Chapter 8: Joints
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Bones are designed for what?
Support and mobility
Joints are?
Articulations - exist whereover two or or more bones meet
Bones may be in direct contact or separated by? (3)
Fibrous tissue
Cartilage
Fluid
Functional and Structural classification of the Joints
What are the three functional classification of the joints?
Synarthrosis (no movement)
Amphiarthrosis (little movement)
Diarthrosis (free movement)
What are the four structural classification of the joints?
Fibrous
Cartilaginous
Bony
Synovial
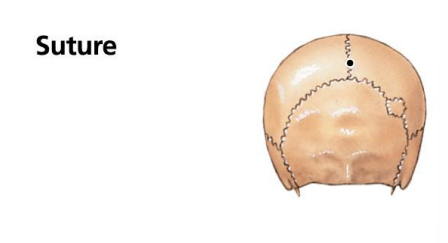
Sutures? What is the functional classification of the joint?
Synarthrosis
Joints found only in the skull - Bones are interlocked together via sutural ligaments
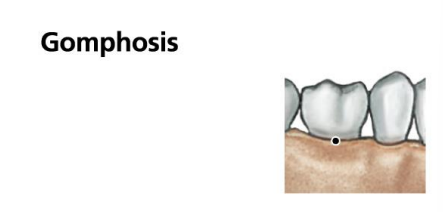
Gomphosis? What is the functional classification of the joint?
Synarthrosis
Fibrous joint between teeth and jaw bones - Periodontal ligaments of the teeth
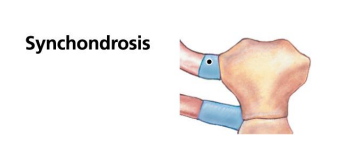
Synchondrosis is?
Cartilaginous bridge between two articulating bones
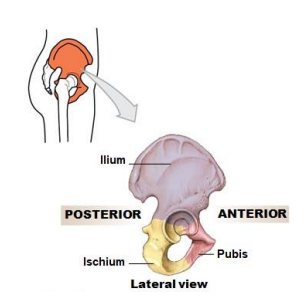
What is Synostosis? Give an example
Bony fusion joint between two bones
Fusion of the three coxal bones
Amphiarthrousis?
Bones of the joint are held together by fibrous cartilage or fibrous connective tissue (a ligament)
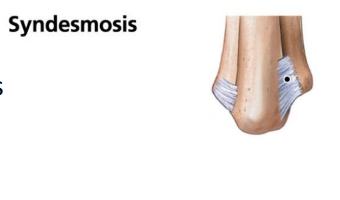
Syndesmosis?
Ligaments that connect two bones
between the radius and ulna
Between the tibia and fibula
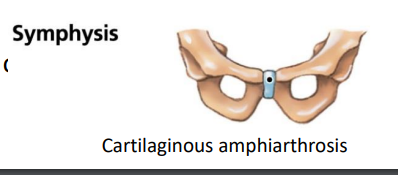
Symphysis?
Bones are separated by a wedge pad of cartilage
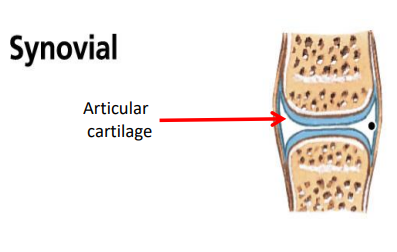
Diarthrosis
(Freely movable synovial joints)
Contain a fluid-filled cavity between the bones of the joint.
Joints with a synovial membrane and contain synovial fluid.
IS diarthrosis are typically found at the ends of … bones
Long bones
What are the examples of diarthroses?
