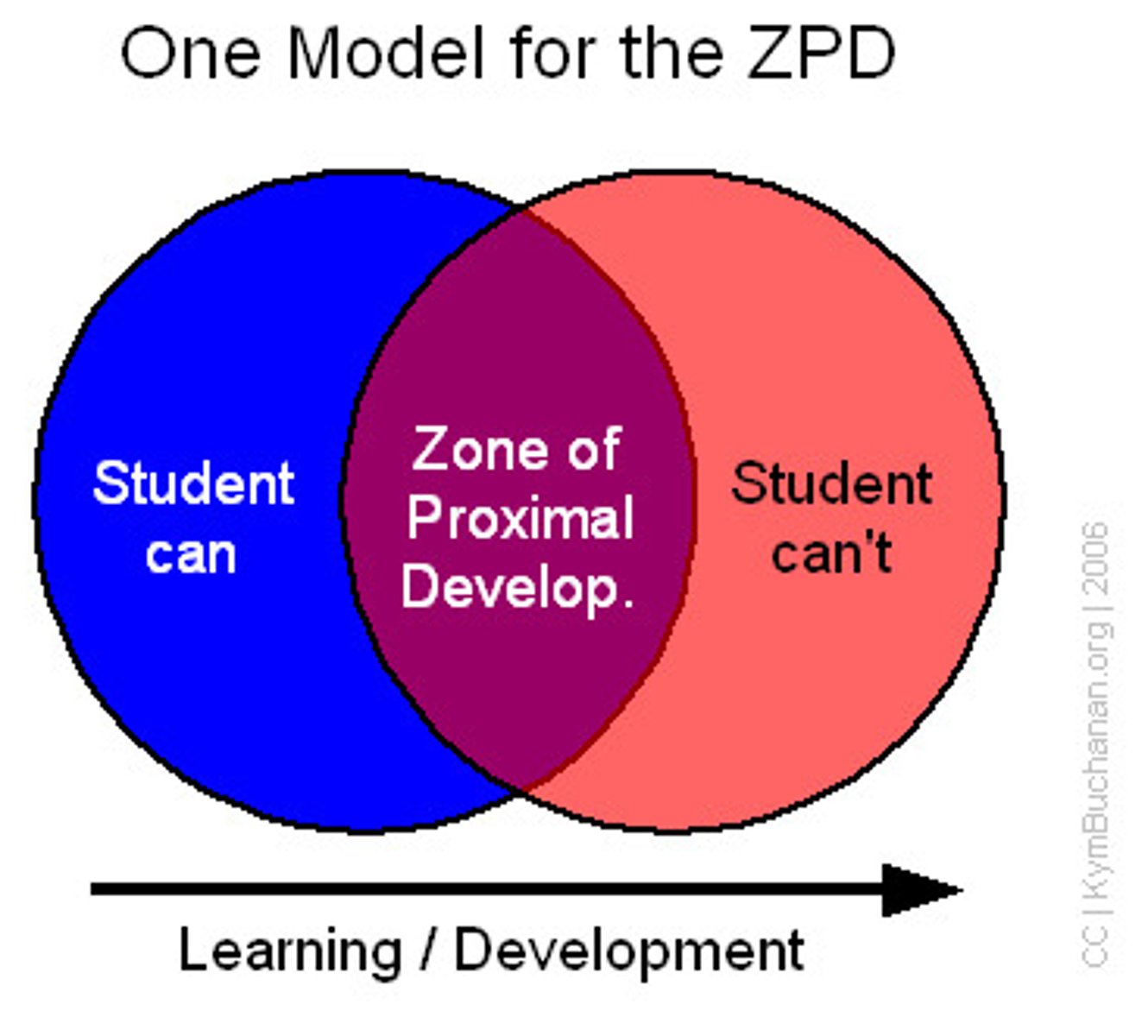
zone of proximal development
In Vygotsky's theory, the range between children's present level of knowledge and their potential knowledge state if they recieve proper guidance and instruction
Avoidant attachment
attachments marked by discomfort over, or resistance to, being close to others

Anxious attachment
demonstrated by babies who seem constantly afraid of potential separation from the caregiver; they cling to caregivers in strange settings and display intense distress upon separation

Disorganized attachment
a type of attachment that is marked by an infant's inconsistent reactions to the caregiver's departure and return

Temperament
basic emotional style that appears early in development and is largely genetic in origin

Emerging adulthood
for some people in modern cultures, a period from the late teens to mid-twenties, bridging the gap between adolescent dependence and full independence and responsible adulthood

symbolic play
play in which children make believe that objects and toys are other than what they are. Also called pretend play.

