cob 487 exam 1 rutherford
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
what is strategy
why is a company doing so well
time horizon
how much time you want to put into your goal
ex. 1 yr vs 100 yr perspecitive like patagonia
strategy is like a what?
jigsaw puzzle
strategy is an _____ process
integrated
ex. you can't be really good at one thing and terrible at the other
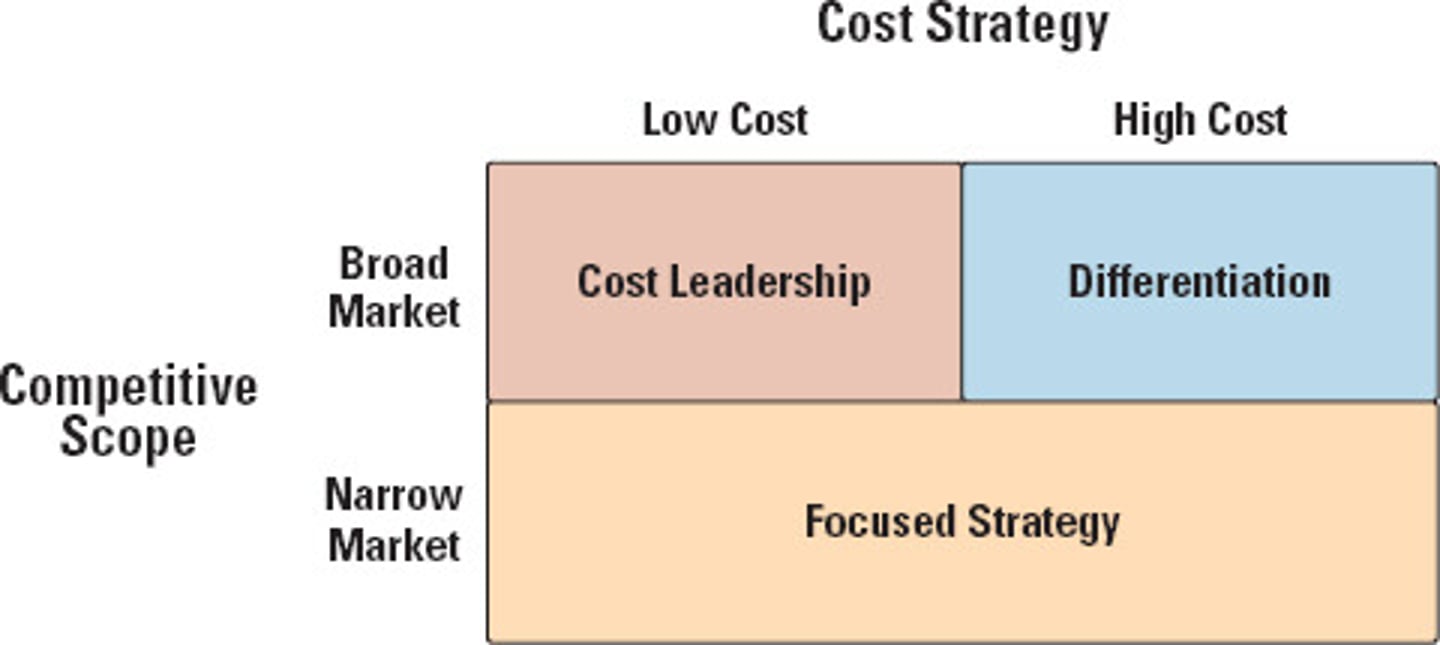
different ways to compete
differentiation, low cost leadership, dual competitive advantage
examples of competiting by differentiation
Apple, Grey Goose, luxury brands
examples of competing by low cost leadership
Dunkin vs Starbucks, Walmart, Aldi, Southwest
the golden circle
why, how, what
start with the why and then the how then the what
they dont buy bc of what the company does, they buy bc of the why they do it
example of competiting by dual competitive advantage
costco
strategy process model
mission vision values --> goals & objectives --> internal & external environment --> corporate strategy --> business strategy --> functional level strategy --> strategy implementation --> results
swot analysis is similar to what levels on the strategy process model
SWOT analysis
corporate level strategy
big huge change on a major business level ; mergers and acquisitions take place on this level
ex. Amazon changing their strategy from selling books to now prime and all items
business level strategy
how will we compete - differentiation, dual comp adv, low cost leadership
the model with the cost, value, consumer surplus
functional level strategy
department level; so like the strategy for hr, marketing, financial, etc. more specialized strategy
strategy implementation
how it is put to action in structures, culture, leadership, etc.