Shoulder joint
Elbow joint
Hip joint
Knee joint
What are Synovial fluid? It acts as a …
Lubricates the surfaces of the articular cartilages and reduces friction
Acts as a Shock absorber
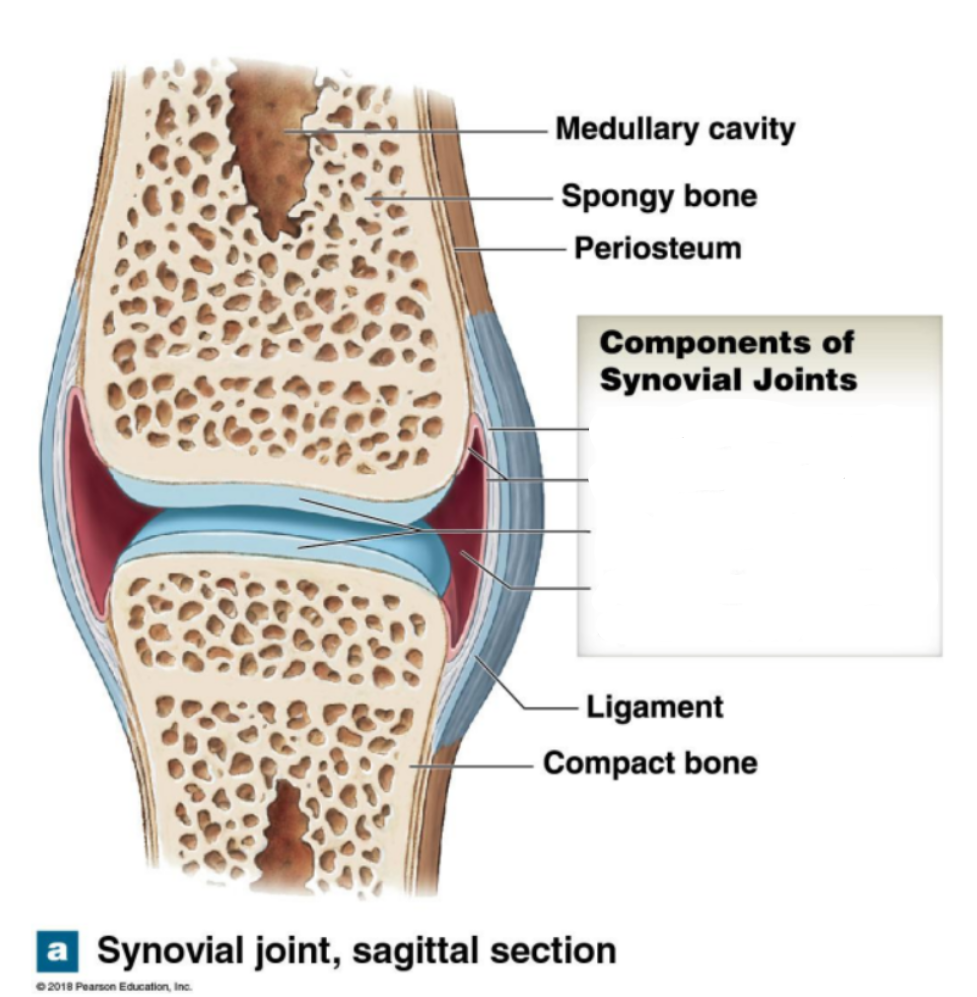
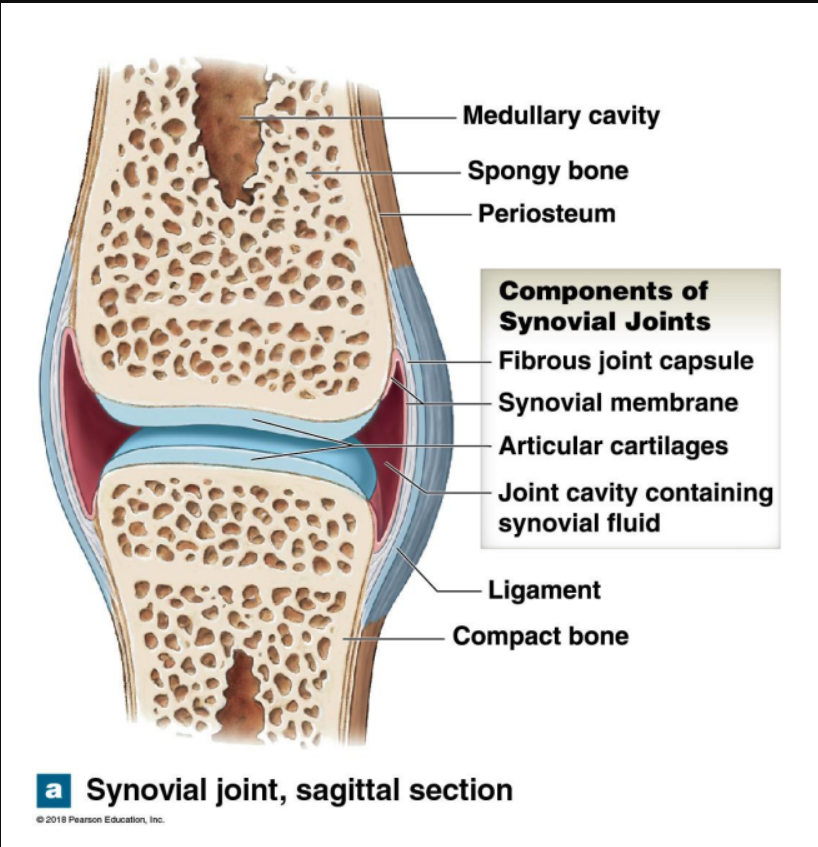
What are the components of synovial joints
Fibrous joint Capsule
Synovial membrane
Articular cartilages
Joint cavity contain synovial fluid
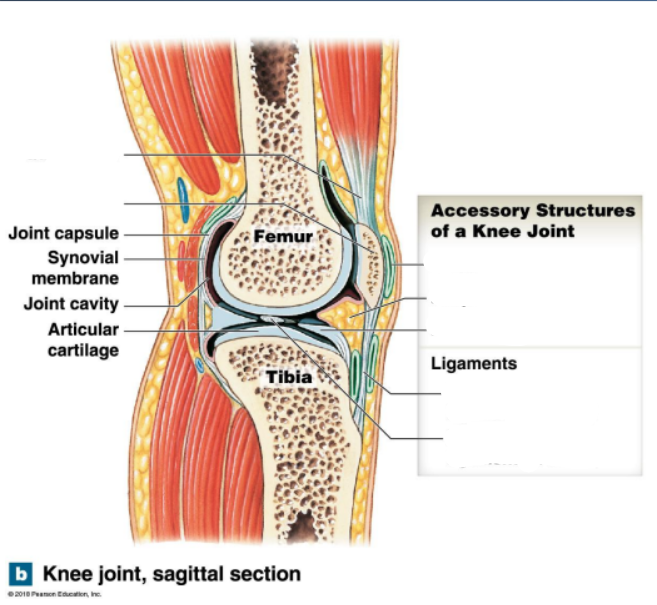
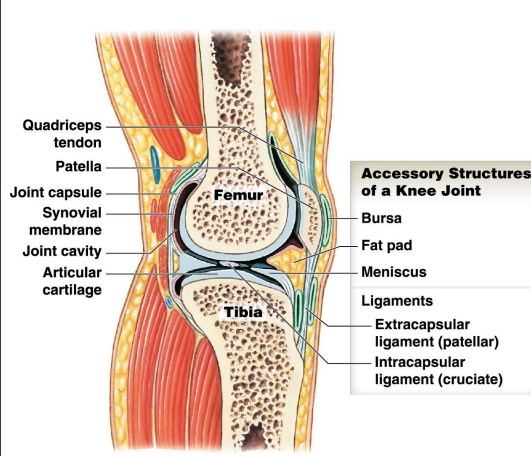
What are the accessory structures of a knee joint?
