Campbell Biology Chapter 48
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Neurons
Nerve cells that transfer information within the body
Electrical signals (long distance) and chemical signals (short distance)
two types of signals that neurons use to communicate
Ganglia
Simple clusters of neurons that process information
Brain
A more complex organization of neurons
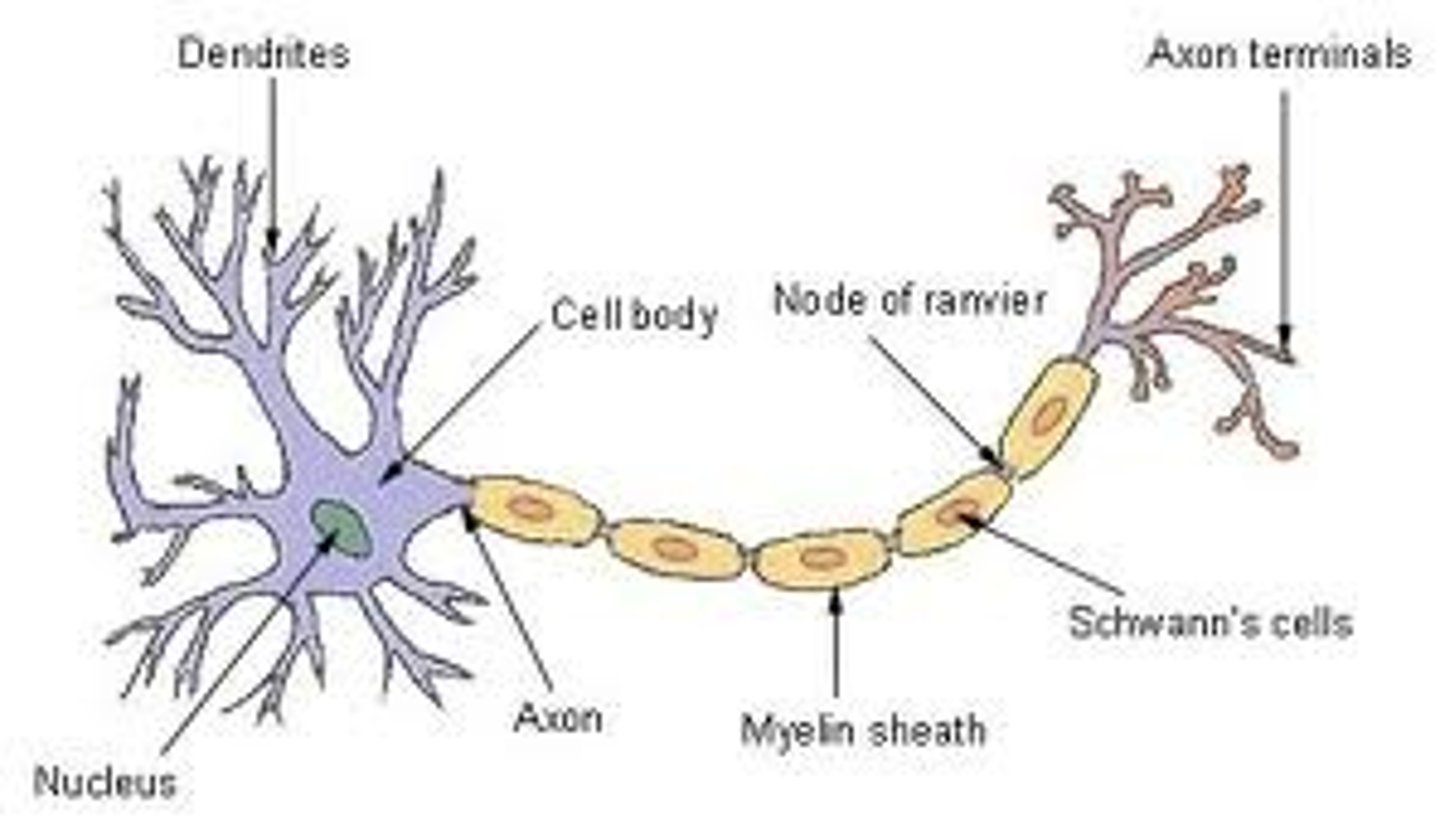
Cell body
The part of the neuron where most organelles are located
Dendrites
highly branched extensions that receive signals from other nuerons
Axon
an extension of a neuron that transmits signals to other cells
Axon hillock
the cone shaped base of an axon
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that pass information across the synapse
Synapse
a junction between an axon and another cell
Neuron structure
dendrite, nucleus, cell body, axon, synapse
Presynaptic cell
neuron
Postsynaptic cell
a neuron, muscle, or gland cell
Glia/Glial cells
Nourishment cells of neurons
Three stages of information processing in nervous systems
sensory input, integration, and motor output
Sensory neurons
Location where information is transmitted from sensors that detect external stimuli and internal conditions.
Interneurons
Cells where sensory information sent to the brain is integrated
Motor neurons
Transports motor outputs through the brain and trigger muscle or gland activity
Central nervous system
Location where tengration takes place; includes brain and a nerve cord
Peripheral nervous system
Carries information into and out of the CNS
Nerves
Neurons of the PNS bundled together
Membrane potential
A difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a cell
Resting potential
The membrane potential of a neuron not sending signals
Concentration levels of a mammalian neuron
K+ highest inside the cell, Na+ highest outside the cell
Sodium-potassium pumps
use the energy of ATP to maintain K+ and Na+ gradients across the plasma membrane
Ion channels
opening in the plasma membrane that converts chemical potential to electrical potential
equilibrium potential
membrane voltage for a particular ion at equilibrium and can be calculated using the Nernst equation
Resting neuron
currents of K+ and Na+ are the same and opposite, the resting potential across the membrane remains steady
Gated ion channels
Channels inside neurons that open and close in response to stimuli
Gated K+ channels open
K+ diffuses out, making the inside of the cell more negative
Hyperpolarization
an increase in magnitude of membrane potential
Depolarization
a reduction in the magnitude of the membrane potential
Graded potentials
changes in polarization where the magnitude of the change varies with the strength of the stimulus
Action potential
A massive change in membrane voltage cause by depolarization
Voltage gated
Ion channels opening or closing when the membrane potential passes a certain level
Refractory period
period after an action potential where a second action potential cannot be initiated
Nodes of Ranvier
gaps in the myelin sheath where voltage-gated Na+ channels are found
Saltatory conduction
Process where action potentials in myelinated axons jump between the nodes of Ranvier
Gap junctions
Location where the electrical current flows from one neuron to another
Chemical neurotransmitter
In a chemical synapse, a transmitter that carries information between neurons
Ligand gated ion channels
For direct synaptic transmission; involves binding of neurotransmitters. located in the postsynaptic cell.
Postsynaptic potential
Happens when a neurotransmitter binding causes ion channels to open
Excitatory postsynaptic potentials
depolarizations that bring the membrane potential toward threshold
Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials
hyperpolarizations that move the membrane potential farther from threshold
Temporal summation
Occurs when two EPSP's are produced in rapid succession
Spatial summation
EPSPs produced nearly simultaneously by different synapses on the same postsynaptic neuron add together
Acetylcholine
a common neurotransmitter in vertebrates and invertebrates involved in muscle stimulation, memory formation, and learning.
Ligand gated and metabotropic
two major classes of acetylcholine receptor
Amino acids, biogenic amines, neuropeptides, and gases
Remainder of neurotransmitters
Major neurotransmitters
Acetlycholine, GABA, Dopamine, Nitric oxide
