l3 - Unipolar Disorders
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Emotion
complex reaction pattern used by an individual to deal with a personally significant matter
the type of emotion depends on the events specific sig
Difference between emotion and feelings
emotion involves feelings but differs from feelings in having an overt or implicit engagement with the word
Feelings are purely mental, whereas emotions are designed to engage with the world
Affect definitions
any experience of feeling or emotion, ranging from suffering to elation
Affect - can be split into
positive and negative affect
Feeling is a
self contained phenomenal experience: subjective, evaluative and independent of the sensations, thoughts or images evoking them, typically evaluated as pleasant or unpleasant
sex specific characteristics that have profound effects on the stress response
females have higher levels of cortisol
adrenal gland (produced cortisol) is larger in females
female increased response to fear and stress
Males secrete less cortisol in response to stress
gender specific characteristics that have profound effects on the stress response
societal gender roles often result in women facing more stressors than men
Men tend to reasons to more stressors involving achievement, whereas women find interpersonal conflict more stressful
Men are less likely to be aware of the impact of stress on their health and less likely to receive treatment
both mood and emotion are ….
affective states
mood definition
a dispostion to respond emotionally in a particular way that may last for hours, days or even weeks.
Moods differ from emotions in…..
lacking an object
What are mood disorders?
mental health conditions in which the principle feature is prolonged, intense and persuasive affective disturbance
two main types of mood disorder in DSM5
unipolar - includes only depressive episodes
Bipolar - includes both manic or hypomanic, & depressive episodes
hypo
‘low ‘
criteria for major depressive disorder and related conditions
A: in a 2 week period, 5 or more symptoms present almost every day for most of the day (must include symptoms 1 +2)
depressed mood
diminished interest
weight loss/ gain
insomnia/hypersommnia
psychomotor agitation/retardation
Fatigue
Worthlessness/ excessive guilt
Concentration/ indecisiveness
Recurrent thoughts of death
B: symptoms cause clinically significant distress/major functional impairment
C: episode not caused by physiological effects of substance or medical condition
D : disturbance not better explained by schizophrenia
E complete absence of manic/hypomanic/ cyclothymic disorder
MDD diagnostic specifiers …. with
anxious distress
mixed features: mania/hypomania
melancholic features
atypical features
psychotic festures
catatonia
permpartum onset
seasonal patterns
How do other depressive disorder differ from MDD? - Persistent depressive disorder (PDD)
Mdd symptoms for more than 2 years
any break from symptoms in less than 2 months
How do other depressive disorder differ from MDD? - Premenstral dysphoric disorder (PDD)
symptoms present 7 days before menstruation
Remit in the week following
How do other depressive disorder differ from MDD? -disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (DMDD)
Onset before 10 years, must be younger than 18 than older than 6 years at diagnosis
more than 3 times a week temper outbursts
mood between outburst persistently irritable
present for more than 12 months
Cognitive changes in MDD
moderate decrease in processing speed, attention, executive function, learning and memory.
Cognitive changes in MDD - cognitive bias
distorted information processing and focus away from positive stimuli and towards negative (especially affective stimuli)
Cog impairments can partially remain during …..
remission
recurrent episodes increase risk of progressive function loss
Negative thinking and depression - beck - negative cogntive triad
negative thoughts about the self, environment and future.
automatic and irretauonal thoughts are responsible for maintaining depression
Forms the basis of CBT
People with MDD that experience symptoms fro more than 2 years
10-20% - leads to diagnosis of PDD
most people’s symptoms remit (gone for less than 2 months)- if reappear = relapse
depression recurrence - when symptoms remit for a longer duration
40—50% of people experience recurrence of MDD
More likely as the number of previous episodes increases if other mental health conditions are present
Depression profile
affects 6% of global pop
young in adulthood
identify as woman
belong to specific ethnic group, although the specific groups vary between regions
Identify as trans
odds ratio of depression in women vs men
women 3x at ages 15ish
women 2x as likely at 25
age is the strongest predictor of effect size for
symptom severity
Why do gender differences in depression exist?