What are the functions of each?
Bursae - Fluid filled pockets of synovial fluid
Fat pads - Packing material
Menisci - fibrous cartilage
Ligaments - support, strength and reinforce
Synovial joints are classified based on? (2)
The axes of motion
Type of movement
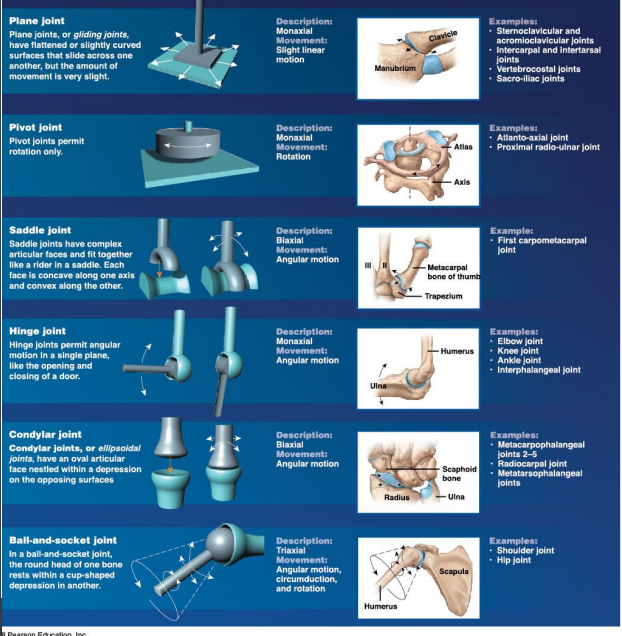
What is the synovial joint Classification
The types of movements allowed by synovial joint
Angular motion (abduction, adduction, flexion and extension
Circumduction
Rotation
Angular motion: Show what
Abduction and adduction
