BIO 189- Chapter6: Glycolysis, Aerobic Respiration and Fermentation
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What does Cellular Respiration do?
CATABOLIZE AND OXIDIZE macromolecules to make ATP
What does Aerobic Respiration use in order to convert food’s potential chemical energy into useable ATP
Oxygen; uses gas as FINAL ELECTRON ACCEPTOR for an electron transport chain
Where does most of the energy transformation during aerobic respiration occur?
In the mitochondria
What is the formula for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + O2 ——> CO2 + H2O + ATP
What are the two processes of photosynthesis that are complementary of glycolysis and respiration?
Anabolic (BUILDS) and endergonic (REQUIRES)
What are the two processes of glycolysis and respiration that are complementary of photosynthesis?
Catabolic (BREAKS) and Exergonic (RELEASES ENERGY)
What do the processes anabolic and endergonic do?
Build LARGER, HIGH-ENERGY molecules from SMALL, LOW ENERGY molecules requires energy input (SUN)
What do the processes catabolic and exergonic do?
Breaking down large molecules into smaller molecules into smaller molecules releases energy for cell to harvest (convert to chemical energy in ATP
When oxidation in cellular respiration occurs uncontrolled and rapidly it causes what?
An explosion
When oxidation in cellular respiration is controlled what occurs?
Mini explosions that can be used to create ATP
What do all eukaryotes have?
Nucleus and mitochondria
Where do Autotrophic aerobic eukaryotes make their sugar products from? What do they use it for?
Photosynthesis and to fuel their own mitochondria’s ATP production
Where does Glycolysis occur?
The Cytoplasm
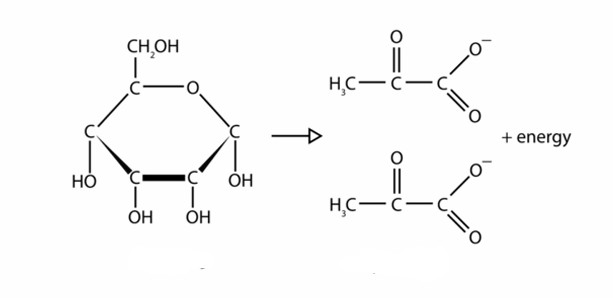
What are the names of the molecules in the image?
Glucose and Pyruvate
What is cytosol?
The fluid-filled interior of the cell (not inside any organelles)
What is the mitochondria?
Two cell membrane layers (result of endosymbiosis)
What are the four parts created by the mitochondria?
Outer membrane layer, inter-membrane space, inner membrane layer, and interior matrix
What are the features of the inner membrane?
Highly in-folded and cristae (finger like projections)
What two things are embedded in the inner membrane?
ETC proteins and ATP Synthase
Folded inner membrane increases _____ , maximizes _____ and ______ and ATP production capacity _____
surface area, ETC proteins and ATP synthase #, increases
What are the four stages of aerobic respiration?
glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, Krebs/citric acid cycle, and electron transport chain
Where does Glycolysis occur?
In the Cytosol
What happens during Glycolysis?
Glucose (6C) is OXIDIZED (split) and generates TWO 3c Pyruvate molecules
What does Glycolysis produce?
ATP and NADH
Where does pyruvate oxidation occur?
In the mitochondria
What happens during pyruvate oxidation?
Pyruvate oxidizes into 2C ACETYL CoA
What does pyruvate oxidation produce?
NADH and CO2 waste
Where does the Krebs/Cirtric Acid Cycle occur?
The mitochondria
What happens during the Krebs/Citric Acid Cycle?
Acetyl CoA is COMBINED with a 4c substrate then oxidized MULTIPLE times
What does the Krebs/Citric Acid cycle produce?
ATP, NADH, FADH2 and CO2
Where does the Electron Transport Chain (ETC) occur?
In the mitochondria
What happens during the Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
NAH and FADH2 DONATE high energy electron into ETC
What does Electron Transport Chain (ETC) produce?
O2 is the FINAL electron acceptor and results in H2O and the MOST ATP produced in process
What stage of cellular respiration is the least efficient at harvesting energy?
Glycolysis
Does glycolysis require oxygen?
No, it will occur with or without oxygen
What are the two phases of Glycolysis?
Energy Investment and Harvest
What occurs during the energy investment phase of glycolysis?
2 ATP spent/hydrolyzed to prime glucose with 2 phosphates (glucose is more active) and 6 carbon glucose split into two identical 3 carbon molecules
What occurs during the energy harvest phase of glycolysis?
3C is oxidized, NAD+ is reduced to NADH, another enzyme adds another phosphate, phosphate transferred to ADP making ATP
What are the major inputs of Glycolysis?
1 6C, 2 ATP, 2 NAD+, 4 ADP
What are the major outputs of Glycolysis?
4 ATP (2 ATP), 2 NADH, 2 pyruvates
What are the major inputs of Pyruvate oxidation?
2 pyruvate, 2 NAD+, 2 Coenzyme A
What are the major outputs of Pyruvate oxidation?
2 NADH, 2 CO2, 2 Acetyl CoA
The cycle allows Kreb’s to continue for?
Indefinitely as long as acetyl-CoA and oxidized NAD+ and FAD are available in mitochondria
What are the major inputs of the Krebs/Citric Acid Cycle?
2 CoA, 2 ADP + P, 6 NAD+, 2 FAD
What are the major outputs of the Krebs/Citric Acid Cycle?
4 CO2, 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2
What happens during a redox reaction in the ETC
Electrons get passed from protein complex to complex
Some ETC complexed are?
active proton H+ pumps
When a ETC pump complex holds electrons, some energy is used to?
Move H+ from the matrix to the intermembrane space
ETC generates what levels of proton concentration gradient and where?
In the inter-membrane is high H+ and in the matrix low H+
What is ATP Synthase?
A membrane enzyme with “facilitated diffusion” has a transmembrane proton channel and a mechanical rotor?
What can H+ move through what and what does the movement cause?
Channel and it turns enzyme and provides kinetic energy
What is theoretical ATP yield?
1 molecule of glucose and ~36 molecules of ATP are produces
What is the actual ATP yield and why?
~30 ATP/Glucose and it’s due to the ATP that was spent to transport NADH, pyruvate and H+ ions leaking
Besides glucose what else can be used to fuel respiration?
Proteins and Lipids
What does fermentation respiration pathway allows?
Cells to dump electrons from NADH to regenerate NAD+ and allow glycolysis to continue
“Formula” for Fermentation?
Sugar + Yeast - Oxygen = Carbon Dioxide + Alcohol
What happens if there is no oxygen during cellular respiration?
ETC and previous steps get backed up because NAD+ stops getting regenerated
What is the energy efficiency of cellular respiration?
37%; the potential chemical energy store in the bonds of glucose makes it into chemical bonds of ATP
What is the energy efficiency of glycolysis?
2%
What is the rest of the energy efficiency go into?
Heat