Basal ganglia and motor systems
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What are the primary functions of the basal ganglia?
Voluntary motor control
Procedural and habit learning
Eye movements
Cognition and emotion
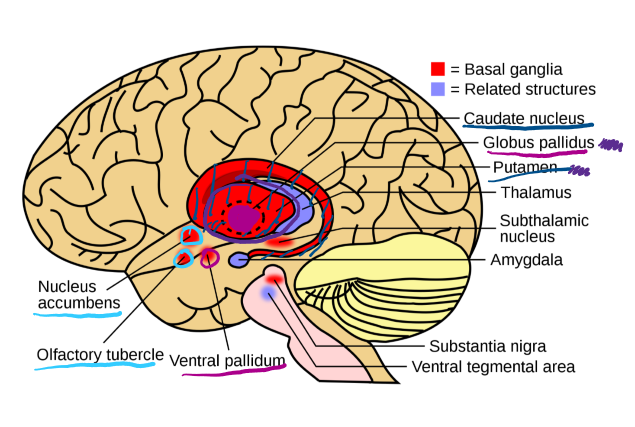
What structures make up the corpus striatum?
Ventral striatum: Nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle
Dorsal striatum: Caudate nucleus and putamen
What structures make up the pallidum
• Globus pallidus (external and internal)
Ventral pallidum
What 2 structures make up the lentiform nucleus
Putamen
Globus pallidus
What are the roles of the 2 structures of the ventral striatum