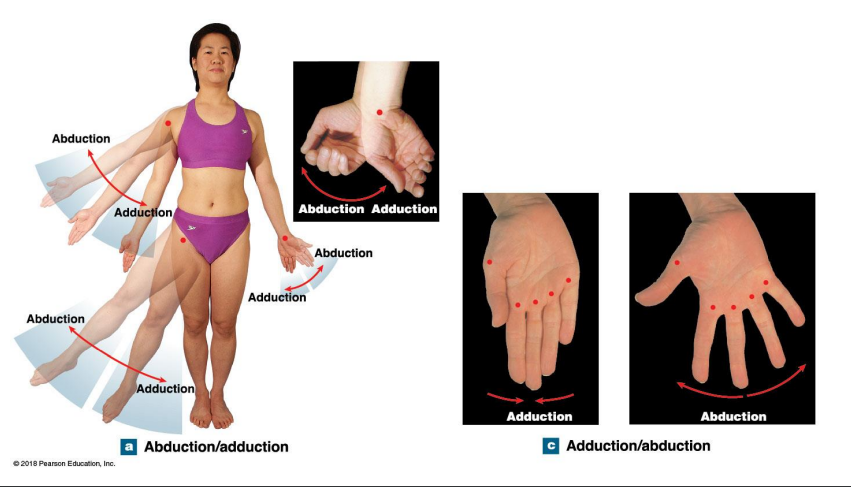
Angular Motion:
Flexion and extension
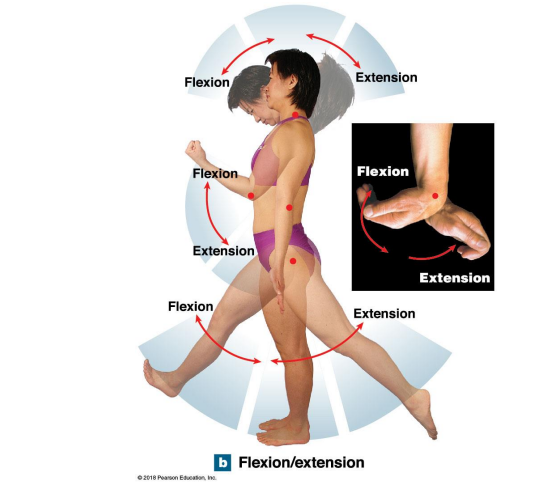
Angular Motion:
Rotation
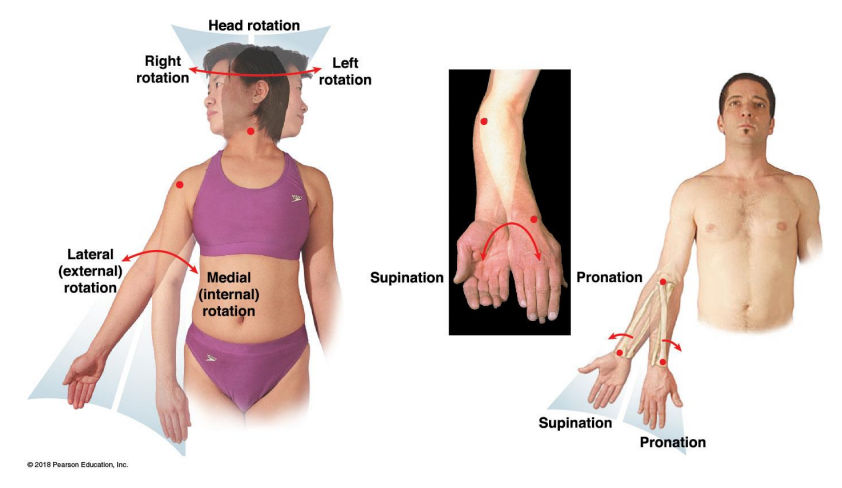
Angular Motion:
Circumduction

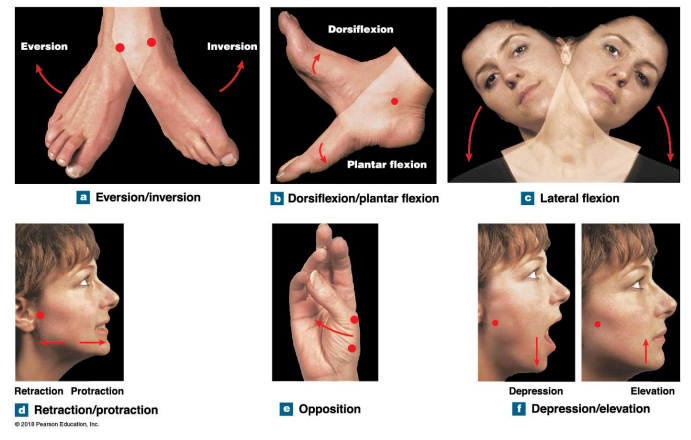
What are the six special movements
Eversion/inversion
Dorsiflexion/plantar flexion
Lateral flexion
Retraction/protraction
Opposition
Depression/elevation
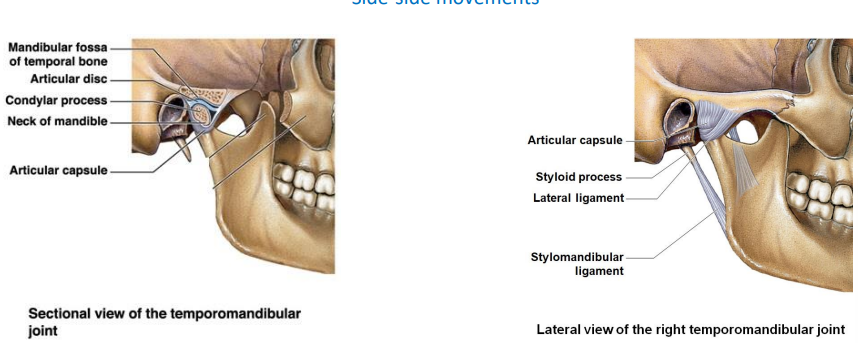
The Temporomandibular joint consist of the?
What is another name for the joint?
What movements?