a company's mission
why we exist
a company's vision
where we are going
a company's values
what behaviors are rewarded/reflects the culture of the company
mission statements
short, simple, memorable
serves as a guide to employee actions
strategic mission statements
focuses on what they do
ex. Google
motivational mission statement
focuses on why it matters
ex. JMU
motivational and strategic mission statement
focuses on what they do and why it matters
ex. Patagonia
vision statement
forward looking, goal oriented, inspirational
ex. JFK's vision statement on space exploration
value statement
entraps the culture; can be very impactful if done well
mizberg's emergent strategy model
intended strategies don't always lead to the realized strategy things can emerge and change along the way; it is very hard to predict the future
intended strategy
what the plan is going in, what you intend to do in the upcoming situation
unrealized strategy
An intended strategy a firm does not actually implement
deliberate strategy
a plan of action that an organization chooses and implements to support specific goals
emergent strategy
consists of reactive strategy elements that emerge as changing conditions warrant
realized strategy
combination of intended and emergent strategy; what actually ends up happening
5 p's of strategy
Plan, Ploy, Pattern, Position, Perspective
5 p's of strategy - plan
90% of the time, used to figure out steps, you need to be able to adapt
ex. D-day planning vs what actually happened
5 p's of strategy - ploy
sometimes the strategy is to mislead a competitor; be secretive
ex. Apple developing the iphone without people knowing
5 p's of strategy - position
a firm's place in the industry relative to its competitors
ex. Marriott's Courtyard vs JW - they are all the mariott brand but different levels based on location and customer base
5 p's of strategy - pattern
their strategy over time; like how the company is consistent in what they do
5 p's of strategy - perspective
the want for people to buy into the reasoning; the "why" behind things
blue ocean strategy
when no one else is doing it so you do it and get the competitive advantage over others
only one out there, innovative, mostly made by companies that already exist
examples of blue ocean strategy
nuuly, cirque de soieli, uber
red oceans
where there is lots of competition in the market, reduced brand loyalty just going for whatever is cheapest, threat of new entry
this is where most companies are at
earnings equation
earnings = profits = net income
what does firm performance mean
financials, employee satisfaction, environment footprint
measures of financial performance that are good to use
stock price, accounting measures, return on sales
problems with net income as a measure of performance
doesn't take into account liquidity, # of stores, size of the company in relation to profit, and there are a lot of things included in net income that make it complicated
2 approaches to firm performance
shareholder approach & stakeholder approach
shareholder approach
goal is to maximize owner's profit & is very owner focused
stakeholder approach
prioritize everyone equally (owners, employees, customer, enviornment, etc.)
this is now the standard but it was shifted recently
3 environments that impact firm performance
macro environment, industry environment, the firm
PESTEL analysis
Political
Economic
Socio-cultural