Nucleus accumbens (preoptic area of hypothalamus): cognitive processing of motivation, aversion, reward
Olfactory tubercle (area of olfactory cortex): locomotor and attentional behaviors, multisensory integration of olfactory information
What are the roles of the 2 structures of the dorsal striatum
• Caudate nucleus: motor processes procedural learning, associative learning and inhibitory control of action
• Putamen: regulates movements at various stages (e.g. preparation and execution) and influence various types of learning
Cell death of the striatum is associated with? and what are the symptoms
Huntington’s disease.
Symptoms: jerky, random, and uncontrollable movements (chorea)
What are the roles of the 2 pallidum structures?
• Globus pallidus: regulation of voluntary movement, primarily inhibitory action that balances the excitatory action of the cerebellum
• Ventral pallidum: regulation of motivational salience, behavior, and emotions.
What is the function of the subthalamic nucleus and substantia nigra?
Subthalamic nucleus: Movement regulation
Substantia nigra: Eye movement, motor planning, reward, learning
What disease is associated with substantia nigra cell death? and symptoms
Parkinson’s disease — characterized by tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and gait difficulties.
Ventral tegmental area and amygdala function
Ventral tegmental area: reward system (mesocorticolimbic circuit), motivation, cognition, and drug addiction
Amygdala: processing of memory, decision making, and emotional responses
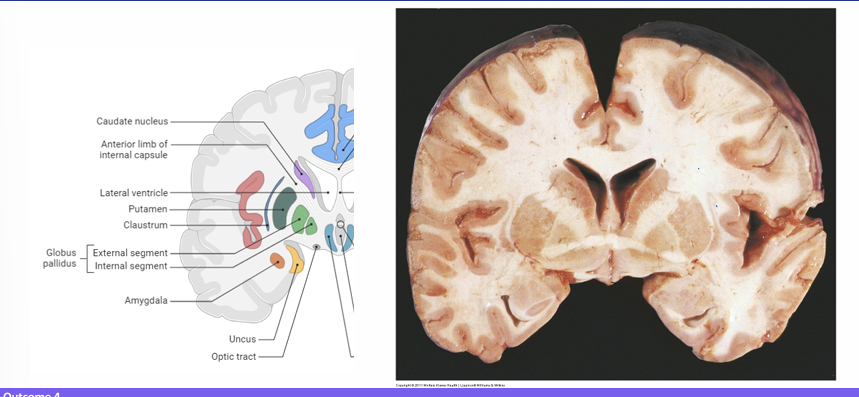
Identify the caudate, putamen, white matter tracts and amygdala
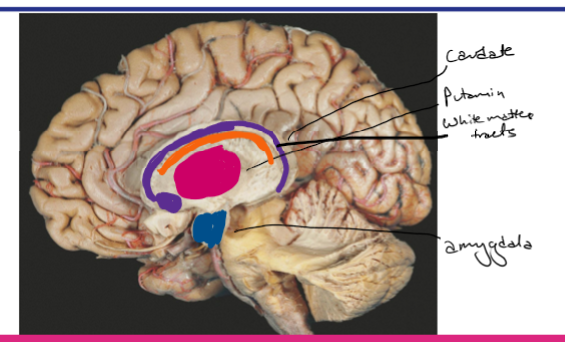

Identify the caudate, putamen, and amygdala
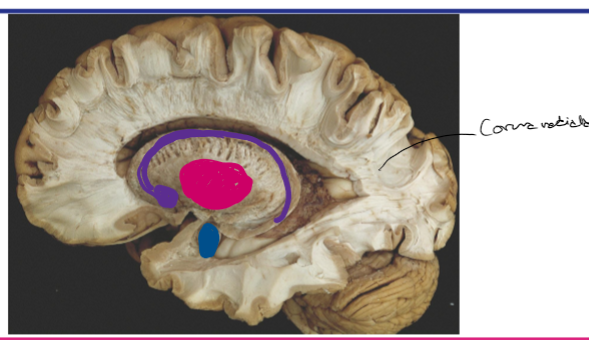
Identify the caudate, putamen and amygdala
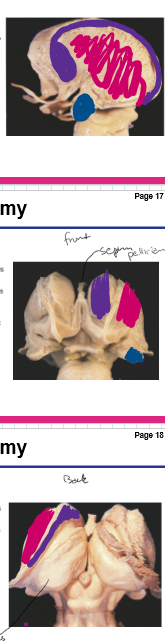
Identify these structures
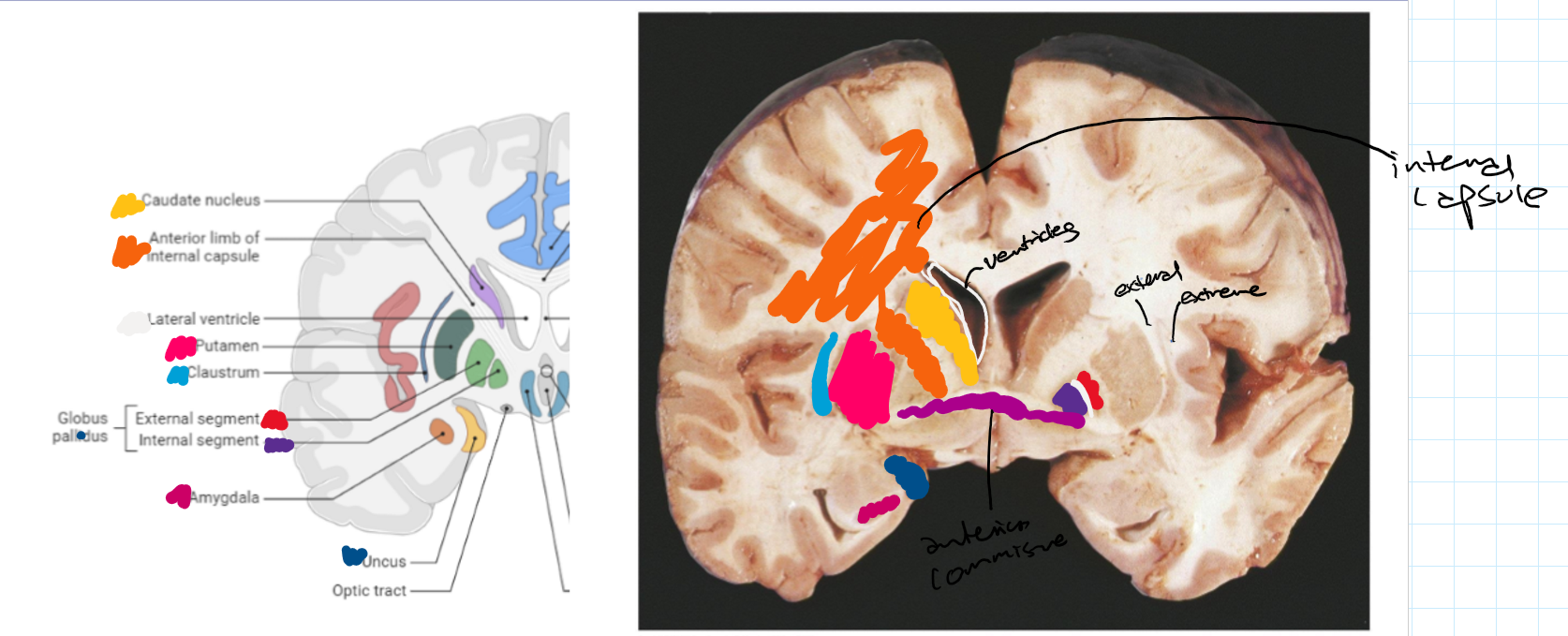