Unconditioned stimulus
in classical conditioning, a stimulus that unconditionally—naturally and automatically—triggers a response.

Conditioned Response
in classical conditioning, the learned response to a previously neutral (but now conditioned) stimulus (CS)

High order conditioning
a procedure in which the conditioned stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus
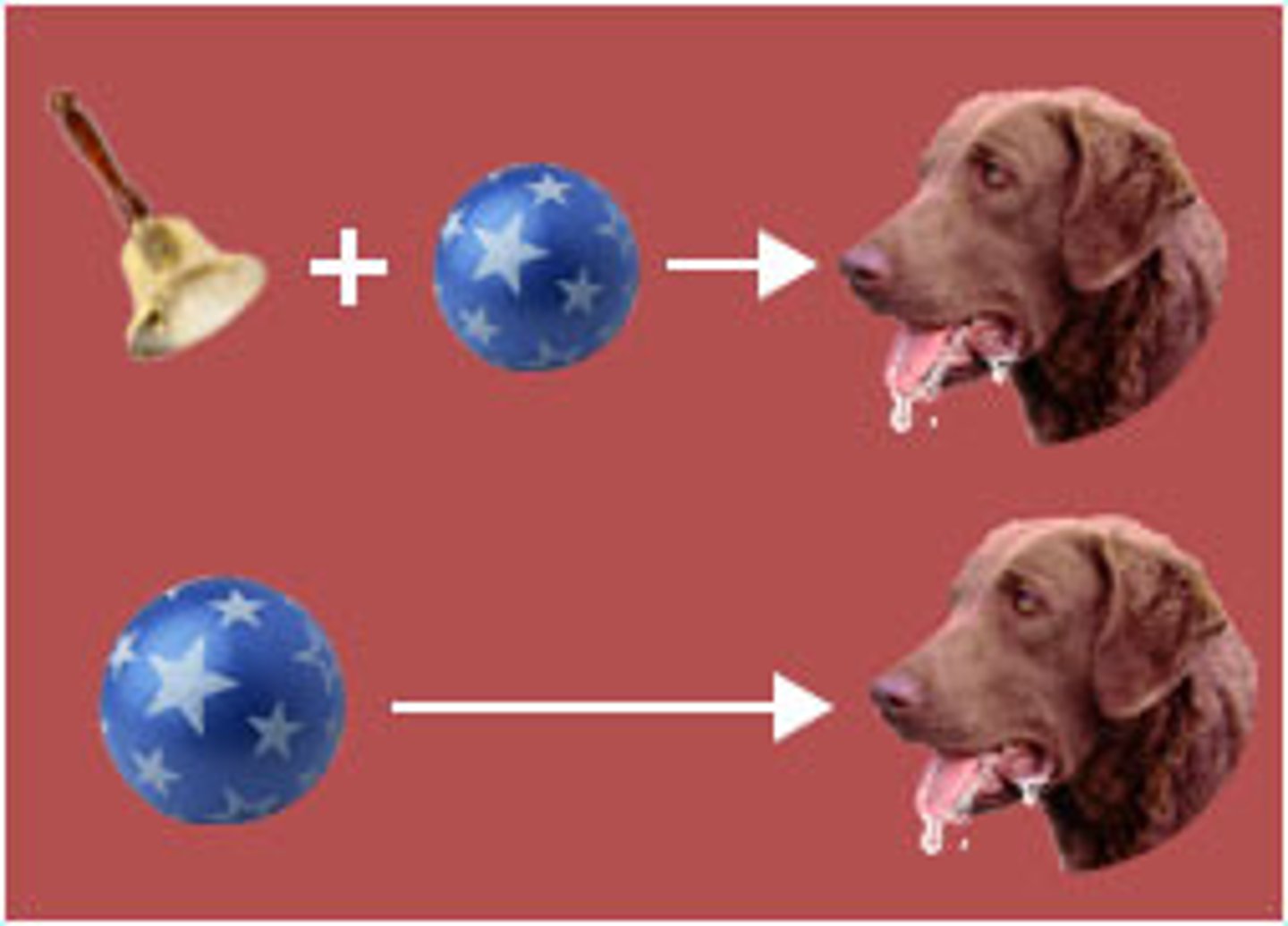
Conditioned stimulus
in classical conditioning, an originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus, comes to trigger a conditioned response

Unconditioned response
In classical conditioning, the unlearned, naturally occurring response to the unconditioned stimulus (US), such as salivation when food is in the mouth.