Condylar process of the mandible and the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone
Hinge joint
Side-side movement
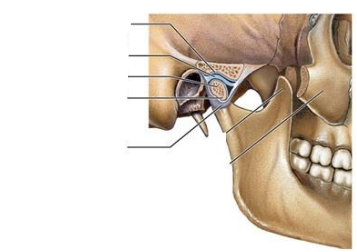
What is the sectional view of the temporomandibular joint? What does it consist of? (5)
Mandibular fossa of temporal bone
Articular disc
Condylar process
Neck of mandible
Articular capsule
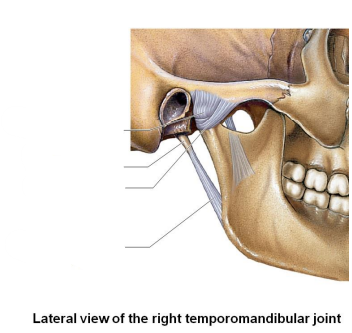
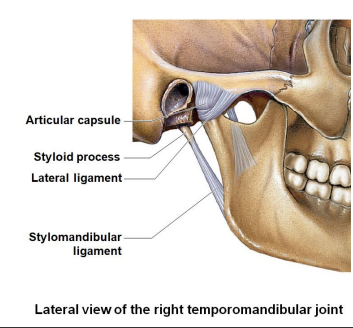
What is the lateral view of the right temporomandibular joint? What are the two ligaments, one process, and one capsule?
Articular capsule
Styloid process
Lateral ligament
Stylomandibular ligament
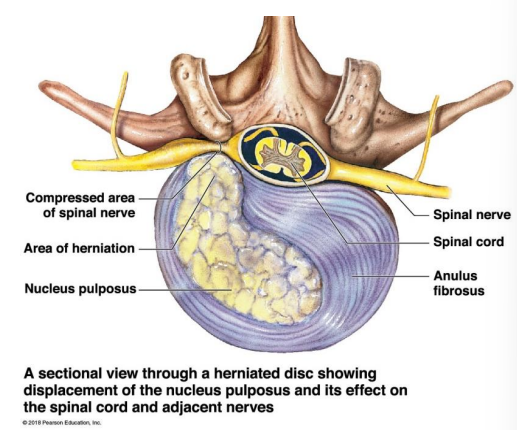
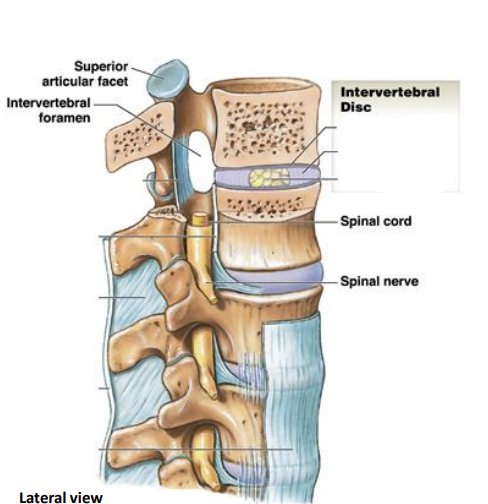
What are Intervertebral disc?
Pads of Fibrous cartilage
C2 - sacrum are what type of joints?
Symphysis joint
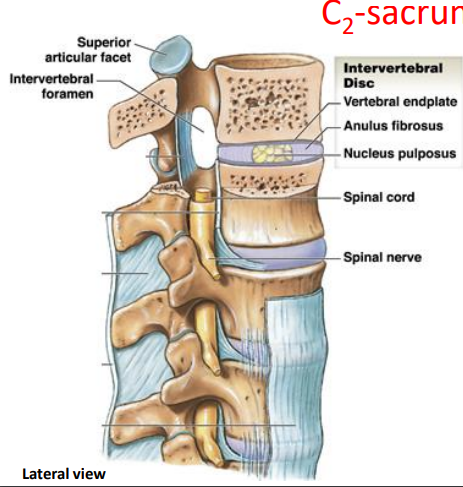
Intervertebral discs are made of?
Anulus fibrosus: outer layer
Nucleus pulposus: inner layer
Vertebral endplate: make up the inferior and superior surfaces
Shoulder joint is what type of joint?
Ball and socket joint
What does the shoulder joint articulates with what?
Articulation of the head of the humerus with the glenoid cavity
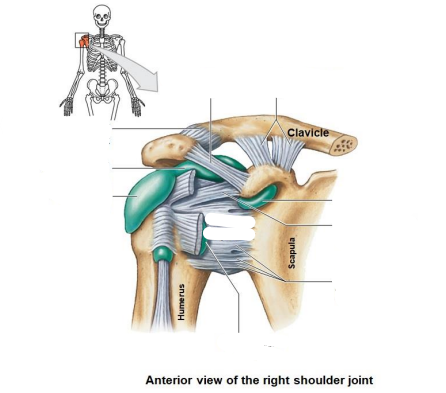
Name the 5 ligaments, 1 capsule, 4 bursa?
