CETRAN30
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Test 1 and additional terms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
P1.5 B
What is the minimum total project cost required for a project to undergo processing by the National Economic and Development Authority Investment Coordination Committee (NEDA-ICC)?
Concession Period
What is the term used to describe the number of years agreed upon in a Public-Private Partnership contract during which the private entity is granted the right to finance, develop, operate, and maintain a project.
Government Appropriations Act
What is the primary source of government funding for local and national infrastructure projects in the Philippines allocated through the annual national budget?
Chapter XII
Which chapter of the Philippine Development
Onitsuka Mexico 66; Yellow/Black
What shoes did sir mark wear last Dec 18?

National Transportation Policy and its Implementing Rules and Regulation
What set of guidelines, issued by NEDA, establishes the framework for the development, regulation, and management of the transport sector in the Philippines?
Sustainable transport planning
In transportation planning, what refers to the policies and strategies implemented to ensure the sustainability and environmental compatibility of transportation systems?
Level of Service (LoS)
In transportation planning, what term is used to describe the measure of the quality of service provided by transportation facility, typically assessing factors like flow, travel time, and user comfort?
Analysis of Performance
This element of transportation planning involves the use of mathematical models for estimating travel demand.
Generational Equity
What dimension of sustainability emphasizes the fair distribution and availability of transportation resources across different generations, ensuring that future generations can also meet their mobility needs without compromising the ability of current generations to do so, as part of the broader dimensions of sustainability in transportation?
Traffic Management
What is the term used to describe the process of managing both travel demand and the overall transport system to ensure smooth traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve the efficiency of transportation networks ?
Transportation Planning
It is a process of defining a framework in various sectors of transportation to ensure accessible, safe economical, and sustainable transport mobility service across all levels of individual ( Mark Cruz 2023)
Situation Definition
Problem Definition
Search for solution
Analysis Performance
Evaluation other alternative
Choice of Project
Specification and Contraction
Basic Planning of Process
Trip Generation and Attraction
Trip Distribution
Modal Split
Traffic Assignment
Sub-models of the class model.
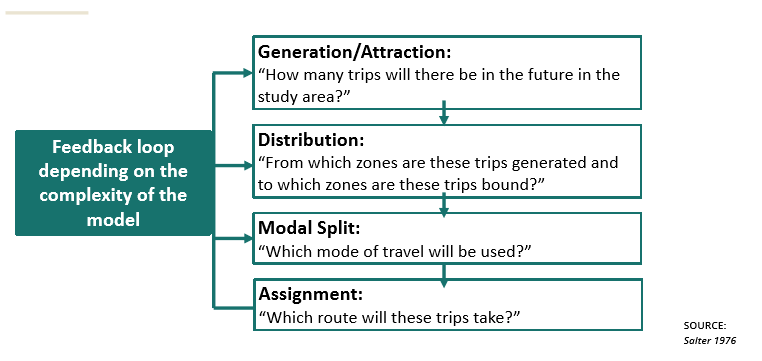
Generation/Attraction
Distribution
Modal Split
Assignment
Four-Step Forecasting Process
Trip Generation
Destination Choice
Mode Choice
Route Choice
Conventional Four-Step Transportation Forecasting Process
Trip Generation
Widely used for forecasting travel demands. It predicts the number of trips originating in or destined for a particular traffic analysis zone.
Trip
Defined as a one-way person movement by a mechanized modes of transport, having two trip ends.
Origin and Destination
Used in terms of direction
Production/Generation and Attraction
Used for land-use associated with each trip.
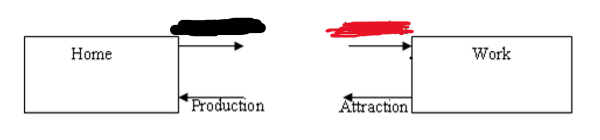
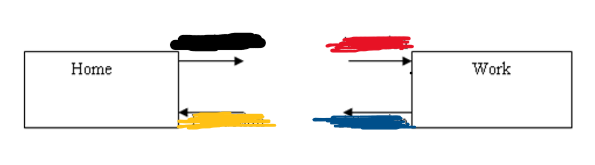
Trip Production
is the home end of home-based trip and is the origin of trip of non-home-based trip.
