Fuels and heats of reaction
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
- Intramolecular bonding =
bonding that occurs within a molecule.
- Intramolecular bonding 3 types:
1. Non-polar covalent bonding
2. Polar covalent bonding
3. Ionic bonding
Non-polar covalent =
The equal sharing of electrons in a bond.
Non-polar covalent = The equal sharing of electrons in a bond.
Because ?
electrons are constantly moving in bonds and they are being shared equally, this results in temporary dipoles being formed.
Polar covalent: = ?
The unequal sharing of electrons in a bond.
Polar covalent: = The unequal sharing of electrons in a bond.
i.e. ?
The pair of electrons is closer to one atom in a bond at any one time. This results in the formation of permanent dipoles.
Dipole =
a partial charge
Ionic bonding =
The force of attraction between two oppositely charged ions.
To determine if a molecule is one of the three
(1. Non-polar covalent bonding
2. Polar covalent bonding
3. Ionic bonding),
we use the ?
electronegativity values.
non polar covalent electronegativity values
<0.4
Polar covalent electronegativity values
0.4 - 1.7
Ionic electronegativity values
>1.7
using electronegativity values
- This has a ?
big affect on solubility.
using electronegativity values
- Water is ? so only ? can ? in it.
polar
polar substances
dissolve
using electronegativity values
- Like substances can only dissolve in
like substances.
- Intermolecular bonding =
bonding that occurs between molecules.
3 types of intermolecular forces
1. Van Der Waals forces (weakest)
2. Dipole - dipole bonding
3. Hydrogen bonding (strongest)
What is the weakest intermolecular force?
Van der Waals
What is the strongest intermolecular force?
hydrogen bonding
Intermolecular forces between molecules are determined by ?
the intramolecular bonding.
- Van Der Waals: forces can only occur ?.
between temporary dipoles
- Dipole-dipole: bonding requires ?
permanent dipoles to form.
- Hydrogen bonding: requires
hydrogen to bond to one of the three (N, O, F)
It can only ever be intermolecular bonding between ?,
positive and negative dipoles
Opposite charges attract
like charges repel
- Intermolecular bonding determines
how strong particular organic molecules are.
- Strength is determined by the ?
boiling point.
- oxidation and reduction agents these ? agents are capable of ?
redox
converting more organic molecule to another.
- The best reduction agent is ?
H2 with a nickel catalyst.
- The best oxidation agent is either ? or ?
acidified potassium permanganate (MnO₄-/H+)
sodium dichromate (Cr₂O₇-).
Organic chemistry=
the study of compounds of carbon
Hydrocarbon=
a compound that contains only carbon hydrogen
Three classes of hydrocarbons=
alkanes alkenes alkynes
the three classes differ because of the presence of
single double or triple bonds
The alkanes:
? compounds due to them only containing ?
saturated
carbon-carbon single bonds
The alkanes:
endings all contain ?
ane
The alkanes:
the first ten alkanes each differ by
one CH₂
Methane
CH₄
ethane
C₂H₆
propane
C₃H₈
Butane
C₄H₁₀
pentane
C₅H₁₂
hexane
C₆H₁₄
Heptane
C₇H₁₆
Octane
C₈H₁₈
Nonane
C₉H₂₀
Decane
C₁₀H₂₂
Alkanes all have ? but there is a ? for every additional ?
similar properties
slight change
CH₂ unit
alkanes feature ? forces
vander waals
ALKANES:
the larger the molecule ?
the greater the strength
ALKANES:
the larger the molecule the greater the strength
this increasing strength between bonds is why alkanes go from ? to ? with ?