Coraco-acromial ligament
Coracoclavicular ligament
Acromioclavicular ligament
Subacromial bursa
Subdeltoid bursa
Subscapular bursa
Subcoraciod bursa
Coracohumeral ligament
Glenohumeral ligaments
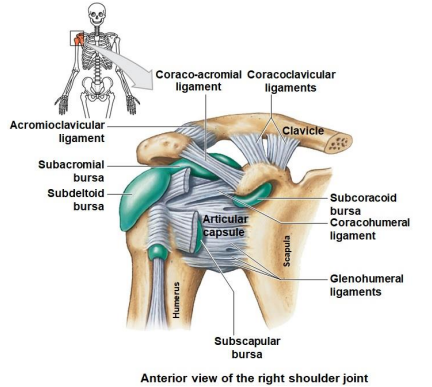
What is bursitis?
Inflammation of these bursa sacs
What is the rotator cuff?
The muscles of the shoulder joint
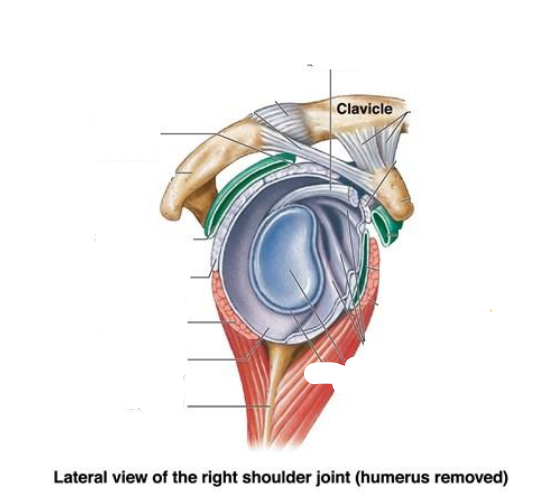
What is the Later view of the right should joint (humerus removed) components
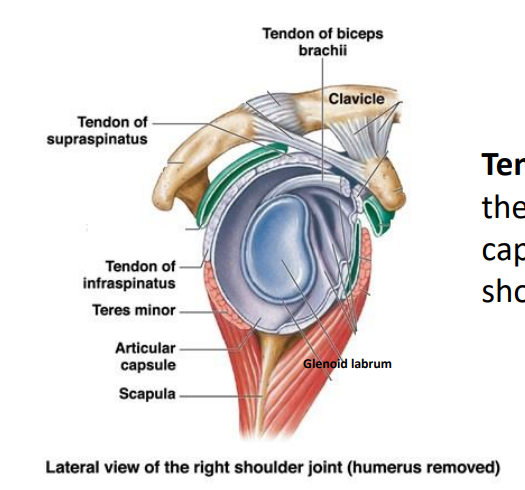
Tendons Passing across the joint reinforce the … and support the…
Capsule and supports the shoulder
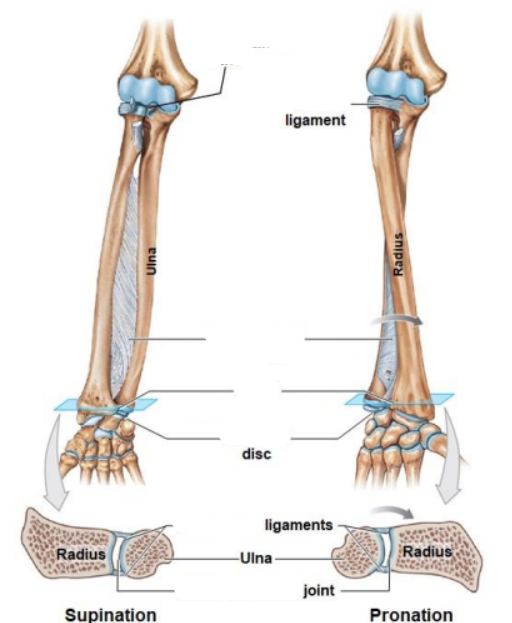
Elbow and radio-ulnar joint consist of?
Proximal radio-ulnar joint
Annular ligament
Antebrachial interosseous membrane
Distal radio-ulnar joint
Articular disc
Radio-ulnar ligaments
ulna
Distal radio-ulnar joint
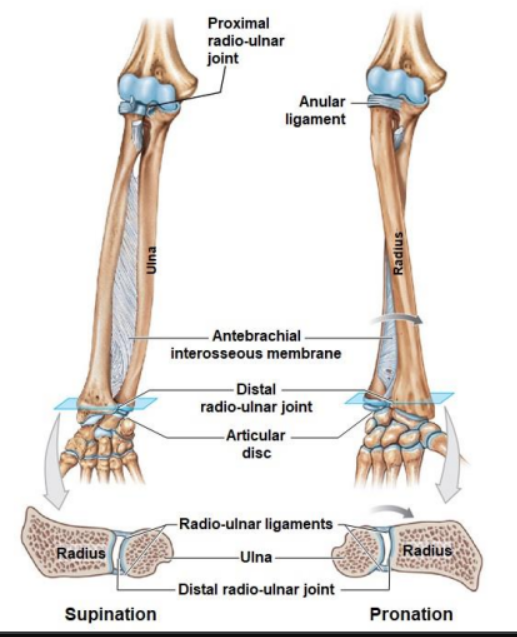
Proximal radio-ulnar joint
Articulates the head of the radius with the radial notch of the ulna
Annular ligament
Hold the head of the radius in position (during pronation)
Distal radio-ulnar joint
Radio-ulnar ligaments
Knee Joints
The Articular Capsule extends from distal femur to proximal tibia and includes the patella (but excludes the fibula)
Knee joints are made of?