Identify these structures
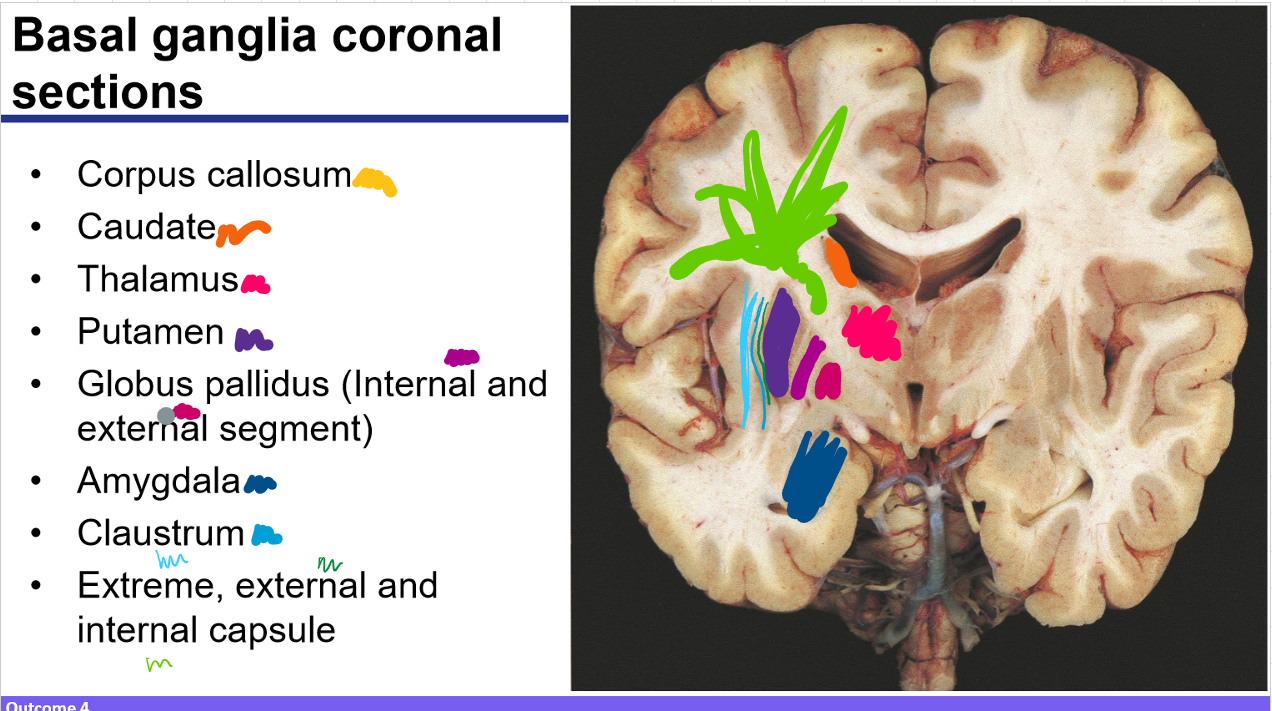
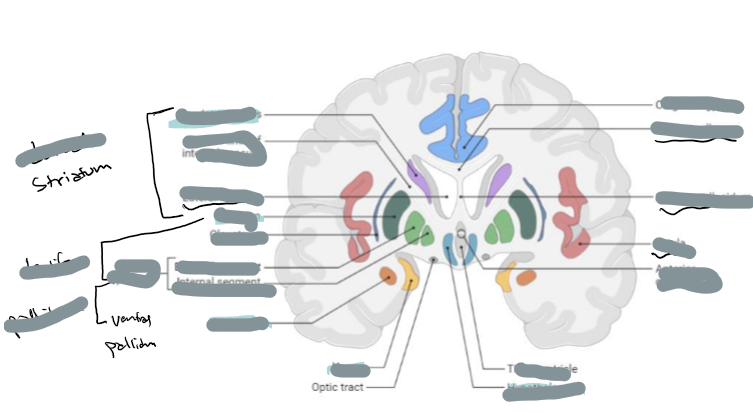
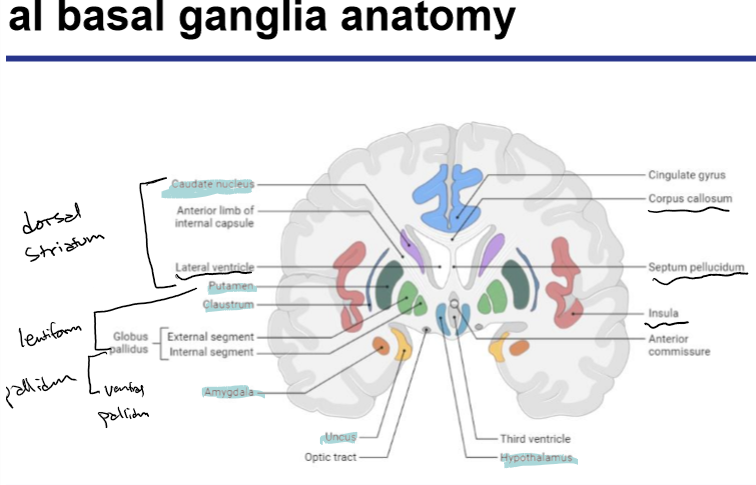
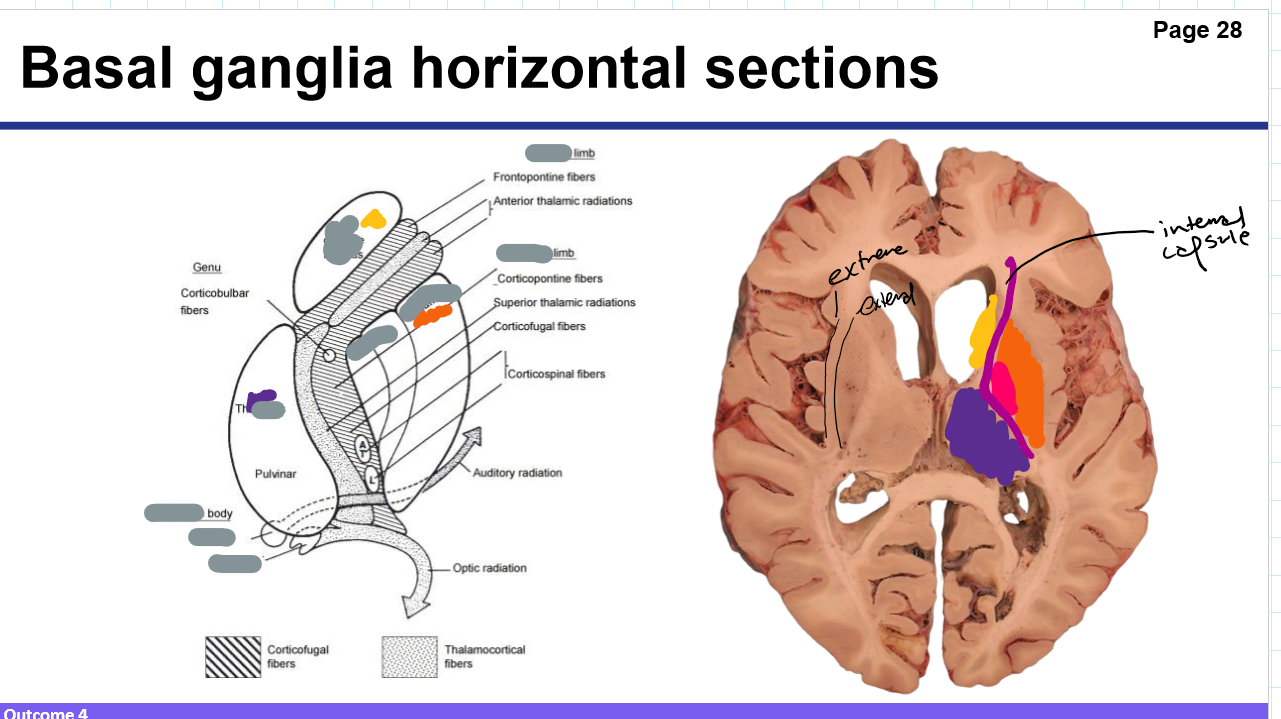
Identify these structures and what part of the basal ganglia it is
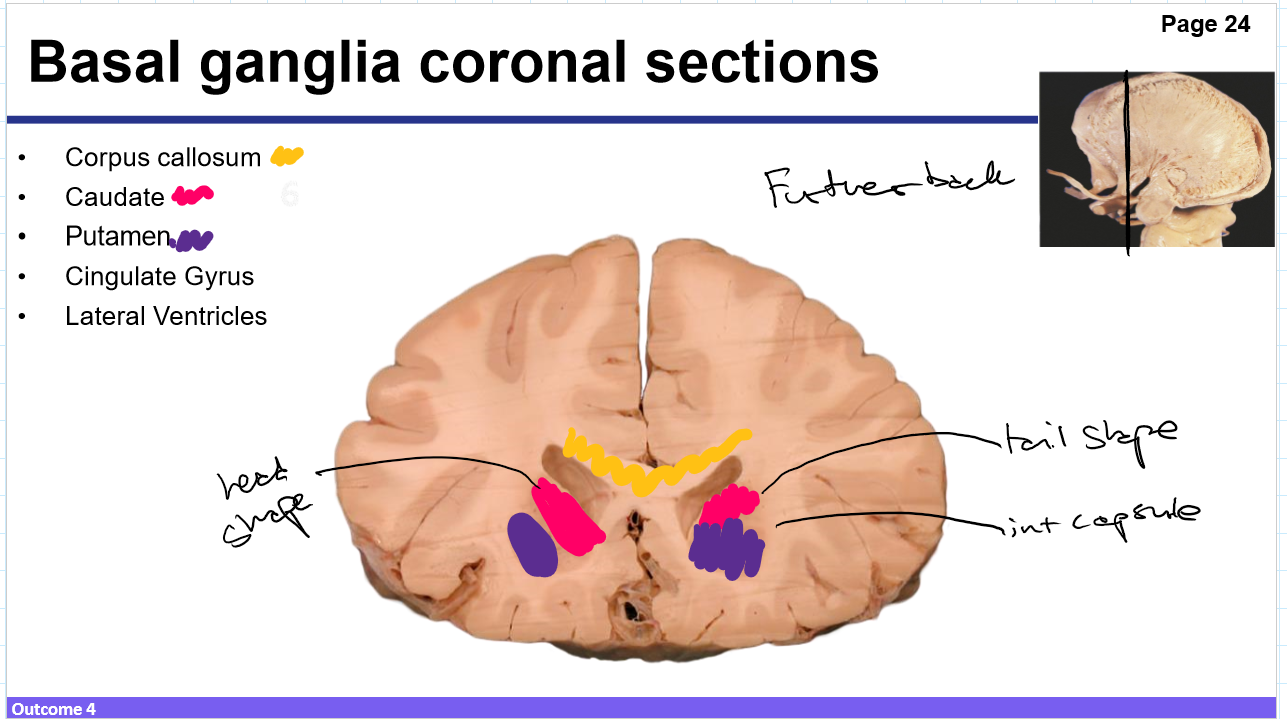
Identify these structures and what part of the basal ganglia it is
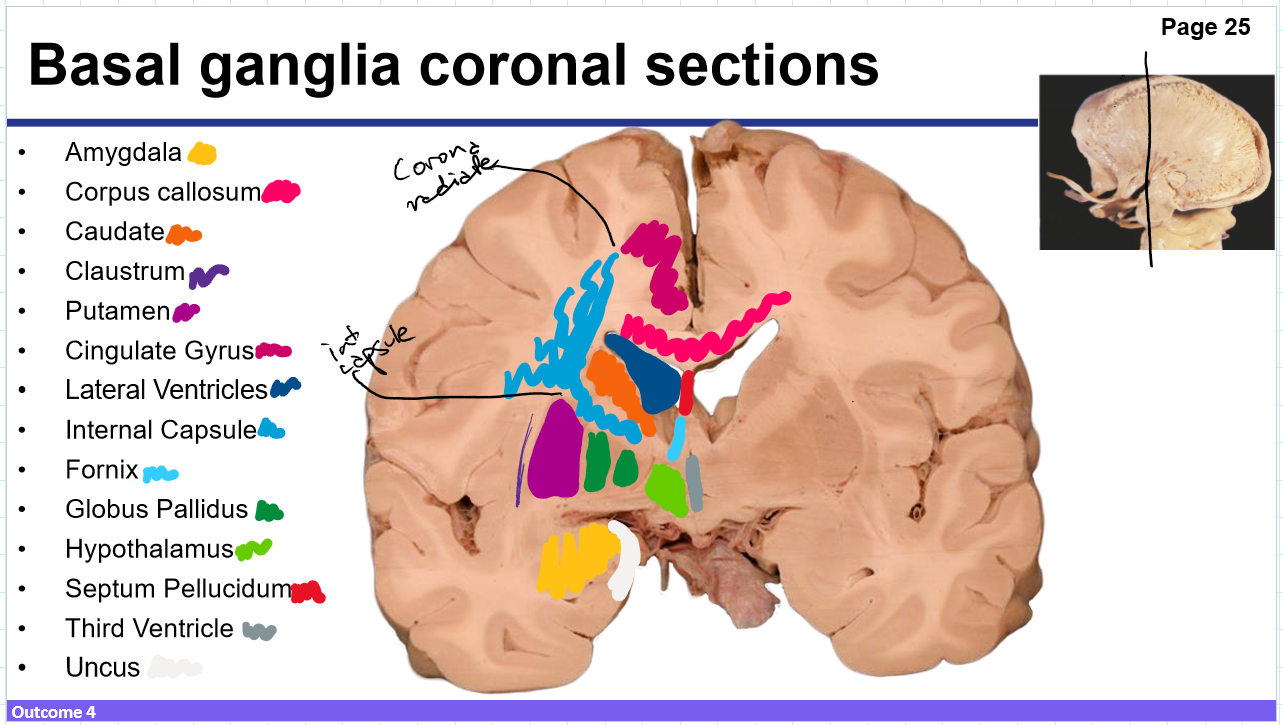
Identify these structures and what part of the basal ganglia it is
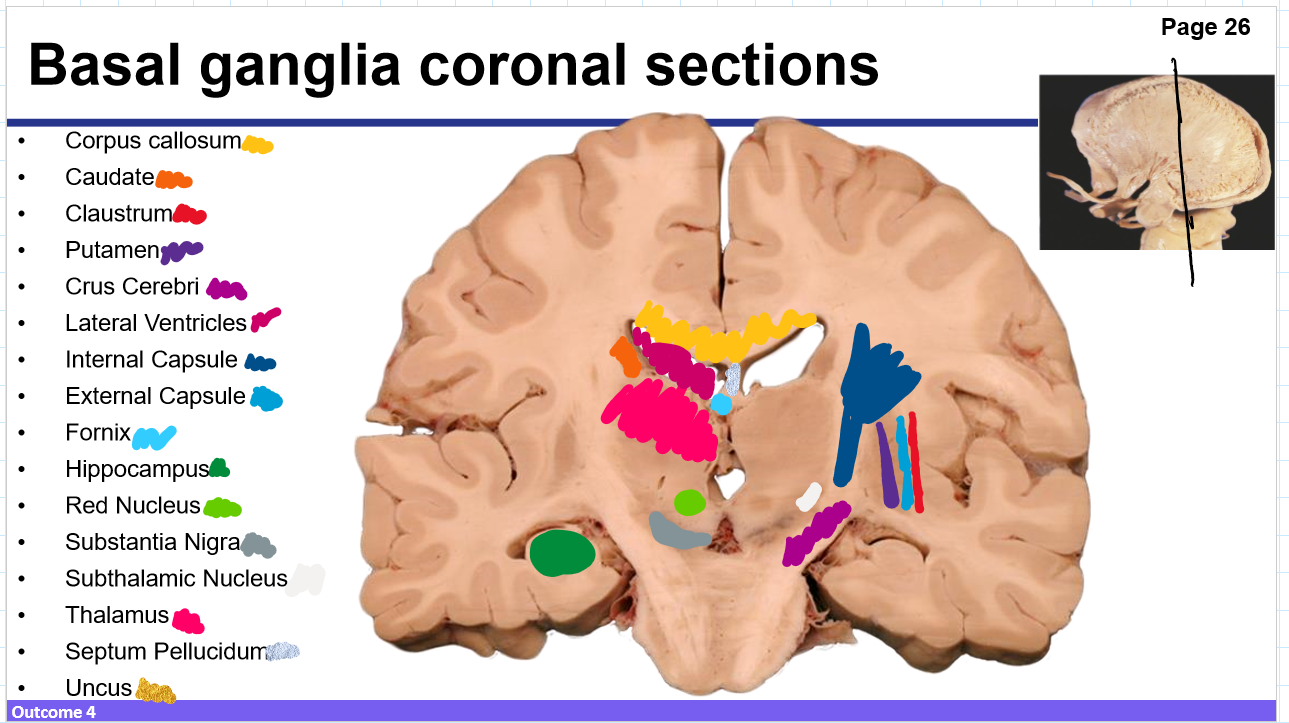
Identify these structures and what part of the basal ganglia it is
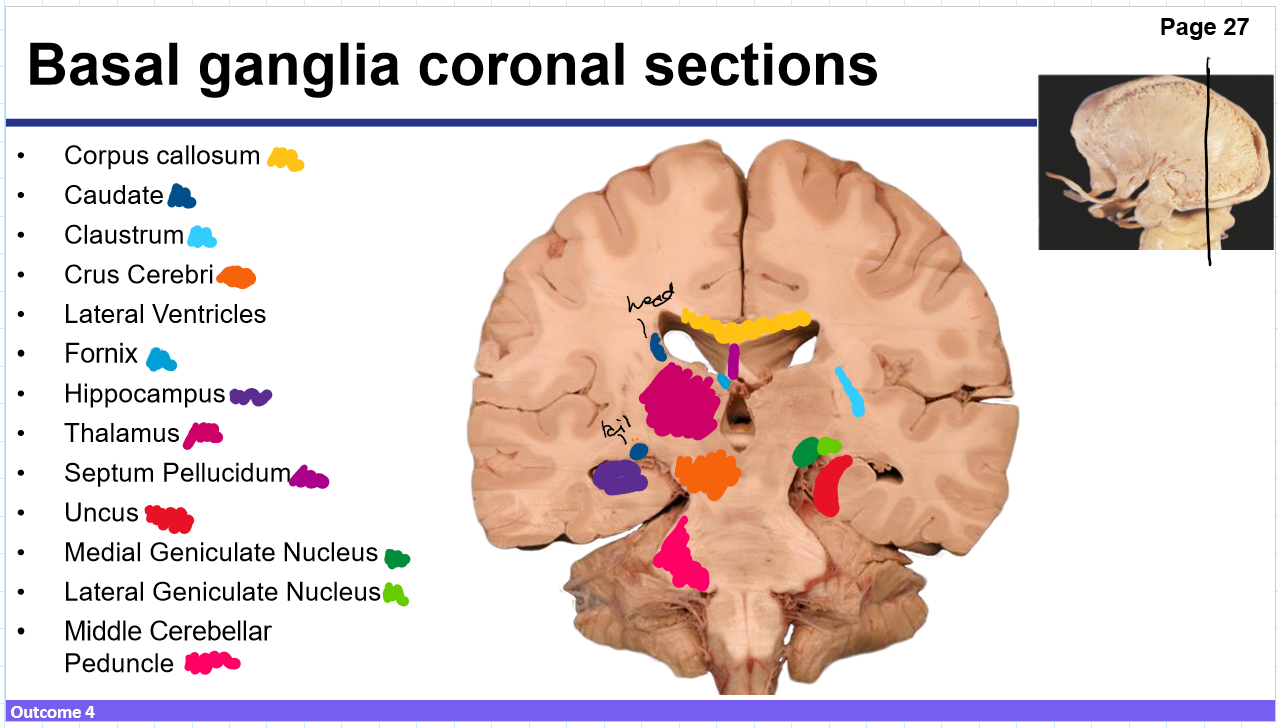
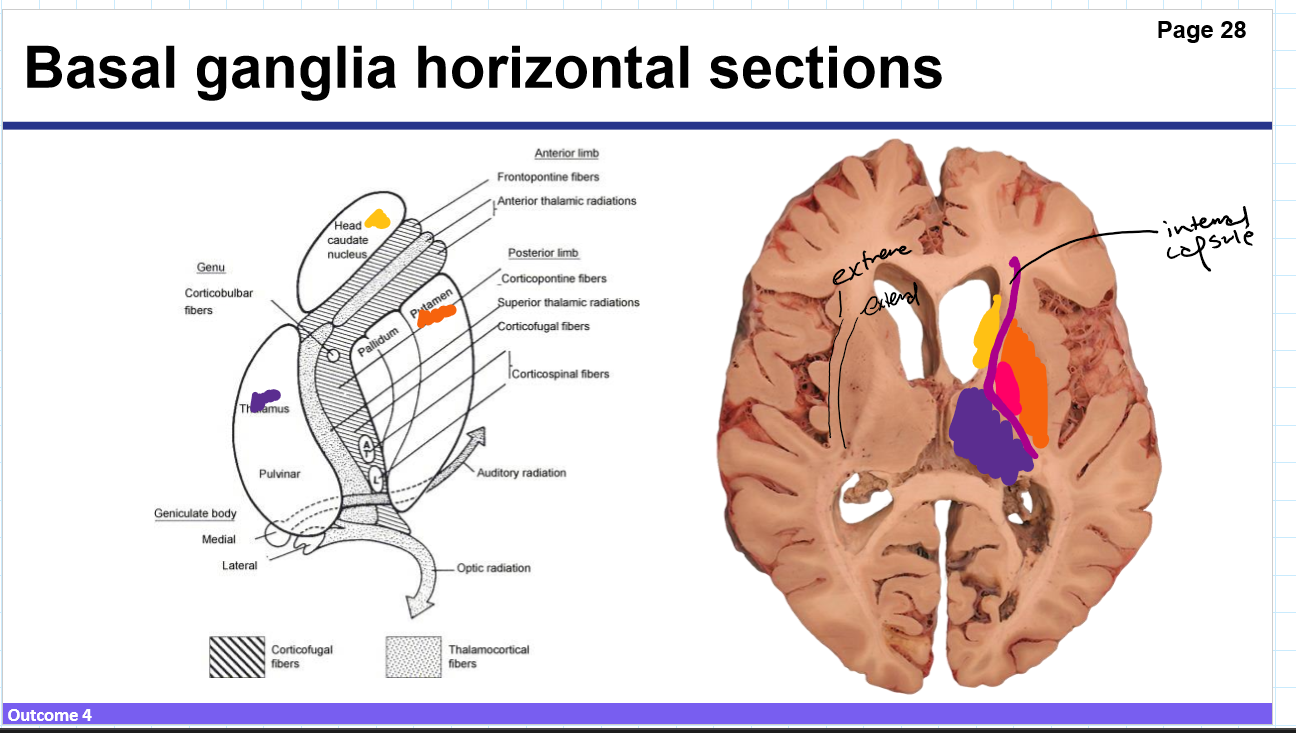