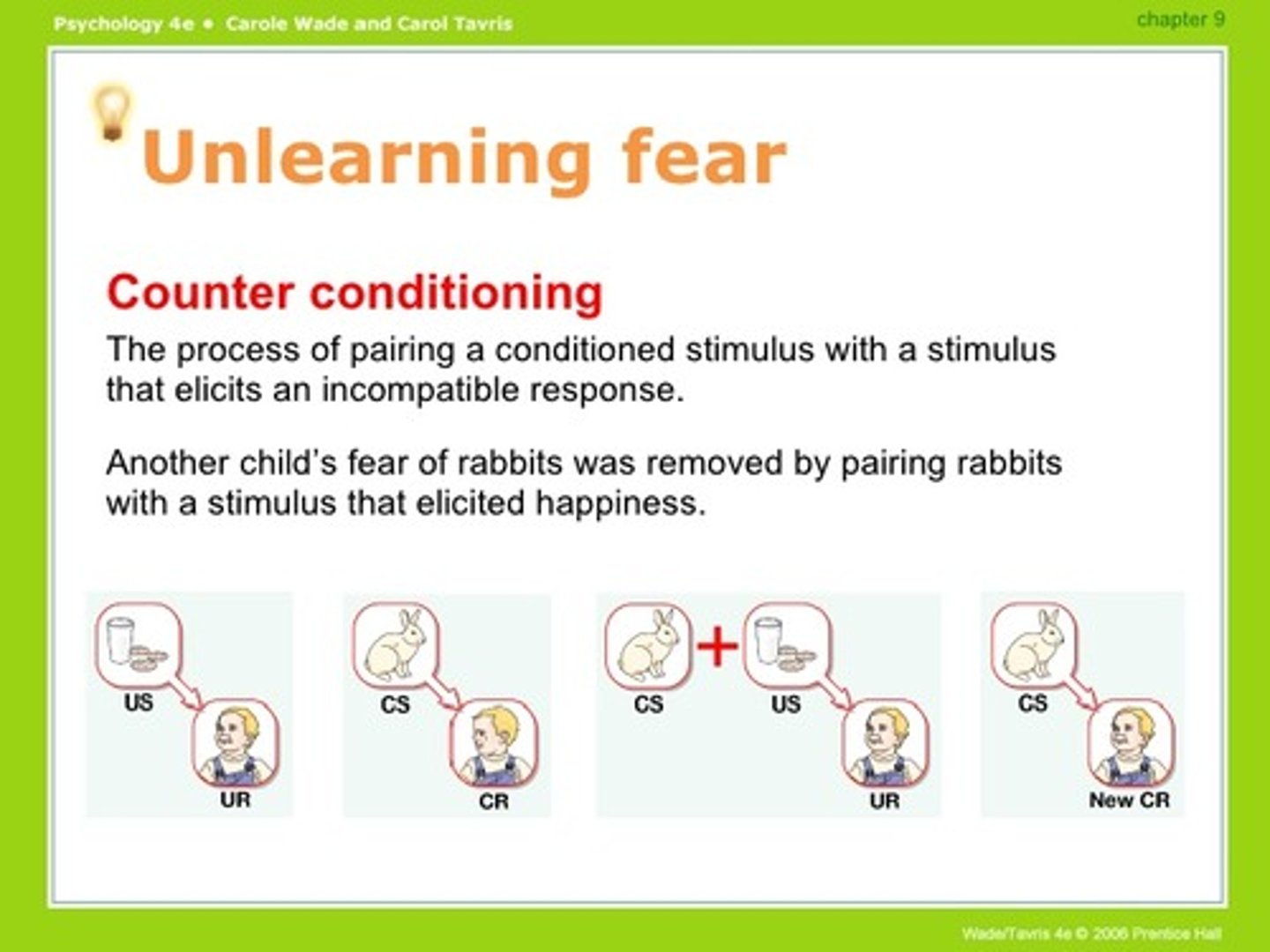
Counter conditioning
a behavior therapy procedure that conditions new responses to stimuli that trigger unwanted behaviors; based on classical conditioning
Preparedness
a biological predisposition to learn associations, such as between taste and nausea, that have survival value