Medial and lateral menisci and fat pads
Medial and lateral menisci function?
Act as cushion
Conform to the shape of the femur as it changes position.
Increase the surface area of tibiofemoral joint
Provide lateral stability
Fat pads function?
Fat pads reduce friction between the patella and other tissues
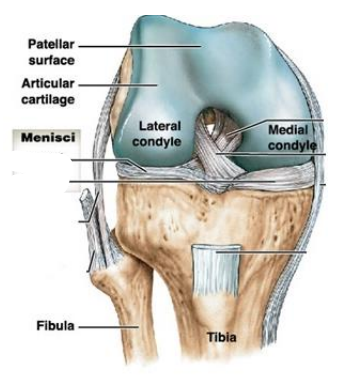
Where is the lateral and medial menisci?
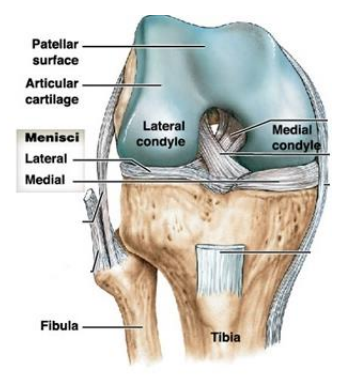
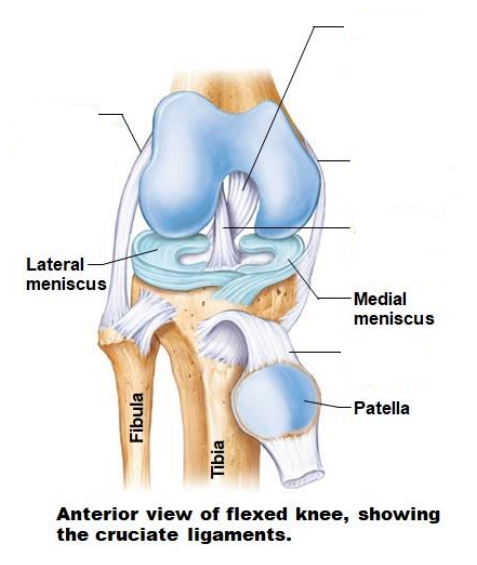
What is the knee joints composed of?
Patellar surface
Articular cartilage
Lateral condyle
Medial condyle
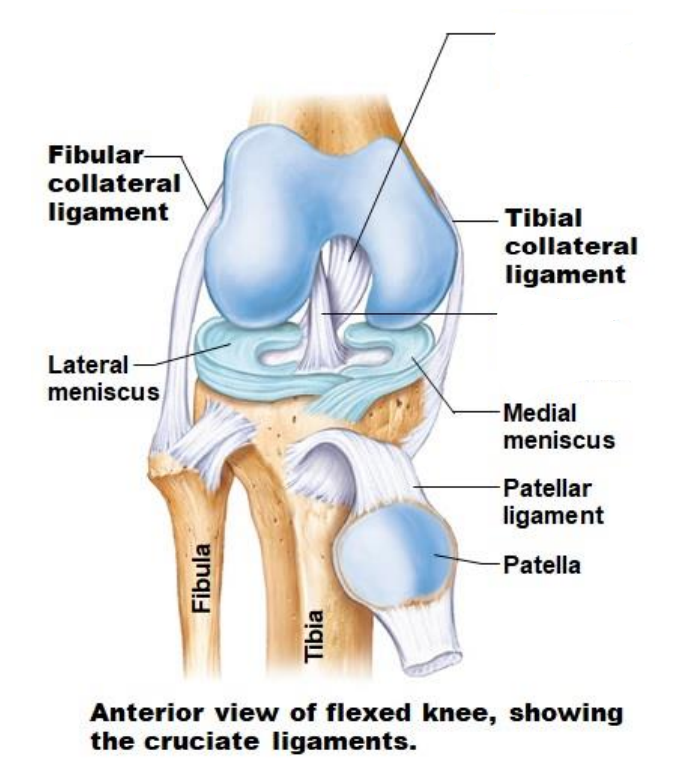
What are the Knee joint ligaments? (supporting ligaments)
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) - Connects the tibia to the lateral edge of the intercondylar fossa of the femur
Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) - Connects the tibia to the medial edge of the intercondylar fossa of the femur (Maintain alignment of tibia and femur)
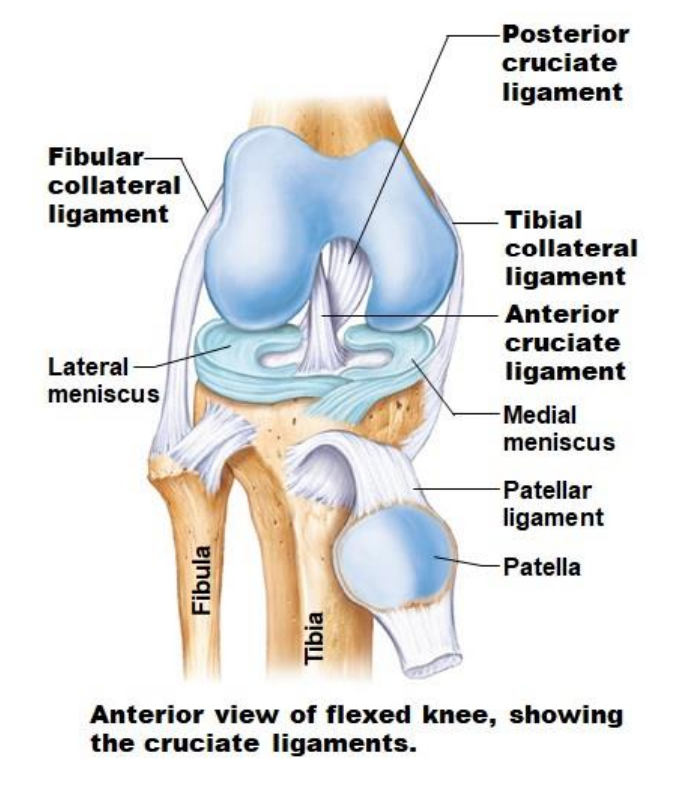