different patterns of risk factors
gender discrimination
differential exposure to childhood or adult adversities
Biologically different stress responses
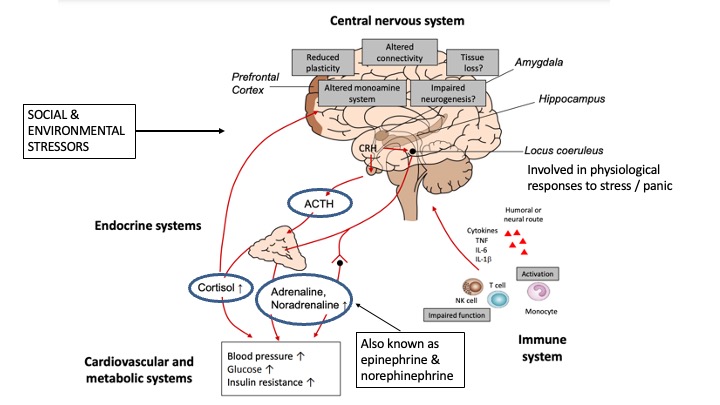
the stress response involved in depression - look at image
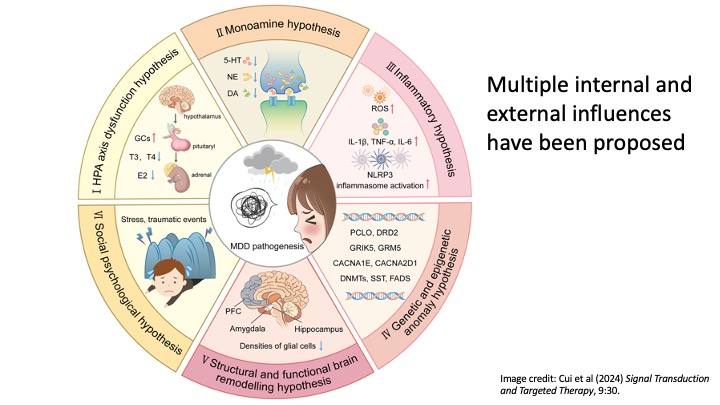
illustration of the multiple causes of depression
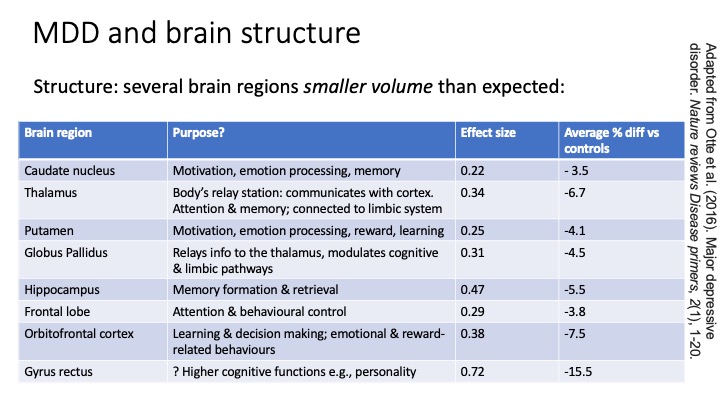
MDD and brain structure - look at image
MDD and brain function - functional differences - affective -salience circuit
amygdala is hyperactivated and hyper-connected with areas including dorsal ACC and insulation
MDD and brain function - functional differences - default mode network
hyperconnectivity correlates with higher levels of self-directed thoughts e.g. rumination
MDD and brain function - functional differences - front-parietal (cogntive control) circuit
hypo connectivity of this circuit may reflect difficulties in goal-directed tasks, under activity is observed at rest and for negative but not positive stimuli
The Brain as part of a bigger system in MDD - the brain communicates with……
the CNS, stress response (HPA axis), the ANS, and the immune system.
The Bain as part of a bigger system in MDD - how might this whole system cause depression when pre-existing risk factors and environmental triggers coincide?
psychological stressors = repeated HPA axis response
over time shows diminished feedback initiation capacity - chronically elevated cortisol and CRH
Chronically elevated levels of inflammatory mediators (cytokines)
Combination of stress response & immune activation affects the central nervous system: alters neural plasticity, connectivity and neurotransmission. May exacerbate tissue loss
May explain structural and functional brain differences seen in MDD
Causes of MDD - Chronic stress leads to chronic inflammation
stress hormones and the behaviours linked to stress cause inflammation e.g. alcohol use, smoking, poor diet etc, which all predispose development of MDD
chronic stress leads to chronic inflammation = MDD, but bidirectional ambiguity
people are more likely to behave in these ways when stressed
Causes of MDD - prolonged stress alters the….