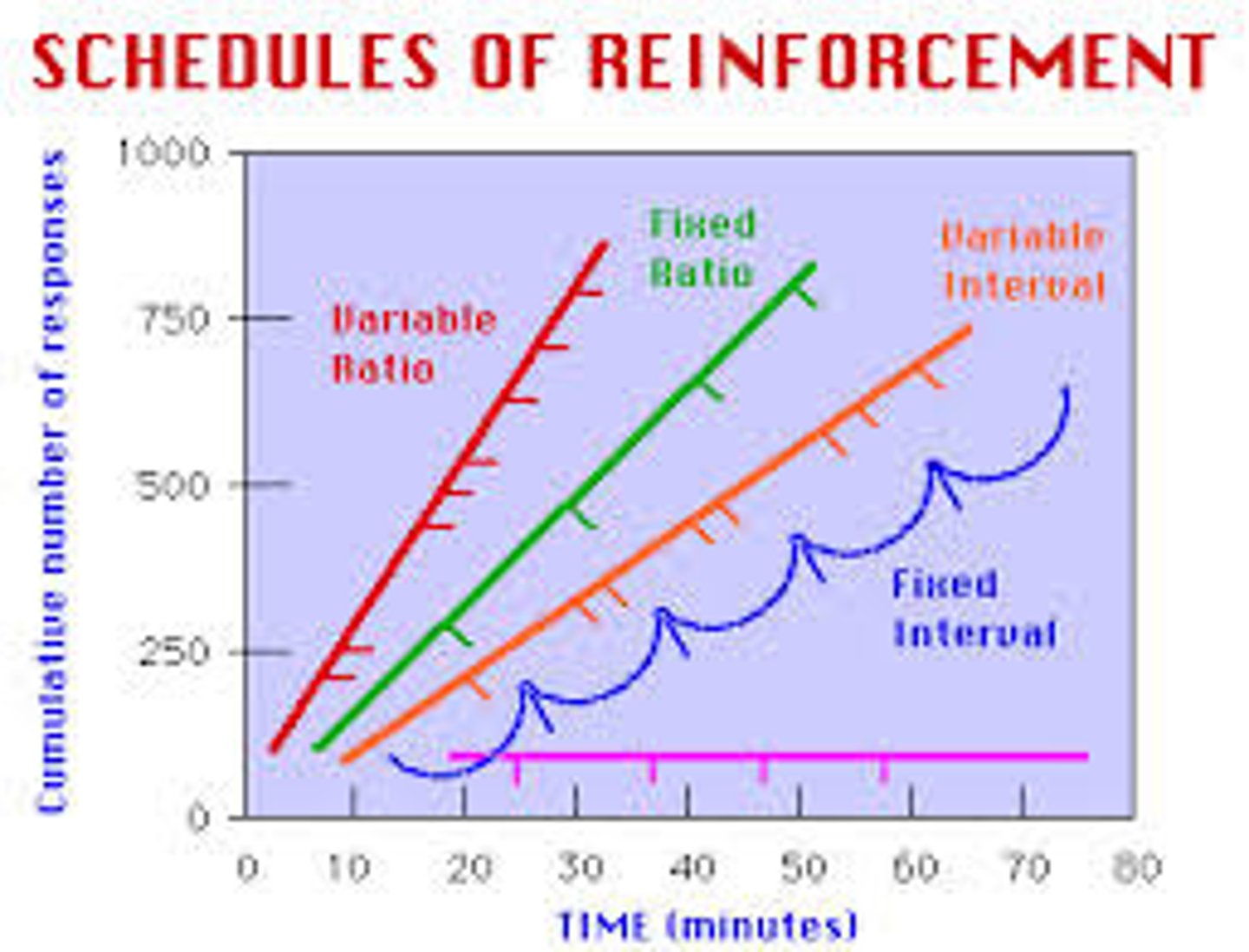
Fixed interval
reinforces a response only after a specified time has elapsed

