Animal Behavior Quiz 5
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Default sex in mammals vs. birds
Default sex mammals : females (no Testosterone)
Default sex birds: Male (no Estradiol)
Studying Hormonal Influences
1) Identify correlation btwn hormone and behavior
2) remove hormone → see if behavior changes (or stops)
excise organ
use drug that blocks hormone production
knockout gene for receptor
progesterone knockout in mice
3) Add hormone → see if behavior returns to normal
Activational effects of Testosterone
In Guinea pigs, male sex drive can recover after castration w/ T implants (Male A,B,C)
Male A has more T receptors
Behavior is directly linked with what
Hormonal activity
Example of activational effects of T
Japanese Quail
male behavior (staring at female) stops with castration but returns with T implant
Aromatase : enzyme that converts T to estrogen
estrogen is what drives this behavior → aromatase inhibitor will stop estrogen production → no longer take T → E
the testosterone has to be converted into estrogen (via aromatase) in the brain, and that estrogen is what activates the staring/sexual behavior.
Testosterone Tradeoffs (BENEFITS)
Benefits of T:
increase atractiveness
increase territory size
increase sperm production
increase # of EPC & EFC
EPC = extra pair copulation (act of doing sex)
EPF = extra pair fertilization (success fertilize)
Testosterone Tradeoffs (COSTS)
Costs of T:
increase metabolism
reduced survival
risk of injury and or predation with courtship and fights
suppression of immune system
reduced parental care
T has a high cost
otherwise animals would always have T, but they do not
McGlothlin et al 2007 study
Male Carolina dark- eyed juncos charged up with T → shitty parents
gave them T → reduced parental and reproductive success
Behavioral tradeoff caused by T
although males w/T implants carve out large home range → spend less time gathering food for young
White Crowned Sparrow Study
Alaska: Only 1 brood → single large T peak before breeding.
Washington: 2 broods → normal T peak before 1st brood, no 2nd T peak.
Reason: High T = needed for territory defense & courtship, but it suppresses parental care.
Adaptation:
Alaska: maximize reproduction in short season → strong T surge.
Washington: males already mated/territories secured → low T for 2nd brood so they can help parent.
Niche
interelationship of a species with all biotic and abotic factors affecting it or way of life of a species
Two types of niches
Fundamental niche
Realized niche
Fundamental Niche
mainly limited by abiotic factors
full range of conditions in which a species can maintain viable pop
Realized niche
limited by biotic factors
space that an animal occupies in presence of competitors, predators, pathogens, and limited food
Outcomes for when species occupy identical niches
1) Competitive exclusion
eviction
extinction
2) Resource partitioning : evolution to use diff resource
Differentiation of niches enables similar species to coexist in a community
Habitat
physical manifestation of species’ niche
Despotic defense
Means the strongest individuals can defend the best resources, but they must balance the cost of defense with the benefit of holding territory.
Strong, dominant individuals take and defend the best resources.
Weaker ones are excluded and forced into poorer habitats, where their success is lower.
Example of despotic defense
European great tit
RS better quality in woodland than hedgerows
“Despots” (dominant individuals who defend territory) : in woodland force others to lower RS habitat (hedgerows) → birds in hedgerows make best of bad situation
Benefits of territorialty
1) greater access to food (also : shelter, hiding places, water, mates, etc)
2) because more resources → breed earlier and have more young in season
Despotic defense comes with cost
costs of activity, defense, predation
cost of T
Example: T implants in lizards
increase patrolling
lower survival
both groups were giving T but one with food supplement and one without
one without food can’t compensate energy loss —> less survival
one with food can compensate energy loss —> better chance of survival
Evidence of balancing cost-benefits : minimizing costs of defense
side blotched lizards defend territories with basking rocks (also rocks attract females)
reduce rocks : territory becomes larger
add rocks : territory becomes smaller
Few rocks → the lizard has to make its territory larger so it can include enough rocks to survive.