Trip Attraction
is the non home end of home-based trip and is the destination of a non-home-based trip.
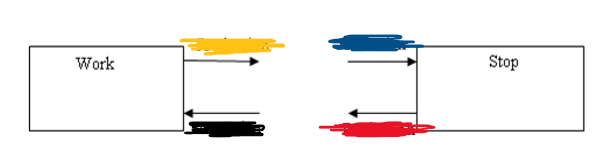
Attraction then Production
From Work to Home, what is blue and yellow?
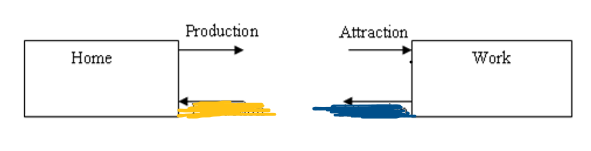
Production then Attraction
From Home to Work, what is black and red?
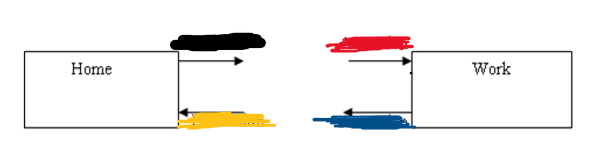
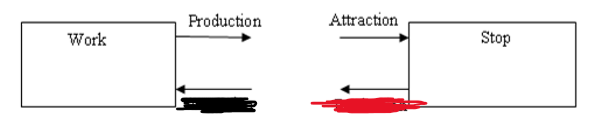
Production then Attraction
From Work to Stop, what is Yellow and Blue?
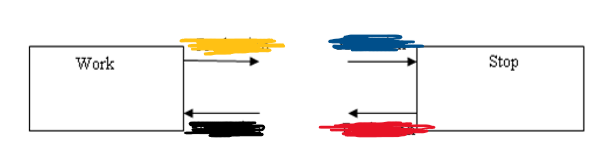
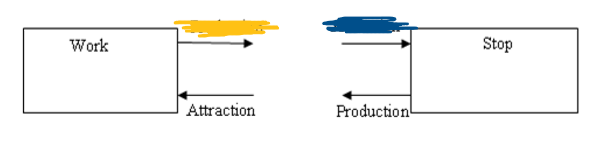
Production then Attraction
From Stop to Work, what is black and red?
1 and 2
Which among this list of purposes of a home-based trip are mandatory trips?
Work Trips
School Trips
Shopping Trips
Social- recreational Trips
Other Trips
3, 4, and 5
Which among this list of purposes of a home-based trip are discretional trips?
Work Trips
School Trips
Shopping Trips
Social- recreational Trips
Other Trips
Home Based Trip
Non-Home-based trip
Time-based trips
Person-type based trips
Classification of Trips
Time based trips
The proportion of journey is different by different purposes usually varies with time of the day. Thus, the classification is often given as Peak and Off-Peak Period Trip.
Person-type based trips
The travel behavior of an individual is mainly dependent on its Socio-Economic attributes. Following are the categories which are usually employed.
a) Income Level- Poor, Middle Class, Rich
b) Car Ownership
c) Household Size
Growth Rate Method
Category Analysis
Regression Model
Modelling Trip Production
*Methods available for estimating trip generation and attraction
Ti = Ti * Fi
Growth Rate Method Formula
Trip Distribution
the second step in the travel demand modeling, in which the generated trips from each zone is then distributed to all other zones based on the choice of destination.
Trip Matrix
The trip pattern in a study area can be represented by means of a trip matrix or origin destination (O-D) matrix. This is a two- dimensional array of cells where rows and columns represent each of the zones in the study area.