Technological
Environmental
Legal
PESTEL analysis - political
when politics can impact businesses;
Brexit, board of supervisor decisions
PESTEL analysis - economic
federal reserve lowering interest rates, exchange rates, unemployment
PESTEL analysis - social
demographics, birth rates decline, tastes of the consumers
PESTEL analysis - technology
how its everchanging, chat gpt and AI and the impact that it has, new drugs)
PESTEL analysis - environment
natural disasters, temperature rising
PESTEL analysis - legal
laws passed, court cases and their impacts
porters 5 forces
*Rivalry among competitors;
*Threat of new entrants;
*Threat of substitute products;
*Bargaining power of buyers;
*Bargaining power of suppliers;
traditional view of strategic fit
when performance is determined by the degree of fit in the market
companies need to be able to adapt and change with the market or else they won't fit in the market for a while and will die out
paradox of fitness
being fit to the environment is partially true to sucess but has to deal w organizational inertia
how to overcome the paradox of fitness
firms should seek minimal... & need to be ambidextrous
- consistency
- consensus
- contentment
- affluence
- rationality
- faith
how else can firms lose competitive advantage
imitation (can someone make the exact thing)
substitution (product that meets the same demand - claritin, allegra & zyrtec)
hold up (buyer and supplier power - HP has to deal with suppliers taking forever and the sellers taking time to make sales)
too much slack (too many resources - hires that do nothing, M&As, too much marketing)
types of resources
financial, physical, human, and technological
VRIO analysis
Value, Rarity, Inimitability, Organization
need ALL 4 things to provide a compeitive advantage
sources of not being able to imitate
path dependence
social complexity
causal ambiguity
uniqueness
must be no substitutes
sources of not being able to imitate - path dependence
menaing that it was created in the past during some historical event
ex. Pfizer and the covid vaccines
sources of not being able to imitate - social complexity
the resource belongs to the company but is in control of others
ex. employee morale, brand loyalty
sources of not being able to imitate - causal ambiguity
uncertain how the resource was created
ex. JMU's culture - no one else can get it
sources of not being able to imitate - uniqueness
literally there is only one of them
ex. employees, Nick Saban, trademark, physical space
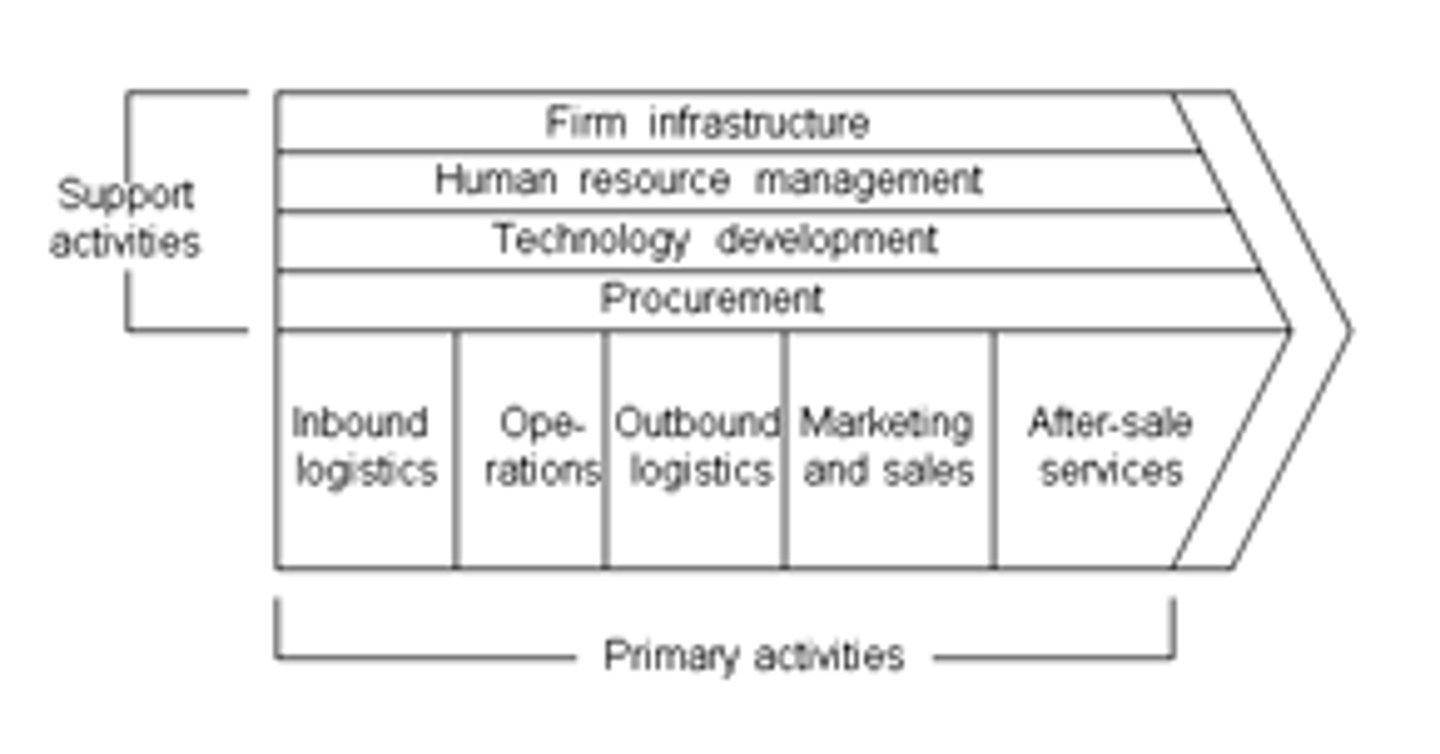
Traditional Value Chain
input --> process --> output
porter's value chain
need to know how the process differs between companies
porter's generic strategies
common sources of differentiation
the attributes of the product itself: Product features, timing of release, location, complexity
The relationship between the firm and customers: marketing, reputation, customization
Linkages within or between firms: Product mix, alliances between firms, service, distribution channels.
common drivers of low cost leadership
- Economies of Scale
- Economies of learning
- Input costs (location, differential access to inputs)
economies of scale
the more you make the cheaper the cost will be per unit & the more you buy the cheaper each unit will be
economies of learning
companies who have been around for a long time have figured out how to make things cheaper