Identify these structures and what part of the basal ganglia it is
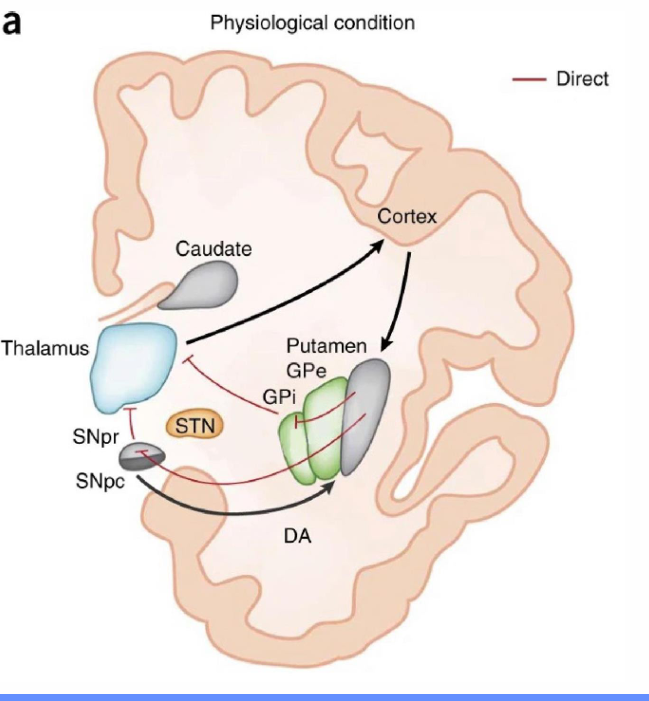
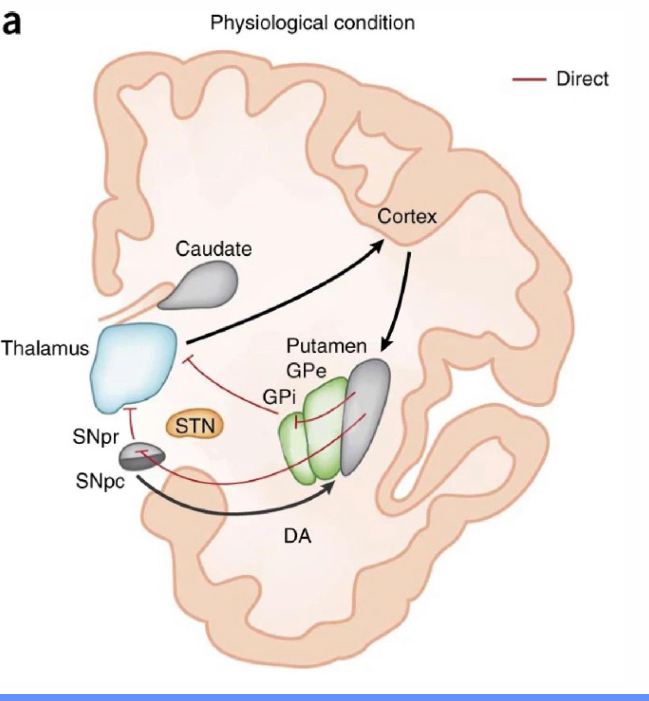
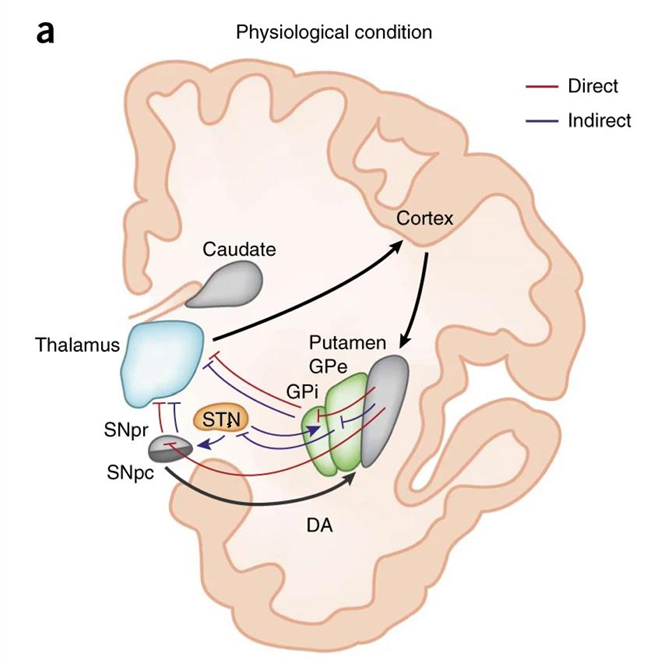
What is the direct pathway of the basal ganglia and its function?
• Cortical activation activates inhibitory projections to the substantia nigra SNpr and the internal globus pallidus (GPi)
• This inhibition of the SNpr and GPi leads to a disinhibition of the thalamic glutamatergic neurons.
Resulting in locomotor activation/movement.
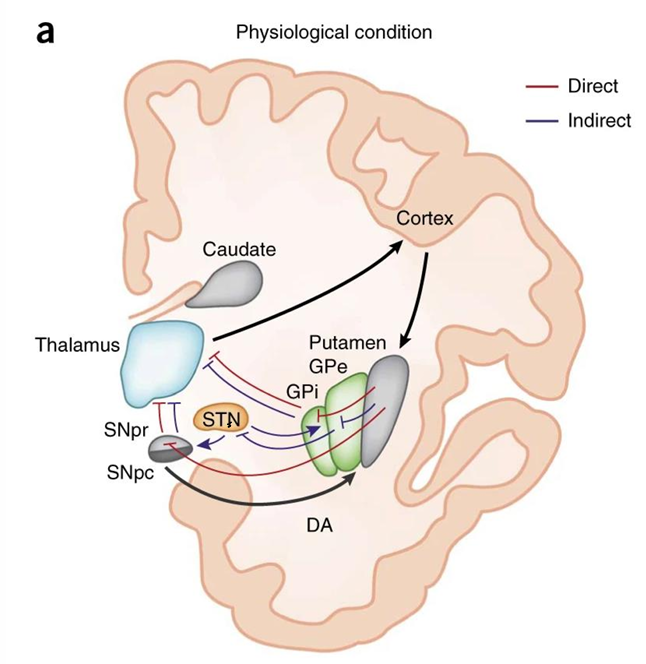
What is the indirect pathway of the basal ganglia and its function?