Growth Factor
Advantages of Model
1. Simple to understand.
2. Preserve observed trip pattern.
3. Useful in short term-planning.
Growth Factor
Disadvantages of Model
Depends heavily on the observed trip pattern.
It cannot explain unobserved trips.
Do not consider changes in travel cost.
Not suitable for policy studies like introduction of a mode.
Gravity
Advantages of Model
1. Trip resistance is considered.
2. Structure of model is easy to understand.
3. Complete OD matrix is not necessarily required.
Gravity
Disadvantages of Model
Reasoning is not clear why human behavior is related to Newton's gravity law.
Index of resistance is arbitrary.
Trip distribution within zone is difficult to treat.
Trip distribution for near zone pairs tends to be larger than real values and vice versa.
Modal Split
The third stage in travel demand modeling is modal split. The trip matrix or O-D matrix obtained from the trip distribution is sliced into number of matrices representing each mode.
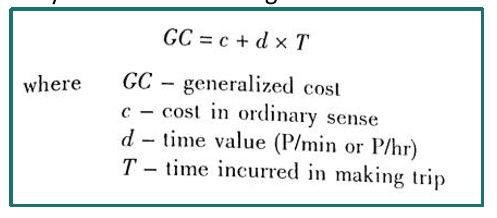
GC = c + d * T
Formula for Generalized Cost
It measures the relative travel cost between two zones. This cost element may be considered in terms of distance, time or money units.
Disaggregate Choice Model
This method originated from microeconomics. It assumes that a person will use a particular mode with maximum utility for him/her.
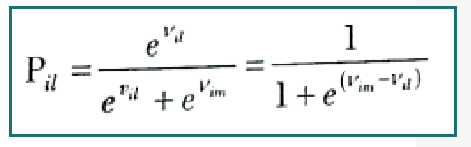
Pil = e^(vil)/ ( e^(vil) + e^(vim) )
Formula for Logit Model
Route Assignment
The process of allocating given set of trip interchanges to the specified transportation system is usually referred to as .
Dijkstra
The Shortest Path: 's Algorithm
Network Assignment
Considers the route that would require the least time or least distance.
All-or-Nothing Assignment
Considering one OD pair, all trips are assigned to the shortest path from point of origin to point of destination. After these trips are loaded into the network, the level of service of the roads in the network may change.
Constant Assignment Ratio
In this method, it is assumed that the number of trips assigned to a route is inversely proportional to the travel time or cost of that route, i.e., more trips will be assigned to a route providing shorter travel time or lesser cost.
Incremental Assignment
This method considers the influence of previously assigned trips. It is based on the Wardrop's Principle, which states that out of several routes available between zones i and j, the routes that are used have equal level of service. The routes that are not used have lower LOS.
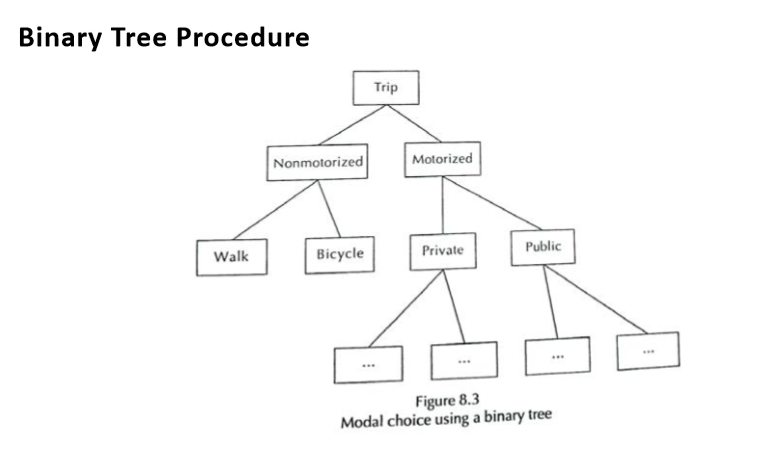
Binary Tree Procedure
Ans: Binary Tree Procedure