Many rocks → the lizard can keep its territory smaller because there are already plenty of rocks nearby, so no need to waste energy defending a huge area
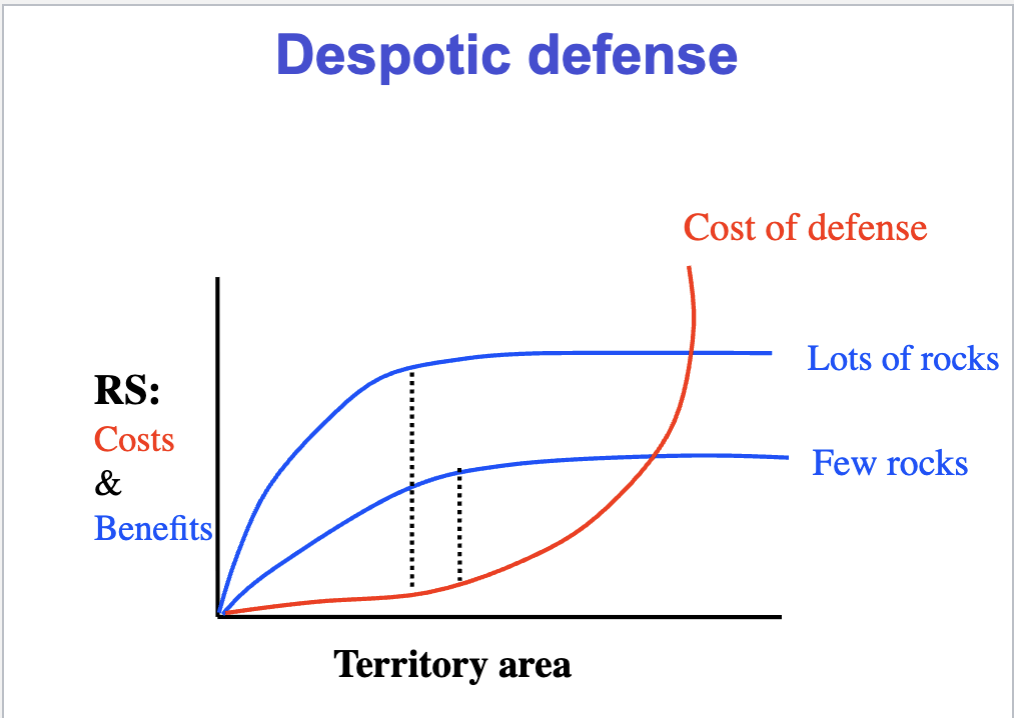
Economics of Defense
Separating benefits and costs
benefits must outweigh cost ( - - - - line)
have the most reproductive success with least cost of defense
Ideal Free Distribution (IFD)
individuals may sometimes settle in sub-prime habitat due to other factors (other than being kicked out by despot)
Example of Ideal Free Distribution (IFD)
Black cap warbler nests are placed in riparian areas (near river) and sub-prime wood lots
we see that RS in two habitats is equal after riparian areas begin to fill up, WHY?
There is a switch point (fitness payoff is the same)
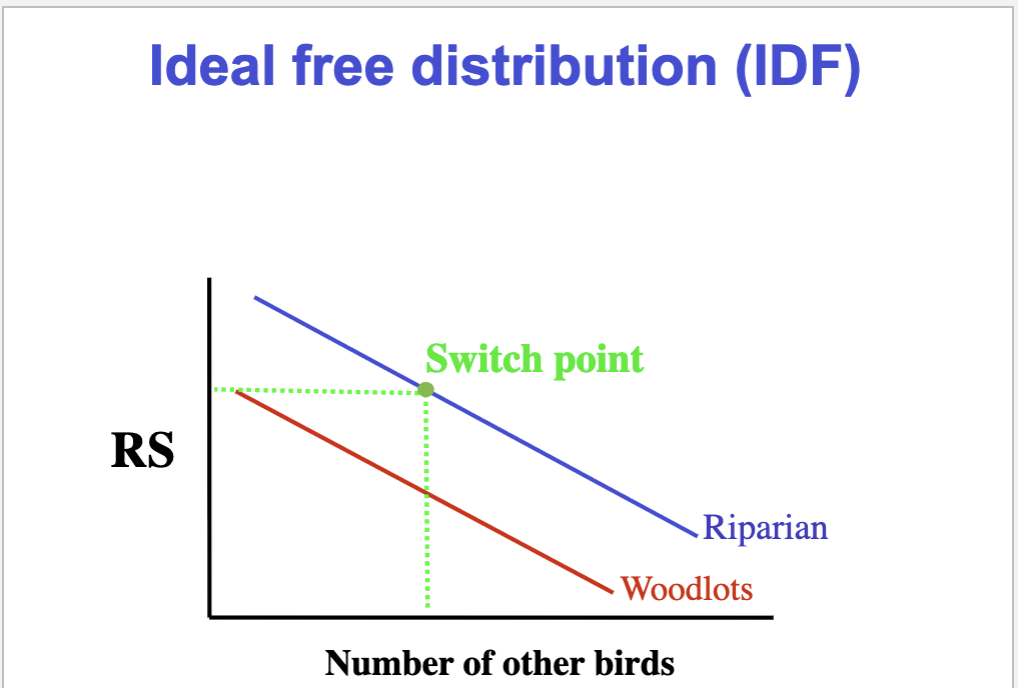
Both despotic defense and IFD
most systems combine despotic defense and IFD
ex) Gall aphids
females fight for access to big leaf (bigger leaf yields more RS) (DESPOTIC DEFENSE)
loser can either be 2nd on big leaf, or choose smaller leaf (CHOICE DUE TO IFD)
within a leaf, the despots monopolize more RS
losing female chooses btwn second place in leaf or being top-aphid on smaller leaf → yield rough equal RS
Evolutionary Stable Strategy (ESS)
behavioral decision rule that everyone plays by, that one in place cannot be replaced by alternative strategies (other strategies have lower RS)