Fixed ratio
reinforces a response only after a specified number of responses

Variable interval
reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals
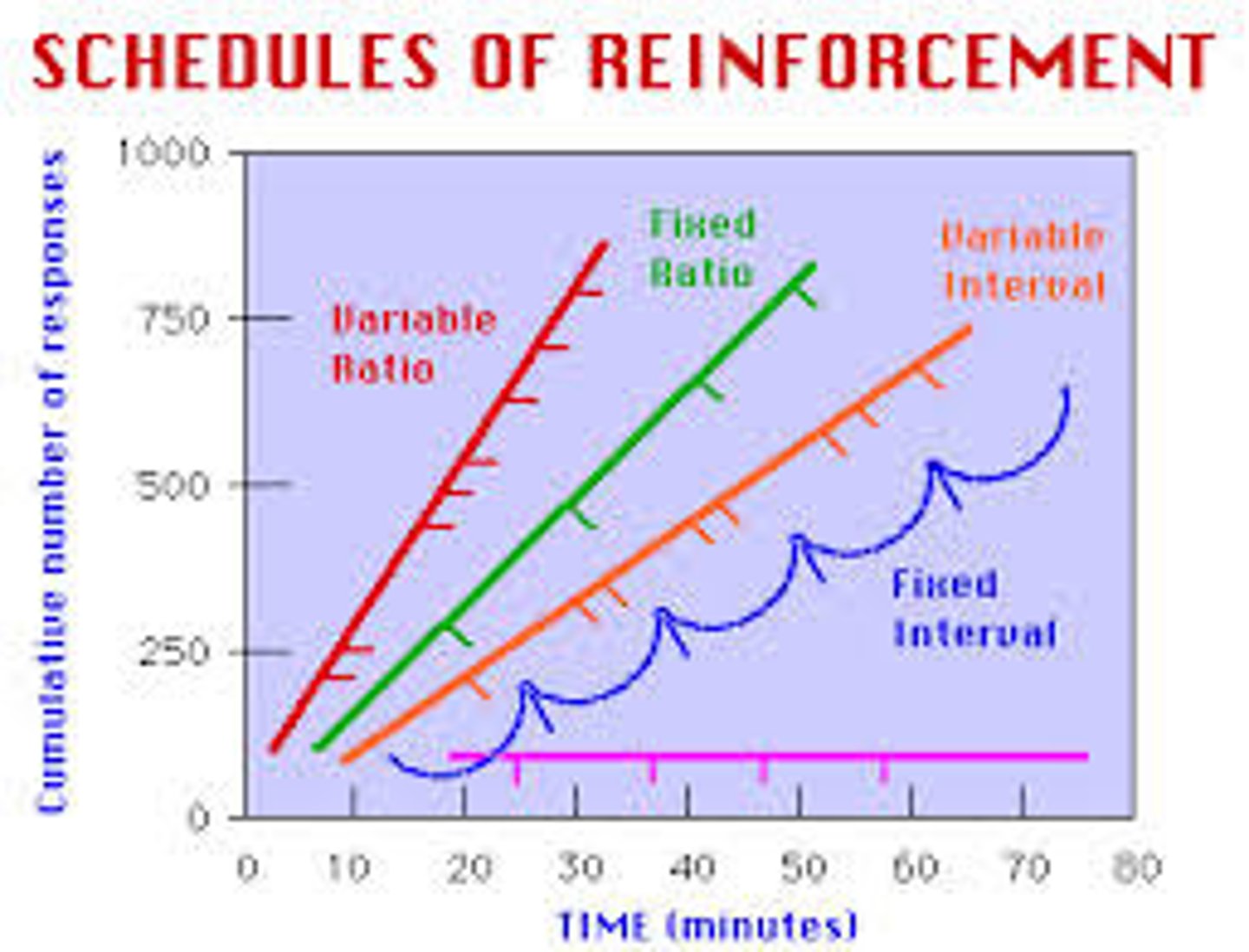
variable ratio
reinforces a response after an unpredictable number of responses

superstitious behavior
a behavior repeated because it seems to produce reinforcement, even though it is actually unnecessary

negative punishment
the removal of a stimulus to decrease the probability of a behavior's recurring

vicarious conditioning
classical conditioning of a reflex response or emotion by watching the reaction of another person

Insight learning
The process of learning how to solve a problem or do something new by applying what is already known

Internal locus of control
the perception that you control your own fate

External locus of control
the perception that chance or outside forces beyond your personal control determine your fate.

emotion focused coping
attempting to alleviate stress by avoiding or ignoring a stressor and attending to emotional needs related to one's stress reaction

problem focused coping
Attempting to alleviate stress directly by changing the stressor or the way we interact with that stressor.