adaptive innate immune stress response and prolongs inflammation.
inflammation itself perpetuates cognitive- affective- behavioural changes that themselves perpetuate stress

Early life experience programme immune and stress responses - MDD causes- intro
altered immune response develops in response to adverse early life events: a proinflammatory phenotype, shaped by the developing organisms exposure to social -environmental threat
Early life experience programme immune and stress responses - socio- environmental threats
childhood adversity linked to subsequent exaggerated cognitive, emotional and biological stress response
childhood obesity, diet and ,low physical activity (early systemic inflammation) predispose inflammatory responses across the life-course
Compounded by socioeconomic disadvantage
social and environmental risk factors in MDD
bereavement, divorce, chronic illnesses, dissemination, violence etc. these interact with genetic risk factors.
Social drift hypothesis
People with mental illness, may expense detonating functioning
Can lead to work and family problems, raises the likelihood of further socioeconomic disadvantage
Compounded by systemic stigma, discrimination and marginalisation based on mental health status and socioeconomic disadvantage
Genetic risk factors for depression
heritability is at 35% and is polygenic
MZZ co-twins of a twin with MDD are 2x as likely as DZ
heritability is higher for more severe, early onset or recurrent depression
Greater proportion of individual differences in risk for MDD can be explained by
non shared environmental influences than genetic factors
Diathesis stress model for Mdd - suggest that stress can ….
precipitate the development of MDD in individuals who have pre-existing vulnerability to depression
Gene - environment interaction: the case of 5- HTTLPR- Kendler (2005)
individual studies suggested that MDD risk was partially determined by numbers of adverse environmental events on pre-existing risk in a dose dependent manner
Gene - environment interaction: the case of 5- HTTLPR- Culverhouse - Method
meta-analysis of 31 datasets, Europeans genotyped for 5-HTTLPR and assessed for depression and stressful life events
analysis’s targeted 2 types of stressors (narrow,broad) and two depression outcomes (current and lifetime)
Gene - environment interaction: the case of 5- HTTLPR- Culverhouse - results
Findings did not support the interaction hypothesis: no sig inetrctaion between stress and 5HTTLPR genotyp
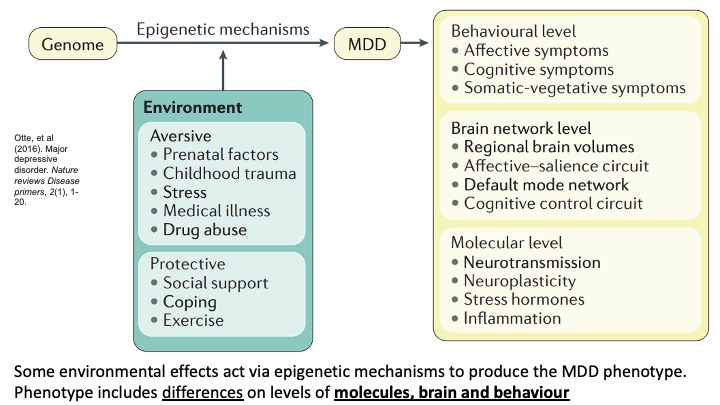
some environmental effects act via the epigenetic mechanisms to …
produce the MDD phenotype, phenotype includes differences on levels of molecules, brain and behaviour
Treatments for MDD - look at image
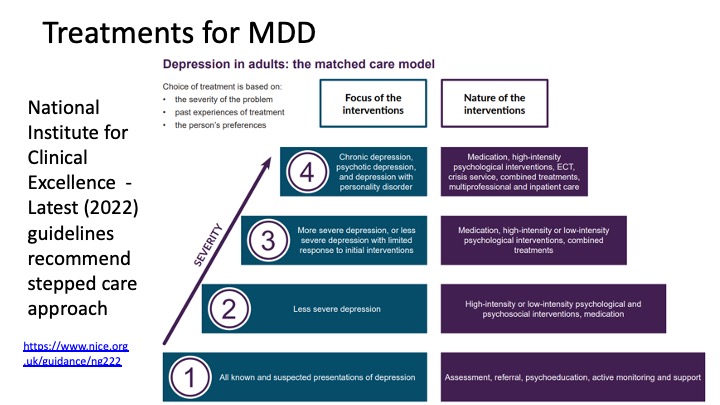
Antidepressant medication - SSRI’s
block the re-uptake Serotonin so it remains in the synaptic cleft for longer
Antidepressant medication - Tricyclic/ tetracyclic antidepressant
block re-uptake of serotonin and norepinephrine so they remain in the synaptic cleft for longer
Antidepressant medication - Monoamine oxidase inhibitors
an enzyme called monoamine oxidase is involved in removing norepinephrine serotonin and dopamine from the brain: Maoi’s stop this happening
Effectiveness of medication - cipriaini
meta-synthesis of antidepressant effectiveness , all 21 varieties exa one performed better than placebo
Nt and MDD - initially monoamine hypothesis focused on hypothetical deficiencies of serotonin, noradrenaline and dopeamine - however it is more complex:
rapid change to 5-HT concentration in the brain is not consistent with the delayed onset of symptom relief in SSRI’s
Lowering 5HT concentration in the brain doesn’t induce depression in people without MDD