• Activation of the indirect pathway inhibits globus pallidus externa (GPe), leading to a disinhibition of the excitatory neurons of the subthalamic nucleus (STN)
• This inhibition of the GPe (by now active STN) increases discharge of excitatory STN neurons and in turn activates the SNpr inhibitory neurons projecting
• Resulting in the reduction of locomotor activity and movement
How does the corticospinal tract influence reflexes?
It adjusts reflex strength and spindle sensitivity via descending input.
What is the function of the lateral vs. ventral corticospinal tracts?
Lateral: Controls fine voluntary movements of limbs (contralateral)
Ventral: Controls trunk movements (bilateral)
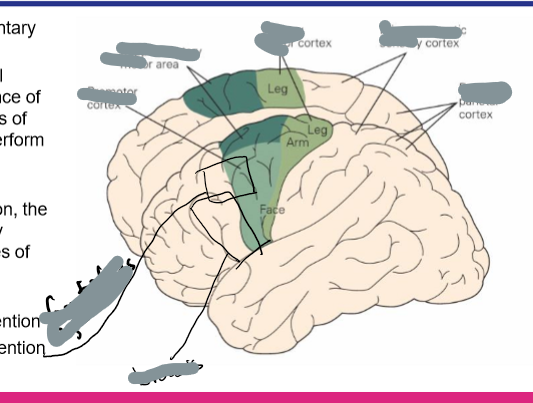
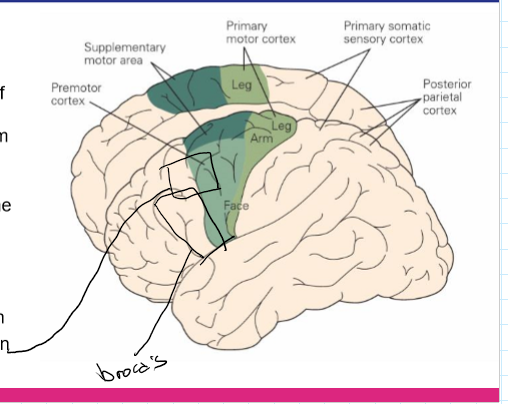
What are the functions of key motor cortical regions?
Primary motor cortex: Executes voluntary movement
Premotor cortex: Plans movement, uses sensory cues
Supplementary motor area: Internally generated movements, sequences
Posterior parietal cortex: Spatial planning, attention
Frontal eye fields: Visual attention and eye movements
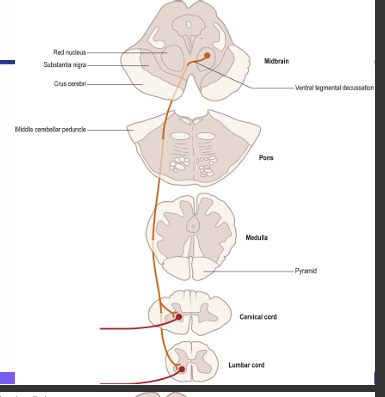
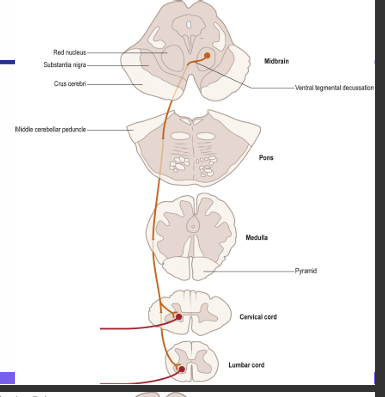
What is the rubrospinal tract pathway and its function?
Function: control over the tone of limb flexor muscles
• Receives input from motor cortex and cerebellum (non-pyramidal route) • Red nucleus • Cross in the ventral tegmental decussation • Descend the spinal cord ventrolateral and partly intermingled with with lateral corticospinal tract
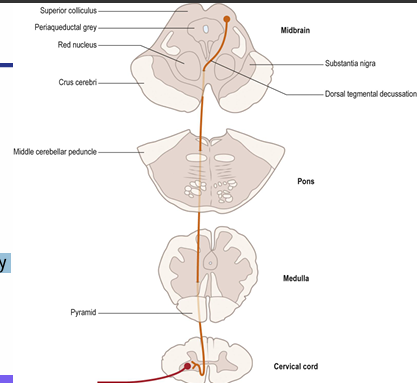
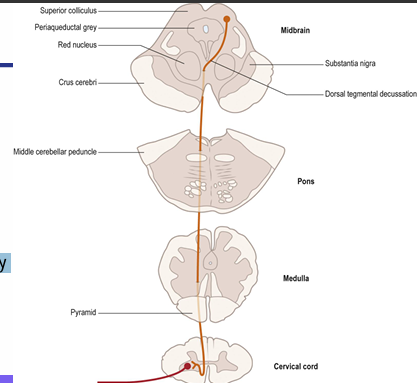
What is the tectospinal tract pathway and its function?