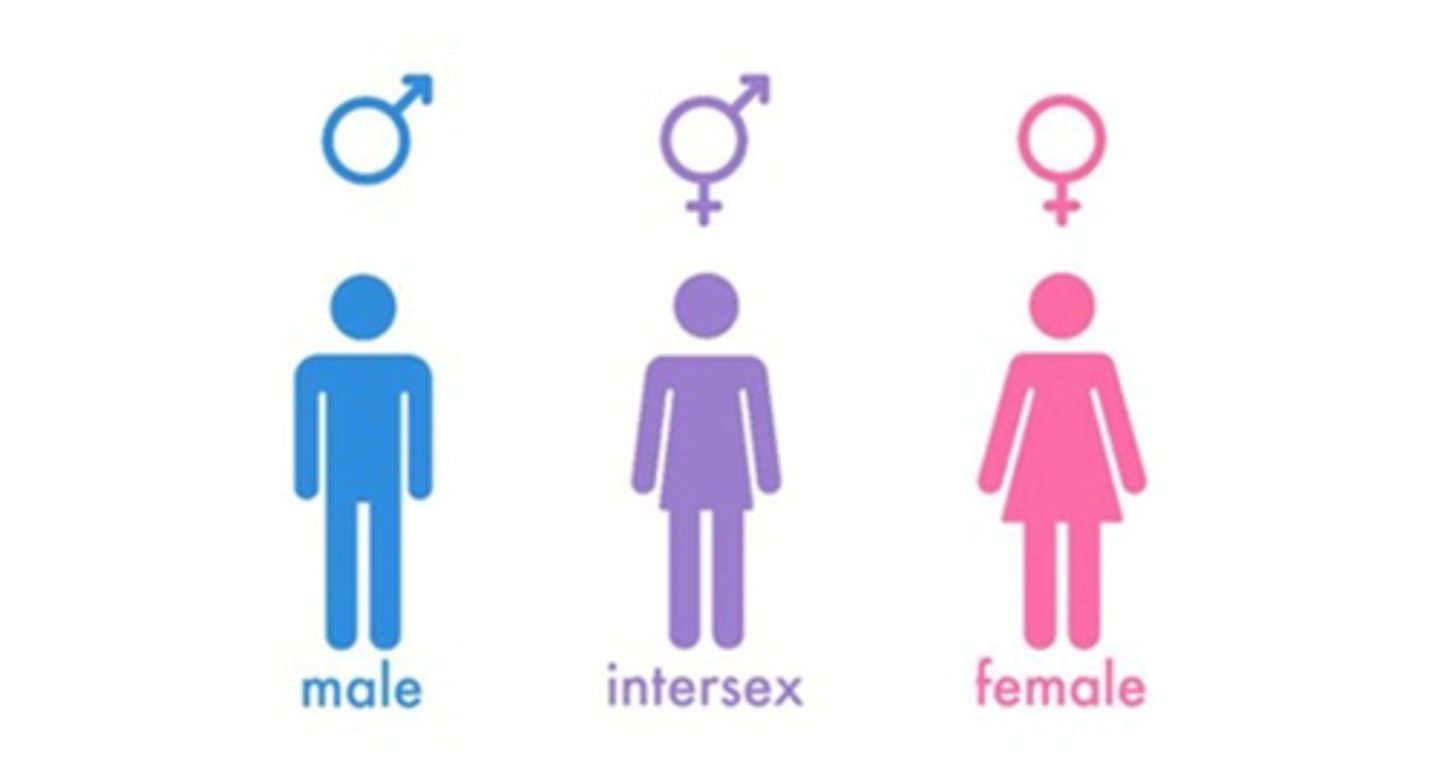
Biological Sex
physical characteristics that define male and female such as X and Y chromosomes and primary and secondary sex characteristics.

Sexual Orientation
an enduring sexual attraction toward members of either one's own sex (homosexual orientation) the other sex (heterosexual orientation), both (bisexual orientation), or neither (asexual orientation)

Gender Expression
the way in which a person expresses their gender identity, typically through their appearance, dress, and behavior. Described as being masculine, feminine or androgynous.

Transgender
an umbrella term describing people whose gender identity or expression differs from that associated with their birth sex

Intersex
a condition present at birth due to unusual combinations of male and female chromosomes, hormones, and anatomy; possessing biological sexual characteristics of both sexes