Long-term antidepressant treatment actually down regulates total 5HT concentration in the brain
No evidence of problems with monoamine receptor dysfunction in the brains of people with MDD
Nt and MDD - initially monoamine hypothesis focused on hypothetical deficiencies of serotonin, noradrenaline and dopeamine - however it is more complex: - CASTING DOUBT ON
A) neurotransmitter concentration B) receptor insensitivity theories as incomplete explanations
Serotonin- targeting drugs: other possible mechanisms - Neuronal growth
the delay in symptom relief when antidepressants drugs are started may suggest that new neurones need to grow (neurogenesis) in ket areas of the brain (e..g hippocampus) in response to antidepressant, for some people
Serotonin- targeting drugs: other possible mechanisms - chronic stress
chronic stress substantially alters neuronal circuits in the brain, including disruption of intracellular signalling and the number and function of synapses
Antidepressants may help reverse some of these changes by increasing neural plasticity - occurs via brain derived neurotrophic factor
treatments for MDD - CB
thoughts, behaviours and emotions can be reciprocally deterministic
AlL these affect how our brain functions, stress levels and how behaviours either increase or decrease inflammation
CBT helps us recognise the relationship between….
thoughts, behaviours and emotions in our lives, making changes to thoughts and behaviours to enhance emotional experiences/ symptoms
CBT for MDD
helps patients indentify negative, distorted thinking patterns that contribute to depression
Provides skills to test and challenge these negative thoughts
Behavioural activation helps patients increase positive activities that provide a sense of pleasure
Processes used to avoid activities are tested and reduced
How many sessions on average for CBT
16-20 sessions over 3-4 months
CBT For MDD - Collaborative empiricisms
patients and the therapist become co-investgators both in ascertaining the goals for treatment and investigating the patients thoughts
Effectiveness of CBT
More effective than doing nothing
Effect size (hedges g) moderate to large, also more effective than usual care or pill placebo
CBT marginally more effective than mediation alone for MDD
Interpersonal therapy to treat MDD
Psychological problems understood as responses to current difficultuies in day to day interactions with others
focus on attachment, grief, role transitions, interpersonal disputes and deficits
How many sessions for intrapersonal therapy
Time limited (12-16 sessions)
IPT aims to improve ….
interpersonal functioning, well being and through helping individuals effectively communicate, resolve interpersonal crises and help patients effectively use social support
effectiveness of IPT reduced depressive symptoms in comparison to placebo, and in combination with….
antidepressant (Cuijpers et al 2011)
Other psychosocial approaches for MDD treatment recomended by NICE - physical activity program
(Mild to moderate symptoms)- increasing social engagement and reducing somatic complaints
Other psychosocial approaches for MDD treatment recomended by NICE - couples therapy
useful when the person has a regular partner and where relationship may contribute to development/maintenance of depressive symptoms
Other psychosocial approaches for MDD treatment recomended by NICE - Counselling and psychodynamic psychotherapy
c - (6-10 sessions over 8-12 weeks)
P - (16-20 sessions over 4 -6 months)
Which is more cost effective ? Psychological therapies or medication?
health economics modelling study based on data from the USA
cBT and second generation antidepressants appear equally cost effective across the course of 5 years