gases
liquids
increasing molecule size
Homologous series -
A series of compounds of similar chemical properties that show gradations in physical properties and have a general formula for its members with each member differing from the previous member by a CH₂ unit
IUPAC
International Union of pure and applied chemistry
IUPAC provide the rules for
the naming of organic compounds
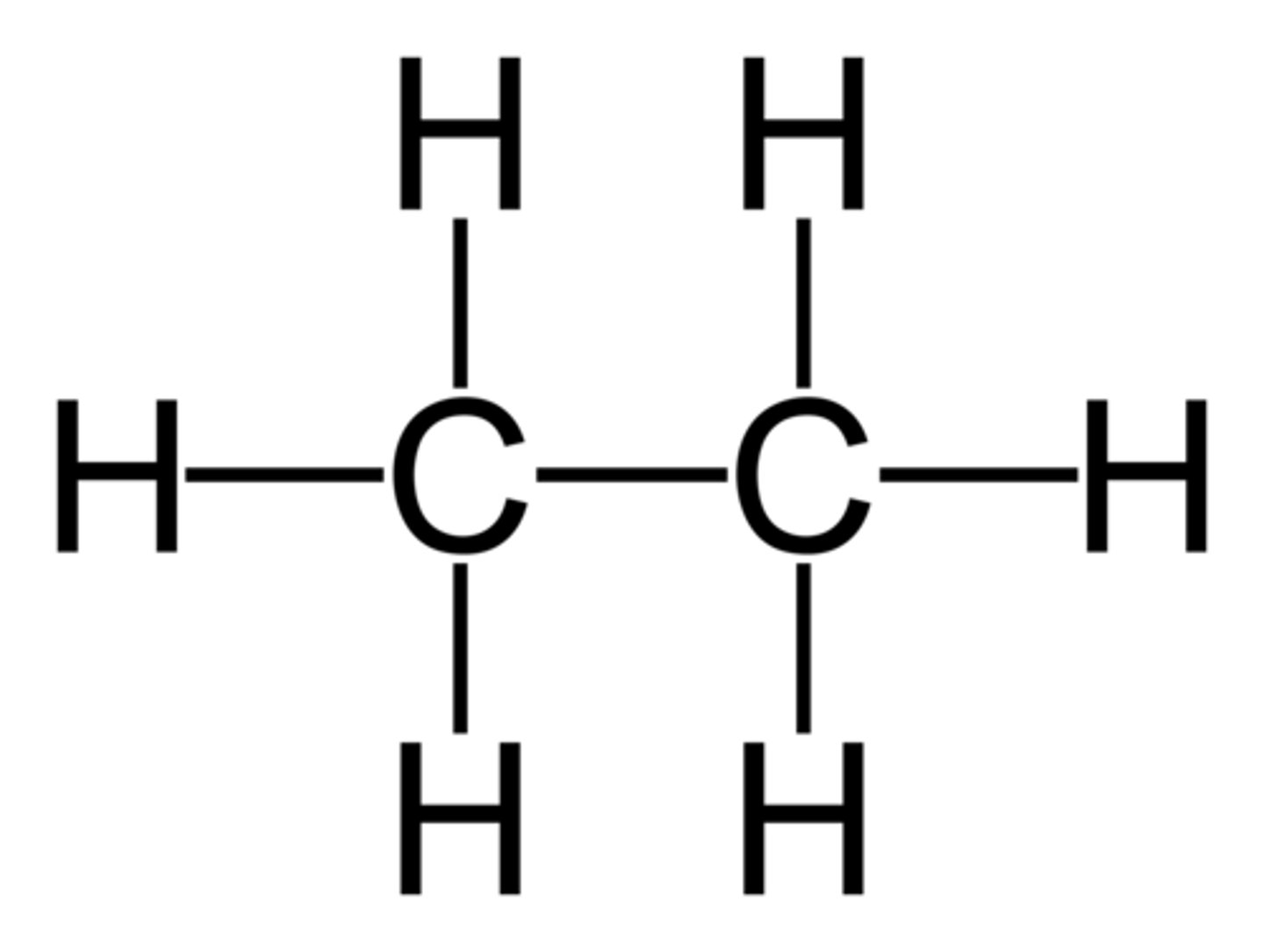
ethane C2H6 equals
C-C
and
6 H's
Alkyl groups 3 types
methyl - CH₃
Ethyl - C₂H₅
Propyl - C₃H₂
Alkyl groups are
side chains "substituents"
Nomenclature rules 1.
number the longest continuous chain of carbons
ensure that the alkyl groups have the lowest number possible
Nomenclature rules 2.
write down the name of the chain
Nomenclature rules 3.
now include the positions and names of the alkyl groups
di
2 alkyl groups
cyclohexane shape
diamond
Structural isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas
isomers
the molecular formulas are the same but their structured formulas are different
isomer of C4H10
butane and 2-methylpropane
carbon always has
four bonds
hydrogen always has
one bond
The alkenes:
? compound due to containing ?
Unsaturated
at least one double bond
The alkenes:
Ending –
ene
The alkenes:
because there is a ? bond between ? there is no such thing as a ? for example ? cannot exist
double
carbon atoms
single carbon alkene molecule
methene
The alkenes:
have a ? bond
double
The alkenes:
each carbon atom still has ?
4 bonds
The alkenes:
ethene C2H4 used as ?
solvents,ripens fruits, plant growth regulator
The alkenes:
there only has to be ? present for it to be classed as an alkene
one carbon - carbon double bond
The alkenes:
banana bags have tiny holes to allow ?
ethene gas in and out
The alkenes:
more ? than alkanes due to ?
reactive
high electron density among double bonds
The alkenes:
boiling points increase with size due to ?
follow a similar trend for boiling points as ?
vander waals forces
alkanes
Naming of Alkenes
Same procedure as naming alkanes
But you have to include the ?
double bond
Naming of Alkenes
1.?
Double bond = ?
no. carbon atoms
lowest no.