Unit 4 Exam Study Guide - Earth Science
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
In a conventional timeline, what is the largest period of history?
The Hadean period
What is the Law of Superposition (Relative)?
In an undisturbed sedimentary rocks, the oldest rock will always be on the bottom and the youngest rock on the top.
What is Cross-Cutting Relationships (Relative)?
The unit or fault which cuts across the strata is younger than the strata it cuts across
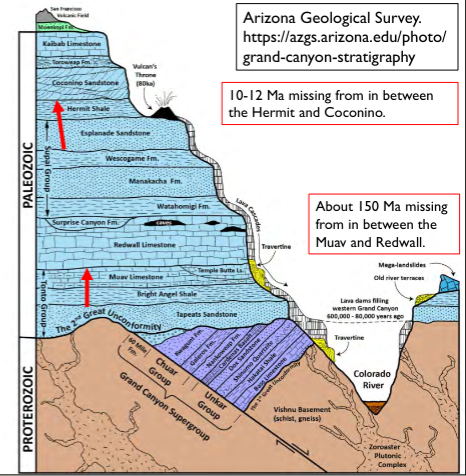
What is an unconformity?
A buried erosional surface
What is a disconformity?
An obvious erosional contact between two sedimentary rocks
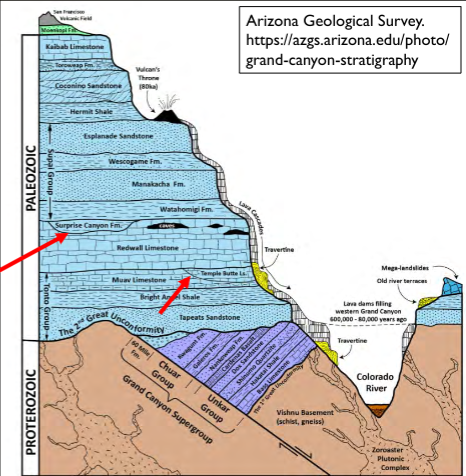
What is an angular unconformity?
When sedimentary rocks below sit at an angle to sedimentary layers above
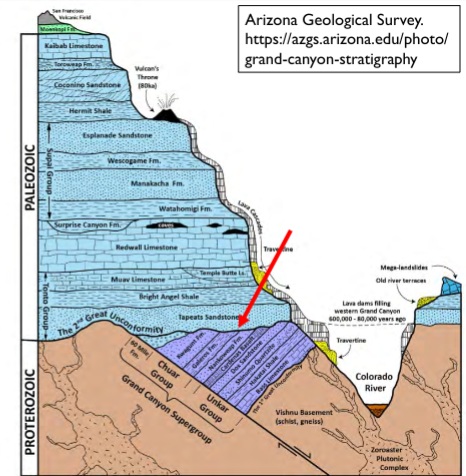
What is a nonconformity?
Sedimentary rocks that unconformable overlie igneous or sedimentary rocks
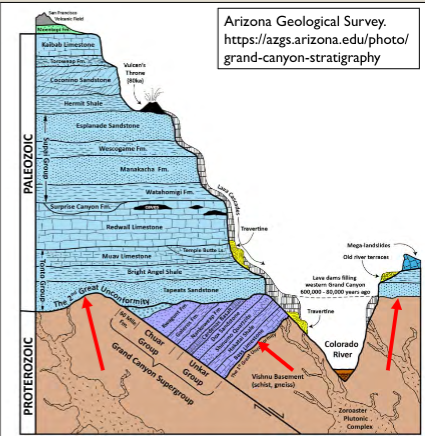
What is a paraconformity?
A supposed erosional surface or break in time (hiatus) that has no obvious reason
What are Inclusions (Relative)?
Older pieces of rock that get incorporated into newer deposits
What is the Order of Events?
Using the Law of Superposition and Cross-Cutting Relationships to determine the order of events
Biostratigraphy (Relative & Absolute)
Dating method based on various animals in certain layers of rock
What are some problems with Biostratigraphy dating?
It is dependent upon the assumption of biological evolution and faunal succession
It assumes that the earth is old and that certain suites of animals lived during certain periods of geologic time
Assumes if the fossils are the same, the rocks are the same age
What type of rock is the only one that can be dated Radioactively?
Igneous rocks
What are the 3 types of decay?
Alpha
Beta
Electron Capture
What is Alpha Decay?
When an unstable Parent nucleus ejects an alpha particle (Helium) to become a stable Daughter nucleus, producing energy in the process.
What is Beta Decay?
When a Neutron sheds a negative Beta particle to become a Proton, producing energy in the process.
What is Electron Capture?
When a Proton grabs an electron to become a Neutron, producing energy in the proces
What is half-life?
The amount of time that it takes for one half of the radioactive isotope to change into its daughter product. Can you draw a progression?
What is fission?
When the Parent isotope splits into two smaller daughter isotopes, often with the release of additional nuclear materials and energy. The two daughters explode out and travel in opposite directions, destroying some of the structure of the mineral.
According to the Conventional time model, what time period were trilobites alive?
Paleozoic
According to the Conventional time model, what time period were the dinosaurs alive?
Mesozoic
According to the Conventional time model, when were most mammals alive?
Cenozoic
Is the fossil record biased towards fragile or durable shells?
The record does not show bias
What time period did the Cambrian Explosion occurr in?
Paleozoic