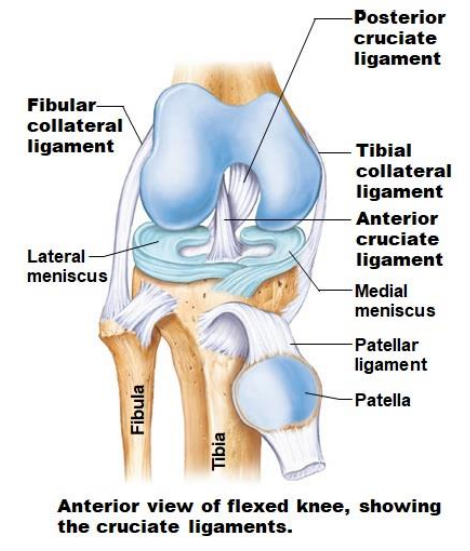
What are the Knee joint ligaments?
Fibular collateral ligament
Posterior cruciate ligament
Tibial collateral ligament
Anterior cruciate ligament
Patellar ligaments
Rheumatism
General term for pain and stiffness affecting the skeletal system, muscular system, or both.
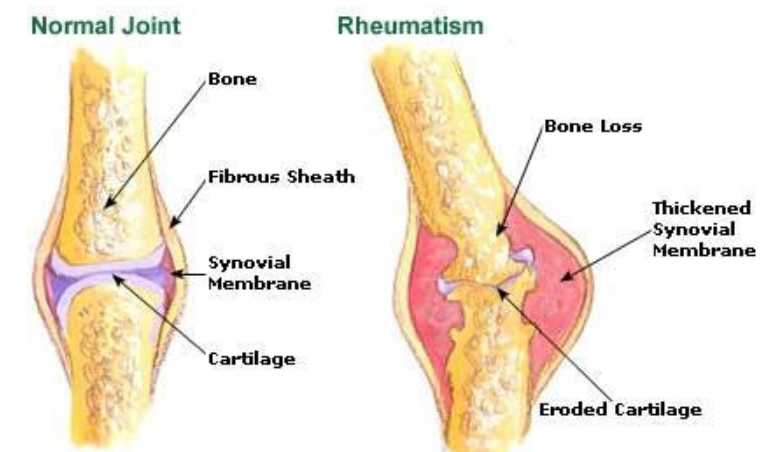
When does Rheumatism happen?
Aging and Joints As we age, joints are subjected to wear and tear
Arthritis
•Type of rheumatic disease that affect synovial joints.
•Inflammation of the joints.
•Involves damage to the articular cartilages.
• Causes include Bacterial or viral infection, injury, metabolic problems and physical stress
Intervertebral discs disease (IVDD)
Lateral view of the lumber region of the spinal column showing normal and bulging intervertebral disc
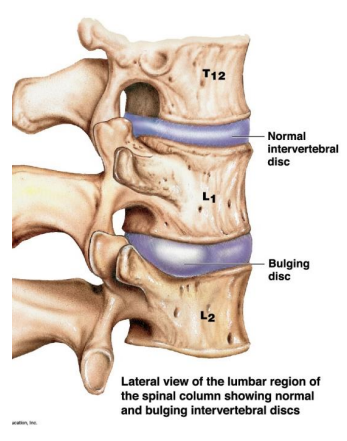
Herniated disc or Bulging disc
Sectional view through a herniated disc showing displacement of the nucleus pulposus and its effect on the spinal cord and adjacent nerves