Function: mediate reflexive eye movements
\• Superior colliculus (non pyramidal route) • Cross in the dorsal tegmental decussation • Descend near the anterior median fissure terminate mostly in cervical segments
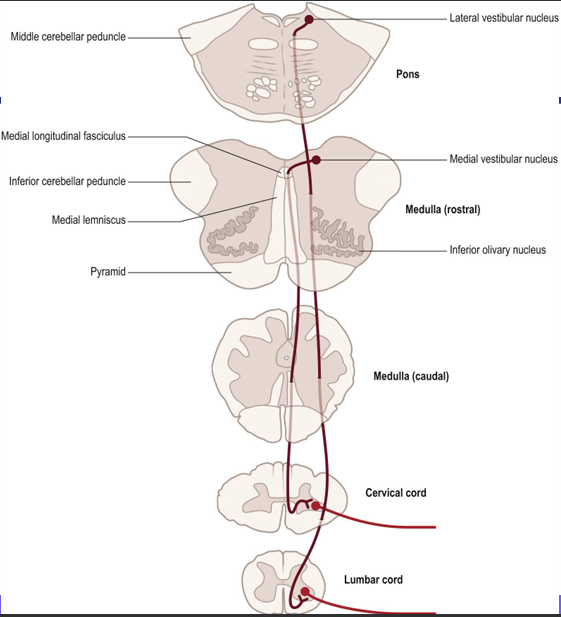
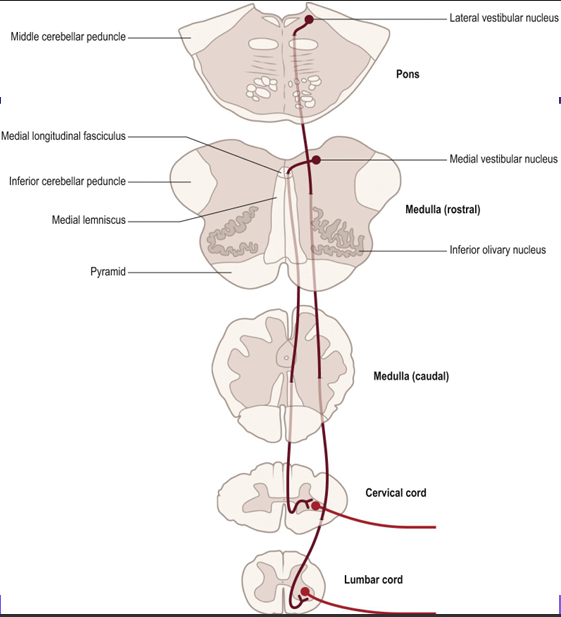
What is the vestibulospinal tract pathway and its function?
Function: maintenance of posture
• Vestibular nuclei receive input from vestibular apparatus (non pyramidal route) • Cells of the lateral vestibular nucleus descend ipsilaterally as the lateral vestibulospinal tract in the ventral funiculus
Define the following motor disorders:
Paralysis
Hypertonia
Ataxia
Chorea
• Paralysis: the loss of the ability to move
• Hypertonia: abnormally high level of muscle tone or tension.
• Ataxia: lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements
• Chorea: spasmodic involuntary movements of the limbs or facial muscles.
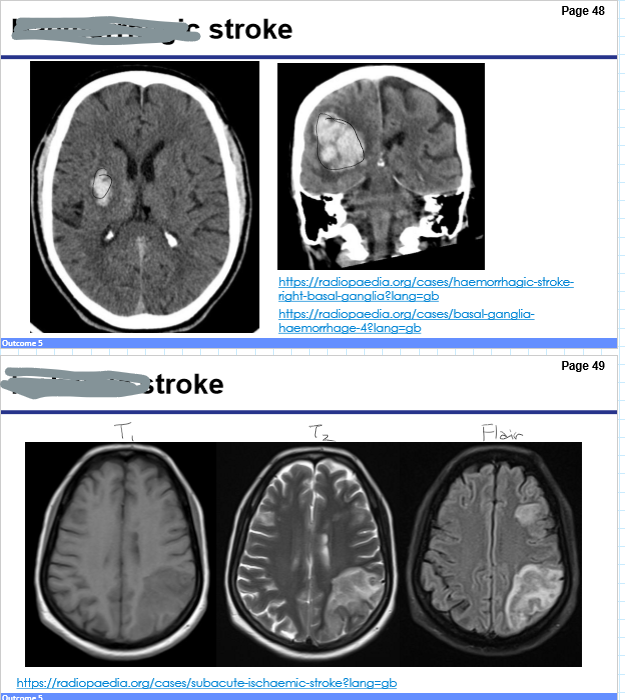
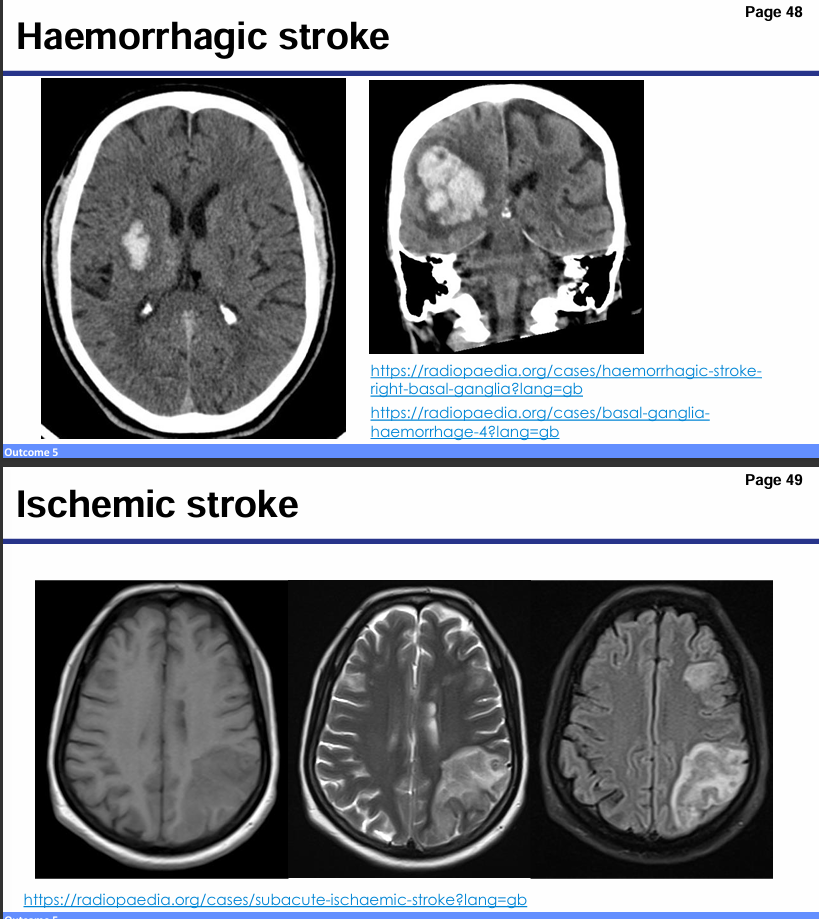
Differentiate between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.
Ischemic stroke: Due to blocked blood flow (e.g., clot or embolism)
Hemorrhagic stroke: Due to bleeding in the brain (e.g., burst aneurysm)